Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2641-6794
Research Article2641-6794 
Inhibition of Keratinolytic Bacteria Acting on Nails by Lemon-Salt-Alcohol Sanitizer Volume 3 - Issue 4
Deeksha Gupta, Shruthi Suthakaran, Vyas Sahaj Rajesh, Rahul Das and Suneetha V*
- School of Biosciences and Technology, VIT University, Vellore, India
Received: August 23, 2019; Published:August 29, 2019
Corresponding author:Suneetha V, School of Biosciences and Technology, VIT University, Vellore, India
DOI: 10.32474/OAJESS.2019.03.000168
Abstract
Keratin found in human nails is a eukeratin [1]. It is degraded by keratinase produced by bacteria like Bacillus sp. Degradation of human nails was brought about by soil inhabiting bacteria isolated from soil samples of Melmaruvathur, Tamil Nadu, India. The growth curve of the bacteria was determined. Inhibition was studied using various mixtures of lime juice, salt and ginger extract in alcohol. The growth of the bacteria producing keratinase isolated by us is found to be inhibited by a mixture of lime juice, salt and alcohol. It was also found that ethanol was more effective than methanol in its inhibitory action [2].
Keywords: Keratin; Inhibition; Sanitizer
Introduction
Keratin is a protein naturally found in skin, hair, feather, wool and nails. Keratin is insoluble in water and not degraded by enzymes such as trypsin, pepsin and papain. Keratin can be present either as α-keratin(α-helix) [3] or β-keratin(β-sheets) in highly coiled structures. This structure actually lends keratin its character to resist breakdown. But it is still digested by enzymes such as keratinase produced by bacteria like some species of Bacillus, a few fungi and actinomycetes. Keratinase acts on keratin to liberate various amino acids like Histidine, Lysine and Arginine [4] which are commercially exploited. Keratin can be classified into eukeratin and pseudo keratin depending on the ratio of the amino acids present. Human nails contain eukeratin.
The treatments available currently to degrade keratin are not as efficient as keratinase since they require large amounts of energy [5]. Microbial degradation using keratinolytic bacteria is a viable alternative. The amino acids produced by degradation of keratin are destroyed by the action of the chemical and physical factors used for industrial degradation. If the process is optimized further, it will be possible to extract amounts of amino acids enough for commercial production [6]. Keratinolytic enzymes are used in various industries like cosmetics, textiles, and leather production. Lime, ginger and garlic have been used traditionally in cooking in our country. It is well known that they possess antibacterial activity. It has been found that citric acid found in lime juice is responsible for its higher efficiency in controlling growth of bacteria. The low pH produced by citric acid causes cytotoxicity which ultimately kills the microbes [7] (Figure 1). project we hope to isolate keratinase producing organism from the area of Melmaruvathur, check the production of keratinase by these microorganisms, study the effect of these microbes on nails and also check the inhibitory action of the lemon-salt-alcohol sanitizer which has been prepared by us.
Materials and Methods
Isolation of Microorganism
Soil samples were collected from places adjoining the head tonsuring areas of Melmaruvathur Adiparasakthi Amman Temple. Serial dilution of this sample was prepared by dissolving 1 g of soil in 9 ml of distilled water. Dilution was performed till a concentration of 10-9wasobtained. Then this dilution was poured on Nutrient Agar and baited using nails since our primary aim is to isolate organisms which can degrade the keratin present in nails. The plates were incubated at 37°C for 24 hours. The colonies obtained thus around the baited nails were sub-cultured further to obtain pure cultures of the required microorganism.
Growth Curve Determination
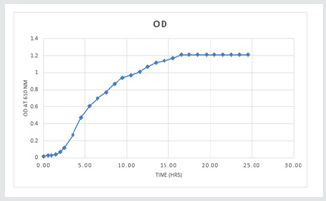
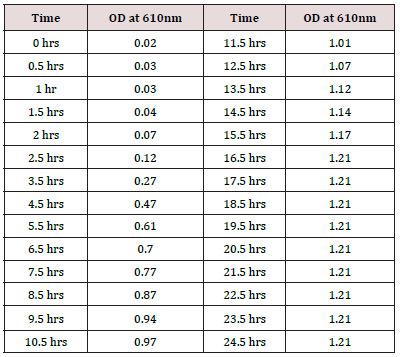
The growth curve of the organism was determined by inoculating one pure colony obtained into 100 ml of nutrient broth containing nails. The readings were taken using a control that contained only nutrient broth and nails. Nails were added to the broth to check the effect of their presence on the growth of the bacteria (Table1) (Figure 2).
Preparation of Sanitizer
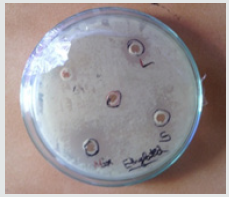
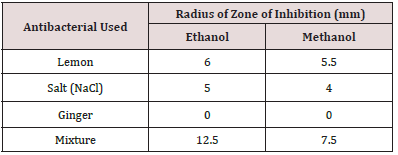
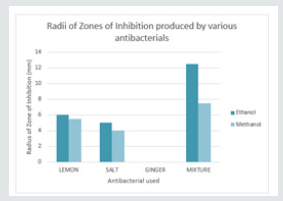
Two sanitizers were prepared by mixing 0.5 ml of alcohol (methanol/ethanol) [2] with 0.5 ml of a solution mixture containing equal proportions of lemon, table salt and ginger. A spread plate culture of our organism was made, and holes were made into it to add the sanitizer to it. Two Petri plates were taken: one each for ethanol and methanol. They were filled with nutrient agar and allowed to solidify. 5 holes were made into the agar and filled with the given solutions: - Hole 1: Control (alcohol only); Hole 2: Alcohol+ Ginger extract; Hole 3: Alcohol+ Lemon; Hole 4: Alcohol+ Salt; Hole 5: Sanitizer. The holes were made to avoid the overlapping of zones of inhibition by mixing of solutions. After incubation at 37°C for 24 hrs the radius of zone of inhibition for each sanitizer used was noted in a table (Figure 3) (Table 2).
Results and Discussion
The mixture of crude extracts of lime, ginger and salt in alcohol is much more effective than the crude extracts separately in alcohol. It was also found that the mixture in ethanol worked better than the mixture dissolved in methanol. This is because methanol is not as effective as ethanol in causing protein denaturation and has a much-reduced bactericidal action. Also, 70% ethanol is better than absolute alcohol in this regard. Fresh ginger extract could not be used due to its unavailability. Ginger extract did not show antibacterial activity when used either in ethanolic or methanolic extract [8] (Figure 4).
Conclusion
It was found that our sanitizer which was a mix of lemon, NaCl, ginger and ethanol is more effective than the one containing methanol in inhibiting the growth of Keratinolytic bacteria. This sanitizer can be made easily as it requires very less ingredients and is cost effective.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank School of Biosciences and Technology, VIT University and our Chancellor, Dr. G. Viswanathan for lending us the support needed to complete this project.
References
- Block, Richard J, Diana Bolling (1939) The Amino Acid Composition of Keratins The Composition of Gorgonin, Spongin, Turtle Scutes, And Other Keratins. Journal of Biological Chemistry 127(3): 685-693.
- Weir, Susan C, Carreno RA, Trevors JT, Lee H, et al. (2002) Efficacy of common laboratory disinfectants on the infectivity of Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts in cell culture. Applied and environmental microbiology 68(5): 2576-2579.
- Astbury WT, Florence O Bell (1941) Nature of the intramolecular fold in alpha-keratin and alpha-myosin. Nature 147: 696-699.
- Block RJ (1951) Chemical classification of keratins. Annual NY Academy Science 53(3): 608-6120.
- Deivasigamani B, Alagappan KM (2008) Industrial application of keratinase and soluble proteins from feather keratins. Journal of Environmental Biolology 29(6): 933-936.
- Srivastava A, Sharma A, Suneetha V (2011) Feather Waste biodegradation as a source of Amino acids. European Journal of Experimental Biology 1: 56-63.
- Tomotake, Hiroyuki (2006) Antibacterial activity of citrus fruit juices against Vibrio species. Journal of nutritional science and vitaminology 52(2): 157-160.
- Onyeagba (2005) Studies on the antimicrobial effects of garlic (Allium sativum Linn), ginger (Zingiberofficinale Roscoe) and lime (Citrus aurantifolia Linn). African Journal of Biotechnology 3(10): 552-554.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...