Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-6695
Research Article(ISSN: 2637-6695) 
A Study on Occupational Exposure Status and Intervention Effect of Clinical Nursing Interns Volume 2 - Issue 2
Dou Xinman1*, Zhang Yufang1, Zhang Junhong1 and Gou Ling2
- 1 Nursing Department, Lanzhou University Second Hospital, China
- 2 School of Nursing, Lanzhou University, Chinaia
Received: February 18, 2019; Published: February 26, 2019
Corresponding author: Dou Xinman, Nursing Department, Lanzhou University Second Hospital leadership, China
DOI: 10.32474/LOJNHC.2018.02.000132
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study is to understand the current situation and influencing factors of occupational exposure of clinical nursing interns, evaluate the intervention effect of occupational exposure of clinical nursing interns, so as to provide a basis for formulating occupational protection measures.
Methods: A total of 2190 clinical nursing interns from May 2012 to December 2018 in a Tertiary Teaching Hospital were selected as research objects to investigate the occupational exposure of clinical nursing interns before and after the implementation of the intervention measures.
Results: Mechanical injury accounted for the first 53.83% of occupational exposure, and education level was related to the incidence of occupational exposure of interns. After intervention, interns’ awareness of standard protection knowledge and measures and standard protection behavior were significantly improved.
Conclusion: It is an effective way to reduce the incidence of interns’ occupational exposure that teaching hospitals complete pre-job training of occupational exposure and occupational protection before interns enter clinical practice and improve the adherence of nursing operation process.
Keywords: Nursing Interns; Occupational Exposure; Intervention; Study
Introduction
With the rapid development of medical technology and the wide application of various high-tech diagnostic and therapeutic technologies in clinic, nurses have been exposed to harmful substances such as biology, physics and chemistry for a long time. Studies have confirmed that the number of occupational exposures of clinical nurses occupies the first place [1]. Due to the lack of occupational protection education and training, lack of awareness and skills of occupational protection, lack of clinical experience, non- standard clinical operation and lack of intervention from instructors, the current situation of occupational exposure of clinical nursing interns is particularly serious. Clinical practice education is an important part of nursing education, and it is also a critical period for interns to transform theoretical knowledge into practical ability. Most interns focus on adapting to the clinical working environment as soon as possible and mastering various clinical nursing operations as soon as possible, but neglect the occupational exposure caused by nursing operations [2]. By investigating the occupational exposure of nursing interns in teaching hospitals, this study explored the current situation and influencing factors of the occupational exposure of interns, evaluated the effect of intervention measures, and provided a basis for teaching hospitals to establish a sound management system for the occupational exposure of interns, improve pre-job training content, and improve the awareness and ability of interns in protection.
Materials and Methods
Objects of Study
2190 clinical nursing interns aged 16-24 years from May 2015 to December 2018 were selected as subjects, including 2082 female students and 108 male students. There are 313 undergraduate students, 986 junior college students and 891 secondary school students. All interns are practicing in Department rotation. Inclusion criteria: Full-time nursing students; Voluntary participation in this study.
Research Methods
a) Survey Tool On the basis of consulting relevant literature on occupational exposure, a self-designed questionnaire was designed. The questionnaire consisted of four parts: personal data of clinical nursing interns, occupational exposure, awareness rate of occupational protection knowledge and occupational protection attitude.
b) Survey Methods 2190 questionnaires were distributed to interns who had completed 16 weeks of clinical practice, 2164 of which were recovered, with an effective recovery rate of 98.81%. 2190 questionnaires were sent to interns again after compensation education, 2149 of which were recovered, with an effective recovery rate of 98.12%.
c) Interventions Measures A compensation education team for occupational exposure was set up to analyze and study the problems found in the first survey and implement occupational exposure and standard preventive compensation education [3].
d) Statistical Methods SPSS13.0 statistical software was used to analyze the results of the survey results. The status quo, related factors and intervention effects of occupational exposure were described by percentage, mean and standard deviation.
Results
Occupational Exposure Status
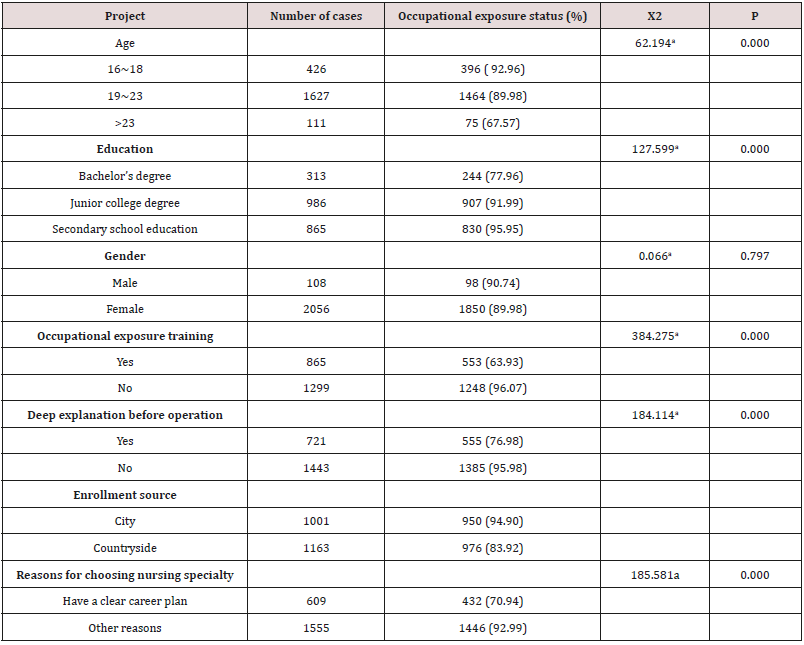
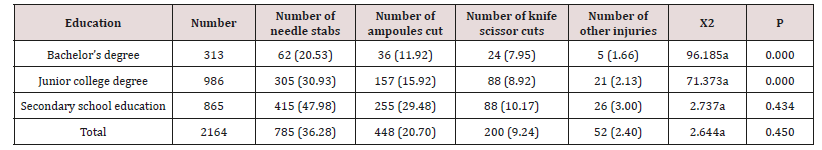
In this study, 1931 of 2164 subjects had more than one occupational exposure, the incidence was as high as 90.41%. The results showed that mechanical injuries accounted for the first place (53.83%) of interns ‘occupational exposure, mainly needle injuries (70.31%), followed by ampoules, scissors and other sharp instrument injuries, and the incidence of injury was related to the level of interns’ education (P<0.01 and P<0.05), with the highest incidence of interns with secondary vocational education. As shown in Table 1.
Table 1:The Present Situation of Mechanical Injury of Interns with Different Educational Levels Per person%.
Relevant Factors of Occupational Exposure
The survey results and data analysis showed that the incidence of occupational exposure was related to the training level of occupational exposure, the depth of pre-operation instruction, age, education level, the reasons for choosing nursing specialty and the source of students (P<0.01), but not to the gender of interns (P>0.05). As shown in Table 2.
Intervention Effect
The positive rates of occupational exposure and standard preventive attitude of nursing interns before and after intervention were significantly different (P<0.01), as shown in Table 3. The awareness rates of occupational exposure related knowledge among nursing interns before and after intervention were significantly different (P<0.01), as shown in Table 4.
Table 3:Positive rates of occupational exposure attitude of nursing interns before and after intervention (%).
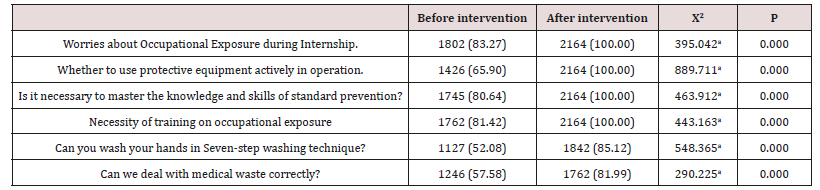
Table 4:Comparison of the awareness rates of occupational exposure knowledge among nursing interns before and after intervention (%).

Discussion
Analysis of Occupational Exposure Status of Clinical Nursing Interns
The results showed that mechanical injuries accounted for the first place (53.83%) of interns’ occupational exposure, mainly needle injuries (70.31%), followed by ampoules, scissors and other sharp instrument injuries. It is consistent with the view of many scholars at home and abroad that mechanical injury is the most common way of occupational exposure of medical staff, and needle puncture caused by used needles in work is the most common way of occupational exposure of nursing interns, which is potentially infectious [4]. Teaching hospitals should pay attention to the universality and severity of needle stick injuries among clinical nursing interns. At the same time, the survey results showed that ampoules, scissors and other sharp instrument injuries were mainly related to nursing operation not completed according to the process, so it is very important to standardize clinical practice teaching, improve the adherence of the operation process, and guide students to take effective protective measures in the operation [5].
Relevant Factors of Occupational Exposure
The results showed that the incidence of occupational exposure was related to the training level of occupational exposure, the depth of pre-operation instruction, age, education level, the reasons for choosing nursing specialty and the source of students (P<0.01), but not to the gender of interns. The risk of occupational exposure of young interns increased significantly, which was related to the younger interns, immature mentality and insufficient care. The data analysis showed that the main causes of occupational exposure were lack of occupational protection knowledge, weak awareness of occupational protection and non-standard operation. After implementing occupational exposure and standard preventive compensation education, the positive rates of occupational exposure attitude and awareness rates of occupational exposure knowledge of nursing interns increased significantly (P<0.01). Therefore, it is particularly urgent for teaching hospitals to establish a sound management system of interns’ occupational exposure, improve pre-job training content, and improve protection awareness and ability.
Evaluation of Intervention Effect
Starting from changing the knowledge, attitude and practice of nursing interns’ occupational exposure, the special lectures on occupational exposure compensation education and occupational protection training were implemented to intervene and control the high-risk links of occupational exposure in nursing operations, and standardize clinical practice teaching to improve the knowledge, attitude and practice of nursing interns’ occupational exposure [6]. This study showed that the positive rates of attitude towards occupational exposure and the awareness rates of knowledge about occupational exposure of nursing interns were significantly improved after the intervention (P<0.01). It shows that the awareness and ability of occupational protection and the ability of on-the-spot treatment have been significantly improved. It fully shows that the pre-job training of occupational exposure and occupational protection is completed before the interns enter clinical practice in teaching hospitals, and the adherence of nursing operation process is improved, which can promote the interns to form good habits of consciously taking protective measures in operation and effectively reduce the incidence of occupational exposure of interns.
References
- Wang J, Cheng WZ, Zhang Y, Xu TL, Xiang XJ (2013) Survey on the distribution of occupational exposure population in a third-class A General Hospital. Occupation and Health 29(6): 762-764.
- Pan XR (2013) Investigation of knowledge, attitude and practice of nursing interns’ occupational exposure. Journal of Nursing Administration 13(2): 121-123.
- Dong GQ, Liu XX, Guan X, Liu YL (2016) Practical research on occupational protection compensation education among orthopedic practice nurses. Journal of Shenyang Medical College 18(5): 370-372.
- Li YL (2002) American nurses’ awareness and measures to prevent blood-borne diseases. Chinese Journal of Nursing 37(8): 633-634.
- Zhao BC, Wei LL, Ge P (2018) Investigation and Countermeasure Analysis on Occupational Hazard and Occupational Protection of Nursing Interns. Chinese and Foreign Medical Research (3): 155-156.
- Yan XF, Wang Y, Tan L (2016) Analysis of current situation of occupational protection awareness and behavior of medical interns. Chinese Journal of Infection Control (10): 796-799.
Editorial Manager:
Email:

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...