Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-4676
Short Communication(ISSN: 2637-4676) 
The Effects of Use Probiotics in Feed Supplement for Mountain female goats on the most important productive indicators Volume 9 - Issue 1
Ali Al-Hawrain, Jawad Sharaf, Iyad Al-Khaled, Rana Al-Shohuf, Wathiq Al-Taqee, Moamen Al-Shamndi and Safwan Abuo Assaf*
- Erra Station, Agriculture Scientific Research Center in Swaida, General Commission for Scientific and Agricultural Research (GCSAR), Syria
Received: September 29, 2020; Published: October 05, 2020
Corresponding author: Safwan Abuo Assaf, Agricultural Engineering, Socio-Economic Researcher- Swaida Research Center, General Commission for Scientific Agricultural Research (GCSAR), Damascus, Syria
DOI: 10.32474/CIACR.2020.09.000304
Abstract
This study was carried out at the Era Research Station for Improvement of the Mountain goats - the General Commission for
Scientific Agricultural Research, Syria. During the seasons (2019-2020), in order to determine the effects of use probiotic growth
factor on the most important productive indicators. 40 female milky goats were used in this study divided into two groups; the first
one contained 20 animals as control while the second where treated by using 0.1% probiotic from the total feed diet. The results
showed a highly significant effect for the use of probiotic in the diet at the level of 0.001 comparing with control for the following
indicators: Milk consumed/kg, head production/kg , Milk value/SP, feed cost/ SP, profit margin/SP, where the mean was about
103.48±18.0 2, 0.81±0.02, 181.31±20.32, 141.90±1.03, 39.4±21.03, respectively, the Relative increases above control were 31.82%,
25.38%, 25.38%, 5.36% and 31.46% respectively.
The study recommended studying the effects of use probiotics in Feed for Mountain female goats in the breeders’ farms, as well
as the effect of its use on the other strains of goats in Syria.
Keywords: Mountain Goat; The probiotic; Milk production; Feed Diet; Yield Indicators
Introduction
Goats are considered among the productive agricultural animals, which are suitable for breeding in Syria, as the average number of heads of milking goats, the total number of goats, and milk production amounted to about 1330851 heads, 1995 208/ head, 131592.3 tons respectively, for the average of the period 2014-2018 (Ministry of Agriculture And agrarian reform-Syria). Despite the suitability of the climatic conditions and the nature of the Syrian lands for this type of activity, the great pressure on pastures, the unavailability of fodder materials and the high prices of them necessitate the search for non-traditional alternatives in nutrition, and natural products to combat diseases, among which were probiotic growth stimuli Basavaraju et al. [1]. Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts beneficial to health, especially for the digestive system in which they are originally present Faujdar et al. [2]. Putting the biological promoter in feed mixtures to different animals as nutritional additives shows a positive effect on the gastrointestinal tract, and inhibition of other pathological microorganisms Anuradha et al. [3]. Probiotics are used to improve productivity indicators by improving the digestive process by affecting the balance of rumen flora, and they help demonstrate the genetic potential of the animal feeding on it Ghorbani et al.[4]. Probiotics increase the production of volatile fatty acids, short and medium chain fatty acids, and thus an increase in the energy available to the agricultural animal Rombeau et al. [5]. It has been found that adding microbial nutrition (probiotics) increases body weight and feed consumption in agricultural animals Emanuelle et al. [6].Lema et al. [7]. There was no effect of adding probiotics on red and white blood cell counts and protein in the blood of agricultural animals Sadieket al. [8]. Sayed [9] found an increase in hemoglobin and protein concentrations, and both leukocyte counts and AST (aminotransferase steroids) were not affected in the goats. WhileAntonovic et al. [10] observed a decrease in the concentration of glucose, urea, ALT, and AST (aminotransferase aspartate) in lambs, and an increase in both bilirubin and triglycerides. The study Al-Rubeii et al. [11], included adding different percentages of probiotics (0.2%, 0.4%, 0.6%) to the diet of Awassi lambs, with the aim of finding out the extent of their effect on some quantitative and qualitative characteristics of meat. The results of the experiment showed the superiority of all biological reinforced treatments over the control treatment, related to carcass characteristics, physical composition, muscle and bone distribution and fat distribution pattern, and the treatment was 0.4% higher than the rest of the treatments in all measurements.
Research Goal
The research aims to find out the effect of growth stimuli/ probiotics/on the diets of dairy mountain goat females on productivity indicators.
Materials and Methods
Location
The experiment was carried out at the Erra Research Station to improve the mountain goat breed at the Syrian General Authority for Scientific Agricultural Research for the seasons 2019-2020. The experiment was applied to forty females of milking mountain goats, which were divided into two parts, Control (20), and the experiment (20). A ratio of (0.010% probiotics) was added from the concentrated diet, in addition to the filling ration. Which lasted until the end of the milk production season for a period of 126 days, periodic milk control readings during the season were taken for each goat?
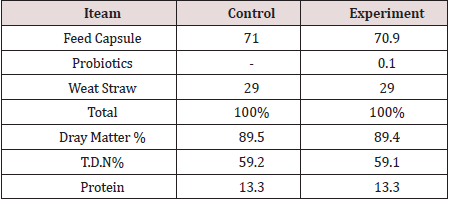
The fodder feed
Ingredients: (Table 1)shows the components of the fodder feed provided to milking mountain goats for both the control and the experiment.
The cost of the daily fodder
(Table 2) the cost of 1 kg daily fodder used for the experiment and control (SP/1 kg).
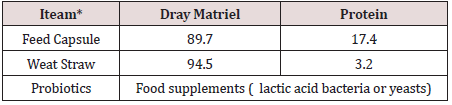
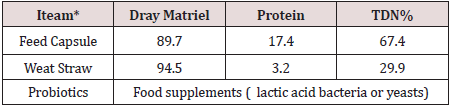
Chemical composition
(Table 3)shows the chemical composition of the feed ingredients as a percentage.The daily feed requirements for animals were calculated based on the American Dietary Needs tables (N R C. 1981) according to the average live weight and the production of 1 kg of milk. Feeding was done on two times at 7 am and 6 pm.
Data Analysis Method
The study relied on descriptive statistics methods to describe
some of the study variables, such as the mean, standard deviation,
and standard error.
Analysis of variance (One way ANOVA), in order to show whether
there is a significant effect of using probiotics on productivity
indicators, and thus the statistical assumptions are:(H0): There are
no significant differences between the averages of the productive
indicators. (H0: μ1 = μ2).
(H1): There are significant differences between the averages of
the productive indicators. (H1: μ1 ≠μ2).
Results and Discussion
Productive indicators
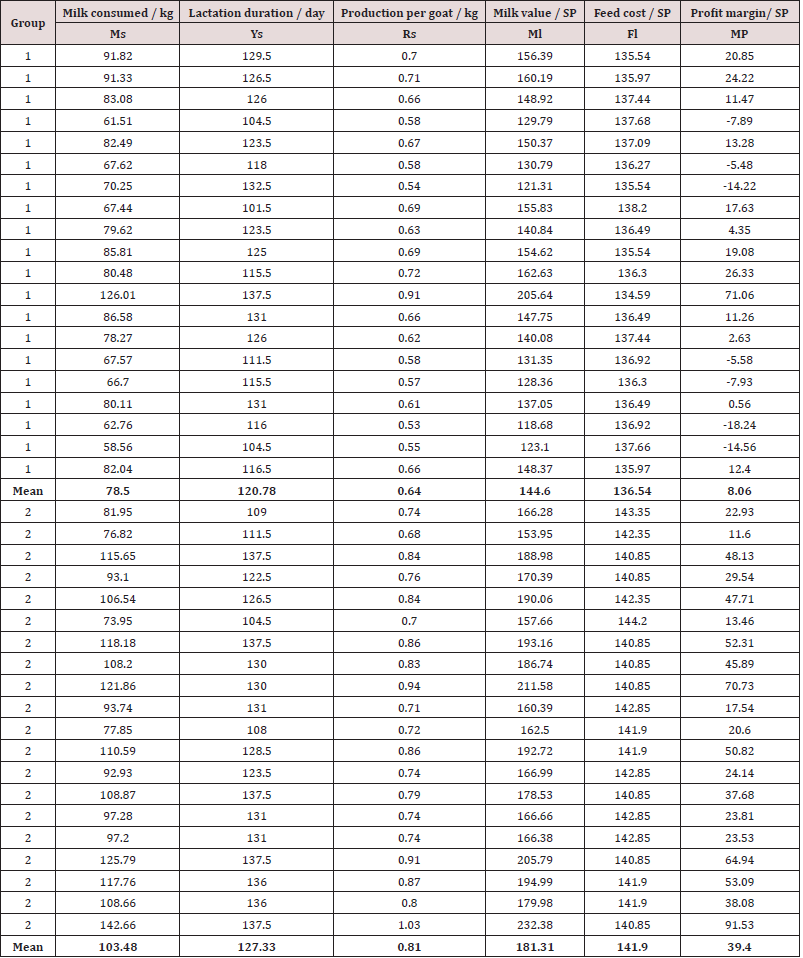
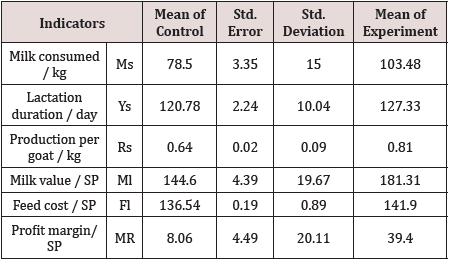
(Table 4) Shows the average values of the productive indicators obtained from the experience and control groups.It was found the negative values of the profit margin in Syrian pounds in the control group, which means loss, and it reached an average of 8.06 SP/ kg. While the positive values were recorded in the experiment, it reached an average of 39.4 SP/kg [12].
The effect of using probiotics
(Table 5,6) shows the results of the analysis of variance and some descriptive indicators:
• There are significant statistically significant differences at
the level of 0.001 between the control and the experiment for
each of the average of the following indicators: milk consumed/
kg, Production per one goat/kg, milk value/SP, feed cost/SP,
profit margin/SP.
• The use of the catalyst in the diet did not significantly
affect the duration of lactation per day.
Conclusion
There is a positive effect of using a probiotic growth stimulator in fodder mixtures for female mountain goats on the most important productivity indicators of dairy goat females compared with the control, except for the milking period indicator, which is in agreement with Ghorbani et al. [4] that adding probiotics to the forage diets improves the level of Productive indicators through improving the digestion process, and also helps to show the inherent genetic potential of the animal fed on it, and Rombeau etal. [5] agrees that the addition of probiotics increases the production of volatile fatty acids and medium and short chain acids that are mainly involved in the composition of goat milk , As it was found that the use of probiotic growth stimulator in the feed had a significant effect on the 0.001 level in favor of the experiment for the control on each of the following indicators: milk consumed / kg, Production per goat/ kg, milk value/SP, cost of feed/SP. Profit margin/SP, where the average of these indicators in the experiment was estimated at about 103.48±18.02, 0.81±0.02, 181.31±20.32, 141.90±1.03, 39.4±21.03, respectively, and the percentage increase represented 31.82%, 25.38%, 25.38%, 5.36% and 31.46% respectively.
References
- Basavaraju, B, Jamil K (2015) Probiotics in Health and Disease: New Approach to Healthier Living. International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR): 2319-7064.
- Faujdar S, Surabhi P, Sharma A (2016) Role of Probiotics in human health and disease: An update. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences 5( 3):328-344.
- Anuradha S, Rajeshwari K (2005) Probiotic in health and disease, JIACM. 6 (1).
- Ghorbani CR, Morgavi DP, Beauchemin KA, Leedle JA (2002) Effect of bacterial direct-fed microbial on ruminal fermentation, blood variables, and the microbial populations of feedlot cattle J Anim.Sci 80(7): 1977-1985.
- Rombeau JL, Kripke SA, Settle RG (1990) Short chain fatty acid. Production, absorption, metabolism, and intestinal effect. In: Kritchesvky D., Ed. Ditary fiber: chemistry, physiology, and health effect. New York and London: plenum press 317-337.
- Emanuelle SM, Horton GMJ, Baldwin JD, Mahana WH (1992) Effect of microbial inoculants on quality of alfalfa hay baled at high moisture and lamb performance. J Dairy Sci 75(11): 3084-3090.
- Lema M, Williams L, Rao DR (2001) Reduction of fecal shedding of enter hemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 in lambs by feeding microbial feed supplement. Small Rumen. Res 39(1): 31-39.
- Sadiek A, Boehm J (2001) Influence of pronifer as aprobiotics on the rumen fluid and blood parameters of sheep fed different roughage concentrate based diets. Wiener TieraztlicheMonatsc shrift 88(1): 4-10.
- Sayed AS (2003) Studies on the influence of pronifer as aprobiotics on the clinical, hematological, and biochemical status of the goats kids. Assiut Vet Med J 99(98).
- Antunovic Z, Marcela S, Liker B, Seric V, Sencic V, Domacinovic M, T. (2005) Influence of feeding of the blood composition. ActaVeterinera (Beogard) 55(4).
- Amera MS Al-Rubeii Ehssan AM AL-kabbani (2011) The Effect of Adding of Probiotic to the Ration in Some of Characteristics for Carcasses of Awassi Lambs. meat Technology
- Ministry of Agriculture & Agrarian Reform, Annual Agricultural Statistical Abstract (2014-2018) Damascus. Syria.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...