Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-6679
Research Article(ISSN: 2637-6679) 
Topical "Medistick" Of Antifungal, the New Future of Drug-Cosmetic Volume 1 - Issue 3
Parth Shah and Bhupendra G Prajapati*
- Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Ganpat University, India
Received: March 14, 2018; Published: March 20, 2018
*Corresponding author: Bhupendra G Prajapati, Associate Professor, Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Ganpat University, Ganpat Vidhyanagar, Mehsana, Gujarat-384012, India
DOI: 10.32474/RRHOAJ.2018.01.000114
Abstract
Main aim of developing medicated stick is to cure topical problems and also for beauty purpose by natural ingredients. This formulation is combination of both branches (drug-cosmetic).The drug used in the formulation is Ketoconazole which is used for antifungal therapy Pre formulation studies revealed that API and excipients were found to be compatible. For the formulation of medstick self emulsify drug delivery system was used. Take a solubility profile then three basic preliminary trials taken for making SEDDS. Optimize the SEDDS. This selection is done by concentration of bees wax, concentration of carnauba wax, concentration of castor oil and concentration of Isopropyl myristate. Evaluation test like breaking load test, softening point, permeability, melting point and antifungal activity etc was performed on the finalized formulation.
Keywords: Ketoconazole; Self emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS); Medicated stick; Fungal diseases; Beautification; Excipients; Optimization; Evaluation; Stability
Cosmetics
Cosmetic products are important with an essential role in human life. Today, consumers worldwide are looking for personal care products that supply multiple benefits with minimal efforts. As per FD&C Act cosmetics are defined as "articles intended to be rubbed, poured, sprinkled, or sprayed on, introduced into, or otherwise applied to the human body for cleansing, beautifying, promoting attractiveness, or altering the appearance." Among the products included in these moisturizers, perfumes, lipsticks, fingernail polishes, eye and makeup, cleanser shampoos, hair colours, and spray, and any substance expected for use as a segment of a corrective item. It does not include soap [1].
Cosmeceutical
It the fastest growing field in pharma. Cosmeceuticals are the blend of naturally dynamic fixings which have restorative or medication like advantages and beautifying agents which helps for beautification of the skin. Cuter variables like air contamination, introduction to radiation from the sun and typical procedure of maturing makes harms indispensable parts of skin like DNA, collagen and cell layers. Different microscopic organisms, infection and growths additionally make harms skin. Different Cosmeceuticals utilized for the healthy skin enhance the working and surface of the skin by upgrading composition development, keeping up the keratinized structure of the skin layer and giving more advantageous skin. Different details of Cosmeceuticals can be figured to guarantee viable healthy skin. The greater part of Cosmeceuticals utilizes vitamin, herbs, different oils and plant remove [2,3].
Introduction
Ketoconazole is chemically 1-[4-(4-{[2-(2, 4-dichlorophenyl)- 2-(1H-imidazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy}phenyl) piperazin-1-yl]ethan-1-ones,broad spectrum antifungal agent active against a wide variety of fungi and yeasts. Ketoconazole is a synthetics antifungal drug used to prevent and cure fungal skin infection. The target tissue in infections skins diseases is the skin itself. Systemic effects are regarded as adverse effects of the treatment of infectious skin reaction. Topical application of antifungal is intended to achieve higher local drug concentrations and to avoid the adverse effects of systemically administered formulations. To achieve desirable therapeutic effect, topical drug delivery for Ketoconazole needs to reside at the sites of infections for prolonged period. Hence there is a need to develop effective drug delivery system that should prolong the contact of drug with infected part.
Ketoconazole have low solubility and high permeability. It is readily but incompletely absorbed after oral dosing and is highly variable due to its poor water solubility leading to shorter half-life i.e. 2 h of the drug. Topically it is used in the treatment of candidal or tinea infections of the skin. Self Emulsifying Drug Delivery System (SEDDS) have been used as drug carrier in topical treatment of diseases, especially in dermatology. This system allows for a high accumulation of drug in the skin, with relatively low permeation flux as compared to the conventional dosage form. SEDDS enhance surface area and so it improve solubility of Ketoconazole, thus drug was easily soluble in formulation then use SEDDS in stick formulation it was enhance bioavailability.
Main objective is to prepare solid self emulsifying drug delivery system containing Ketoconazole using appropriate oil, surfactants and co-surfactants to improve solubility. The formulation of Ketoconazole drug contain medicated Stick is intended for the purpose of beautification of lips and curing lip with fungal infections. For this rational it was formulate one cannot go outside applying Ketoconazole cream on lip but applying Ketoconazole medistick is better. Medistick contain lake oil soluble colour pigment they does not interfere in formulation and also use as medistick and transparent medistick use for other body organ which are infected from fungal like eyebrows, neck, ear back side this type site it is apply. Ketoconazole is very safer drug it is not harmful even if people or child eats. Medistick is cosmetic formulation for the modification of colour and prepared by moulding a dispersion of colours in a waxy base, in the form of stick [4].
Topical Drug Delivery System
Figure 1.
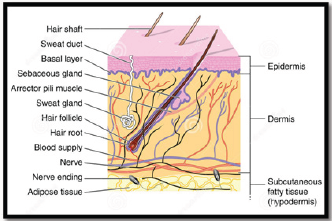
Topical drug delivery can be explained as "The application of drug containing formulation to the skin to directly treat cutaneous disorders (e.g. acne) or the cutaneous manifestations of a general disease (e.g. psoriasis) with the intention to contain the pharmacological or effect of the drug on the surface of the skin or within the skin. Semi solid formulation contribute in the system for topical drug delivery, but foams, spray, Medistick, medicated powder, solution are in use(Figure 1).
i. External delivery that are rolling stick ,spread, sprayed or otherwise isolated on to cutaneous tissues to cover the infected area.
ii. Internal delivery that are applied to the mucous membrane orally, virginally or rectal tissues for local activity.
This topical preparation penetrate throw underline layer of skin or mucus membrane and produce localized effect.
a. Merits
i. It is convenient to apply and use and avoids first pass metabolism.
ii. The risk of inconvenient intravenous therapy is avoided and also varied condition of absorption it avoided, like pH changes, presence of enzymes, gastric emptying time etc.
iii. It contains ability to deliver drug more selectively to specific site and avoids gastro-intestinal incompatibility.
iv. Utilization of drugs with short biological half-life, narrow therapeutical window and Improves physiological and pharmacological response and patient compliances.
v. It is suitable for self-medication and is easy to terminate the medications, when needed.
vi. Efficiency is achieved throw lower total daily dosages of drug by inputting continuous drug.
vii. It avoids changes in drug levels, inter &intra patient variations.
viii. It is applied on large area as compare to buccal or nasal cavity.
b. Demerits
i. Skin irritation may occur due to the drug and/or excipients on contact dermatitis.
ii. Due to poor permeability of some drugs possibility of allergenic reactions may caused through the skin.
iii. Enzyme present in epidermis may change the nature drugs.
iv. Larger size of drugs particles is not easy to absorb by the skin.
Material and Method
Material
a. For Sedds
i. Oils
Long chain triglyceride and medium-chain triglycerides oils with proportionate degree of saturating have been used in the design of SEDDS. Recent novel semi synthetic medium chain triglyceride oils have sufficient property and vastly replace regular medium chain triglyceride. Oleic acid which is use in formulation.
ii.Surfactants
Invariably a surfactant or emulsifier having a good binding force to attach SEDDS within. High number of hydrophobic drugs can be dissolve in naturally obtained surfactant due to its amphiphilic property. But emulsification process needs two big issues to be satisfied, HLB and Safety. If one needs higher emulsification then HLB value should be greater (high hydrophilicity). High emulsification of SEDDS Formulations prevents drug precipitation in gastro intestinal lumen ( due to raped o/w droplet formation ) side by side prolong duration of action would be assure. Non-ionic surfactants are also considered as safer than the ionic ones. The surfactant concentration should be in the range of 30-60%w/w while dissolving high amount of hydrophobic drugs.
But high concentration of surfactant can irritate GI lumen that could be a big challenge for pharmaceutical scientist. However augmentation of particular droplets at critical concentration is amenable during high concentrated emulsification process, due to this the interfacial disruption caused by enhanced water penetration into the oil droplets, mediated by the increased surfactant concentration, thus leading ultimately to the ejection of oil droplets into the aqueous phase.
iii.Co surfactants/co-solvents
The production of an optimum SEDDS requires relatively high concentrations (generally more than 30% w/w) of surfactants. Organic solvents such as, ethanol, propylene glycol (PG), and polyethylene glycol (PEG) are suitable for topical drug delivery, and they enable the dissolution of large quantities of either the hydrophilic surfactant or the drug in the lipid base. These solvents can even act as co-surfactants in SEDDS systems. On the other hand, alcohols and other volatile co-solvents have the disadvantage of evaporating into the shells ofthe soft or hard gelatine, sealed gelatine capsules in conventional SEDDS leading to drug precipitation. Thus, alcohol free formulations have been designed, but their lipophilic drug dissolution ability may be limited. Rapid emulsification occurs on optimised 35%w/w concentration. Systems containing 20-50% w/w Tween 85 are very fatly in nature. 50%w/w accelerates, produce viscous gels. By homogenisation technique fine dispersion could be possible. Advance is Transcutol P which one used.
b. For Medistick
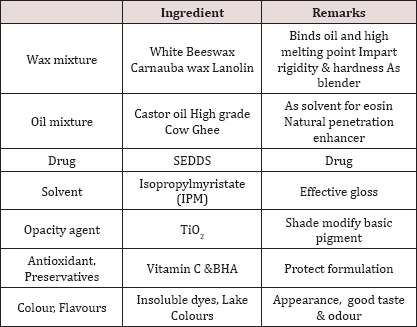
i.Waxes
Waxes The gloss & hardness are generally depends on characteristics & quantity of waxes Best characteristic is obtained by using mixture of waxes of different m.p & adjusting the final melting point by incorporating a sufficient amount of high melting point wax: beeswax, carnauba wax, hard paraffin wax, soft paraffine, lanolin etc
ii.Oils
The oil mixture is required to blend properly with the waxes to provide a suitable film on the applied lip skin. Also acts as solvent in some formulation, acts as dispersing agent for insoluble pigments the ideal mixture of oil should produce the product, easily spread & produce a thin film with good covering power. Examples: Castor oil, Tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol (THFA) & esters, Isopropyl myristate, Isopropyl palmitate, Butyl stearate.
iii.Colors
Colors most important from commercial & appearance point of view. In olden days, carmine was widely used, but nowadays various other are available. Color in lipstick is imparted by two ways: Soluble dyes: By staining the skin with soln of dyestuff which can penetrate the outer layer of skin. Insoluble dyes by covering the lips with a colored layer which serves to hide any skin roughness & give a smooth appearance.
iv. Preservatives
Preservatives used to prevent microbial growth Example: 0.1% Propyl parahydrohybenzoate in 0.1% higher conc. of preservative can cause slightly burning sensation or allergic reaction.
v.Fragrance
Fragrance Essential component of medistick used to mask bad odour of fatty or wax. Used to impart attractive flavour Conc. 2-4% Qualities for selection: Free from irritating effect Free from disagreeable taste Stable.
vi. Antioxidants
Antioxidants Incorporated to prevent Rancidification of oily base during storage. Generally used in combination Example: BHA, BHT, Propyl gallate, Citric acid, Surfactants & Other Additives
Surfactants: Used to promote wetting & stabilize the dispersion of insoluble pigments in medistick base.
Additives: used for various purposes
Oil - soluble sunscreen: filter the sunrays & protect lip skin from sun burn.
Silicon fluid: used as fixative & prevent colors, from bleeding on lips.
PVP: (conc. 0.5-1%) film former on lips & reduce allergic reaction in medistick.
Isopropyl linoleate: prevent drying effect.
Method
First of all check the solubility profile of Ketoconazole then use which one is of higher solubility. Then prepare SEDDS because drug was not directly incorporate in formulation either incorporate it was uneven distribute. SEDDS use in preparation of Medistick.
Preparation of liquid SEDDS formulation
For making 2% Ketoconazole Medistick requires 200mg API. The plans were set up by dissolving the detailing measure of 2% Ketoconazole (0.2g) in the blend of oil (Oleic Acid), surfactant (Tween 80), co-surfactant (Transcutol-P) at 37 °C. The blend was homogenized with mixing with the help of magnetic stirrer until drug completely soluble. It is liquid SEDDS. Optimize the SEDDS.
Preparation of Medistick: (Table 1)[5]
Table 1.
i. Weight wax mixture, oil mixture, solvent, antioxidant, preservatives, TiO2, flavour & colours all the ingredients.
ii. Take wax mixture in a china dish and put on the water bath till wax mixture dissolve and Take a beaker into other water bath for warming oil mixture.
iii. Add wax mixture and SEDDS into oil mixture with continues stirring.
iv. Take the solvent of IPM, colours, flavours, antioxidant &preservatives and TiO2in another beaker and mix properly.
v. Pour the 4) into 3) with continuously stirring and then mould it in medistick moulders. First Cool it at room temperature then freeze & scrap it out.
Evalution Parameters [6-9]:
a. Color: Visual technique
b. pHparameter: The pH of defined natural was resolved utilizing computerized pH meter.
c. Skin disturbance test: It is followed by applying medistick on the skin for 10 min.
d. Solubility test: To check the solubility of medistick in different solvents.
e. Perfume test: The medistick were tested after 30 days, to record fragrance.
f. Melting Point: Medistick sample was filled into a glass capillary tube open on both the closures. This tube was cooled in ice and secures it to a thermometer. This assembly was immersed into a beaker full of water and was warmed with nonstop mixing. The temperature at which the material moves along capillary tube was viewed as its dissolving point.
g. Breaking Load test: Breaking point was done to determine the strength of medistick. The medistick was held horizontally in a socket at the midpoint from the edge of help. The weight was continuously expanded by a specific value (10 gm) at specific interval of 30 second and weight at which medistick breaks was considered as the breaking point.
h. Softening Point: The medistick sample inserted in to an aluminium ring, after removing extra mass above and below the orifice. This was placed in a fridge (6°C) for 10 min. After removing it from the fridge, the ring was fastened onto a stand. This assembly was dipped in to a beaker full of water. This was heated with a constant stirring. Temperature was observed utilizing a thermometer. Softening point was the temperature at which the medistick mass was starting to melt and falls into the beaker.
i. Stability Studies: The medistick were placed for stability studies at room temperature, Refrigerator and 40 ± 2 °C/75 ± 5% RH and were observed for any physical changes.
j. Permeability Study: Cellophane membrane was soaked in ethanol and allowed to evaporate. 50 mg of medistick mass was applied on the membrane and it was placed on the diffusion cell. Hydro alcoholic Mixture (30% ethanol in distilled water %v/v) was used as receptor media. This was magnetically stirred (600rpm).The experimental temperature was kept up at 32 °C by circulation thermostatic water inside the cell jacket. Sampling was done at 1hr interval and analyzed under UV at 283nm for 6hrs.
k. Thixotrophy character: It is sign of thixotropic quality and is finished by utilizing penetrometer. A standard needle of specific diameter is allowed to penetrate for 5 seconds under a 50 gm load at 25 °C. The depth of penetration is a measurement of the thixotropic structure of to be 10.5mm.
l. Antifungal activity: Ketoconazole is fungistatic and inhibits the biosynthesis of ergosterol, the major sterol found in the fungal cell layer. The antifungal activity of ketoconazole from the formulation as well as from standard (Drug dissolved in 30% v/v of ethanol) was determined using Candida albicans as a representative fungus; by the cup plate method. It determines antifungal activity of inhibition zone.
m. Force of application: It is test for comparative measurement of the force to be applied for application. A piece of coarse brown paper can be kept on a shadow graph balance and medistick can be applied at 45o angle to cover a 1 sq. inch area until fully covered. The pressure reading is an indication of force of application and it depends on the operator.
n. Surface anomalies: It is study of the surface defects, such as formation of crystals on surface, contamination by fungus etc. No surface anomalies must be recorded in the formulated medistick.
o. Rancidity: It rancidification is the decomposition of fats, oils and other lipids by hydrolysis or oxidation. Is the oxidation of castor oil or other waxy or lipoidal ingredients? It leads to obnoxious odour, bad taste & sticky product & sometimes changes of colour of the product. Testing of rancidity can be done by determining its peroxide number.
p. Rupture Test: Rupture test medistick is placed in two holders, in the extended position. Weight is added to the holder on the medistick portion at 30-second intervals until the medistick ruptures. The pressure required to rupture the medistick is then checked against the manufacturer's standards. Since there are no industry standards for these tests, each manufacturer sets its own parameters.
q. Spreadability Test: Medistick was spread over transparent glass in angle of 45°. The surface was observed and the picture was taken with dark background. Good spreadability was seen.
r. Calibration curve: Accurately weight 10mg of Ketoconazole was transferred to a 100ml volumetric flask and dissolved in 60ml methanol. The volume was adjusted to the mark with methanol to prepare stock solution (100mcg/ ml) the above solution is further diluted with methanol to get concentration of Ketoconazole in the range of 3-15mcg/ml.Absorbance of each solution was measured at 222nm against a reagent blank solution prepared similarly without drug UV spectrophotometer. Then plot the concentration versus absorbance graph. Same do for phosphate butter pH 7.4.
Conclusion
After Completion of my research work, I found it more effective formulation. Medistick has several advantages in beauty & fungal diagnosis. Medistick is combine two field Cosmetic and drug. One cannot go outside applying Ketoconazole cream on lip but applying Ketoconazole medistick is better medistick work within a second. It use on specific site. Medistick is not easily removed as compare to other formulation like cream, ointment, gel. This medistick helps in quicker, safer and easy to carry.
References
- (2018) FDA, US Food and Drug Administartion, USA.
- Arora N, Agarwal S, Murthy RSR (2012) Latest Technology Advances in Cosmaceuticals, International. journal of pharmaceutical sciences and drug research 4(3): 168-182.
- Dharkar DP Formulation and Evaluation of Mango Butter Based Cosmeceuticals.
- SP Chauhan, AD Kanojiya, PA Patel, AK Seth, NV Shah, et al. (2013) ketoconazole loaded solid self emulsifying drug delivery system: formulation and in-vitro characterization. Department of Pharmacy, Sumandeep Vidyapeeth, Piparia, Vadodara, Gujarat, India 4(4): 441.
- (1994) Text book of Control of microbial contaminations in the manufacture of cosmetics chep. 16 Lipstick.
- (2011) For Dermatological Use. International journal of drug discovery and herbal research 1(4): 210-211.
- Nabde MK, Halle PD, Dadge KK, Kale SV, Nalwad DN (2013) Cosmeceutical: An Emerging Concept. International journal of universal pharmacy and life sciences 3(2).
- Satish S, Mahesh CH, Saikat D, Lavanya V, Suresh B (2012) Preparation and Evaluation of Salicylic Acid Medicated Lipstick. Journal of advanced pharmaceutical sciences 2(2).
- Saba S, Kiran B (2008) Formulation and Evaluation of Medicated Lipstick of Allantoin. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutics 2 (2): 90-95.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...

.png)