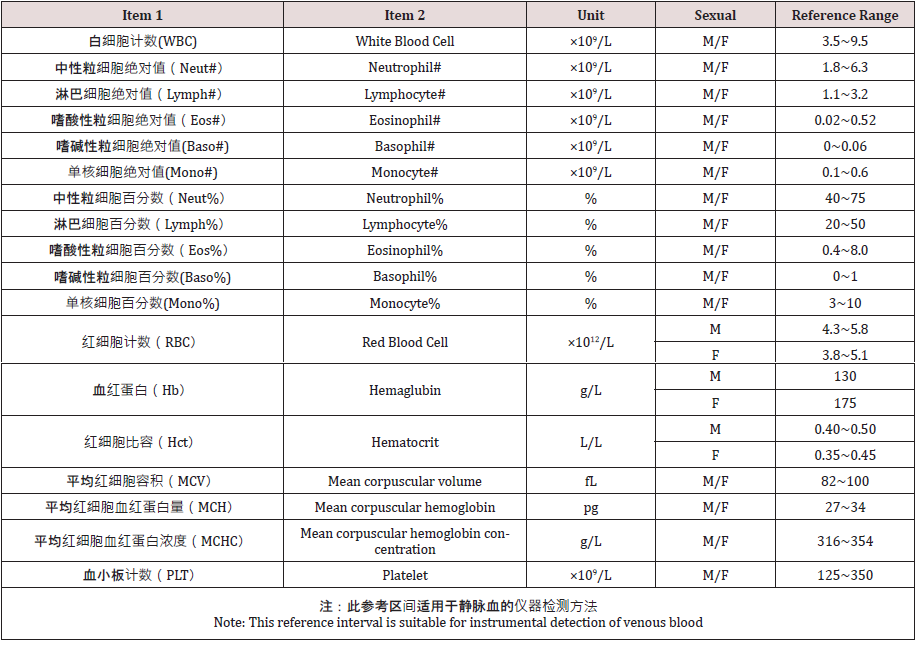
Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
Research Article(ISSN: 2641-6875) 
Thoughts on the Reference Range of Laboratory Tests Volume 1 - Issue 5
Shi-min Zhang1 and Ying Lan2*
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Microbial Resources, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Received:February 17, 2020; Published: June 17, 2020
*Corresponding author: Ying Lan, State Key Laboratory of Microbial Resources, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100101, China
DOI: 10.32474/CTBM.2020.01.000121
Abstract
This article discusses the value research data in Guan’s paper published on medRxiv, February 9, 2020. In terms of experimental data, the preprinted paper is by far the largest sample number of 2019-new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infected patients. Including 552 hospitals from 31 provinces in China as of January 29, 2020, a total of 1,099 cases. Laboratory evaluations include multiple blood cell counts, blood chemistry, coagulation tests, liver and kidney function, electrolytes, C-reactive protein,
Keywords: Reference range; 2019-nCoV, SARS-CoV-2, 2019-nCoV ARD, COVID-19
Introduction
Professor Guan et al. [1] recently published an article “clinical
characteristics of 2019 novel coronavirus infection in china”. It is
a preprinted version of medRxiv on BMJ publishing platform. The
authors of the article covered all frontline anti-epidemic frontlines
including Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Disease, Wuhan Jinyintan
Hospital, Institute of Hematology, Union Hospital, Tongji
Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology,
The Central Hospital of Wuhan, Huanggang Central Hospital,
Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, et al. The Chinese
University of Hong Kong. In this retrospective study, the authors
extracted the data on 1,099 patients with laboratory-confirmed
2019-nCoV ARD (COVID-19) from 552 hospitals in 31 provinces/
provincial municipalities through January 29th, 2020. So far, it is
the largest number of cases collected, the clinical characteristics
of the patients with the most complete distribution, and the most
comprehensive Chinese experience of SARS-CoV-2 treatment are
released to the world.
In the preprinted paper, the authors found that fever occurred
in only 43.8% of patients with 2019-nCoV ARD (COVID-19) but
developed in 87.9% following hospitalization. Demographic data
showed a median age of 47.0 years (IQR, 35.0-58.0 years). 2.09%
were healthcare workers. The median incubation period was 3.0
days (range, 0 to24.0). Patients who underwent chest computed
tomography on admission, 76.4% manifested as pneumonia. There
are normal radiological manifestations in some infected patients. In
addition, the researchers obtained a series of laboratory findings,
such as 82.1% and 36.2% of patients had lymphopenia and
thrombocytopenia, respectively. Overall, leukopenia was observed
in 33.7% of patients. Most patients demonstrated elevated levels
of C-reactive protein, rare increases in D-dimer levels, and so on.
The standards used by the authors in analyzing laboratory data do
not meet the standards of the People’s Republic of China’s health
industry (WS/T 405-2012). We will take this article “Clinical
Characteristics of New Coronavirus Infections in China 2019”as an
example to explore the reference scope of laboratory test.
Methods and Results
The report delineated 1,099 patients with 2019-nCoV ARD (COVID-19) from 552 hospitals in 31 provinces/province-level municipalities. Cases were diagnosed based on the WHO interim guidance [2]. Patients were classified into severe and non-serious 2019-nCoV ARD (COVID-19) based on the guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Disease Society of America [3]. Radiologic and laboratory findings was also based on the grouping of severe and non-severe case patients. Table 1 showed lymphopenia was observed in 82.1% of patients on admission (79.3% in nonsevere cases; 95.5% in severe cases), and thrombocytopenia in 36.2% (31.6% in non-severe cases; severe cases 57.7%). Overall, leukopenia was observed in 33.7% of patients (28.1% in nonsevere cases; 61.1% in severe cases).
Hemoglobin (Hb) showed almost no significant decrease. There
are significant differences of Hb level between non-serious cases
and severe cases. It should be noted that only 978 of the 1099
cases provided complete blood routine test data, while the data of
absolute value of lymphocytes and platelet counts were less than
978 cases. This indicating that there is no uniform requirement for
the integrity of test data.
Most patients (60.7%) demonstrated elevated levels of
C-reactive protein levels (56.4% in non-severe cases; 81.5%
in severe cases), rare increases in alanine aminotransferase,
aspartate aminotransferase, creatine kinase, and D-dimer. The
authors only provided 560 cases of the D-dimer detection value,
in which 46.4% patients manifest the increase tendency (43.2% in
non-severe cases; 59.6% in severe cases). Severe cases had more
prominent laboratory abnormalities (i.e., leukopenia, lymphopenia,
thrombocytopenia, elevated C-reactive protein levels) as compared
with non-severe cases (all P<0.05).
Discussion
In terms of experimental data, the preprinted paper is by far
the largest sample number of 2019-new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2)
infected patients. We noticed that the author analyzed laboratory
data, especially blood routine test data, and reached conclusions
such as leukopenia, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, and elevated
C-reactive protein in COVID-19 patients according to certain
criteria, which is not conform to the standards of the People’s
Republic of China’s health industry document WS/T405-2012.
For example, the leukopenia defined in the article is based
on less than 4.0×109/L; the lymphocyte reduction is based on
less than 1.5×109/L; the thrombocytopenia is based on less than
150×109/L; and the C-reactive protein level is based on be equal or
greater than 10mg/L was abnormal (Table 1).
Table 1: Radiographic and laboratory findings of 1,099 patients with 2019-nCoV ARD.
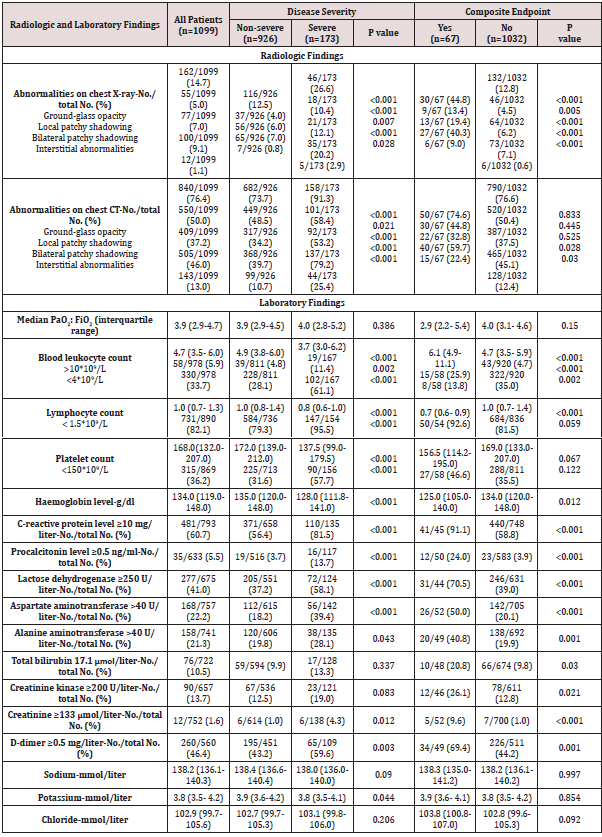
Plus-minus values are means ± SD. Lymphopenia denoted the lymphocyte count of less than 1,500 per cubic millimeter.
Thrombocytopenia denoted the platelet count of less than 150,000 per cubic millimeter. PaO2:FiO2 was defined as the ratio of the
partial pressure of arterial oxygen to the fraction of inspired oxygen.
P values denoted the comparison between mild-moderate cases and severe cases.
As for D-dimer, the author took greater than or be equal 0.5mg/L as the standard for abnormal. However, the different hospitals in China, the difference in methods and reagents used, it is generally considered that the reference interval is less than 0.3mg/L or less than 0.5mg/L. The article uniformly took be equal or greater than 0.5mg/L as the standard for abnormal elevation. Obviously, the 552 hospitals as the participating units are unlikely to use exactly the same methods and reagents.
The China national industry standard blood routine test
reference range was released in 2012, and it has been nearly eight
years. The following table lists the reference range for the analysis
of venous blood in the Chinese adult population for instrumental
detection methods (Table 2).The preprinted article did not adopt
this health industry standard, which shows that the criterion has
not been accepted and recognized by Chinese clinicians. It is a very
important topic whether national industry standards, especially
reference ranges, are recognized by the majority of Chinese
clinicians. Reference range is the basis for clinicians diagnosing
diseases.
In view of the fact that the research object is Chinese, we suggest
that researchers should try to adopt the domestic recommended
standards instead of using the previous concepts and foreign
standards. If domestic industry standards are used in this article,
their statistical results and proportions may be quite different. In
particular, the absolute value of lymphocytes should be significantly
different, which may lead to large differences in conclusions. As we
all know, the new coronavirus epidemic recently occurred in Wuhan
city, Hubei Province, China has spread to other parts of China and
abroad. As an acute respiratory infectious disease, the disease has
been included in the Class B infectious diseases stipulated in the Law
of the People’s Republic of China on the Prevention and Control of
Infectious Diseases and is managed as a Class A infectious disease.
The National Health Committee of the People’s Republic of China
has continuously revised the “Diagnosis and Treatment Program
for Pneumonia of New Coronavirus Infection”, which is currently in
its fifth edition on a trial basis. The guidelines point out that the
diagnosis of suspected cases of COVID-19 should be combined with
a comprehensive analysis of epidemiological history and clinical
manifestations.
The clinical manifestations include
1. Fever and / or respiratory symptoms
2. The imaging characteristics of pneumonia described
above (abbreviated in this article)
3. The total number of white blood cells is normal or
decreased in the early stage of onset, or the lymphocyte count
is decreased.
Any case with epidemiological history that meets any two of the
clinical manifestations can be determined as a suspected case. Once
a misdiagnosis occurs due to a misjudgment of the reference value
range, it is likely to cause severe unforeseen consequences.
The biochemical test results involved in the preprint version
of the article also did not adopt domestic standards, and the
determination of many biochemical indicators is also related to
gender, which are issues that clinicians should pay attention to.
If the author team includes medical laboratory experts, I believe
that the aforementioned laboratory data and reference ranges,
and methodological flaw may be avoided. As stated by the authors,
some cases had incomplete documentation of the exposure
history, symptoms and laboratory testing given the variation in
the structure of electronic database among different participating
site and the urgent timeline for data extraction. Some cases were
diagnosed in out-patient settings where medical information was
briefly documented, and incomplete laboratory testing was applied.
On the other hand, in clinical laboratory practice, we
recommend that laboratory technician communicate with clinicians
to scientifically explain the clinical significance and reference range
of laboratory data. Only in this way, a new reference range can
be adopted and applicated in the hospital. Secondly, whether it is
fully adopted or partially adopted, it depends on how technicians
connect closely with the clinician and perform corresponding
verification. The national industry standard is only a recommended
standard, not a mandatory standard. Clinicians are generally
rigorous when selecting a standard for disease diagnosis. The
preprint article illustrates exactly this problem. When clinicians
judge the test data, they have not adopted our health industry
standards as the judgment standard. It is a typical example of the
disconnection between laboratory and clinical. This is a problem
worthy of laboratory physician’s reflection and deep thought.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China 2016YFE0205800, and Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Bioelectronics, Southeast University.
References
- Guan W, Ni Z, Hu Y, Liang W, Ou C, etal.(2020) Clinical characteristics of 2019 novel coronavirus infection in China. medRxiv.
- Metlay JP, Waterer GW, Long AC, Anzueto A, Brozek J, et. al. (2019) Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia: An official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Disease Society of America. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 200(7): e45-e67.
- World Health Organization (2020) Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when Novel coronavirus (nCoV)infectionissuspected:interimguidance, Switzerland.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...