Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-4749
Mini Review(ISSN: 2637-4749) 
Health Benefits of Camel Milk Volume 3 - Issue 2
Iqra Bano1*, Shokat Jamal2, Mohammed Zeb khan3, Hira Sajjad4, Changaiz Baloch4, and Khurram Shahzad4
- 1Department Veterinary Physiology & Biochemistry SBBUVAS Sakrand, 67210 Pakistan
- 2Animal Quarantine Department Khunjrab, Ministry of National Food Security and Research Islamabad Pakistan
- 3Department of Preventive Veterinary medicine, Northeast Agriculture University Harbin China
- 4Sindh Agricultural University, 70060 Tandojam, Pakistan
Received: November 23, 2019; Published: December 02, 2019
Corresponding author: Iqra Bano, Department Veterinary Physiology & Biochemistry SBBUVAS Sakrand, 67210 Pakistan, Pakistan
DOI: 10.32474/CDVS.2019.03.000156
Abstract
The camel is domesticated in various regions of Asia and Africa, it is considered as a friendly and harmless animal that can survive in hard environmental conditions and provides sources of income to its owners in form of milk, meat, and skin by-products. Camel milk is highly nutritive and possesses some unique characteristics which are being investigated nowadays by many researchers and surprising results revealed that it can be utilized as a natural cure for various life-threatening diseases. This work is aimed to review and highlight the importance of camel milk and its therapeutic properties.
Keywords: Camel; Milk; Health
Mini Review
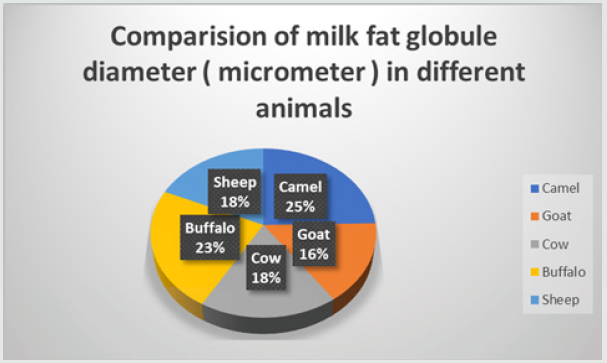
The Camels also called ship of the desert is one of the most abundant type of animal present in mostly arid zones of Asia and Africa. Since ancient times camels have been domesticated for their products like skin, meat and milk [1]. Milk is the most valuable by product of camel, so it is called as “white gold of desert”. According to some researchers, the camel produces more milk than any other livestock species and its duration of milk production is also longer. The whole lactation periods are comprising of almost 12- 18 months and daily production of milk is almost 3-10kg. The milk of camel consists of a 30 % annual caloric intake of the pastoral community diet [2]. The camel milk is having sharp salty taste with pungent smell and appears as dark white in color. Its taste can vary slightly depending on breed, feeding, health status as well as amount of water consumption by camel. When compared to cow milk which retains its properties for just 2-3 days the camel milk retains its quality for up to 12 days when stored at 2 °C temperature. Moreover, it is also stable for 8-10 hrs. at room temperature. The pH of fresh camel milk is normally neutral but can be tasted slightly acidic if kept for longer period of time [3]. The camel milk has some unique physiological characters like the fat globule diameter is also bigger than that of cow, goat, sheep milk (Figure 1).
Camel milk is very much healthy and is consumed in many regions of the world to cure some diseases as well [4]. It contains many vitamins and also higher amount of zinc so it plays a major role in immune system of body as cells of immune system are sensitive to zinc deficiency [5]. Moreover, some studies have revealed that camel milk also possesses insulin-like properties and can control blood sugar due to hypoglycemic properties in diabetic patients. It can be used as a natural medicine for diabetic patients. Along with that properties this miraculous milk has been also proved by many scientists as a natural medicine for autism and some food allergies [6]. Camel milk naturally consists low lactose as compared to cow milk so according to research, it was suggested that camel milk can be utilized by patients having lactose intolerance issues [7]. An animal study carried out in 2010 revealed that fermented camel milk possess increased number of electrolytes including sodium and potassium and it has therapeutic effects on diarrhea in rats. Thus, it can be decided that fermented camel milk can be consumed food for improving nutritive status of the body and also as therapeutic applications [8]. Naturally camel milk has various enzymes that have immunological as well as antibacterial properties and contains varieties of bacteriocins as shown in Table 1. The main enzyme is lysozyme which attacks common invading pathogens by developing primary immune system of the body. Camel milk is naturally rich in this enzyme. Moreover, it possesses natural lactoferrin which prevents microbial growth within the body and kills germs. The concentration of lactoferrin is much more in camel milk as compared to cow, sheep and goat milk [9].
The Lacto-peroxidase enzyme has negative effects on tumor growth and is associated with the iodination of thyroid hormones by acting on thyroid peroxidase enzymes they are naturally present in camel milk. The highest concentration of these enzymes is also having impacts on suppressing metastasis of breast cancer cells [10]. A previous study has revealed that camel milk has effect on oxidative stress in autistic children by increasing the concentration of some antioxidant enzymes like glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase along with myeloperoxidase enzyme when they consumed camel milk for two weeks the levels of these antioxidant enzymes were significantly increased as well as autistic behavior was also improved [11]. More experiments were conducted to evaluate the therapeutics properties of Camel milk in some case reports, invitro as well as in vivo experiments and in some clinical trials also. These studies suggest that camel milk can be utilized to cardiovascular diseases, tuberculosis, hepatitis, autoimmune disorders, rickets and liver cirrhosis [12-16] Although various reviews have been done on properties of milk of different domestic animals the camel milk properties are still lacking till now. Thus, this paper is designed to review accessible evidence on the dietary as well as medicinal worth of camel milk and indorse further study regarding the nutritional and medicinal worth of camel milk built on the data from this literature review.
Conclusion
Camel milk is consisting of important nutrients that are required to keep the body healthy. It contains adequate ratio of antibacterial and antifungal agents that are useful for the prevention of various diseases, like diabetic, cancer, cardiovascular diseases, autism, Rota virus diarrhea, lactose intolerance, autoimmune disorders. It is miraculous milk but lacks plenty of research on its qualities, therefore many people are still unaware of its qualities. Thus, further research should be done at molecular levels to evaluate its qualities and impacts on health.
References
- SchwartzHJ,Dioli M (1992) The one-humped camel in Eastern Africa. A pictorial guide to diseases, health care and management.
- Farah Z (1993) Composition and characteristics of camel milk. Journal of Dairy Research 60(4): 603-626.
- Mal G, Sena DS, JainVK, Sahani MS (2006) Therapeutic value of camel milk as a nutritional supplement for multiple drug resistant (MDR) tuberculosis patients. Israel Journal of Veterinary Medicine 61(3-4): 88.
- Attia H, Kherouatou N, Dhouib A (2001) Dromedary milk lactic acid fermentation: microbiological and rheological characteristics. Journal of industrial Microbiology and biotechnology, 26(5): 263-270.
- Hansen MA, Fernandes G, Good RA (1982) Nutrition and immunity: the influence of diet on autoimmunity and the role of zinc in the immune response. Annual review of nutrition 2(1): 151-177.
- Shabo Y, Barzel R, Margoulis M, Yagil R (2005) Camel milk for food allergies in children. IMAJ-RAMAT GAN 7(12): 796-798.
- Cardoso RR, Santos RMDB, Cardoso CRA, Carvalho MO (2010) Consumption of camel's milk by patients intolerant to lactose. A preliminary study. RevistaAlergia de Mexico57(1): 26-32.
- Mona E, Ragia OM, Abeer AKH, Mosa TE (2010) Biochemical effects of fermented camel milk on diarrhea in rats. New York Science Journal 3(5): 106-111.
- Conesa C, Sánchez L, Rota C, Pérez MD, Calvo M, et al.(2008) Isolation of lactoferrin from milk of different species: calorimetric and antimicrobial studies. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 150(1): 131-139.
- Ueda T, Sakamaki K, Kuroki T, Yano I,Nagat, S (1997) Molecular cloning and characterization of the chromosomal gene for human lactoperoxidase. European journal of biochemistry 243(1‐2): 32-41.
- Gizachew A, Teha J, BirhanuT, Nekemte E (2014) Review on medicinal and nutritional values of camel milk. Nature and Science 12(12): 35-41.
- Yagil R (2004) Camel milk and autoimmune diseases: historical medicine.
- Asresie A,Adugna M (2014) A Review on dromedary camel milk products and their uses. Global Journal of Animal Scientific Research2(3): 285-90.
- Sharma C, Singh C (2014) Therapeutic value of camel milk–a review. Advanced Journal of Pharmacie and Life Science Research 2(3): 7-13.
- Thomson ISI (2018) Ahmed M. Abdel-Salam and Mona AAl-Damegh. International Journal of Pharmacology 14(3): 397-406.
- El-AgamyEI (2006) Camel Milk. Handbook of Milk of Non-Bovine Animals. YWH Park, GF Ames, Iowa.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...