Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2638-6070
Research Article(ISSN: 2638-6070) 
Studies on Antibiotic Residues in Beef and Effect of Cooking and Freezing on Antibiotic Residues Beef Samples
Volume 2 - Issue 1Fahim A Shaltout1*, Mohamed A El shatter2 and Heba M Fahim3
- 1Food Hygiene Department, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Benha University, Egypt
- 2Animal Health Research Institute, Egypt
- 3General organization of veterinary services, Egypt
Received: June 24, 2019; Published: July 08, 2019
*Corresponding author: Fahim A Shaltout, Food Hygiene Department, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Benha University, Egypt
DOI: 10.32474/SJFN.2019.02.000129
Abstract
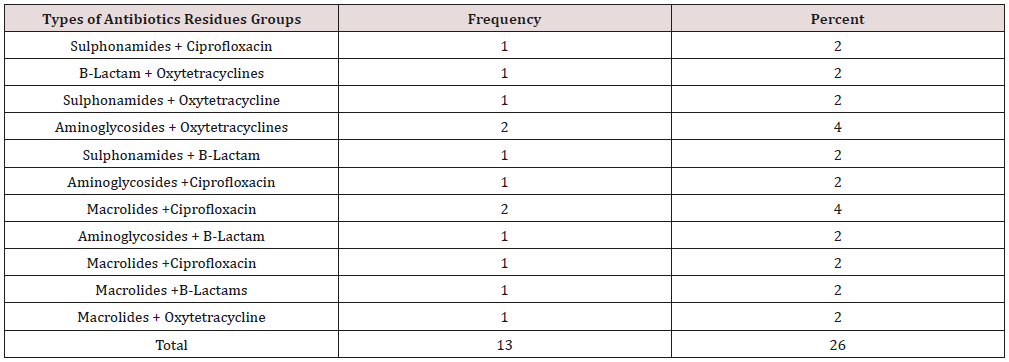
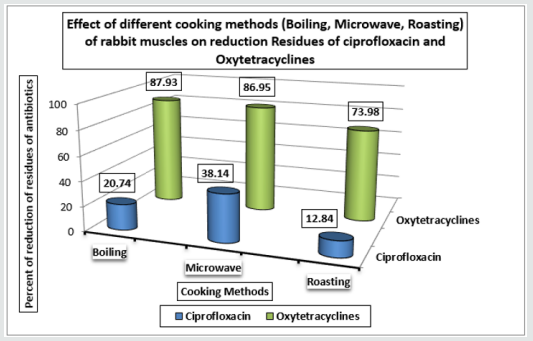
The study was performed to determine the presence of antibiotic residues in 50 random samples of fresh beef marketed at Giza governorate, Egypt. The detection of antibiotics residues was carried out according to methods recommended by Hietzman (1994) (4-plates test) and USDA (2011) (Bioassay test).the obtained results indicated that the incidence of antibiotic residues in the examined samples was 3 samples of amino glycosides, 2 samples of B-Lactams (penicillin), one sample of Ciprofloxacin one sample of oxytetracycline. It was shown that 2% of the samples contain Sulphonamides and Ciprofloxacin, (B-Lactam +Oxytetracyclines), (Sulphonamides + Oxytetracycline), (Sulphonamides plusB-Lactam), (Aminoglycosides plus Ciprofloxacin),(Macrolides plus Ciprofloxacin) (Aminoglycosides plus B-Lactam), (Macrolides plus B-Lactams), (Macrolides plus Oxytetracycline. on the other hand, 4% of the samples were regarded for Aminoglycosides plus Oxytetracyclines, Macrolides plus Ciprofloxacin. The study revealed that 13 samples of beef out of 50. The experimental part of this study determines the residues of ciprofloxacin and Oxytetracyclines in experimentally treated rabbits’ samples (50 rabbit) after cooking treatments (Boiling; Microwave; Roasting) and freezing of the rabbit samples. The method of determination of the residues using HPLC. It found that, In Boiling for 30min : reduction of ciprofloxacin residues by 20.74% and oxy tetracyclines residues by 87.97%, and in Microwave for 20min reduction of ciprofloxacin residues by 38.14% and oxy tetracyclines residues by 86.95% , And Roasting for 30min. at 100 °C .reduction of ciprofloxacin residues by 12.84% and oxy tetracyclines residues by 73.98% , Three thigh and breast from each group were kept deep freeze at -20 °C. reduction of ciprofloxacin For 6 months freezing is 65.73% and 12 months freezing is 100% and reduction of oxy tetracycline’s residues For 6 months freezing is 4.41% and 12 months freezing is 30.01%. The public health significance of the antibiotic residues in beef and their probable sources of their presence as well as some recommendation to prevent to gain access to such food items were discussed.
Keywords: Beef; Residues; Oxytetracycline
Introduction
The veterinary drugs used in food producing animals has led to residues occurring in animal products as (meat, milk, eggs and honey), poses a health hazard to the consumer. Due to drug's properties and their pharmacokinetic characteristics, physicochemical or biological processes of animals and their products are subsidiary factors for occurring of residues of veterinary drugs and Improper drug usage and disrespect the withdrawal period. The major public health significances of drug residue are development of antimicrobial drug resistance, hypersensitivity reaction, carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, teratogenicity, and disruption of intestinal normal flora [1]. Nowadays Antibiotics are applying for control of infectious diseases in chickens' digestive system; incorrect use of these drugs deposits some residue in product. Impacts of different types of cooking and freezing on antibiotic residues in chicken meat were done by determination the residues of ciprofloxacin and oxytetracycline in experimentally treated chickens' muscles after cooking treatments (Boiling, Microwave, Roasting) and freezing of the chicken muscles [2]. Treatment of food animals with therapeutic and sub therapeutic dosage forms of antibiotic-antimicrobial drugs has increased in the last decade. This has been due to the advent of modern mass production operations that involve the maintenance of thousands of animals simultaneously and requires the utilization of carefully formulated and medicated diets that serve to maximize growth, minimize production costs, and provide an acceptable consumer product that is wholesome and affordable. Animal feed that contain antibiotics and other antimicrobials as a prophylactic are used routinely in beef, swine, chicken, and turkey production. In this way the antibiotics antimicrobials help to maintain the optimal health of the animals so treated antibiotics may be co-administered with antimicrobial drugs resulting in increase in drug effectiveness compared to individual drug administrations [3]. Indirect consumption of food contaminated with aflatoxins revealed public health risk to human. Aflatoxicos is leads to hepatocellular carcinoma and growth impairment. Many researches have suggested a link between antibiotic administration in food animals and increase in bacterial resistance in human populations. In this cross-sectional study, the screening for antibiotic residues in kidneys was done using Microbial Inhibition six (6) plate method to provide baseline data for the prevalence of antibiotic residues in animals slaughtered in Abattoir and non- Abattoir slaughterhouse in Negeri Sembilan district areas. Basically, the agar diffusion method uses six media which have been separately cultured with different types of bacteria that are relatively susceptible and resistant towards specific antimicrobial at certain pH level. Forty-one (41) kidney samples and another fourteen (14) samples were obtained from non-abattoir and approved (Senawang, Negeri Sembilan Abattoir) slaughterhouses respectively. 14 (34 %) of the 41 kidney samples from non-abattoir slaughterhouses and 1 (7%) of the 14 samples from non-abattoir slaughterhouses were positive for antibiotic residues. The result of the study revealed significant association (p<0.05) between types of slaughterhouse positive for antibiotic residues using chi-square test and confirmed using Binomial logistic Regression. The test divulged seven times possibility of the samples taken from non-abattoir slaughterhouse to test positive. However, there were no significant differences between all groups of antibiotics from the positive samples. From this study, it is imperative to include more study areas and sample size to conclude the safety of the meat for consumers in [4] boiling for 30 minutes caused a great degradation of tetracyclines residues "oxytetracycline" residues in rabbit meats but not complete destruction. Freezing at -20 ºC caused a lower degradation than that caused by boiling, so neither boiling nor freezing could be used as reliable methods to get rid of tetracyclines residues "oxytetracycline" residues in rabbit meats [5]. demonstrated that ordinary cooking procedures boiling decreased the initial concentrations of tetracycline residues by 56 to 82%. Also, microwaving degrades the initial concentrations of tetracycline residues by 56 to 82% [6].
Material and Methods
Collection of samples
A total of 50 fresh raw beef meat from different cuts of carcasses were collected from Giza governorates shops. The average weight of each sample 250g; each sample was put in sterile polyethylene bag then sealed and labeled. The samples were transferred to the laboratory in ice box without delay. The samples were frozen at (-18 °C) until examined within few days. The detection of antibiotics residues was carried out according to methods recommended by Hietzman (4-plates test) and USDA (2011) (Bioassay test).
Determination of ciprofloxacin: (Agar diffusion by Lieve Okerman, 1998)
samples were confirmed by HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) by pooling all positive samples for ciprofloxacin in only two samples [7].
Determination of (Tetracyclines) Oxytetracycline Residues in meat Tissues (USDA 2011)
samples were confirmed by HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) by pooling all positive samples for ciprofloxacin in only two samples [8].
Experimental study
This study was planned to determine the residues of ciprofloxacin and Oxytetracyclines in experimentally treated rabbits’ samples after cooking treatments (Boiling; Microwave; Roasting) and freezing of the rabbit samples. The method of determination of the residues using HPLC. The experiment was Planned as follow:
Rabbits: fifty rabbits (New Zealand species each weighed3kg) were divided into 3 groups (each 5 five rabbits) free from any antibiotics.
Drugs: Ciprofloxacin 10% ALNASR (Injection I/V) and Oxytetracyclines (20%, S/C, ADWIA).
Procedures: The first group was injected single dose (10mg/kg BWT(I/V) of ciprofloxacin. The second group was injected single dose oxytetracyclines S/C 5mg/kg Bwt. The third group was kept as control. The groups of rabbits were kept in cages for 24hr then slaughtered.
Samples: From each rabbit group (3 thighs and breast) was treated as follow:
Cooking: Boiling for 30min, Microwave for 20min, Roasting for 30minat 100 °C. Each cooked group was three of each (thigh and breast).
Freezing: Three thigh and breast from each group were kept deep freeze at -20 °C For 6 and 12 months. All for mentioned treated groups were either cooking or freezing were examined for the presence of ciprofloxacin and oxytetracyclines residues using HPLC according to [7].
Results
Tables 1-12
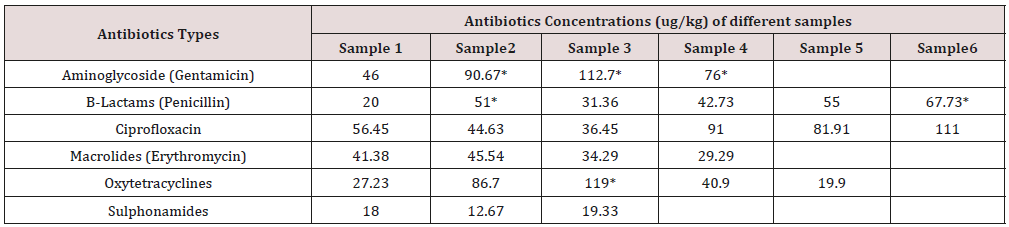
Table 1: Concentrations (ug/kg) of different antibiotics residues in each individual raw beef samples.
Discussion
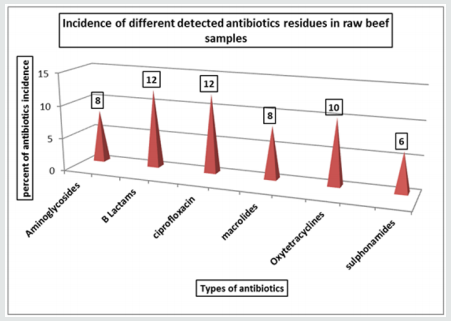
Wrong use of antibiotics in food animal production causes wide spreading of resistant pathogens, resistance genes and antimicrobial resistant bacteria in food animals, whereas they enter the food chain so national authorities should put a serious laws and programs aimed to reduce the excessive using of antibiotics in food animals and ensure their risky usage. Due to farmers and meat producers don't follow the laws about withdrawal times of the products [9]. Spreading of antibiotic-resistant bacteria showed serious problems among public heath as mortality rates were increased in cases when resistant infections occurred and increase length of treatments so, require using more expensive antibiotics or antibiotic cocktails [10]. The Concentrations (ug/kg) of different antibiotics residues in each individual raw beef samples were illustrated in Table 1 and Chart1, the result showed 3 samples of amino glycosides, 2 samples of B-Lactams (penicillin),one sample of Ciprofloxacin were rejected according to EEC (1990).The Frequency Distribution of different types of antibiotics Residues in raw beef samples was shown in Table 2 and Chart 2, the frequency range of Aminoglycosides (Gentamicin), B-Lactam(Penicillin), Ciprofloxacin, Macrolides(Erythromycin),Oxytetracyclines, Sulphonamides were 4, 6, 6, 4, 5 and 3 respectively. 56% of samples were contained antibiotic residues [11]. Table 3 & 4 were viewed the effect of boiling on reduction for both ciprofloxacin and Oxytetracycline Residues in Rabbit muscle were 20.74% and 87.97%, respectively. The effect of microwave on reduction for both ciprofloxacin and Oxytetracycline Residues in Rabbit muscle were 38.14% and 86.95%, respectively that shown in (Table 5-8 chart 3), showed that the roasting effect on reduction for both ciprofloxacin and Oxytetracycline Residues in Rabbit muscle were 12.84% and 73.98%, respectively. Gehad [12] mentioned that Since the most of foods-producing animals are always cooked before consumption and the variations in oxytetracycline levels in the meat are dependent on type of cooking. More findings about the effect of cooking on oxytetracycline residue are needed to accurately determine consumer exposure to this drug. The boiling for 30 minutes and roasting at 150°C for 30 minutes caused a complete degradation of drug residues. After 6 months of freezing treatment at -18°C the ciprofloxacin reduced to 65.73% whereas after 12 months the same residues were not detected which viewed in Table 9 & 10. Aboul El [13] that said Controlling of ciprofloxacin residues by freezing at -18 c had a positive effect on degradation of its residues Morshdy et al. [5] said that Freezing at -20ºC caused a lower degradation than that caused by boiling so, neither boiling nor freezing could be used as reliable methods to get rid of oxytetracycline residues in rabbit meats [14,15].
Chart 2: Frequency incidence of presence of more than antibiotics residues groups in examined raw beef samples.
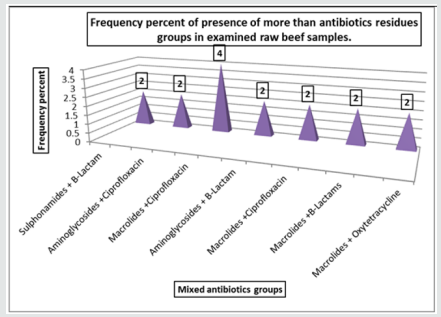
Chart 3: Effect of different cooking methods (Boiling, Microwave, Roasting) of rabbit muscles on reduction Residues of ciprofloxacin and Oxytetracyclines.
Conclusion and Recommendation
From results in this study it is concluded that:
a. Misuse of antibiotics in large animals for treatment without follow of the withdrawal periods of drugs
b. High incidence of antibiotic residues beef meat due to excessive use of antibiotics [16].
c. The effect of cooking on some groups of antibiotic residues (ciprofloxacin and oxytetracyclines), showed
d. Freezing are the only effective methods to degrade ciprofloxacin residues to safety level then microwave, ciprofloxacin is heat stable compound degrade less by heat treatment process.
e. Microwaving and boiling and roasting are the effective heat treatment methods on degrading oxytetracycline residues to safe level. Microwaving and boiling could degrade oxytetracycline residues higher than roasting but freezing had low degrading effect on oxytetracycline residues [17].
Recommendation
It was concluded that The Application of HACCP system is recommended for beef production and other meat products.
References
- Beyene T, Sultan A, Dinka A, Tariku J, Fanos T (2016) Assessment of Rational Veterinary Drugs Use in Livestock at Adama District Veterinary Clinic, Central Ethiopia. Journal of Veterinary Science and Technology 7(3): 2157-7579.
- Fahim Aziz eldin Shaltout (2019) Professor of Meat Hygiene, Department of Food Hygiene and control Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Benha University, Impacts of Different Types of Cooking and Freezing on Antibiotic Residues in Chicken Meat, Research gate.
- Francis FJ (2000) Encyclopedia of food science and technology (2nd edn). 1: 5.
- Marimuthu M, Adamu L, Abdullah FJ, Sadiq MA, Zin MB (2014) Antimicrobial Residues in Beef Animals Slaughtered in Abattoir and Non-Abattoir Small Holders Slaughterhouses in Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia. Alexandria Journal of Veterinary Sciences 44: 1-8.
- Morshdy AM, Hussein MA, EL Gohary AE (2014) Studies on oxytetracycline residues depletion in rabbit meat. Assiut Veterinary Medicine J 60(141): 158-166.
- Gratacós Cubarsí M, Fernandez García A, Picouet P, Valero Pamplona A, García Regueiro JA, et al. (2007) Formation of tetracycline degradation products in chicken and pig meat under different thermal processing conditions. J Agric Food Chem 55(11): 4610-4616.
- Verdon E, Couëdor P, Sanders P (2004) Validation of a multi- quinolone, multi-matrix, multi-species method for the determination of quinolone residues by HPLC with fluorescence detection. Afssa.
- Hamide SE, Tuncel OZ, Deniz YS (2000) High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Oxytetracycline Residue in Cured Meat Product. Instrumental Analysis Centre, Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) 06530, Ankara-TURKEY.
- Sattar S, Hassan MM, Azizul Islam SKM, Alam M, Al Faruk Md (2014) Antibiotic residues in broiler and layer meat in Chittagong district of Bangladesh. Veterinary World 7(9): 738-743.
- WHO (World Health Organization) (1974) Control of harmful residues in food for human and animal consumption? The public health aspects of antibiotics in feed stuffs. Report of a working group, Berman, 1-5 October 1973, WHO Regional office for Europe, Copenhagen, pp. 37.
- Ramatla T, Ngoma L, Adetunji M, Mwanza M (2017) Evaluation of Antibiotic Residues in Raw Meat Using Different Analytical Methods. Antibiotics (Basel) 6(4): 34.
- Gehad FA (2002) Stability of some Veterinary Drug Residues in animal meats, during storage, Preparation and Processing. Ph.D. Thesis Fac Vet Medicine zagazig University.
- Aboulel NM (2006) Effect of boiling and freezing on ciprofloxacin residues in chicken tissues. Assuit Vet Med J 52: 111-120.
- (1990) EEC (Council Regulations). Veterinary medicinal products in food stuff of animal origin (OJL, 224, 18.8 Laying down community procedures for the establishment of MRLs of P.I).
- Heitzman RJ (1990) VETERINARY DRUG RESIDUES Residues in food producing animals and their products: Reference Materials and Methods, (2nd edn), Published on behalf of Commission of the European Communities.
- USDA (2011) Laboratory Guidebook. Bioassay for detection, identification, and quantitation of Antimicrobial residues in Meat and poultry tissues. United state Department of Agriculture (USDA).
- Wild CP, Gong YY (2010) Mycotoxin and human diseases a largely ignored global health issue. Carcinogenesis 31(1): 71–82.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...