Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-4609
Research Article(ISSN: 2637-4609) 
Spectrum Subtraction Method for Simultaneous Determination of Paracetamol and Diclofenac sodium in their Combined Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms Volume 4 - Issue 3
Mahmoud M Sebaiy1* and Amr A Mattar1,2
- 1Medicinal Chemistry Department, Zagazig University, Egypt
- 2Pharmaceutical Medicinal Chemistry Department, Egyptian Russian University, Egypt
Received: February 04, 2020; Published: February 18, 2020
*Corresponding author: Mahmoud M Sebaiy, Medicinal Chemistry Department, Zagazig University, Egypt
DOI: 10.32474/AOICS.2020.04.000188
Abstract
A simple, specific, accurate and precise spectrophotometric method was settled for simultaneous determination of paracetamol and Diclofenac Sodium in their pure form and in their pharmaceutical formulation. Spectrum subtraction technique has been used in simultaneous determination of both drugs without prior separation. Spectrum subtraction method parameters were validated according to ICH guidelines in which accuracy, precision, repeatability and robustness were found in accepted limits. Advantages and disadvantages of spectrum subtraction technique were discussed and statistical comparison between the proposed method and the reference one was also performed.
Keywords: Spectrophotometric; Paracetamol; Diclofenac Sodium; Spectrum subtraction; ICH guidelines; Statistical comparison.
Introduction
Paracetamol (PAR); N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl) acetamide (Figure 1) is related to NSAID (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) which can act both centrally and peripherally for the treatment of non-inflammatory conditions in patients having gastric symptoms [1]. Diclofenac sodium (DCL); 2-(2,6-dichloroamino)phenylacetic acid (Figure 1) [2], is an analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent which can act by the inhibition of the synthesis and the release of leukotrienes and prostaglandins [3]. DCL can be combined with PAR as the latter can provide basic relief before DCL and enhances its pain-relieving and antipyretic effect. PAR & DCL combination can be used in treatment of several diseases not only inflammation [4].The literature demonstrated that several methods were accomplished for the analysis of PAR and DCL in their mixture form or in combination with other drugs. PAR & DCL have been determined by spectrophotometric methods [5-9], HPLC methods [10-13], TLC methods [14,15], capillary zone electrophoresis method [16], voltammetric method [17], a method based on poly (diallyldimethylammonium chloride) functionalized graphene [18] and a method based on Au nanoparticles - functionalized graphene/ poly ( L-Arginine ) glassy carbon electrode [19]. To the best of our knowledge, no method for the estimation of this drug mixture by using spectrum subtraction technique was yet reported. As such, the aim of the current work is to develop a new spectrophotometric method which is accurate, fast and non-complicated for determination of PAR & DCL combination without the interference of their additives or their excipients in pharmaceutical formulations.
Experimental Apparatus
JASCO dual beam (Japan) UV-visible spectrophotometer model V-630, connected to an ACER compatible computer with spectra manager II software was used. The spectral slit width is 2 nm at speed up can be increased up to 8000 nm/min. All the measurements have been carried out in 1 cm quartz cell. The wavelength ranges were 200 - 400 nm at room temperature. Also, PASW statistics 18 software program was used for statistical analysis.
Materials and Reagents
Pure standards
PAR and DCL were kindly provided by EIPICO(Egypt). Their purity was claimed to be as 99.50% and 99.80 % for PAR & DCL, respectively.
Pharmaceutical formulations
Diclocin® tablets were purchased from the market (label claim: PAR 250 mg + DCL 50 mg) produced by Cipcopharmaceuticals, India.
Solvents
HPLC grade Methanol was purchased from LiChrosolv, Merck KGaA (Germany). All of measurements have been accomplished by using 90% Methanol.
Standard solutions
Standard stock solutions (1 mg/mL) of PAR and DCL were prepared in 90% methanol. Working standard solution of PAR (40 μg/mL) and DCL (50 μg/mL) were prepared by further dilution with 90% methanol.
Laboratory prepared mixtures
Different ratios of PAR & DCL were performed by transferring aliquots from their standard solutions to volumetric flasks (10 mL) and then dilution was carried out with 90% methanol.
Procedure
Construction of calibration curves
For PAR: Working solutions equivalent to 4-22 μg/mL were prepared by addition of aliquots (1, 1.50, 2, 2.50, 3, 3.50, 4, 4.50, 5, 5.50 mL) of PAR working standard solution (40 μg/mL) to 10 mL volumetric flasks followed by dilution with 90% methanol. For DCL: Working solutions equivalent to 5-45 μg/mL were prepared by adding aliquots (1, 1.50, 2, 2.50, 3, 3.50, 4, 4.50, 5, 6, 7 mL) of DCL working standard solution (50 μg/mL) to 10 mL volumetric flasks followed by dilution with 90% methanol. Measurements of the absorption spectra were carried out at room temperature over the wavelengths (200-400 nm).
For Spectrum Subtraction method
The method relies on subtracting the spectrum of Y from the spectrum of the mixture (X + Y), therefore we can obtain the zeroabsorption spectrum of X again. This can be summarized as the following:
(X + Y) - Y = X
Figure 2: Spectrum subtraction of DCL & PAR from their mixture resulting in absorption spectra of PAR and DCL, respectively.
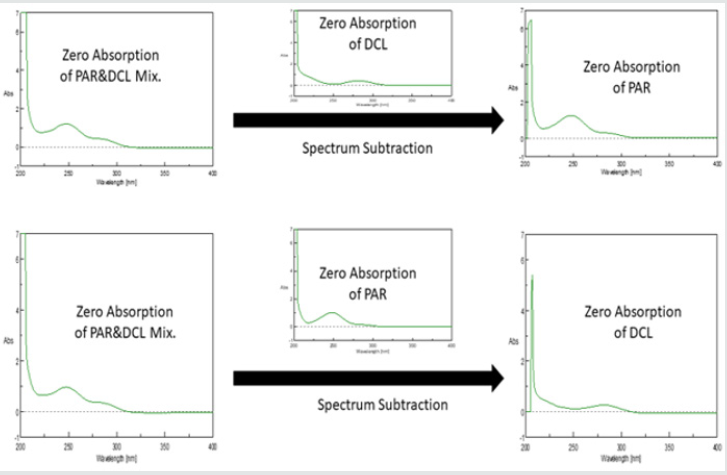
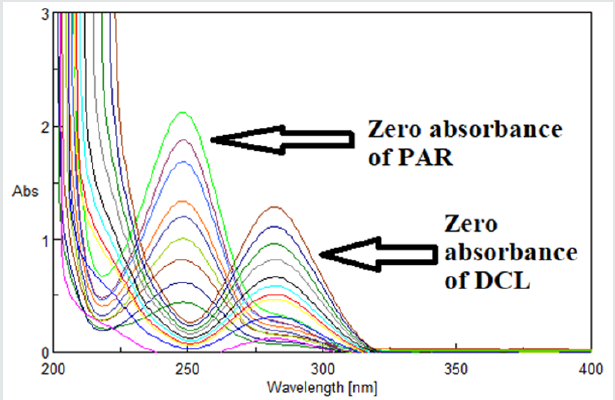
The concentration of X is calculated from the corresponding regression equation obtained by plotting the absorbance values of the zero order absorption spectra of X at its λmax against the corresponding concentrations. Zero absorption spectra of PAR & CAF can be recovered from their mixture through spectrum subtraction of CAF and PAR, respectively (Figure 2). Zero absorption spectra of CAF and PAR are shown in (Figure 3).
Analysis of laboratory prepared mixtures
The spectra of the mixtures were measured after preparation of different ratios of the laboratory prepared mixtures then handled in the same conditions as described under each method.
Application to pharmaceutical formulation
10 tablets of Diclocin® were weighed and crushed then an amount equivalent to 50 mg PAR and 10 mg DCL in each tablet was transferred into a volumetric flask (50 mL) and diluted with 90% methanol as follow: First, 30 mL of 90% methanol were added and sonicated then dilution was carried out to the mark and filtered. Second, 10 mL of the dilution was transferred into a 100 mL volumetric flask to give a concentration equivalent to 100 μg/mL PAR and 20 μg/mL DCL. Third, any further dilutions were carried out in volumetric flasks (10 mL) and treated in the same way as described under each method.
Results and discussion
Method Optimization
Two major problems were found during the analysis of PAR & DCL binary mixture; first, the overlapped spectra between the absorptivity of both drugs, and second, PAR, the main (major) constituent, had unfortunately very high absorbance, while DCL, the minor component, had low absorbance value. Intrinsically, sample enrichment technique [20] was used in which the concentration of DCL (the minor component) in their dual mixtures was increased to facilitate its determination. This was carried out by adding a fixed amount of standard DCL to each experiment when combined with PAR, then subtraction of its concentration before the calculation of the required concentration of DCL. Sample enrichment technique has been used for solving the same problem in the analysis of other drug mixtures of different drug ratios [21,22].
Spectrum Subtraction method
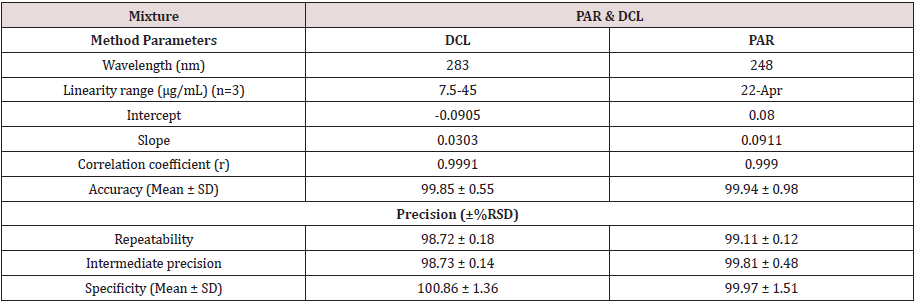
248 and 283 nm absorbances were used for determination
of PAR & DCL in presence of each other, respectively. The
calibration curves revealed accepted linear relationships between
concentrations and absorbance in a range of 4-22 μg/mL for PAR
and 7.5-45 μg/mL for DCL with correlation coefficients of ≥ 0.9990
for both drugs. The accuracy of the method illustrated accepted
values with 99.94% ± 0.98 for PAR and 99.85% ± 0.55 for DCL.
The specificity of the method demonstrated accepted values with
99.97% ± 1.51 for PAR and 100.86% ± 1.36 for DCL. The results are
detailed in Table 1.
Spectrum subtraction is very easy and simple as it depends on
zero absorption spectra without the need of extra processing. It is
having few steps to get the zero order spectra of the desired drug,
but it suffers from noise interference while acquiring the desired
drug concentration by subtraction.
Method validation
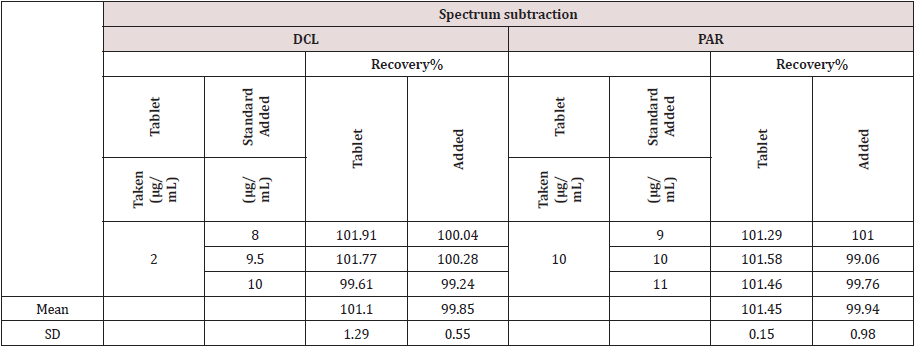
The method was validated according to ICH guidelines [17] . The linear regression data for the calibration curve showed good linear relationship. (Table 1). The accuracy was calculated by analyzing the standard addition where satisfactory results were obtained as shown in Table 1.The specificity of the method was calculated by assaying the laboratory prepared mixtures of PAR & DCL within the linearity range and good results were obtained (Table 1).The intra- and inter-day precisions were calculated by the analysis of 3 different concentrations of the drugs 3 times on the same day and on 3 successive days (Table 1).
Application to Pharmaceutical Formulation
determination of PAR and DCL in their pharmaceutical formulation (Diclofenac Sodium plus tablets). The results were acceptable and with sufficient agreement with the labeled amounts. The standard addition technique was applied and showed that no interference of the excipients was observed (Table 2).
Table 2: Analysis of the pharmaceutical preparation (Diclocin® tablets) by applying proposed method.
Statistical Analysis
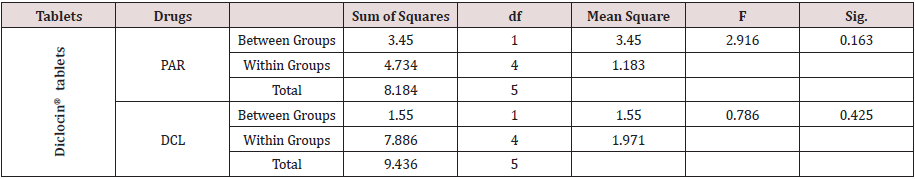
Statistical comparison of the proposed method was performed through One-way ANOVA method by using PASW statistics 18 software program in which there was no significant difference between the proposed method and the reference one [4] as shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Statistical comparison of the results obtained by the proposed method and the reference method using One-way.
Conclusion
Spectrum subtraction method was successfully applied for the determination of paracetamol and Diclofenac Sodium in their binary mixtures and in their dosage form. The proposed method is simple, sensitive and accurate and could be used for routine analysis by using simple technology or instruments. By comparison with the previous reported methods, it was concluded that spectrum subtraction method is very simple and doesn’t require extra processing. Statistical comparison revealed that there was no observed significant difference between the proposed method and the reference one.
References
- Yehia AM, Abd El-Rahman MK (2015) Application of normalized spectra in resolving a challenging Orphenadrine and Paracetamol binary mixture. Spectrochimica Acta - Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, Elsevier BV 138: 21-30.
- Barry M, Mahood AJ, Hamezh M (2009) Spectrophotometric Determination of Diclofenac sodium in Pharmaceutical preparations. Journal of Kerbala University 7(2): 310-316.
- Scholer DW, Boettcher I, Ku EC, Schweizer A (1985) Pharmacology of diclofenac sodium (Voltaren®). Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, Grune & Stratton Inc 15(2): 61-64.
- Brogden, RN, Heel RC, Pakes, GE, Speight TM, Avery GS (1980) Diclofenac Sodium: A Review of its Pharmacological Properties and Therapeutic Use in Rheumatic Diseases and Pain of Varying Origin. Drugs 20(1): 24-48.
- Saheb DJ, Reddy NR, Chakravarthy IE (2004) Simultaneous determination of paracetamol and diclofenac sodium from combined dosage forms by absorbance difference method. Asian Journal of Chemistry 16(2): 767-72.
- Hegazy MA, Elshahed MS, Toubar SS, Helmy MI (2018) Efficient processing of Single and Multiple Spectral Variables for Resolution and Quantitation of Paracetamol, Chlorzoxazone and Diclofenac. Journal of Advanced Pharmacy Research 2(4): 269-282.
- Phaneemdra D, Nagamalleswar G (2012) Quantitative analysis of paracetamol and diclofenac in combined dosage form by first derivative and simultaneous equation method in application to the determination of dissolution study. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research 3(10): 3871-3876.
- Sharma R, Pathodiya, G, Mishra GP, Sainy J (2010) Spectrophotometric Methods for Simultaneous Estimation of Paracetamol and Diclofenac Sodium in Combined Dosage Form by Application of Hydrotropic Solubilization. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research 2(12): 821-826.
- Sebaiy, MM, El-adl SM, Mattar AA (2020) Spectrochimica Acta Part A : Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy Different techniques for overlapped UV spectra resolution of some co-administered drugs with paracetamol in their combined pharmaceutical dosage forms. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy Elsevier BV 224: 117429.
- Walash MI, Ibrahim F, Abo S, Abass E (2017) Development and Validation of HPLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Famotidine, Paracetamol and Diclofenac in their Raw Materials and Pharmaceutical Formulation. Analytical Chemistry Letters 7: 421-437.
- Jana K, Adhikari L, Moitra S, Behera A (2011) Analysis of multicomponent drug formulations (diclofenac and paracetamol). Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research 4: 2-4.
- Badgujar MA, Pingale SG, Mangaonkar KV (2011) Simultaneous Determination of Paracetamol , Chlorzoxazone and Diclofenac Sodium in Tablet Dosage Form by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. E-Journal of Chemistry 8(3): 1206-1211.
- Nayak VG, Bhate VR, Purandare SM, Dikshit PM, Dhumal SN, et al. (1992) Rapid Liquid Chromatographic determination of Paracetamol and Diclofenac Sodium from a combined pharmaceutical dosage. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy 18(3): 369-374.
- Dighe VV, Sane RT, Menon SN, Tambe HN, Pillai S, et al. (2006) Simultaneous Determination of Diclofenac Sodium and Paracetamol in a Pharmaceutical Preparation and in Bulk Drug Powder by High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography. Journal of Planar Chromatography 19(112): 443-448.
- Mohammad ALI, Sharma S (2009) Separation of Co-existing Paracetamol and Diclofenac Sodium on Silica Gel “H” Layers using surfactant mediated mobile phases: Identification of Diclofenac Sodium from human urine. Farmacia 57: 201-11.
- Solangi A, Memon S, Mallah A, Memon N (2010) Determination of ceftriaxone , ceftizoxime , paracetamol , and diclofenac sodium by capillary zone electrophoresis in pharmaceutical formulations and in human blood. Turk J Chem 34(6): 921-933.
- Transactions ECS, Society TE (2018) Voltammetric Determination of Diclofenac in the Presence of Paracetamol and Naproxen by an Artificial Neural Network Model Using a Carbon Paste Electrode G. Y. Aguilar-Lira. ECS Transactions 84(1): 195-205.
- Okoth OK, Yan K, Liu L, Zhang J (2015) Simultaneous Electrochemical Determination of Paracetamol and Diclofenac Based on Poly (diallyl dimethylammonium chloride) Functionalized Graphene. Electroanalysis 28(1): 76-82.
- Afshar Esmail, Jalali F (2016) sensitive simultaneous determination of paracetamol and diclofenac based on au nanoparticles - functionalized graphene/poly (l-arginine) glassy carbon electrode. Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society 61(1): 2846-2851.
- Lotfy HM, Tawakkol SM, Fahmy NM, Shehata MA (2014) Successive spectrophotometric resolution as a novel technique for the analysis of ternary mixtures of pharmaceuticals. Spectrochimica Acta - Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy Elsevier BV 121(5): 313-323.
- Moussa BA, Mahrouse MA, Fawzy MG (2018) Different resolution techniques for management of overlapped spectra: Application for the determination of novel co-formulated hypoglycemic drugs in their combined pharmaceutical dosage form. Spectrochimica Acta - Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, Elsevier BV 205: 235-242.
- Lotfy HM, Mohamed D, Mowaka S (2015) A comparative study of smart spectrophotometric methods for simultaneous determination of sitagliptin phosphate and metformin hydrochloride in their binary mixture. Spectrochimica Acta - Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy Elsevier BV 149: 441-451.
- ICH (2005) Validation of Analytical Procedure: Text and Methodology Q2 (R1). ICH Steering Comittee 1994.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...