Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-4676
Review Article(ISSN: 2637-4676) 
Contradiction of Human Selection Activities to the Evolutionary Development of Ground Plants Will Lead to the Ecological Disaster Volume 8 - Issue 5
Chikov Vladimir Ivanovich*
- Doctor of Biological Sciences, Kazan Institute of Biochemistry and Biophysics, FRC Kazan Scientific Center of RAS, Russia
Received: July 29, 2020; Published: August 26, 2020
Corresponding author: Chikov Vladimir Ivanovich,Doctor of Biological Sciences, Kazan Institute of Biochemistry and Biophysics, FRC Kazan Scientific Center of RAS, Russia
DOI: 10.32474/CIACR.2020.08.000299
Abstract
A contradiction has been established between human breeding activity and the evolutionary development of terrestrial plants, which lead to ecological disaster in the ocean. Experimental data are presented, and the conclusion is drawn that the elimination of these contradictions can not only maintain high productivity, restore soil fertility, but also get rid of a brewing ecological catastrophe in the oceans.
Keywords: Mineral fertilizers, root growth, drought tolerance, plant evolution; ecological disaster in the ocean.
Introduction
A billion years ago, plants that emerged from the ocean to live
on land faced with an unknown factor – a drought. This required
a revolutionary change in the structure of land plants. Waterconducting
root growth intensification was probably one of the
main tasks for plants throughout their history on land. But with the
human development and selection of high-yield plants, this process
was significantly influenced. Cultivated plant breeding by man, first
of all, was aimed at gain in weight of the economically important
organ (ear, +fruit, root tuber). The evolutionary useful organs
such as roots have been ignored by the breeders and developed
spontaneously. As a result, the root system of all cultivated plants
was formed with a reduced weight as compared to the wild
foregoing crops.
A great number of new and high-yield plant varieties were
selected in the breeding process in the 20th century. However, as
a result, the cultivated plants lost the root system size and became
sensitive to adverse environmental factors (primarily to drought).
The agronomists explained these phenomena by the fact that very
favorable conditions were created for the plants to form a high yield
and there was no need for them to develop a strong root system.
But it is obvious that the drought tolerance is determined primarily
by the water-conducting roots’ ability to keep pace with the water
going deep into the soil rather than by the water molecule state in
the cells.
The literature data accumulated to date allow us to conclude
that the key activator for the growth of roots and other neoplasms
in plants is nitric oxide NO [1].which can be formed in the apoplast
of root cells from nitrate, including non-enzymatic way [2].
However, the more fertilizers were applied, the greater part of them
was washed out by groundwater into the rivers and seas. According
to the data of (the World Ocean Atlas 2013), by 1995, there were
305 dead zones with low oxygen level in the ocean across the globe.
In 2007, there were 405 of them, and over the past decade, their
number has increased tenfold. Such conclusions are contained in
the results of studies of the international group of scientists. River
mouths, coastal waters, and even remote from the shore areas
become dead. The marine life could not be supported in dead zones.
This is the fault of nitrogen-phosphate fertilizers entering the water
from the river flows. This results in rapid single-celled algae bloom
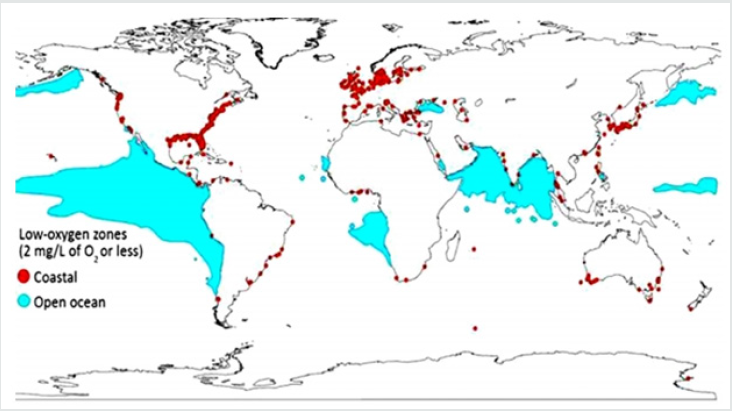
- the food for oxygen consuming bacteria. In combination with global warming, the process is only accelerating, as the high temperature is optimal for the algae (Figure 1).
World map with dead zones in the ocean. Low oxygen zones
are spreading around the world. Red dots indicate locations on the
coast where oxygen has fallen to 2 milligrams per liter or less, and
blue areas indicate areas with the same low oxygen content in the
open ocean.
(RJ Diaz/phys.org) Low-oxygen zones are spreading around
the globe. Red dots indicate places on the coast where oxygen has
plummeted to 2 milligrams per liter or less, and blue areas indicate
zones with the same low-oxygen levels in the open ocean. Intensive
selection of cultivated plants, particularly after the discovery of
Chilean saltpeter, really enabled creation of conditions to provide
high-yield plants with a low mass of roots. In fact, this has saved
millions of human lives. But the breeders’ work in this direction
resulted in an increase in energy-intensive production of mineral
fertilizers and their application to the soil. In Western Europe, this
figure reached 1.5 – 2.0 tons of fertilizers per hectare annually.
Our researches of different drought-tolerance varieties of
barley carried out in Kazan Biochemistry and Biophysics Institute
(in cooperation with the Tatar Agricultural Research Institute)
showed that, early in ontogenesis, the root system of droughttolerant
plants is two times larger [3]. Experimental variation
of photosynthetic product mass (partial removal of leaves) or
inhibition of their export from the leaves (increased nitrate level)
showed that this process can be controlled. Our researches of
different drought-tolerance varieties of barley carried out in
Kazan Biochemistry and Biophysics Institute (in cooperation
with the Tatar Agricultural Research Institute) showed that, early
in ontogenesis, the root system of drought-tolerant plants is two
times larger [3]. Experimental variation of photosynthetic product
mass (partial removal of leaves) or inhibition of their export from
the leaves (increased nitrate level) showed that this process can be
controlled.
As can be seen from the above, breeding activity of human is
in contradiction with the evolutionary development of land plants.
In this regard, the purpose of our research was to check how root
formation depends on the nitrates contained in the soil near the
roots. It was assumed that if there are few nitrates in the soil,
the roots will grow more intensively. Tests with different mineral
nutrition levels (growing plants in soil or sand) have shown
[4] that the root growth can be increased by 2-3 times (Figure
2). To this effect, it is necessary to reduce the nitrate level in the
area of germinating seed (washed sand). An additional effect can
be obtained [5] when plants are sprayed with zinc and copper
ammoniates, which enhance the carbohydrate orientation of
photosynthesis [6] and their export from leaves to economically
important organs [7]. Since our previous works on the study
of the photosynthetic carbon metabolism orientation showed
its dependence on the photosynthetic product use intensity by
acceptors [8], which also depends on the nitrate nutrition level
[9], in conditions of low nitrate nutrition, when it is difficult to
use carbohydrate photosynthetic products, sugars can be used for
the synthesis of cellulose of cell walls only. In this stage of plant
development, the latter is possible in the synthesis of root cell walls
only.
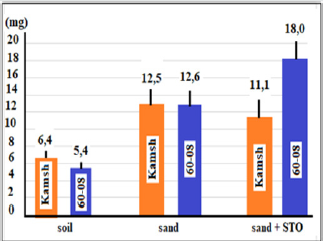
Figure 2: The mass of roots before tillering in resistant (Kamashevsky) and unstable (60-08) varieties of barley. On the abscissa axis is the soil in which the plants were grown (soil,sand and sand, but the plants were sprayed with a solution of (10-4 M) ammoniate STO.
The question now arises, what structures can be synthesized in sufficiently large amounts from pure carbohydrate substrates? It is obvious that these are carbohydrate polymers. This can not be a starch, since its accumulation is limited by the capacity of the respective compartments, and beside that, it does not solve the nitrogen deficiency problem of plants. Therefore, the end product of photosynthesis at this time is most likely the cell wall cellulose. Where can the cellulose be used in a plant? The answer is also obvious — in the building of cells with limited functionality (Figure 3).
Photo
At this stage of plant ontogenesis, these are highly vacuolated
cells that grow by extension. These, of course, are cells of roots
growing inland. Further developing this concept, one can expect
a sharp relative increase in the proportion of cellulose in the dry
mass of root tissues in plants growing in sand. Leaf cells cannot
tolerate this without losing their functionality.
There is another aspect of the problem. In conditions of
nitrogen deficiency and reduced amino acid synthesis, the carbon flux through the glycolytic route and photorespiration are reduced.
This leads to attenuation of the stomata closure mechanism in case
of inconsistency between light and dark reactions of chloroplasts,
as we have shown it in [10]. The increased flow of СО2 into the
leaf probably even more enhances the carbohydrate orientation
of photosynthesis. Testing of this idea in the conditions of artificial
drought showed (photo) that if seeds are sown in a small zone of
sand (furrow of 5 x 5 cm), the root availability increases almost
twice (Table 1).
Table 1: Growing conditions influence on dry root mass of different varieties of string barley, (g).
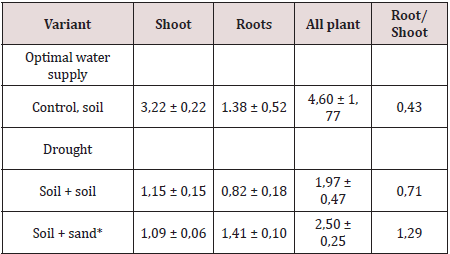
*The sand was added before sowing into the groove with a section of 5[5 cm, where the seeds were sown.
Thus, the root growth, which means drought tolerance and increased symbiosis of the plant with soil microorganisms, increases with a decrease in the nitrate concentration near the seeds. This idea was tested in the field on barley sowing. For this purpose, the seed and fertilizer flows were separated during the sowing.
Checking The Idea Forcing The Production Process Of Plants By Separating Seeds From Fertilizers At Seeding
Field test method. The tests were carried out using industrial seeds of Nur-R3 barley variety. In the absence of the required sowing machine, conventional sowing machine SZS-3,6 was used, but it was transformed as follows (Figure 4). This sowing machine has 24 openers, each supplies seeds from one box, and mineral fertilizers from the other through corrugated plastic tubes. Both flows can be controlled and even (for fertilizers) completely blocked by latches. Therefore, we left one opener unchanged (where both seeds and fertilizers are supplied), in two next openers the fertilizer flow was completely blocked. As a result, eight openers of the sowing machine worked normally. In these openers, seeds were sown together with fertilizers, and the remaining sixteen ones (two after each regular one) sowed only seeds. As a result, the fertilizer amount per unit area decreased three-fold, while the total number of seeds sown remained unchanged.
Figure 4:The scheme of regulation of coulters of the SZS- 3.6 drill for partial separation of seed flows during sowing.
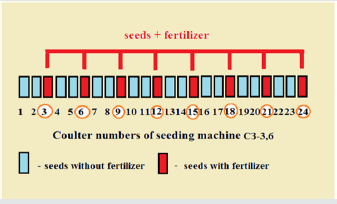
Therefore, the initial stage of development of seeds sown in sixteen openers was in a fertilizer-free environment. But these plants could obtain the required quantity of mineral nutrition from the next row later, as necessary. Therefore, the fertilizer use efficiency should increase. Due to the cold weather during the test, the sowing was completed on May 9, 2018. The number of seedlings in different drill rows was tested on May 30, 2018. The number of plants per linear meter in the row was calculated. And so that, by moving a ruler across the drill rows to the right (each time one row further), the number of plants in seven-eight rows was calculated repeatedly. On June 5, 2018, plants were sprayed with ammoniate solution (concentration of 10-4М) at a selected section of the levelled planting area (3 x 7 m). Then, at the end of tillering, on 16th of June, plant samples from different rows were collected (including sprayed with ammonia) for evaluation of tilling capacity and weight of the whole plant. The sampling procedure was the same as for the germinating capacity evaluation. The samples were collected from each next row by moving from the initial row to the right, step by step. The reference samples (not treated with ammonia) were sampled from the same rows as the samples of plants sprayed with ammoniates. The total number of plants in each test option was 12- 15 (for fertilized options) and 18-24 for the unfertilized ones. The tables show the average statistical data with a standard error.
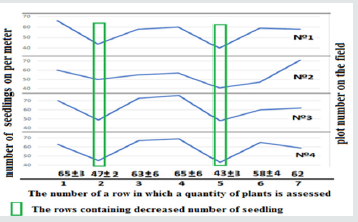
Results and Discussion
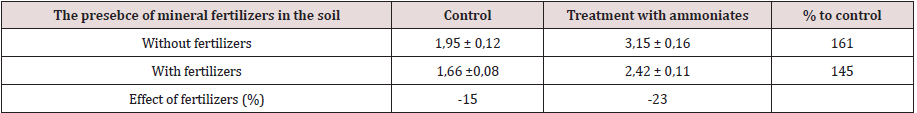
The calculation of plant number per meter in the adjacent rows showed explicit dependence on fertilizers in the soil near the seeds (Figure 5). In fertilized areas, the seedling number was less (by 27%). This fact confirms the well-known depressing effect of mineral fertilizers on the germinating ability. Therefore, it is possible to considerably save expensive seed material by dividing the seed and fertilizer flows when sowing. The further morphometric analysis of the test barley showed its reliable dependence both on fertilizers in soil and on plant treatment by ammoniates. These effects had an impact on sprout formation (Table 2). Fertilizers reduced tilling capacity both in the reference plants (without ammoniate treatment), and in the treated ones. It should be noted that the ammoniate effect on tilling capacity manifested itself to a greater extent in the absence of mineral fertilizers. This shows somewhat of an antagonism of fertilizer and ammoniate effect on the plant metabolism.
Table 2: The effect of the presence in the row of mineral fertilizers and the treatment of sowing with ammoniates on the number of tillering shoots in the Nur-R3 barley plants at the end of the tillering phase.
Our previous researches [5,6] of the mineral fertilizer
(particularly nitrates) and ammoniate effect on photosynthesis
allow to assume that they effect mainly through the change of
photosynthetic metabolism and transport of the main end product
of photosynthesis ̶ saccharose from the leaves. Evaluation of
photosynthetic metabolism of 14C [8] showed its dependence on
the intensity of assimilant export from the leaves and the activity of
photosynthetic product use by acceptors, which decreased under
the influence of nitrates [9]. In terms of lower nitrate nutrition,
when the use of carbohydrate photosynthetic products in synthetic
processes of new tissues is complicated, sugars can be used only
for synthesis of cell wall cellulose. The latter is possible only for the
synthesis of the root cell walls, as these cells are highly vacuolated
and cellulose is the the basis of their dry weight. Table 2. The effect of the presence in the row of mineral fertilizers and the treatment
of sowing with ammonia on the number of tailoring shoots in the
NurR3 barley plants at the end of the tillering phase.
Hence, it follows that the crops should be sown in the
unfertilized soil to increase the root mass. The symbiosis of
plants with soil microorganisms is of great importance. The
abovementioned process created the well-known two-meter
chernozemic soil. But mineral fertilizers suppress microorganism
activity. Similar effects of these factors were found in the analysis of
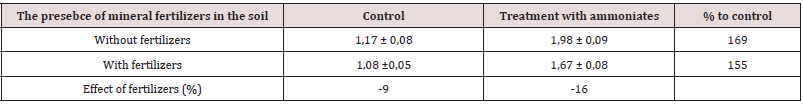
dry mass of plants (Table 3). However, in this case, the ammoniate
effect with mineral fertilizers was less significant. This allows
making a conclusion about the possibility of further intensification
of the root formation process after determination of details of this
mechanism. It should be noted that ammoniates work in very low
concentrations (up to 10-5– 6M), which suggests that metal ions
affect not the pH of the entire aquatic medium in the intercellular
space, but directly the protein molecule of invertase and changes its
reactive center conformation (to be determined in further studies).
But data available show that the cost of the agent is negligible and
the efficiency is high. Moreover, the leaves treated with ammoniates
retain increased sugar export function and photosynthesis intensity
(more open stomata) until the end of their effect. Conclusion The
experiments clearly indicate the need to abandon mineral fertilizers
in agriculture.
Table 3: The effect of the presence in the row of mineral fertilizers and the treatment of sowing with ammoniates on the mass of plants of the Nur-R3 barley plants at the end of the tailoring phase.
The plant root system in the area of low nitrate level will be more
actively interacting with the soil microbial flora, which would supply
the required amount of nitrogen due to microbiological absorption
of air nitrogen. In addition, microbes will increase the availability
of soil-bound phosphorus and potassium to plants. Finally, it is
necessary to step-by-step adopt the agricultural practices that will
allow to intensify development of cultivated plant root systems to
a degree which will gradually exclude the use of mineral fertilizers.
The increased root mass will be the basis for accumulation of soil
organic mass which will increase its fertility over time. It requires
the efforts of agricultural researchers and scientists to search the
ways to maximize the root mass. It is worth to note that symbiotic
microorganisms work in drought conditions as well. Furthermore,
microorganisms protect the plant from water loss, as they isolate
the wet root with their bodies. Less rain-wash of mineral fertilizers
from soil will reduce their transfer to rivers, which would improve
the ecological situation in nearshore zone (Figure 2).
Since the development and serial production of a new sowingmachine
that will separate the seed and fertilizer flows in the
sowing process will take time and requires optimization studies,
in the next vegetation year, the extended testing followed by
application of the above technology using the old sowing-machines
can be carried out as the first step in validation through elaboration
of this technology. This technology will most likely urge to change
the plant distribution pattern in the sowing area (at optimal
distance from the applied fertilizers). This will provide formation
of a strong photosynthetic apparatus of the plant to ensure a high
yield. All this will allow getting the following benefits as compared
to the old agricultural technology: — saving (by three to four times)
of mineral fertilizers applied into the soil, since away from the plant
root system, more than half of them are washed out by rainwater
and affects the environmental situation. — increase of drought
tolerance in high-yield varieties of cultivated plants sensitive to
even minor drought. — increase of cultivated soil natural fertility,
since they contain increased amounts of postharvest organic
matters. — implementation of this agricultural technology is an
important way to reduce CO2 in the air. If the human efforts will be
aimed at gain in the plant root mass, it will not only increase the
soil fertility, but also will gradually bind the great amount of the
atmospheric carbon dioxide in the organic matter of the soil. And all
this is feasible, because the formation of thick (2 m) chernozems in
nature occurred without mineral fertilizers. It is only necessary to
fully develop the root system not only in agricultural plants, but also
in meadow and forest ones. It should be noted that the reduction
in the use of mineral fertilizers in agriculture is also an important
factor in energy saving, since their production consumes about half
of all energy resources of mankind. And this is the main way to save
from, yet unconscious, probability of ecological catastrophe and, as
a consequence, the disappearance of humanity on Earth.
If the efforts of mankind will be aimed at increasing the mass
of roots in plants, this will not only increase soil fertility, but will
gradually bind a huge amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide in the
organic matter of the soil. And all this is doable, because in nature,
the formation of thick (2 m) chernozems occurred without mineral
fertilizers [11]. There is reason to believe that the fires that have
become more frequent in recent years in the forests of Siberia and
America are also associated with a reduction in the mass of tree
roots as a result of the transfer of mineral fertilizers by winds along with dust from agricultural areas. For example, fertilizers can be
brought into Russian Siberia with Avganz (dust clouds covering
the summer sun) from Central Asia, where mineral fertilizers are
used intensively. The negative role of forest fire is also played by
incinerators, which emit nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere.
Getting directly into the leaves, they activate the synthesis of calose,
which clogs the pores in the walls of the phloem vessels, preventing
the transport of sugars to the roots. In such trees (with a small root
size), even from a small drought, there is a possibility of a fire.
References
- Sun CH, et al. (2017) Nitrate: a crucial signal during lateral roots development. Front. Plant Sci 8: 485.
- Neill S, Desikant R, Hancock JT (2003) Nitric oxide signalling in plants. New Phytologist 159: 11-35.
- Blokhin VI, Tagirov MSH, Chikov VI (2016) Influence of mineral nutrition on tillering process of different morphological biotypes of spring barley Niva Tatarstana (2-3): 40-42.
- Chikov VI, GA Akhtyamovaa, SN Batasheva, Diurbin DS, Tagirov MSH, Blokhin VI (2017) Root formation in the pre-heading period in different morphobiotypes of barley Niva Tatarstana (3-4): 50-52.
- Chikov VI, GA Akhtyamova (2018) Breeding genetics and evolution of plants: metabolic link enetics and bioengineering 22 (4): 13-19.
- Chikov VI, GG Bakirova, SN Batasheva, AA Sergeeva (2006) The influence of ammoniates on 14CO2 assymilation in flax // Biologia Plantarum 50(4): 749-751.
- Chikov VI, Abdrakhimov FA, Bakirova GG, Batasheva SN (2009) The role of sink-source relationships between different organs in regulation of photosynthesis and productivity. Acta Horticulture 835: 87-98.
- Chikov VI (1987) Photosynthesis and transport of assimilates. Moscow: Science. 188p.
- Batasheva SN, Abdrakhimov, Bakirova GG, Chikov VI (2007) Effect of nitrates supplied with the transpiration flow on assimilate translocation. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology 50: 373–380.
- Chikov VI, Akhtyamova GA, Batasheva SN, Mikhailov FL, Khamidullina (2015) Effect of silencing of the apo plastic invertase gene on photosynthesis in tomato. Russ J Plant Physiol 62: 39-44.
- Kovda VA, Pachepsky PA (1989) Soil resources of the USSR, their use and restoration. Pushchino.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...