Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2641-6921
Mini Review(ISSN: 2641-6921) 
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Composite Laminates in The Industries Volume 3 - Issue 2
RandbaranE*, DayangL, Zahari R, Sultan MTH and Mazlan N
- Department of Aerospace Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, West Malaysia
Received: July 05, 2020; Published: August 20, 2020
*Corresponding author: Randjbaran E, Department of Aerospace Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor DarulEhsan, West Malaysia
DOI: 10.32474/MAMS.2020.03.000158
Abstract
With today’s growing interest toward composite materials and their augmentation as part of integrated business from aerospace engineering, medical applications and others, which are getting increasing dependency on composite materials in recent operations. However, the most sophisticated composite materials still need to rely on the other integrated sub-sets of components. On the other hand, there certain limitation and flaws that exist within composite materials’ component that can cause and error to grow way beyond control and can impact its main master component. These sorts of limitation and flaws also would impact the engineering targets from perspective of resiliency built into the daily operations that is also pointed it out in current article.
Keywords:Composite material; laminate; carbon nanotubes; carbon fibre reinforced composites (CFRP)
Introduction
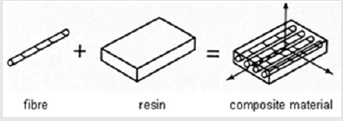
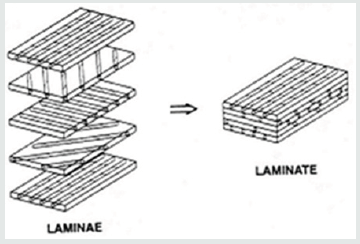
The composite materials are produced when two or more different materials are laminated together. These laminae were found to have numerous uses due their high strength to weight ratio and resistance to corrosion and surface degradation.(Figure 1)briefly explains the composition of a composite material. Optimizing the construction of composites, multiple adjusted layers (laminae) use to form a laminate. (Figure 2) illustrates layers of individual laminates having different fibre directions combined to form a laminate. By changing the direction of the fibres in the resin, the material properties can be tailored to fit the required properties in a structure.The fibre reinforcement plays a major role in determining the structural properties in a composite material. Since the fibre is held together with the matrix resin, it optimizes the properties in the final part such as strength and stiffness, while still minimizing weight. The primary function of the fibers is to carry the loads along their longitudinal directions. Common fiber reinforcing agents include:
a. Carbon (Graphite)
b. Glass (E-glass, S-glass, D-glass)
c. Polyamide (Aromatic polyamide, Aramid), e.g., Kevlar 29
d. Quartz (Fused silica)
e. Titanium
Resins have a wide variation in properties, and they are
relatively low cost. Due to this, most composite matrices are made
of resins. Aside from protecting the fibres from mechanical and/or
environmental damages, the matrix also serves to transfer stresses
between the reinforcing fibres. Common resin material includes:
a. Epoxy
b. Phenolic
c. Polyester
d. Polyurethane
e. Vinyl Ester
Benefits and Drawbacks of Using Composites
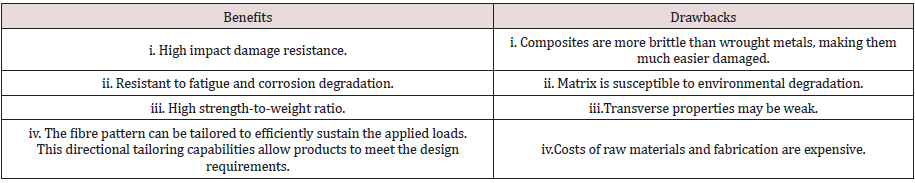
Polyesters are the most widely used resin systems. Epoxies comes in second for their higher cost, with advantages of having higher adhesion and less shrinkage than polyesters. Using composites has their own pros and cons. Depending on their purposes, trade-offs should be considered when implementing composites in a design. (Table 1)summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of composites.
Composites have been incorporated in many fields. This includes from household items to construction parts. Several household items which incorporated composites are window frames, bathtubs and doors.[1] Sporting goods such as rackets and bicycles also implemented the use of carbon nanotubes and carbon fibre reinforced composites (CFRP) respectively. In public infrastructures, several bridges and utility poles have been using composites in its construction. Among the composites implemented were carbon composites and glass composites(Figure 3). Due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, composites are highly demanded in the aerospace industry. Weight is a critical parameter in aerospace. It affects the flying capabilities of an aircraft. Previously, aircraft structures consisted of only metal, which results in a heavy overall structure. Once composites were introduced, they were found to be able to significantly reduce the weight of the aircraft while providing comparable or even higher structural integrity than that of metals at the same time.
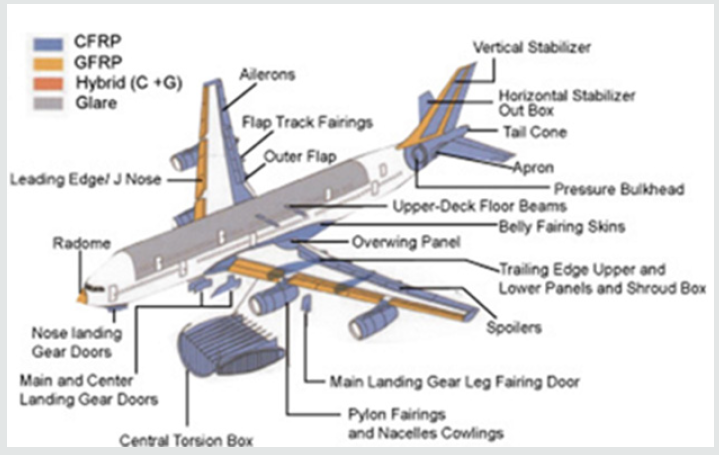
Nowadays, more and more aircrafts are incorporating composites in its design to make it lighter. A lighter aircraft also means less fuel consumption and therefore allows lower emission of greenhouse gasses. Among commercial aircrafts which incorporated composites in its design are the Airbus A380 and Boeing 787 Dreamliner. The A380 contains about 25-30 tons of composites, 85% of which is CFRP. On the other hand, 50% of the B787 Dreamliner is comprised of composites, with the remainder being 20% aluminum and 30% titanium.(Figures 4&5) show the composition of composites implemented in the aircrafts respectively.
Fibre-reinforced composite materials own various functions
in most industries, especially the aerospace industry, due to the
high specific stiffness. Nonetheless, the expense of conventional
composites is also noticeable. Ordinarily, Haphazard divided
fibre reinforced composite materials appeared as affirming the
most outstanding alternative materials for unique manufacturing
challenges, joining the methods and the basic material selection
considerations for multi-material lightweight structures due to
the mass production capabilities and low cost [2]. For instance,
the possible use in the automotive industry was recorded. In
contemplation of expanding the application, meticulous material
characterisation is needed. Subsequently, the major complication
in the quite exploring models of the geometry at the micro-level of
35-40% fibre volume ratios, which is even more appeared at the
highest aspect ratio among the different types of reinforcements
[3].
Glass-fibre reinforced composite materials showed limited
applications in terms of construction and building industry for
several years. Recently, well potential for the applications of fibrereinforced
composite materials for the numerous applications due
to expeditiously retrofit and repair deteriorating infrastructure
is being achieved [4]. Moreover, mechanical properties of fibrereinforced
composite materials closely depend upon the properties
of the component materials such as void content, type, orientation,
fibre distribution and quantity. On the other hand, the main concept
of the interfacial bonds and the mechanism of load transfer at inter
laminar also play a vital role [5].Accordingly, varied researchers discuss about the design process of short fibres reinforced
composite materials. Therefore, they are ready for using to aim
attention at the strength properties of the composite materials
that reported the effects of them on shapes of the fibres in shortfibres
glass composite materials [6]. The flexural strength, vertical
stress generated by bending moment of avoided short-fibres
reinforced composites were studied by considering the effects of
fibre orientation and length on mechanical properties. In addition,
a short while ago, efforts to reduce the weight of automobiles by
the increased use of plastics and their composites, have led to a
growing penetration of short-fibre reinforced injection moulding
thermoplastics into fatigue-sensitive applications [7]. Mainly, shortfibre-
resin matrix composite materials are minor fatigue resistance
than the correspondingly continuous fibre reinforced composites,
which is extensively applied in the piping and pipeline systems and
the pressure vessels for all major chemical industries [8].
Summary
The flexural strength, vertical stress generated by bending moment of avoided short-fibres reinforced composites were studied by considering the effects of fibre orientation and length on mechanical properties. In addition, a short while ago, efforts to reduce the weight of automobiles by the increased use of plastics and their composites, have led to a growing penetration of shortfibre reinforced injection moulding thermoplastics into fatiguesensitive applications. Mainly, short-fibre-resin matrix composite materials are minor fatigue resistance than the correspondingly continuous fibre reinforced composites, which is extensively applied in the piping and pipeline systems and the pressure vessels for all major chemical industries[9-15].
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
References
- Loganathan TM, Sultan MTH, Jawaid M, Shah AUM, Ahsan Q, et al. (2020) Physical, thermal and mechanical properties of areca fibre reinforced polymer composites-an overview. Journal of Bionic Engineering 17(1): 185-205.
- McIlhagger A, Archer E, McIlhagger R(2020) Manufacturing processes for composite materials and components for aerospace applications. In Polymer composites in the aerospace industry, Woodhead PublishingPP. 59-81.
- Ashraf W, Ishak MR, Zuhri MYM, Yidris N, Yaacob AMB, et al. (2019) Investigation of different facesheet materials on compression properties of honeycomb sandwich composite. Semin. EnauKebangs. Bahau, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia 129-132.
- HazrolMD,Sapuan SM,Zuhri MYM,Ilyas RA (2019) Electrical properties of sugar palm nanocellulosefiber reinforced sugar palm starch biopolymer composite. In Prosiding Seminar EnauKebangsaanPP. 57-62.
- Ilyas RA,Sapuan SM,Norizan MN,Atikah MSN,Huzaifah MRM,et al. (2019) Potential of natural fibre composites for transport industry: a review. In Prosiding Seminar EnauKebangsaan pp. 2-11.
- Johari AN, Ishak MR, Leman Z,Yusoff MZM,Asyraf MRM,et al. (2019) Fabrication and cut-in speed enhancement of savonius vertical axis wind turbine (SVAWT) with hinged blade using fiberglass composites. In Proceedings of the Seminar EnauKebangsaan pp. 978-983.
- Alias NA,Fauzi NM, Yusuf B, Razali MM (2020) Lab Scale Study on Integrated GSI for Urban Drainage Systems. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing 1529(4): 042008.
- Najeeb MI, Sultan MTH,AndouY, Shah AUM,EksilerK, et al. (2020) Characterization of lignocellulosic biomass from malaysian’syankee pineapple ac6 toward composite application. Journal of Natural Fibers 1-13.
- Mohamed SAN,Zainudin ES,Sapuan SM,Azaman MD,Arifin AMT (2020) Effects of Different Stress Ratios on Fatigue Crack Growth of Rice Husk Fibre-reinforced Composite. BioResources, 15(3): 6192-6205.
- Yusof NSB,Sapuan SM, Sultan MTH, Jawaid M (2020) Conceptual design of oil palm fibre reinforced polymer hybrid composite automotive crash box using integrated approach. Journal of Central South University27(1):64-75.
- Noryani M,Sapuan SM,Mastura MT,ZuhriMYM, Zainudin ES (2020) Statistical inferences in material selection of a polymer matrix for natural fiber composites. Polimery 65: (2)
- Mazlan AA, Sultan MTH,Safri SNA,Saba N, Shah AUM,et al. (2020)The Effect of Fibre Length on Flexural and Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Pineapple Leaf Fibre Composites. Journal of Renewable Materials8(7): 833.
- Mazlan N, Chai Hua T, Sultan MTH,Abdan K(2020)Thermogravimetric and dynamic mechanical analysis of woven glass/kenaf/epoxy hybrid nanocomposite filled with clay. Advances in Materials and Processing Technologies 1-14.
- Loganathan TM, Sultan MTH,JawaidM, Ahsan Q, Naveen J,et al. (2020) Characterization of New Cellulosic Cyrtostachysrenda and PtychospermamacarthuriiFibers from Landscaping Plants. Journal of Natural Fibers 1-16.
- McHugh LN, Terracina A, Wheatley PS, Buscarino G, Smith MW et al. (2019) Metal-Organic Framework‐Activated Carbon Composite Materials for the Removal of Ammonia from Contaminated Airstreams. AngewandteChemie International Edition 58(34): 11747-11751.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...