Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2644-1217
Research ArticleOpen Access
Tongluo Decoction Blocks Apoptotic Mitochondrial Pathway and Inhibits Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis of Coronary Microembolization Rats Volume 2 - Issue 3
Xuefeng Li1*, Junnan Zhao1,2, Jiaying Zhang1, Yanbing Shi1, Yinghuan Dou1, Jing Zhou1, Yang Luo1, Yan Zhu3, Yang Yuan1, Ying Wang1, Mengru Zhou1 and Miao Li1
- 1Lanzhou University, school of Basic medical sciences, Lanzhou, China
- 2Xiangyang Hospital of traditional Chinese medicine, Xiangyang, China
- 3Gansu Provincial hospital, Lanzhou, China
Received: February 02, 2020; Published: April 20, 2020
*Corresponding author: Xuefeng Li, Lanzhou University, school of Basic medical sciences, Lanzhou, China
Abstract
Background: We found that Tongluo Decoction has had good protection for myocardial cells injury of CME rats. But it is not clear whether Tongluo Decoction has inhibitory effect on myocardial apoptosis. So we want to study the effect and mechanism of Tongluo decoction to cardiomyocyte apoptosis following coronary microembolization in rats. Methods: 46 male Wistar rats were randomly divided into blank group (n=6), model group (n=10), Tongluo Decoction low dose group (n=10), Tongluo Decoction high dose group (n=10) and Tongxinluo group (n=10). In addition to the blank group, the rats of other groups were established the model of autologous thromboembolism microembolism by interventional method. The low dose group of Tongluo Decoction was given 7.8g/kg for gavaging, the high dose group of Tongluo Decoction was given 23.4g/kg, Tongxinluo group was given 0.2g/kg, once-a-day, for 12 day. The judgment of the model was done with HE and HBFP staining, the myocardial apoptosis rate was observed by TUNEL staining. Western Blot was used to detect Bcl-2, Bax and Caspase-3 in cardiac myocytes.
Results: The microembolization vessel count ratio, ischemic myocardial area ratio and the apoptosis rate of myocardial cells in model group were significantly higher than that in blank group, bcl-2 and bcl-2/bax decreased, and bax and caspase-3 were significantly increased (P < 0.05).Compared with model group, Tongluo Decoction low dose group, Tongluo Decoction high dose group and Tongxinluo group microembolization vessel count ratioischemic myocardial area ratio apoptosis rate decreased (P < 0.05), bcl-2, bcl-2/bax increased, Bax and caspase-3 decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with Tongxinluo group, the ratio of ischemic myocardial area, microembolization vessel count ratio, apoptosis rate, the expression of bax and caspase-3 proteins decreased (P > 0.05), bcl-2 and bcl-2/bax ratio increased in Tongluo Decoction high dose group (P > 0.05). bcl-2 and bcl-2/bax ratio increased obviously in Tongluo Decoction low dose group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Tongluo Decoction can inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis following coronary microembolization in rats, and its possible mechanism is related to blocking mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.
Keywords: Tongluodecoction; Rat; Coronary microembolization; Cardiomyocyte apoptosis
Abbrivations: Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI); Coronary microembolization (CME); Hematoxylin-Eosin staining (HE); Hematoxylin basic fuchsin picric staining (HBFP); Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP Nick End-Labeling (TUNEL); High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC); Tongluo decoction (TLD); Optical density (OD); Bcl-2 Assaciated X protein (Bax); Cysteinyl aspartate specific protease-3 (Caspase-3); B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2)
Introduction
In the process of percutaneous coronary intervention which is used to treat coronary heart disease, the small fragments that come from mechanical injury of coronary atherosclerosis, with the flow of blood circulation to the distal coronary artery, block the distal microvascular, which leading to the obstruction of coronary microvascular circulation, that is coronary microembolization(CME). CME is a serious complication of PCI, which can cause myocardial ischemia and cardiac dysfunction, and even lead to death. Numerous experimental studies [1, 2] have shown that apoptosis plays an important role in CME lesions. The research showed that Chinese materia medica can improve myocardial injury caused by coronary microembolization [3]. We found that Tongluo Decoction has had good protection for myocardial cells injury of CME rats. The Tongluo decoction could inhibit the pathological change of CME in rats, reducing the ingury of myocardial cells, inhibiting the expression of inflammatory cytokines and promoting the microemboli vascular recanalization [4]. But it is not clear whether Tongluo Decoction has inhibitory effect on myocardial apoptosis of CME rats. Therefore, in this study, we established coronary artery microembolization model of rats by injecting autologous thrombus through the right common carotid artery by interventional method with balloon catheter [5]. The effect and mechanism of Tongluo Decoction on cardiomyocyte apoptosis following CME in rats were studied.
Methods
Preparation and quality control of tongluo decoction
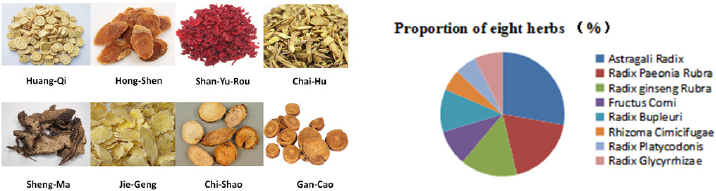
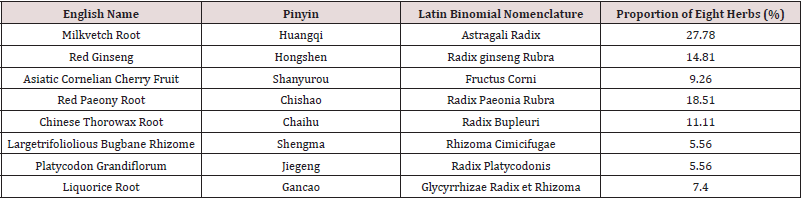
Tongluo Decoction mainly consisted of eight herbs: [6- 8] The composition and proportion of herbs are shown in the diagram (Figure 1, Table 1). The herbs was purchased from the Hui ren Tang Pharmaceutical Company, and they were identified by Jianyin Li, a teacher of Lanzhou University school of pharmacy.(The voucher specimen numbers of the stored herbarium specimen are 62032120180807063LY for Astragali Radix, 620031220010918321LY for Radix ginseng Rubra, 62062319980910435LY for Fructus Corni, 62032120180811156LY for Radix Paeonia Rubra, 62032120180807062LY for Radix Bupleuri, 62062320130815322LY for Rhizoma Cimicifugae, 62032120180805049LY for Radix Platycodonis, 62032120180812164LY for Radix Glycyrrhizae. ) This herbs that was conformed to the prescription, all of them were qualified, decocted, concentrated, and then put in refrigerator at 4. The chromatographic conditions were Diamonsil C18 (2) column (200×4.6mm, 5μm), the liquid phase of the calycosin glycoside (batch number 111920-201606, National institutes for food and drug control) mobile phase: acetonitrile -0.2% formic acid solution (15:85), flow velocity:1ml/min, column temperature: 30, detection wavelength: 260nm, sample size: 10μl. Paeoniflorin (batch number X27F8C30162, Shanghai source leaf Biological Technology Co., Ltd.) mobile phase: acetonitrile-0.1% phosphoric acid solution (16:84). Flow velocity, column temperature and sample size remain unchanged. Detection wavelength: 230nm; Ginsenoside Rb1 (batch number Z06M8L30693, Shanghai source leaf Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) mobile phase: acetonitrile -0.1% phosphoric acid solution, gradient elution. Flow velocity, column temperature and sample size remain unchanged. The detection wavelength: 203nm. To calculate the content of calycosin glycoside, paeoniflorin and ginsenoside Rb1.
Preparation of autologous thrombus suspension
1ml blood was collected from the caudal vein of each rat , then drying, the dry blood was grinded into powder like particles. The thrombus particles with a diameter between 41μm and 80μm were mixed into a suspension, and 2×105 thrombus particles were injected into the the aortic root through the right common carotid artery for establishing coronary artery microembolization model.
Animals grouping and model establishment
46 SPF healthy adult male Wistar rats (weight 350g±30g) were randomly divided into blank group (n=6), model group (n=10), Tongluo Decoction low dose group (n=10), Tongluo Decoction high dose group (n=10), Tongxinluo group (n=10). The experimental animals were purchased from the experimental animal center of Lanzhou University. The laboratory animal license number SCXK (Gan) 2013-0002. The experimental process adhered to the ethical regulations of animal experiments. The rats were anesthetized with 0.4% pentobarbital sodium solution, separated the right common carotid artery and cut the “V” incision at its distal end. The balloon catheter, which was soaked with heparin sodium saline, was pushed to the root of the aorta (about 4cm from the incision of right common carotid artery to the aortic root ), and the blood flow of the ascending aorta was blocked for 3-5s, rapidly withdrawing the guide wire during the period, and the autologous thrombus suspension was injected. Balloon catheter was pulled out, the proximal heart segment of the right common carotid artery was ligated. Penicillin 4×105 U/each was given for 3 days after the operation to prevent infection.
Drug intervention
The daily dosage of the low dose group of Tongluo Decoction was calculated according to the conversion ratio of the 1:6.25 in the rats [5]. The dosage of the high dose group of Tongluo Decoction was 3 times that of the low dose group of Tongluo Decoction. Tongxinluo capsule (Shijiazhuang Yiling pharmaceutical Limited by Share Ltd) uses 9grains/day dose, dissolve it in double steamed water and intragastric gavage. Tongxinluo capsule is purchased from Hui Ren Tang Pharmaceutical Company and its specification is 0.26g/ granules. The rats of each group were given the corresponding drug by intragastric gavage for 12 days. During the test, 3 rats died in each of the model group, low dose group of Tongluo Decoction, high dose group of Tongluo Decoction and Tongxinluo group during the modeling process, and 1 died in Tongxinluo group after gavage.
Collection of heart specimens
After the drug intervention, all rats were sacrificed by cervical dislocation under anesthesia by intraperitoneally injected 0.4% sodium pentobarbital solution 1ml per 100g body weight. Then rat heart was collected. The apex of heart was fixed in 4% polycondensation formaldehyde solution. After dehydration and paraffin embedded, 5μm consecutive paraffin sections were used to HE and other staining. The base of the heart was immediately placed in a pre-freezing storage tube, stored at liquid nitrogen, and used to detect cardiomyocyte apoptosis protein by Western Blot.
HE and HBFP staining of rat myocardium
After the apex staining of heart paraffin section of rats in each group with HE and HBFP, the staining sections were observed by three researchers under 400× and 100× microscope respectively to calculate the microembolization vessel count ratio, ischemic myocardial area ratio.
Detection of cardiomyocyte apoptosis by TUNEL
The pathological tissue section of the rat in each group was treated with anti-shedding. According to the TUNEL instructions (Boster Co., Ltd., Wuhan) to stain. The number of cardiomyocyte apoptosis and the number of total cells under the microscope were observed by three researchers under 400× microscope, and the apoptosis rate of myocardial cells was calculated and the apoptosis level of cardiac myocytes was evaluated. Apoptosis rate (%)=(the number of apoptotic cells/the total cell number under microscope)×100.
Western Blot was used to detect the expression of cardiomyocyte apopt-osis proteins
To extract the protein of myocardial tissue, according to the instructions of the kit (Solarbio Science and Technology Co., Ltd. Beijing). The OD value was measured, and the standard protein curve was drawn. Then calculating the protein concentration. Prepare 12% separation glue and 5% concentration glue, 160 V constant pressure electrophoresis 100min, and PVDF membrane was then transferred, followed by incubation for 2h with blocking buffer containing 5% Non-fat milk powder. Diluting and putting relevant primary antibodies, bcl2, bax, caspase3, and GAPDH respectively (Biosynthesis biotechnology Co., Ltd. Beijing), with gentle shaking overnight at 4. Afterwards, the membrane was incubated with secondary antibody(purchased from SAB) for 1h at room temperature, then washing and exposing.
Data statistics method
The SPSS 22.0 statistics software was used to analyze the data, and the measurement data were expressed with mean±standard deviation (x±s). Single factor variance( one-way ANOVA) was used in comparison of multiple groups. And P < 0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant.
Results
Quality control results of tongluo decoction
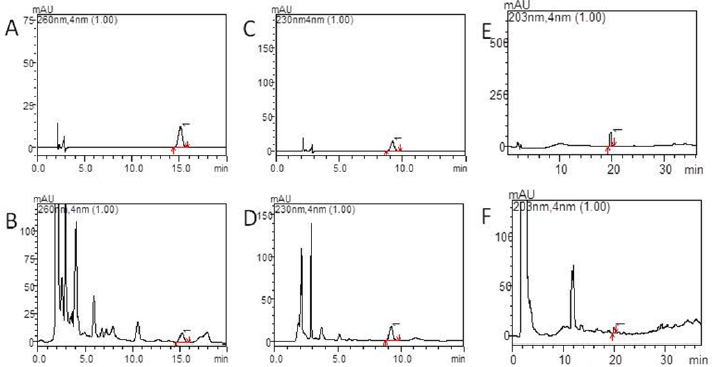
As shown in Figures 2(a)-2(f), the separation of the components to be tested is good and has no interference with other components. High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) shows the peak appearance time of the calycosin glycoside standard and Tongluo Decoction for test sample was 15.0±0.5 min, while the paeoniflorin standard and Tongluo Decoction for test sample was 9.0±0.5 min, and the ginsenoside Rb1 standard and Tongluo Decoction was 20.0±0.5 min, and the effective components of three herbs are compared with their respective standard products, some impurity peaks appeared. However, the separation efficiency of the effective components of the three herbs were not affected. The above results indicated that the effective components of Tongluo Decoction contained of calycosin glycoside, paeoniflorin and ginsenoside Rb1. The results showed that the effective components of Tongluo Decoction included calycosin-7-glucoside, paeoniflorin and ginsenoside Rb1, and the quality of the decoction was stable and could be used for the follow-up drug intervention test.
Figure 2:
a) High performance liquid chromatography of Tongluo Decoction, calycosin-7-glucoside standard.
b) High performance liquid chromatography of Tongluo Decoction. A calycosin-7-glucoside standard, Tongluo Decoction, calycosin-7-glucoside.
c) High performance liquid chromatography of Tongluo Decoction,paeoniflorin standard.
d) High performance liquid chromatography of Tongluo Decoction, Tongluo Decoction, 1 is paeoniflorin.
e) High performance liquid chromatography of Tongluo Decoction, ginsenoside Rb1 standard.
f) High performance liquid chromatography of Tongluo Decoction, Tongluo Decoction, 1 is ginsenoside Rb1.
HE staining results of rat myocardium
As shown in Figures 3(a)-3(f), the microembolus were not found in the microvessels of the coronary artery in the blank group. A large number of microembolus were found in the coronary microvessels in the model group, and around the microembolus there were inflammatory cell aggregation. Some of microembolus were found on the low dose group of Tongluo Decoction, the high dose group of Tongluo Decoction, and the Tongxinluo group in the coronary microvessel. The positive microembolization vessels count ratio (PMVR) in the model group was significantly higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05). Compared with the model group, the low dose group of Tongluo Decoction, the high dose group of Tongluo Decoction and the Tongxinluo group were significantly lower than those in the model group (P < 0.05). Compared with the Tongxinluo group, the PMVR in the Tongluo Decoction low dose group was increased while the Tongluo Decoction high dose group was decreased(P > 0.05). The PMVR of high dose group of Tongluo Decoction was lower than that in the low dose group of Tongluo Decoction (P < 0.05). (Figures 4(a)-4(f)).
Figure 3: Comparison of HE staining of myocardial positive microembolic blood vessels of rats in each group(400×). A blank group, B model group, C TLD(LD) group, D TLD(HD) group, E TXL group. F Comparison of HE staining of myocardial positive microembolic blood vessels of rats in each group. (▲)P<0.05, versus model group; (★)P<0.05, TLD(LD) group versus TLD(HD) group. PMVR:Positive microembolization vessel count ratio.
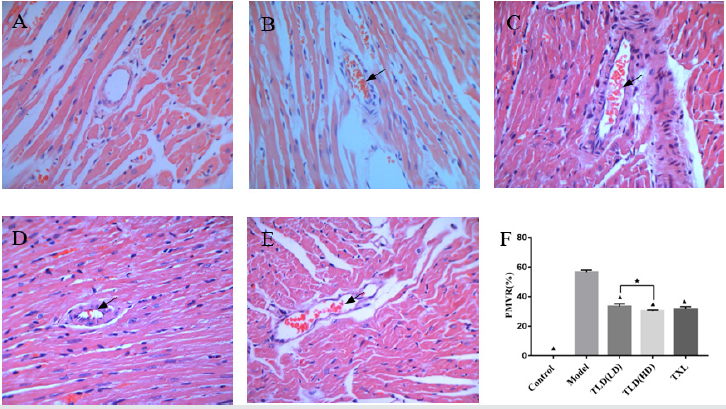
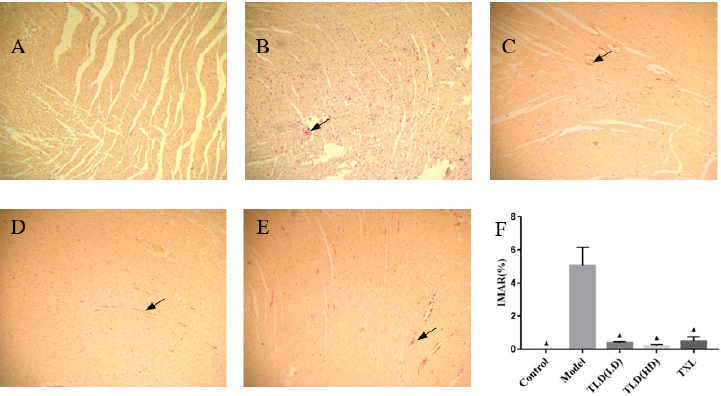
Figure 4: Comparison of HBFP staining of ischemic myocardium of rats in each group(100×). A blank group, B model group, C TLD(LD) group, D TLD(HD) group, E TXL group, F Comparison of HBFP staining of ischemic myocardium of rats in each group. (▲)P<0.05, versus model group. IMAR:Ischemic myocardial area ratio.
HBFP staining results of ischemic myocardium
In Figures 5(a)-5(f), almost no red myocardium tissues was found in the blank group. A large number of red myocardium tissues were found in the model group. Tongluo Decoction low dose group, Tongluo Decoction high dose group and Tongxinluo group found some red myocardium tissues. Compared with the blank group, the ratio of ischemic myocardial area ratio in the model group was significantly higher (P < 0.05). Compared with the model group, the ratio of ischemic myocardial area ratio in Tongluo Decoction low dose group, Tongluo Decoction high dose group and Tongxinluo group decreased significantly (P < 0.05). Compared with Tongxinluo group, the ratio of ischemic myocardial area ratio(IMAR) in Tongluo Decoction low dose group, Tongluo Decoction high dose group was decreased, but the difference was not statistically significant (P > 0.05) .
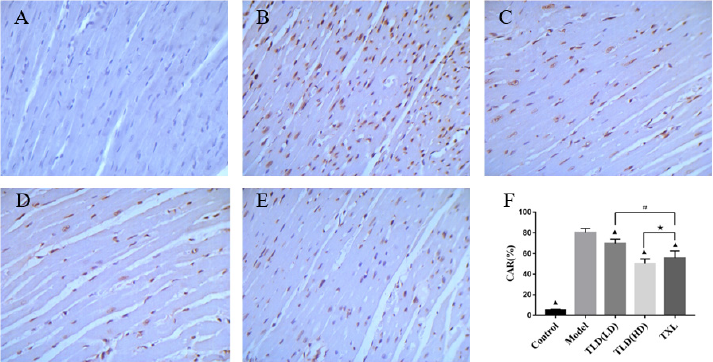
Figure 5: Comparison of TUNEL staining(400×)and apoptosis rate of myocardial cells in each group of rats. A blank group, B model group, C TLD(LD) group, D TLD(HD) group, E TXL group. F Apoptosis rates of cardiomyocytes in TUNEL staining groups were compared, (▲)P<0.05, versus model group; (#)P<0.05, TLD(LD) group versus TXL group; (★)P>0.05, TLD(HD) group versus TXL group. CAR: cardiomyocyte apoptosis ratio.
Detection of cardiomyocyte apoptosis by TUNEL
As shown in Figure 6, TUNEL staining showed that the normal nuclei were pale blue, the apoptotic nuclei were tan, nuclear chromatin was concentrated, and the nuclei were broken into unequal nucleus fragments, accompanied by the formation of apoptotic bodies. There were almost no tan nuclei in the control group, and a number of tan nuclei in the model group. Tongluo Decoction low dose group, Tongluo Decoction high dose group and Tongxinluo group have some tan nuclei. The apoptosis rate of myocardial cells in the model group was significantly higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05). Compared with the model group, the cardiomyocyte apoptosis rate in Tongluo Decoction low dose group, Tongluo Decoction high dose group and Tongxinluo group decreased significantly (P < 0.05). Compared with Tongxinluo group, the decrease of cardiomyocyte apoptosis rate in Tongluo Decoction low dose group was small (P < 0.05) , but the decrease of cardiomyocyte apoptosis rate in Tongluo Decoction high dose group was much more (P > 0.05).
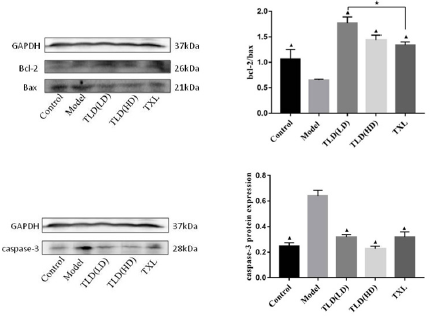
Western Blot detect the expression of Bcl-2, Bax and caspase-3
Protein in Cardiac Myocytes
As shown in Figures 3(a)-3(f)) and (Table 2), compared with the control group, the expression of Bcl-2 protein and bcl-2/bax of the model group were decreased, the expression of Bax and Caspase-3 in the model group were significantly increased (P < 0.05). Compared with the model group, the expression of Bcl-2 protein, bcl-2/bax were increased and the expression of Bax and Caspase-3 were decreased in the Tongluo Decoction low dose group, Tongluo Decoction high dose group and Tongxinluo group (P < 0.05). Compared with Tongxinluo group, the expression of Bcl-2 protein, bcl-2/bax increased (P < 0.05), the expression of Bax and caspase-3 protein decreased in the Tongluo Decoction low dose group and the Tongluo Decoction high dose group (P > 0.05). These results indicate that the coronary microembolization(CME) can induce cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and Tongluo Decoction and Tongxinluo can inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
Table 2: The results of bcl-2/bax ratio in each group of rats (x ± s ).
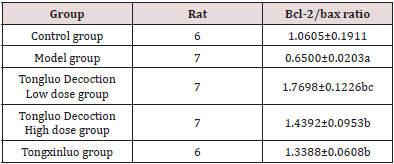
Note: Comparison with control group.
aP﹤0.05; Comparing with model group.
bP﹤0.05; Comparing with Tongxinluo group, cP﹤0.05.
Discussion
CME is an common complication in the interventional therapy of coronary heart disease. It is one of the important reasons for the occurrence of “no reflow” and “slow flow” of coronary artery. It is an important factor of poor prognosis and even death in some patients after PCI. The secondary myocardial apoptosis and necrotic myocardium irreversible injury are independent predictors of no reflow and poor prognosis. Research shows [4] that a stable, reliable and economical model of coronary arteria microembolism can be established by injecting autologous thrombus to the aortic root of rat through the right common carotid artery. In this study, we followed this method and established the rat CME model successfully. After the drug intervention 12 days, we found that both Tongluo Decoction and Tongxinluo could contribute to the narrowing of the microembolus, promote the blood circulation of the coronary microembolic vessels and improve the condition of myocardial ischemia. Tongluo Decoction is composed of many kinds of Chinese medicinal materials according to the rule of monarch(Jun), minister(Chen), assistant(Zuo) and guide(Shi). It has the effects of benefiting qi for activating blood circulation and disperse blood stasis and dredge collateral circulation. Among this Chinese medicine compound, Astragali Radix(Huangqi) as the monarch, compatible with Radix ginseng Rubra (Hongshen) can tonify Qi of spleen and Lung significantly. It made QI and blood own a recourse to metaplasia. Compatibility of Radix Paeonia Rubra (Chishao) have an effect on blood stasis runs and relieve pain, cooling blood and subsidence of a swelling. Assistance of Radix Bupleuri(Chaihu), Rhizoma Cimicifugae(Shengma), Radix Platycodonis(Jiegeng) for lifting Yangqi and carrying medicine upgoing. Qi running leads to blood circulation. Then add Fructus Corni(Shanyurou) to nourish the Yin of liver and kidney. Radix Glycyrrhizae(Gancao) as guide plays an harmonization of all drugs role in the compound. All drug compatibility, reflect a efficacy of tonifying qi and yin and promoting blood circulation to remove meridian obstruction. Zhang Zhenguo and other studies [6] found that Tongluo Decoction could inhibit the pathological process of coronary microembolism, reduce myocardial damage, inhibit the expression of inflammatory factors and promote the role of microembolic vascular recanalization.
Apoptosis is an active and orderly death process, which is produced by the body in the physiological and pathological conditions to maintain the homeostasis of its own internal environment [7]. Studies have shown that apoptosis is one of the possible mechanisms of ventricular dysfunction induced by coronary microembolization [8]. Anti apoptotic therapy can significantly inhibit the apoptosis of cardiomyocytes after CME in rats [9-11]. Studys showed that Tongxinluo capsule could inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis [12, 13]. In our study, Tongxinluo was used as a positive control group to further study the mechanism of Tongluo Decoction from the perspective of apoptosis. Mitochondria mediated apoptosis pathway is one of the most important apoptotic pathways. Numerous studies have shown [14-16] that inhibition of mitochondrial mediated apoptosis plays an important role in improving CME induced myocardial damage and cardiac dysfunction. The regulation of mitochondrial apoptosis is mainly mediated by the regulation of Bcl-2 family proteins [17, 18]. After the destruction of mitochondria, the release of cytochrome C increased. Under the regulation of Bcl-2 family protein, the release of cytochrome C was induced by anti apoptotic members and inducing apoptotic members, eventually causing the activation of Caspase-3, resulting in the apoptosis [19]. Cysteinyl aspartate specific protease (caspase) is the main effector factor of apoptosis.
Wang JiangYou and other studies [20] showed that increased the expression of Caspase-3 in rat cardiomyocytes after CME, and pretreatment with atorvastatin could downregulate the expression of Caspase-3. Liu Tao and other studies [21] found that after CME bcl-2 expression decreased, Bax and Caspase-3 expression increased, silence LOX-1 can reverse Bcl-2, Bax, caspase-3 protein expression. Bcl-2 can inhibit apoptosis, while Bax can promote apoptosis [22]. The ratio of Bcl-2/Bax is an important parameter of mitochondrial signaling pathway, and the ratio between them is one of the important causes of apoptosis [23, 24] Our study showed that the apoptosis rate of myocardial cells in the CME model group was significantly increased. The expression of Bcl-2 protein, bcl-2/bax were decreased and the expression of Bax and Caspase-3 were significantly increased in the model group. It was indicated that CME induced the cardiomyocytes apoptosis. The apoptosis rate of cardiac myocytes in Tongluo Decoction low dose group, Tongluo Decoction high dose group and Tongxinluo group was significantly lower than that of model group (P < 0.05), and the expression of Bcl-2 protein and bcl-2/bax increased, and the expression of Bax and caspase-3 protein decreased (P < 0.05). It indicates that Tongluo Decoction and Tongxinluo capsule can inhibit the cardiomyocytes apoptosis of rat after CME. Compared with Tongxinluo group, the degree of decrease on cardiomyocyte apoptosis rate in Tongluo Decoction low dose group was lower (P < 0.05) while Tongluo Decoction high dose group was higher (P > 0.05). The results of Western Blot showed that, compared with Tongxinluo group, the expression of Bcl-2 protein, bcl-2/bax increased (P < 0.05), the expression of Bax and caspase-3 protein decreased in the Tongluo Decoction low dose group and the Tongluo Decoction high dose group (P > 0.05). It shows that Tongluo Decoction is almost equivalent to Tongxinluo capsule in the treatment of CME, which can inhibit the apoptosis of myocardial cells of rats after CME, and its mechanism may be related to the blocking of mitochondrial apoptosis pathway.
Conclusion
Tongluo Decoction may inhibit the cardiomyocytes apoptosis of CME rats by blocking mitochondrial apoptosis pathway and protect their myocardium.
References
- RiXin Dai (2010) Role of mitochondria pathways apoptosis on Myocardial contractile dysfun-tion with coronary microembolization. Medical University, china.
- Feilong Zhang, LiangLong Chen, WeiWei Wang, FaYuan Fu (2010) Effects of non-selectivity coronary microembolization on myocardial apoptosis and the left ventricular function of rats. Journal of Clinical Cardiology 26(8): 624-628.
- YunChang Yu, ZaiXiang Shi, LiangDuo Jiang (2008) Effect of Shengjietongyu Tang in protecti-ng the Myocardium of rats from Ischemia-reperfusion Injury. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 29(6): 747-749.
- ShuQin Zhang, ZhenGuo Zhang, Xue Feng (2017) Effect of TongluoDecoction on the CoronaryMicroembolization in Rats. Chinese Journal of Integrative medicine on cardio/ cerebrovascular disease 15(05): 551-555.
- ZhenGuo Zhang, XueFeng Li, ShuZhen Zhu (2018) Establishment of a model of coronary microembolization in rats by intervention. Journal of Chongqing Medical University 43(3): 338-342.
- XinYou Shi (2000) Experimental zoology of modern medicine. (1st edn), People's Milit-ary Medical Press, China pp: 334-335.
- QuanQuan Wang, WenLi Zhang, XiaoDong Yuan (2015) Effect of Mitochondria in Apopto-sis. Medical Innovation of China 12(6):143-146.
- YaFei Mi, XiaoYing Li (2006) Advances in coronary heart failure models induced by coronary microembolization. Academic Journal of PLA Postgraduate Medical School 27(4): 308-310.
- Qiang Su, Lang Li, YongGuang Lu (2013) Effect of atorvastatin on apoptosis of myocardiocytes and activation of caspase-12 in rats following coronary microembolization. Journal of Geriatric Heart Brain and Vessel Diseases 15(7): 748-752.
- JiangYou Wang, Han Chen, Hua Yan (2018) Effect of levosimendan on cardiomyocyte apoptosis after coronary microembolization in swin. Journal of Geriatric Heart Brain and Vessel Diseases 20(1): 78-82.
- Su Qiang, Li Lang, Liu Yang-Chun (2013) Effect of metoprolol on myocardial apoptosis after coronary microembolization in rats. World J Emerg Med 4(2): 138-143.
- Geng Wei, Junqing Liang, Bing Yao (2018) Effect of Tongxinluo Treated Conditioned Medium of Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells on Rats’ Embryo Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis. Circulation Journal 33(3): 279-284.
- Ting Huang, Shaodan Li, Han Li (2017) Protective Mechanism of Tongxinluo Capsule on Inflammatory Responses Induced by Degranulation of Mast Cells against Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Journal of Integrative medicine on cardio/cerebrovascular disease 15(23): 2973-2976.
- Li Lang, Su Qiang, Wang Yan (2011) Effect of atorvastatin (Lipitor) on myocardial apoptosis and caspase-8 activation following coronary microembolization. Cell Biochemitry and Biophysics 61(2): 399-406.
- Su Qiang, Li Lang, Liu Yang-Chun (2013) Effect of metoprolol on myocardial apoptosis and caspase-9 activation after coronary microembolization in rats. Exp Clin Cardiol 18(2): 161-165.
- Liu YC, Li L, Su Q, Liu T, Tang Z (2015) Trimetazidine Pretreatment Inhibits Myocardial Apoptosis and Improves Cardiac Function in a Swine Model of Coronary Microembolization. Cardiology 130(2):130-136.
- Shi Jiaojiao, Jiang Qi, Ding Xiangwei (2015) The ER stress-mediated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and MAPKs modulate tachypacing-induced apoptosis in HL-1 atrial myocytes. PLoS ONE 10(2): 1-15.
- Lurlaro R, Muñoz-Pinedo C (2016) Cell death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. The FEBS Journal 283(14): 2640-2652.
- Hu Ling-Ai, Sun Yu-Kun, Zhang Hong-Sheng (2016) Catalpol inhibits apoptosis in hydrogen peroxide-induced cardiac myocytes through a mitochondrial-dependent caspase pathway. Biosc Rep 36(3):1-9.
- Wang Jiang-You, Chen Han, Su Xi (2016) Atorvastatin Pretreatment Inhibits Myocardial Inflammation and Apoptosis in Swine After Coronary Microembolization. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics 22(2):189-195.
- Liu Tao, Zhou You, Wang Jiang-You (2016) Coronary Microembolization Induces Cardio-myocyte Apoptosis in Swine by Activating the LOX-1-Dependent Mitochondrial Path-way and Caspase-8-Dependent Pathway. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology andTherapeutics 21(2): 209-218.
- Jianzhi Wang, Lianhua Yin (2013) Pathophysiology. (8th edn.), People's Medical Pu-blishing House pp: 130-147.
- Haiyan Ding, Rong Han (2016) Clematichinenoside (AR) Attenuates Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced H9c2 Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis via a Mitochondria-Mediated Signaling Pathway. Molecules 21(6): 1-13.
- Xingqin Tan, Yupei Chen (2007) Apoptosis factor bcl-2/bax and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Chongqing medicine 36(18): 1885-1887.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...