
Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-6679
Review Article(ISSN: 2637-6679) 
Why to Not Rely on Nature? Volume 4 - Issue 1
Shah Murad1*, Akbar2, Salman Iftikhar3, Abdul Ghaffar4, Jamila Shah Murad5 and Ghazi Mahmood6
- 1Department of Pharmacology, Islamabad Medical College, Islamabad, Pakistan
- 2Niazi Teaching Hospital and IMDC, Islamabad Seema, Gynecologist at NMC, Karachi Pakistan
- 3Department Pharmacology at RLMDC Lahore Pakistan
- 4SWO at LMDC/DANTH Islamabad Pakistan
- 5Cl Psychologist at Bahria University, Pakistan
- 6ENT Surgeon at MMC Multan
Received: July 23, 2019; Published: September 09, 2019
Corresponding author: Shah Murad, Department of Pharmacology IMDC, Islamabad-Pakistan
DOI: 10.32474/RRHOAJ.2019.04.000176
Abstract
Metabolism is the process your body uses to make energy from the food you eat. Food is made up of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Chemicals in your digestive system (enzymes) break the food parts down into sugars and acids, your body’s fuel. Your body can use this fuel right away, or it can store the energy in your body tissues. If you have a metabolic disorder, something goes wrong with this process. Dyslipidemia is main etiological factor leading to develop coronary artery disease (CAD). Allopathic drugs used in cure of hyperlipidemia, have unwanted effects, so have poor compliance. Now a day’s nutraceuticals are getting popularity due to their moderate hypolipidemic actions with fewer adverse effects. Niacin or vitamin B-3 is used as hypolipidemic agent which increases HDL-cholesterol and decreases LDL-cholesterol, VLDL, TGs by different mechanisms. But its main adverse effects are flushing due to synthesis of Prostaglandin D-2 which has vasodilatory effect causing flushing. Cardamom is herb having hypolipidemic potential if used in specific concentration for long time. In this work we did try to compare these two medicines hypolipidemic effects. Study was single blind placebo-controlled conducted at Jinnah Hospital Lahore-Pakistan from July to November 2018. Seventy-five hyperlipidemic patients were selected and divided in three groups. Their base line lipid profile was determined at laboratory of the hospital. Patients were divided in three groups. Group-1 was on placebo therapy, Group-II was on Niacin 1.5 grams daily in divided doses, and Group-III was on Cardamom 1 gram daily in three divided doses. It was two months therapeutic design. At completion of therapeutic regimen after two months we measured all patient’s lipid profile. When results were compiled and pre and post treatment values were analyzed statistically, it was observed that both drugs hypolipidemic potential is different, although both have hypolipidemic characteristic, but Niacin is the best for treating Hyperlipidemia. For statistical analysis we used SPSS version 5.0 and paired ‘t’ test was applied to understand significant changes in two tested group’s lipid profile.
Introduction
Lipid metabolism disorders, such as Gaucher disease and Tay- Sachs disease, involve lipids. Lipids are fats or fat-like substances. They include oils, fatty acids, waxes, and cholesterol. If you have one of these disorders, you may not have enough enzymes to break down lipids. Or the enzymes may not work properly, and your body can’t convert the fats into energy. They cause a harmful amount of lipids to build up in your body. Over time, that can damage your cells and tissues, especially in the brain, peripheral nervous system, liver, spleen, and bone marrow. Many of these disorders can be very serious, or sometimes even fatal. High LDL-cholesterol and low HDL-cholesterol in blood are cause of synthesis of atherosclerotic plaques which get deposited with inner endothelium of coronary arteries, leading to develop coronary artery disease (CAD) [1,2]. Hyperlipidemia either primary or secondary is challenge for scientists of 21st century due to this disease’s complications like coronary artery disease, Hypertension, Cardiac Arrhythmias, and Myocardial Infarction [3,4]. Hyperlipidemia causes LDL particle’s oxidation, which initiate formation of atherosclerotic plaques leading to development of coronary artery disease. From this single complication of Hyperlipidemia, all major heart diseases are developed leading to morbidity and mortality due to last lethal major heart disease Ventricular Fibrillation [5-8]. Hypolipidemic drugs commonly used include Statins, nicotinic acid, bile acid binding resins and fibric acids, but all have potential for low patient compliance due to wide range of side effects [9].
Niacin increases apolipoprotein A1 levels due to anti catabolic effects resulting in higher reverse cholesterol transport. It also inhibits HDL hepatic uptake, down-regulating production of the cholesterol ester transfer protein gene. Finally, it stimulates the ABC-A1 transporter in monocytes and macrophages and upregulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ results in reverse cholesterol transport. It reduces secondary outcomes associated with atherosclerosis, such as low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and triglycerides, but increases high density lipoprotein cholesterol [10]. Despite the importance of other cardiovascular risk factors, high HDL was associated with fewer cardiovascular events independent of LDL reduction. Other effects include anti-thrombotic and vascular inflammation, improving endothelial function [11]. To get good drug-patient compliance many health-related modern researchers have started to put their haeling potential for developing alternatives drugs used in primary or secondary Hyperlipidemia. Cardamom or in urdu ILAICHI is one of the hypolipidemic herb, widely encouraged by cardiologists to be used for prevention of atherogenesis, and coronary artery disease [12]. Cardamum’s antioxident effect is well established in many research studies on medicinal herbs. This nutraceutical contains Flavenoids and Phenolic compounds which scavenge Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), reducing risk of developing CAD. Oral administration of cardamom extracts significantly reduced total cholesterol, highdensity lipoprotein (HDL), low-density lipoprotein, and very lowdensity lipoprotein and triglycerides in HL patients [13].
Patients & Method
Design: It was single blind placebo-controlled study conducted at GENERAL HOSPITAL Lahore from July to November 2018.
No of Patients: Seventy-five hyperlipidemic patients were selected and enrolled for the study. Written, already explained and approved consent was taken from all patients.
Inclusion Criteria: Inclusion criteria were age limit from 18 to 70 years of both gender male and female primary or secondary hyperlipidemic patients.
Exclusion Criteria: Patients suffering from any vital organ disease or their impaired functions were excluded from the study. Alcoholics, cigarette smokers and patients taking regular medicine for their any physical or mental disease were also excluded.
Grouping: Seventy-five patients were divided in three groups, comprising 25 patients in each group. Group-I was on placebo therapy. They were provided capsules containing grinded rice and mixed wheat. They were advised to take one capsule before meal, thrice daily for two months. Group-II patients were advised to take 1.5 grams of Niacin in three divided doses for the period of two months. Group-III were advised to take one-gram grinded green Cardamom powder mixed in black tea, thrice daily after each meal for the period of two months.
Methods Used: At start of study all patients’ blood pressure was recorded and kept in their personal file. Lipid profile of all patients was determined by Frei Dewald Method. Total-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol and HDL-cholesterol were main parameters we required for further calculation of change in these parameters. All patients were advised to visit clinic fortnightly for their follow up. After two months therapy their lipid profile was measured again by same Frei Dewald Method. Blood Pressure of all participants was again measured and compiled for further statistical analysis.
Statistical Analysis: Data were expressed as the mean ± SEM and paired “t” test was applied to determine statistical significance as the difference. A probability value of <0.05 was considered as non-significant and P<0.001 was considered as highly significant change in the results when pre and post-treatment values were compared
Results
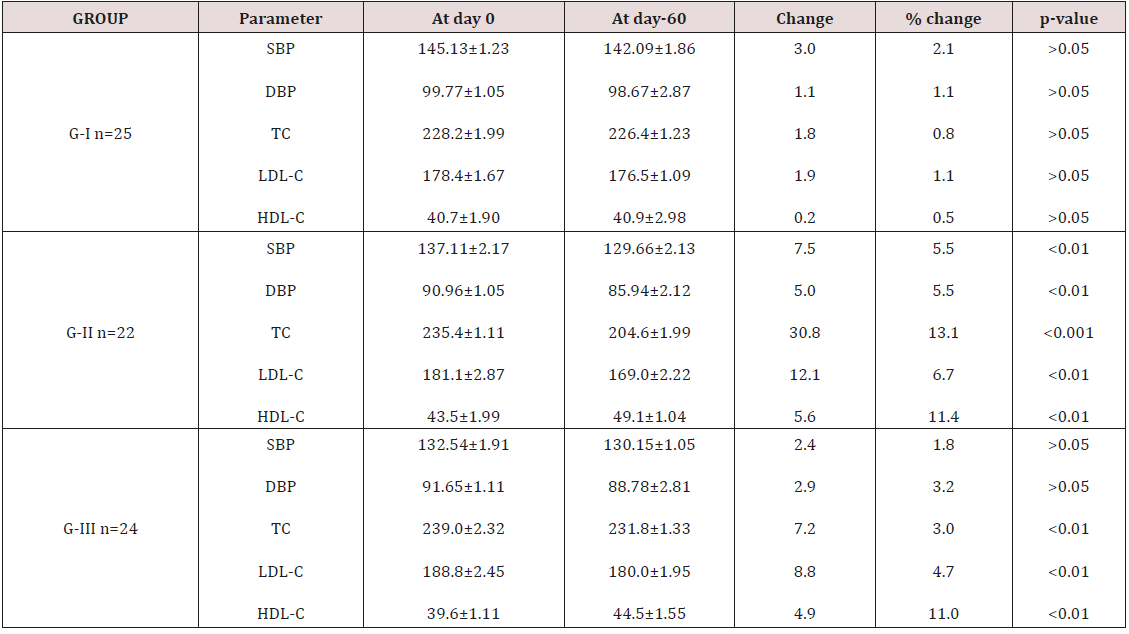
Results are shown in Table 1 with detail and all parameter’s values and changes in these parameters are self-explanatory.
Table 1: Results of pre and post treatment values, measured in mg/dl (tc, ldl-c, hdl-c) & mm of hg (sbp, dbp).
Current Statistics: (Pakistan SUN Secretariat Report 2017-18, P&D Department)
Discussion
Nutraceuticals like vitamins, and nutritional substances like fruits, vegetables, and indian spices are getting popularity in medical research regarding their therapeutic characteristics. Vitamin B-3 or niacin, and Cardamum (illaichi) are well known nutraceuticals which have been proved to have hypolipidemic potential. Metabolic syndrome is cluster of complications in lipid, protein and carbohydrate metabolism in human body. Hyperlipidemia is main fraction and part of this complication. High plasma LDL particles are prone to be oxidized leading to synthesis of atherosclerotic plaques which deposit to endothelial wall of arteries including coronary arteries (CAD). To reduce high plasma fats can prevent individual from being vulnerable for development of CAD. In our results two months therapy with Niacin decreased total and LDL cholesterol 13.1 and 6.7 % respectively. Statistically decrease in total cholesterol is highly significant while change in LDL-cholesterol is significant biostatistically. These results match with results of study conducted by Capuzzi DM et al. [14] who agree with our results. They almost saw same changes in LP (lipid profile) of primary and secondary hyperlipidemic patients.
They mentioned effects of blood pressure which was nonsignificant when they analyzed pre and post treatment values in systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Our results of change in HDL cholesterol also match with results of Alam K et al. [15] who proved 11% increase in HDL-cholesterol which is highly significant change in pre, and post treatment values of the parameter mentioned. Cantarella L et al. [16] proved significant change in systolic blood pressure of hyperlipidemic patients but non-significant effects on diastolic blood pressure. Goto T et al. [17] explained cause of flushing by using Niacin in hypolipidemic doses. They recommended titration of Niacin dose to improve patient drug compliance. Kawaguchi K et al. [18] did research on Cardamom and found phenolic compounds of this herb as antioxidant. They agree with many researcher’s idea or viewpoint that phenolics work as scavenger of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS). Mittal MK et al. [19] proved that hypolipidemic effects of any herb are not as potent as Statins or Niacin. They have encouraged researchers that active ingredients of medicinal herbs should carefully be extracted and utilized efficaciously when you could preserve all for long time. Our research study proved significant changes in total and LDL cholesterol in 24 hyperlipidemic patients, i.e. 7.2 mg/dl reduction in total cholesterol and 8.8 mg/dl decrease in LDL cholesterol. Changes in both parameters are biostatistically significant.
Almost same results were observed by Bruckert, Eric et al. [20] who again said and advised patient not totally to depend on medicinal herbs, for, it is difficult to treat the disease by monotherapy when they start to develop metabolic syndrome and its serious complications. Babu PV et al. [21] has described that too much active ingredients or chemical compounds present in herbal medicines made it (Cardamom) unpopular because unexpected effects may be observed by using large amount of grinded Cardamom. He warned individuals using large amount of drug may harm metabolic pathways of body, producing unexplained metabolites which can harm body tissues. NA Lokan et al. [22], Temokarr Y et al. [23] explained that there are remarkable number of medicinal herbs and other chemical compounds which scavenge ROS (reactive oxygen species) in human body, preventing development of CAD.
References
- Reeka VS, Neuendorf HA, Roth JL (2008) Nutrition protocols for the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Nutr Clin Pract 23: 468-76.
- Jagarnath T, Maluava YB (2015) Adipose tissue, inflammation and atherosclerosis. Journal of atherosclerosis and thrombosis 20(1): 466-9.
- Shah M, Ghaffar A, Niaz K, Sheikh AS (2014) ROS and Dyslipidemia. Ethan Bot J 12(3): 321-326.
- Gidda RT, Semonja VC, Faru KK (2014) What about cure of dyslipidemia? J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 17: 19.
- Iyer A, Panchal S, Poudyal H, Brown L (2009) Potential health benefits of Indian spices in the symptoms of the metabolic syndrome: a review. Indian J Biochem Biophys 46: 467-481.
- Kunitomo M (2007) Oxidative stress and atherosclerosis. Yakugaku Zasshi 127(12): 199-206.
- Khitan Z, Kim DH (2013) Fructose: A key factor in the development of metabolic syndrome and hypertension. J. Nutr. Metab13: 1-12.
- Jia G, Aroor AR, Whaley Connell AT, Sowers JR (2014) Fructose and uric acid: Is there a role in endothelial function? Curr. Hypertens Rep 16: 434.
- Poudyal H, Panchal SK, Waanders J, Ward L, Brown L (2011) Lipid redistribution and metabolism. J Cardiol 126(87): 28-30.
- Tappy L, Le KA, Tran C, Paquot N (2010) Niacin is used as hypolipidemic agent. Nutrition 26: 1044-1049.
- Gass JD (2013) Primary Hyperlipidemia can be treated well by Vitamin B-3 (Niacin). Lipid Res J 23(6): 500–510.
- Verstraeten SV, Fraga CG, Galleano M, Oteiza PI (2010) Basic biochemical mechanisms behind the health benefits of cardamom. Mol Aspects Med 31: 435-45.
- Jenner A, Halliwell B, Rafter J (2010) Use of Cardamom in dyslipidemia. Am J Clin Nutr 81: 268-276.
- Capuzzi DM, Morgan JM, Brusco OA, Intenzo CM (2010) "Niacin dosing: relationship to benefits and adverse effects". Curr Atheroscler Rep 2(1): 64-71.
- Alam K, Pathak D, Ansari SH (2011) Evaluation of Antihyperlipidemic activity of green cardamom. Int J Pharm Sci Drug Res 3: 35-37.
- Cantarella L, Gallifuoco A, Malandra A, Martínková L, Spera A, et al. (2011) Hypolipidemic and Hypotensive effects of Niacin. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 48(4): 345-350.
- Goto T, Teraminami A, Lee JY, Ohyama K, Funakoshi K, et al. (2012) Niacin is good hypolipidemic effects, but it causes flushing. J Nutr Biochem 23: 768-776.
- Kawaguchi K, Mizuno T, Aida K, Uchino K (2011) Green Cardamom and blood lipids. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61: 102-104.
- Mittal MK, Florin T, Perrone J, Delgado JH, Osterhoudt KC (2010) ‘Use of niacin to beat high plasma lipids as compared to hylipidemic herbs. Ann Emerg Med 50(5): 587-590.
- Bruckert, Eric, Labreuche, Julien, Amarenco, Pierre (2010) Herbs have hypolipidemic effects, but their wide range of pharmacological effects should be considered. Atherosclerosis 21(2): 353-361.
- Babu PV, Liu D, Hubbarad LR, Kulin MD (2008) Hypilipidemic characteristics of Green Cardamom. Curr Med Chem 15: 1840-1850.
- NA Lokan, HH, Julalu, and TT Tulsik (2015) Do use nutraceuticals for dyslipidemia. J Thromb 29(7): 677-679.
- Temokarr Y. Hulasa V, Fusadaj B (2014) free radical scavenger chemicals found in medicinal plants. Der J 6(6): 40-47.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...

.png)


