Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-4706
Research Article(ISSN: 2637-4706) 
Identification of Sirtuin Drug Targets (Homosapiens) For Lung Cancer-Molecular Docking and ADME Analysis Volume 3 - Issue 4
Sameer* and Sudhakar Malla
- Department of Biotechnology, Indian Academy Degree College, Bangalore
Received: April 25, 2020; Published: May 20, 2020
Corresponding author: Sameer, Department of Biotechnology, Indian Academy Degree College, Bangalore
DOI: 10.32474/DDIPIJ.2020.03.000168
Abstract
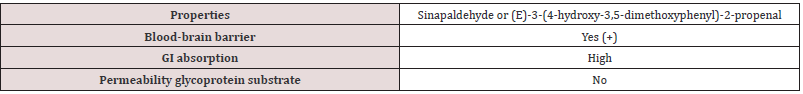
The objective of this study was to investigate the specific drug targets (Sirtuin 1,2,3,4,5, and 6) for lung cancer employing molecular docking simulation and ADME analysis against Sinapaldehyde. The three-dimensional structure of the protein was retrieved from Protein Data Base and of the ligand from Pubchem database. Molecular docking simulation of the compounds was performed using Ligpep 2.3, Schrodinger Suite 2009. In the present study, drug likeness analysis was performed through Lipinski filter & Admesar analysis using Swissadme online server and none of the compounds breached Lipinski’s and ADME parameters, making them prominent agents for bio-activities. And the outcome represents the compounds (Sinapaldehyde) possibly serve as for the cure of lung cancer.
Keywords: Sirtuin; Sinapaldehyde; Molecular docking; Lipinski; ADME analysis, Anti-cancer
Introduction
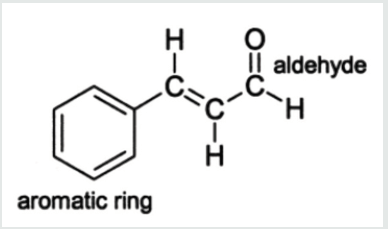
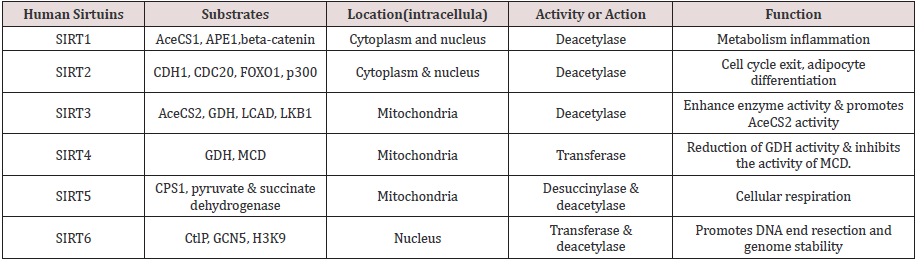
Lung cancer is the prominent source of cancer associated death across the world with a survival rate of 20% [1]. Lung cancer can be differentiated into small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer [2]. In the earlier decades, a huge number of metabolic pathways like EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) signaling pathway have been observed in the carcinogenesis family indulging lung cancer & are used as specific targets in drug development [3,4]. Sirtuins are group of proteins homologous to yeast regulator (Sir 2) that was identified in 1984 as a gene obligatory for continuing silent chromatin in yeast [5]. Sirtuins family of proteins also came out to play a major role in various pathological & physiological processes. Sirtuins genes (SIRT1-7), in mammals [6,7]. Sirtuins genes are basically classes of proteins which acquire nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-dependent deacetylase (SIRT1, SIRT2, SIRT3, SIRT5, SIRT6, and SIRT7) and monoribosytransferase (SIRT4, and SIRT6) activities [8-15]. Except SIRT5, all mammalians Sirtuins have been noted to be indulged in cancer development but the roles of Sirtuins proteins in cancer are very complex and attribute to cancer cells promotion or suppression [16]. The selected ligand was recognized for prediction against novel targets and predicted to interact with Sinapaldehyde also called (E)-3-(4-hydroxy- 3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-propenal, representative of the class of compounds called as methoxyphenols which are water-insoluble and a very weak compound (Table 1). (acidic in nature). During lignin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana, an enzyme called dihydroflavonol-4-reductase utilizes NADPH & Sinapaldehyde to generate sinapyl alcohol & NADP+ (Figure 1). In the present study, comparative investigation of the specific human sirtuin proteins was carried out using molecular docking techniques which identified the drug likeness of the respective ligand.
Methodology
Active binding site
The 3D structure of sirtuin (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6) proteins (PDBID: 4kxq.1.B, 1j8f.1.A, 4bn5.1.A, 5oj7.1.A, 5bwl.1.A, 3pki.1.A) was build using SWISS-MODEL. Recognition of protein binding sites were identified by FT site server and Pro-Bis server [17]. Recognition of binding site has a broad range of pertinences which indulges functional relationships between proteins, structure-based prediction, and drug design. And FT site server also exposed a specific method for protein binding identification [18].
Ligand formation
Ligands are tiny molecules which bind to the Protein’s binding sites. Sinapaldehyde structure obtained from Pubchem database [19]. The compounds were converted to three-dimensional structure with the help of PyMol version 1.3 [20]. And physicchemical properties of the ligands are measured by Pubchem database.
Study of drug likeness of ligands
Lipinski filter were used for ligand prediction, according to drug likeness criteria namely cLogP, hydrogen donor and acceptor, molecular mass & molar refractive index [21]. SWISS-ADME was used as convenient tool in drug investigation [22] and ligand properties with respect to adsorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME). BOILED-EGG (Brain or Intestinal Estimated permeation method) is approached as an accurate model that works properly by computing the polarity of tiny molecules [23].
Molecular docking simulation
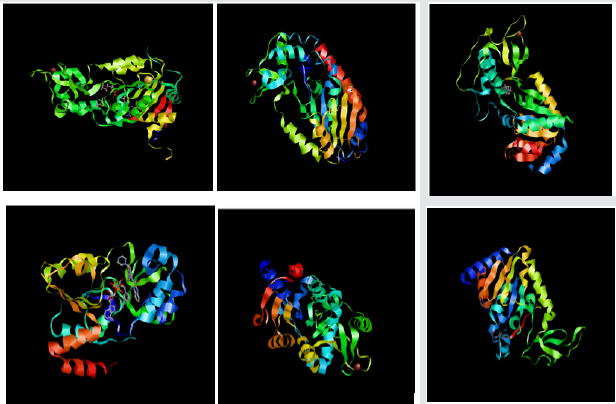
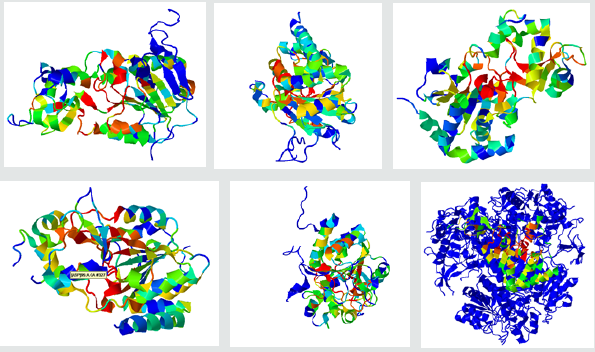
The purpose of molecular docking is to assume or predict the binding aspects of ligand and identify the orientation of molecule with respect to active site. In docking method, all the binding poses of molecules innards the catalytic site of an enzyme is being concluded. After that, preparation of protein of the specific target sirtuin proteins 1,2,3,4,5,and 6 (PDB ID: 4kxq.1.B, 1j8f.1.A, 4bn5.1.A, 5oj7.1.A, 5bwl.1.A, 3pki.1.A) was performed with employing Protein preparation wizard of Schrodinger 09 in which missing hydrogen bond were assigned subjected by energy minimization (Figure 2-4).
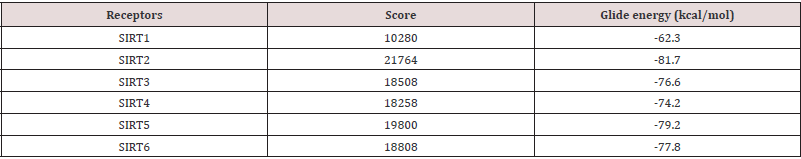
The receptor network was groomed keeping ligand (Sinapaldehyde) at the centre of framework with 20A edges bearing catalytic site. Primarily docking simulation on the cocrystal was groomed on prepared receptor for cross validating the binding ability with subject to X-ray crystal structure binding mode. Moreover, molecular docking method was implemented against PDB ID employing Glide XP 5.8 [24-26]. and top analogs on docking score as well as binding synergy with catalytic fragments were allowed for induced fit docking and outcomes were compared after Glide XP. The lowest energy suggested by Glide program was noted as the most probable binding pose of top compound (Table 2).
Results and Discussion
Active binding sites of protein molecule
In this study, FT site server was used to predict the active sites of the targeted proteins (sirtuin 1, 2,3,4,5, and 6).
Ligand
Drug likeness analysis
Lipinski filter analysis was used to explain the rigidity of all compounds to be considered for structure-based drug design (Table 3-5).
Molecular docking simulation
According to molecular docking simulation, results observed from induced fit docking of compounds at the binding site of sirtuin proteins showed better docking score than the already known drugs for anticancer which predicts that the compounds have the better binding affinity to the receptors. The molecular docking result showed good binding affinity in all specific targeted proteins (Figure 5,6).
Figure 5: Physico-chemical space of molecules with highest probability of being utilized by the GI tract shown in white region, whereas the yellow region shown the physic-chemical space of molecules with highest probability to penetrate the brain.
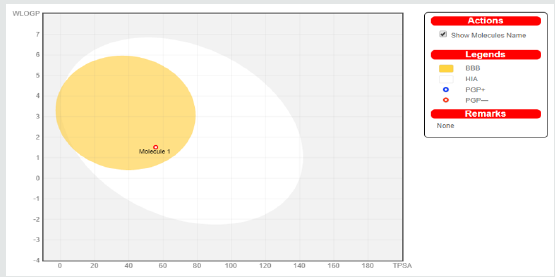
Figure 6: Molecular docking simulation of sirtuin proteins (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6) with ligand namely Sinapaldehyde. The docking results showed that all selected compounds for docking exposed an excellent binding affinity. SIRT2 showed highest glide energy (-81.7) followed by SIRT5 (-79.2).
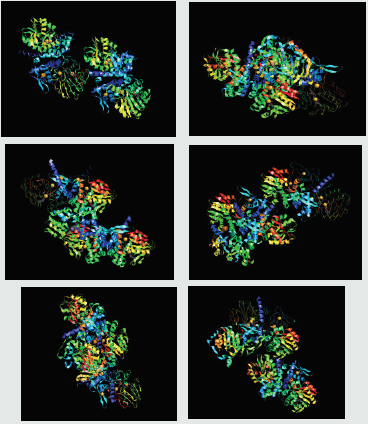
Conclusion
In silico studies of the selected sirtuin proteins (1,2,3,4,5, and 6) showed the favorable result against ligand namely Sinapaldehyde. The selected compounds exposed better outcomes in silico analysis and characterization with good efficiency in aspects of docking score and glide energy. According to ADME predictions, Gastrointestinal absorption is very high and absence of permeability glycoprotein substrate. Hence, it has assumed or predicted that the compound (Sinapaldehyde) possibly serve as for the treatment of lung cancer and might be in future be utilized in in vivo studies to predict their effects on the abilities for the cure of cancer.
References
- Torre LA, Siegel RL, Jemal A (2016) Lung cancer statistics. Adv Exp Med Biol 893: 1-19.
- Travis WD (2011) Pathology of lung cancer. Clin Chest Med 32(4): 669-692.
- Pao W, Girard N (2011) New driver mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol 12(2): 175-180.
- Park SJ, More S, Murtuza A, Woodward BD, Husain H (2017) New targets in non-small cell lung cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 31(1): 113-129.
- Shore D, Squire M, Nasmyth KA (1984) Characterization of two genes required for the position-effect control of yeast mating-type genes. EMBO J 3(12): 2817-2823.
- Frye RA (2000) Phylogenetic classification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic Sir2-like proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 273(2): 793-798.
- Frye RA (1999) Characterization of five human cDNAs with homology to the yeast SIR2 gene:Sir2-like proteins(sirtuins) metabolize NAD and may have protein ADP-ribosyl transferase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 260(1): 273–279.
- Imai S, Armstrong CM, Kaeberlein M, Guarente L (2000) Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. Nature 403(6771): 795-800.
- Landry J, Sutton A, Tafrov ST, Heller RC, Stebbins J, et al. (2000) The silencing protein SIR2 and its homologs are NAD-dependent protein deacetylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(11): 5807-5811.
- North BJ, Marshall BL, Borra MT, Denu JM, Verdin E (2003) The human Sir2 ortholog, SIRT2, is an NAD+-dependent tubulin deacetylase. Mol Cell 11(2): 437-444.
- Tanner KG, Landry J, Sternglanz R, Denu JM (2000) Silent information regulator 2 family of NAD-dependent histone/protein deacetylases generates a unique product, 1-O-acetyl-ADP-ribose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(26): 14178-14182.
- Haigis MC, Mostoslavsky R, Haigis KM, Fahie K, Christodoulou DC, et al. (2006) SIRT4 inhibits glutamate dehydrogenase and opposes the effects of calorie restriction in pancreatic beta cells. Cell 126(5): 941-954.
- Liszt G, Ford E, Kurtev M, Guarente L (2005) Mouse Sir2 homolog SIRT6 is a nuclear ADP-ribosyltransferase. J Biol Chem 280(22): 21313-21320.
- Barber MF, Michishita-Kioi E, Xi Y, Tasselli L, Kioi M, et al. (2012) SIRT7 links H3K18 deacetylation to maintenance of oncogenic transformation. Nature 487(7405): 114-118.
- Michishita E, McCord RA, Boxer LD, Barber MF, Hong T, et al. (2009) Cell cycle-dependent deacetylation of telomeric histone H3 lysine K56 by human SIRT6. Cell Cycle 8(16): 2664-2666.
- Roth M, Chen WY (2014) Sorting out functions of sirtuins in cancer. Oncogene 33(13): 1609-1620.
- Kozakov D, Grove LE, Hall DR, Bohnuud T, Mottarella SE, et al. (2015) The FT Map family of web servers for determining and characterizing ligand-binding hot spots of proteins. Nat Protoc.10(5): 733-755.
- Ngan CH, Hall DR, Zerbe BS, Grove LE, Kozakov D, et al. (2012) FT Site: high accuracy detection of ligand binding sites on unbound protein structures. Bioinformatics. 28(2): 286-287.
- Wang Y, Xiao J, Suzek TO, Zhang J, Wang J, et al. (2009) PubChem: a public information system for analyzing bioactivities of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res.
- PyMol - The PyMol Molecular Graphics System, Schrodinger LLC.
- Lipinski CA (2005) Lead and drug-like compounds: the rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discov Today Technol 1(4): 337-341.
- Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V (2017) Swiss ADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci Rep 7: 42717.
- Daina A, Zoete V (2016) A BOILED-Egg to predict gastrointestinal absorption and brain penetration of small molecules. Chem Med Chem 11(11): 1117-1121.
- Halgren TA, Murphy RB, Friesner RA, Beard HS, Frye LL, et al. (2004) Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring 2 Enrichment factors in database screening. J Med Chem 47(7): 1750-1759.
- Friesner RA, Banks JL, Murphy RB, Halgren TA, Klicic JJ, et al. (2004) Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring 1. J Med Chem 47(7): 1739-1749.
- Friesner RA, Murphy RB, Repasky MP, Frye LL, Greenwood JR, et al. (2006) Extra Precision Glide: Docking and Scoring Incorporating a Model of Hydrophobic Enclosure for Protein-Ligand Complexes. J Med Chem 49(21): 6177-6196.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...