Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
Review Article(ISSN: 2641-6875) 
The Science and Biotechnology Behind Bio-E’s Marine Collagen + Caviar Daily Supplement Volume 3 - Issue 2
Douglass Seymour Jones*
- Australia
Received: November 07, 2022; Published: November 15, 2022
*Corresponding author: Douglass Seymour Jones, Australia
DOI: 10.32474/CTBM.2022.03.000158
Introduction
In light of the ascending need for high-quality oral beauty supplements, Bio-E has launched its new Marine Collagen + Caviar Daily Supplement. Containing selected rare ingredients from all over the world, the Marine Collagen + Caviar Daily Supplement is cultivated with scientific formulation, which aims at penetrating and revitalizing skin cells in order to stabilize their elastic structure, thus generating cell renewal and delaying the ageing process. Caviar contains multiple nutrients such as protein, multiple amino acids, highly unsaturated fatty acids, folic acid, vitamins and trace elements, which can promote collagen synthesis, and improve the mitochondrial function of cells while inhibiting protein cross-linking [1,2]. Due to its cell structure being similar to that of the human skin, it can be readily absorbed by the skin, thus accelerating the synthesis of collagen and increasing skin elasticity. Different varieties of microelements including more than 47 minerals and proteins, amino acids and recombinant basic fatty acids required by the skin not only effectively nourish the skin, but also keep the skin delicate and smooth and protect it against ageing [3]. Bio-E’s Marine Collagen + Caviar Daily Supplement contains carefully selected sturgeon caviar powder from France, and marine roe protein peptides harvested from Japanese salmon, to help energise billions of living cells. The highly bioavailable Japanese deep-sea salmon marine roe protein peptides are of small molecular weight at around 500 Da and contain “cytokines” that can increase the metabolism of ageing cells and revitalize new cells by IGF-1 activation, due to their abundance in amino acids, collagen, chondroitin sulphate, hyaluronic acid, elastin and so on. Benefits also include estrogen regulation that delays menopause, reduction of wrinkles and hair growth promotion [4]. Top-grade French sturgeon caviar powder has always been highly praised by aristocrats due to a traditional belief in its ability to nurture the cells, hence improving collagen regeneration as well as mitochondria function, resulting in more delicate and smooth appearances [5].
Human skin is composed mostly of type I collagen and type III collagen, accounting for 80%~85% and 10%~15% of the entirety of the skin’s collagen respectively [6]. Type I collagen mainly resides in the dermis with thick fibers, supporting the skin contour and enhancing skin elasticity. In the meantime, type III collagen exists in the superficial dermis as small fibers. The type III collagen content is at its peak when we are in fetus form, accounting for circ. 60% of the total amount of collagen. Hence the softness, elasticity and moisture of a baby’s skin are unmatched compared to those of adults. Not only is a baby’s skin extremely soft and plump, but it also possesses the ability to recover quickly after injury without leaving much of a scar, due to its high content of type III collagen. Because of this, type III collagen has also been referred to as “baby collagen” [7]. However, type III collagen dwindles continuously to less than 20% for adults, resulting in the inability of the skin to repair scars, sharply deteriorated elasticity and shrunk skin [8]. However, type III collagen diminishes continuously to less than 20% in adults, resulting in the skin’s inability to repair scars, rapidly deteriorated elasticity and collapsed looks [8].
In line with the functionalities of different types of collagen, Bio-E has formulated its marine collagen peptides complex with fish collagen peptides type I and III in conjunction with fish collagen tripeptide. The fish collagen peptides type I and III are harvested from sashimi grade salmon of the western Norwegian sea close to the Arctic Ocean, where the temperature is low throughout the year with very little human pollution. Then, a dual patented enzyme degradation technology is used to extract fish collagen peptides type I and III with over 500 active peptides, making it one of the fastest absorbing and bioavailable supplements on the market, with a digestibility of over 98%. It is also a trial tested to promote the body’s absorption of dietary iron and increase hemoglobin levels [9]. As type III collagen is highly sought after in the market due to its rarity, Bio-E’s Marine Collagen + Caviar Daily SupCurrent plement stands out as one of the few top-level products with both collagen type I and III added. Low molecule weight type I collagen peptides with thick fibers provide support for the skin, resulting in a firm and less wrinkly appearance, while type III collagen peptides with thin fibers promote the fibroblasts to further synthesize type III collagen and hyaluronic acid. In addition, a multi-patented fish collagen tripeptide is added because of its high bioavailability with a low average molecular weight between 250 to 500 Da. While most competitors are still with molecular weights between 1000 to 2000 Da, this 3rd gen collagen tripeptide achieves an absorption rate 5 times of its competitors [10]. A patented enzymatic hydrolysis technique is utilized to target cleave the “beauty fragments” GPH (Glycine-Proline-Hydroxyproline) to a global leading level of no less than 3.4%. It is certified by the Korean FDA with an efficacy claim of helping promote skin hydration. Furthermore, 3 human trials and multiple animal tests were conducted to validate its ability to help improve the plumpness and moisture in the skin, reduce the loss of hydration, diminish wrinkles caused by photoaging, and promote the synthesis of hyaluronic acid and ceramide [11-12].
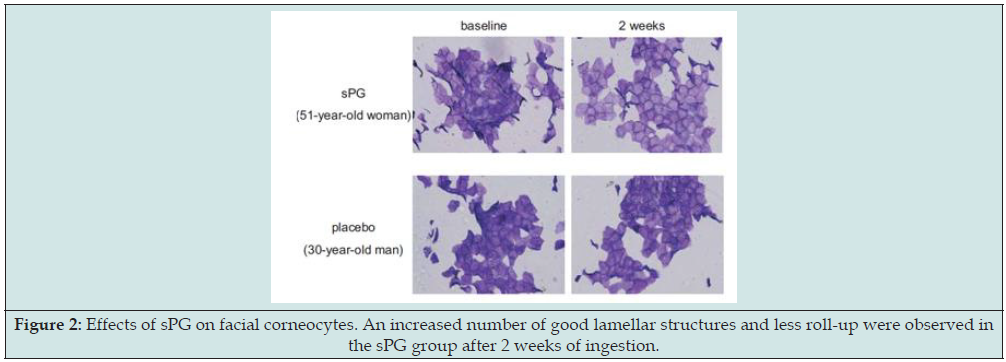
To further improve the efficacy in improving skin conditions, Bio-E incorporates proteoglycan and ceramide into its formulation, to help with the dermis’ hydration retention capacity and hydration loss prevention respectively. The proteoglycan comes from fish nasal cartilage powder of wild salmon in Hokkaido, Japan. The extraction ratio is extremely low, for only 1 kg of proteoglycan is extracted from 1600 salmons, making it one of the most expensive and exquisite inner beauty ingredients in the world. Proteoglycans can help lock in the water molecules in the multi-layers of the glycosaminoglycan chain while the unique structure of proteoglycans promotes the production of hyaluronic acid in fibroblasts, resulting in a higher hydration retention capacity than that of hyaluronic acid alone. Moreover, by combining with the EGF receptors, proteoglycans help promote the production of type I collagen, increase skin elasticity and reduce fine lines. In a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial, ingestion of salmon nasal cartilage-derived proteoglycans showed improvement of the dermis conditions, including enhancement of skin elasticity, moisture, and smoothness, and reduction of wrinkles, facial pores, and blotches (Figure 1) adapted from reference [13]. Proteoglycans also contribute to the gut microbiota as a prebiotic, generating metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids to reduce the production of the inflammatory cytokines and improve the epidermis conditions such as lamellar structures (Figure 2) adapted from reference [13] and dry peeling [14]. The gut-skin axis is a very critical target for skin conditions and should not be ignored for any orally administered product intervention [15].
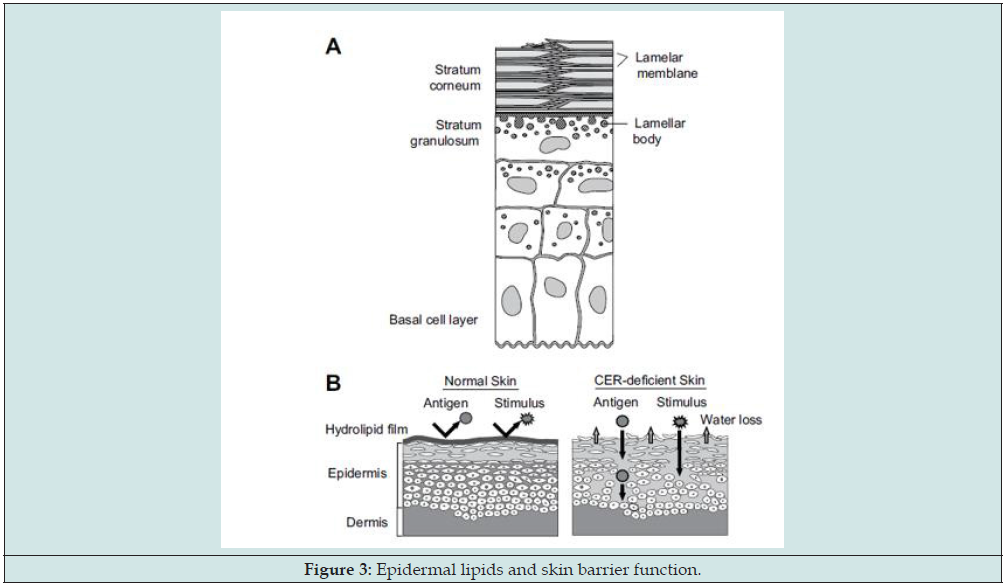
On the other hand, the prevention of water loss through the skin and defense from antigenic stimulus are critical for mammalian cells. These functions are served by the epidermal permeability barrier, which resides primarily in the extracellular domains of the stratum corneum as ceramide shown in Figure 3 adapted from reference [16].
Figure 1: The ratio of (length of red circle diameter) / (length of blue circle diameter) represents the proportion of ellipse axis length. The smaller the gap between the red circle and the blue circle becomes, the greater the improvement in skin looseness.
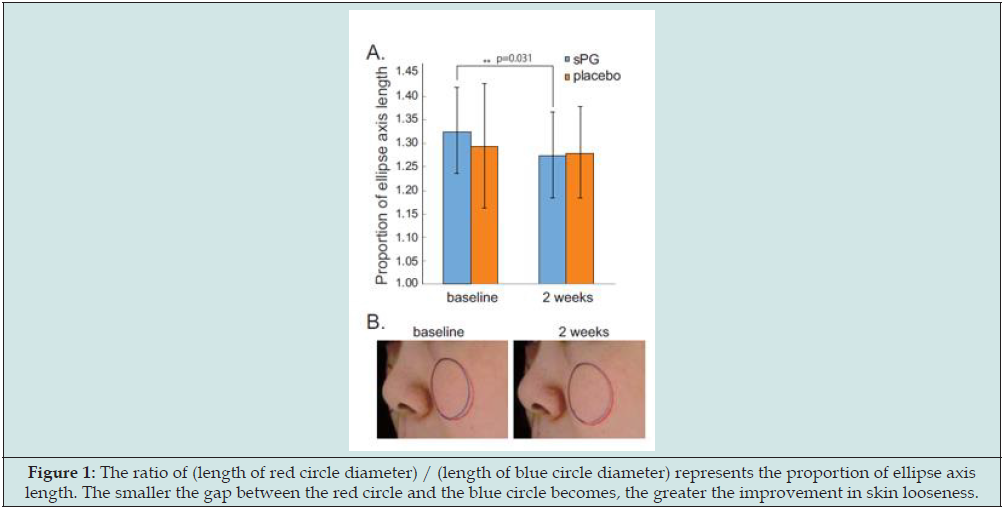
Figure 2: Effects of sPG on facial corneocytes. An increased number of good lamellar structures and less roll-up were observed in the sPG group after 2 weeks of ingestion.
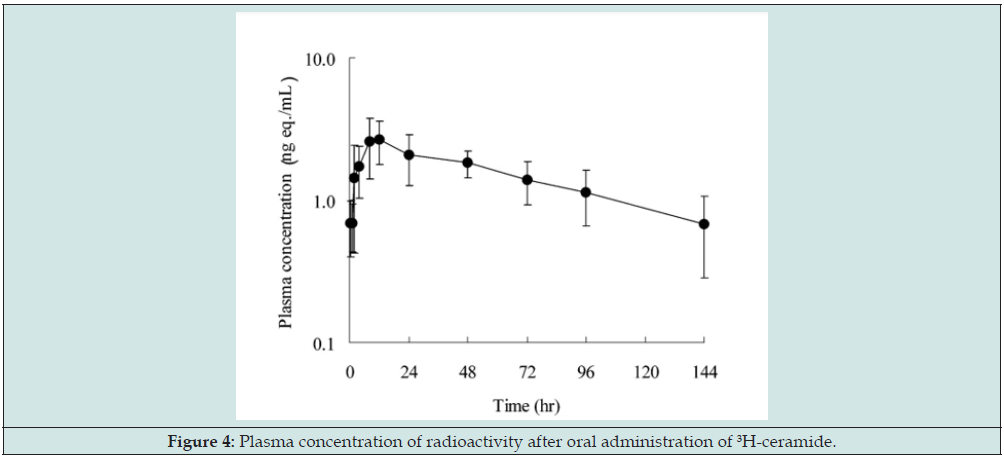
It is observed orally supplemented with a normal diet with ceramide (from rice bran and germ) for the 4 weeks reduced trans-epidermal water loss and improved stratum corneum flexibility. In Bio-E’s formula of Marine Collagen + Caviar Daily Supplement, ceramide is sourced from the precious essence of Japanese rice and comes in the form of rice bran oil powder. Only 1-2g glucose ceramide is extracted from one ton of Japanese rice through a dual-patented process. A number of clinical studies showed that this Japanese- patented ceramide can help repair corneum, establish skin protection barrier, and improve other skin problems such as dehydration, roughness, dry lines, sensitivity, redness, itching and so on [17,18]. Each tablet of Marine Collagen + Caviar Daily Supplement contains 2 mg of added ceramide, which is way higher than that of those on the market (Figure 4). The advantage of rice-derived ceramide lies in its high bioavailability for the following reasons: (1) the radioactivity concentration in the blood gradually increased to attain Cmax at 10.67 h after the administration, followed by gradual elimination with a T1/2 of 67.12 h, so it can be retained by the body for a long period (2) the rates of remaining ceramide in the body and skin were 34% and 16%, respectively, of the total absorbed ceramide, so the retention of ceramide in the body was high [19].
Last but not least, Bio-E Marine Collagen + Caviar Daily Supplement contains bonito elastin peptides, which are sourced from the aortic bulb of Japanese bonitos and research has shown that the signature indicator amino acids of elastin, desmosine and iso-desmosine, are only detected in the aortic bulb of bonitos, but not in their skin or any other tissues [20]. However, due to the aortic bulb’s size being only 2-3 cm long, only milligrams of elastin peptides can be extracted per fish. Research and questionnaires have suggested the ingestion of bonito elastin peptides generates multiple benefits including skin elasticity enhancement, reduction of wrinkles, vascular aging prevention, relief of joint pain and female chest sagging improvement [21].
Conclusion
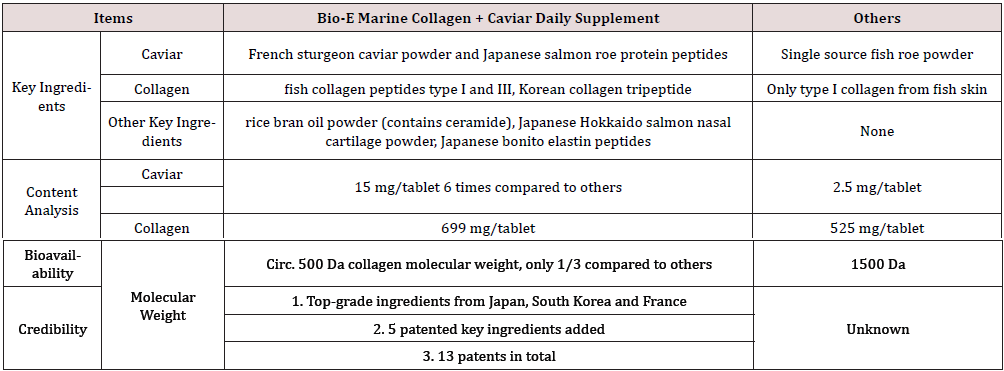
Compared to similar inner beauty products on the market, Bio- E’s Marine Collagen + Caviar Daily Supplement is formulated with top-notch patented ingredients from all over the world (Table 1). The science and biotechnology of type I and III collagen peptides, low molecular weight tripeptides, EGF stimulating theory and gut-skin axis target were also unprecedentedly combined in this product.
Table 1. Comparisons of Bio-E Marine Collagen + Caviar Daily Supplement and other products on the market.
References
- Lee KE, Nho YH, Yun SK, Park SM, Kang S, et al. (2020) Caviar Extract and Its Constituent DHA Inhibits UVB-Irradiated Skin Aging by Inducing Adiponectin Production. International journal of molecular sciences 21(9): 3383.
- Caprino F, Moretti, VM, Bellagamba F, Turchini GM, Busetto ML, et al. (2008) Fatty acid composition and volatile compounds of caviar from farmed white sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus). Analytica chemical acta 617(1-2): 139-147.
- Rustad AM, Nickles MA, McKenney JE, Bilimoria SN, Lio PA (2022) Myths and media in oral collagen supplementation for the skin, nails, and hair: A review. Journal of cosmetic dermatology 21(2): 438-443.
- Hung S (2017) Recent advances in sturgeon nutrition. Animal nutrition (Zhongguo xu mu shou yi xue hui) 3(3): 191-204.
- Fore J (2006) A review of skin and the effects of aging on skin structure and function. Ostomy/wound management 52(9): 24-37.
- Jensen BA, Reimann I, Fredensborg N (1986) Collagen type III predominance in newborns with congenital dislocation of the hip. Acta orthopaedical Scandinavica 57(4): 362-365.
- Volk SW, Wang Y, Mauldin EA, Liechty KW, Adams SL (2011) Diminished type III collagen promotes myofibroblast differentiation and increases scar deposition in cutaneous wound healing. Cells, tissues, organs 194(1): 25-37.
- Bomi (2015) J Nutr Food Sci 5: 4
- Sontakke SB, Jung JH, Piao Z, Chung HJ (2016) Orally Available Collagen Tripeptide: Enzymatic Stability, Intestinal Permeability, and Absorption of Gly-Pro-Hyp and Pro-Hyp. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 64(38): 7127-7133.
- Choi SY, Ko EJ, Lee YH, Kim BG, Shin HJ, et al. (2014) Effects of collagen tripeptide supplement on skin properties: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. Journal of cosmetic and laser therapy : official publication of the European Society for Laser Dermatology 16(3): 132-137.
- Pyun HB, Kim M, Park J, Sakai Y, Numata N, et al. (2012) Effects of Collagen Tripeptide Supplement on Photoaging and Epidermal Skin Barrier in UVB-exposed Hairless Mice. Preventive nutrition and food science, 17(4): 245-253.
- Takahashi, Immun, Endoc, Metab (2015) Agents in Med. Chem 15: 160-167.
- Iozzo RV, Schaefer L (2015) Proteoglycan form and function: A comprehensive nomenclature of proteoglycans. Matrix biology: journal of the International Society for Matrix Biology 42: 11-55.
- Ota S, Yoshihara S, Ishido K, Tanaka M, Takagaki K, et al. (2008) Effects of proteoglycan on dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis in rats. Digestive diseases and sciences 53(12): 3176-3183.
- Mizutani Y, Mitsutake S, Tsuji K, Kihara A, Igarashi Y (2009) Ceramide biosynthesis in keratinocyte and its role in skin function. Biochimie 91(6): 784-790.
- Ueda O, Hasegawa M, Kitamura S (2009) Distribution in skin of ceramide after oral administration to rats. Drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics 24(2): 180-184.
- Castro BM, Prieto M, Silva LC (2014) Ceramide: a simple sphingolipid with unique biophysical properties. Progress in lipid research 54: 53-67.
- Coderch L, López O, De La Maza A, Parra JL (2003) Ceramides and skin function. American journal of clinical dermatology 4(2): 107-129.
- Mithieux SM, Weiss AS (2005) Elastin. Advances in protein chemistry 70: 437-461.
- Weihermann AC, Lorencini M, Brohem CA, De Carvalho CM (2017) Elastin structure and its involvement in skin photoaging. International journal of cosmetic science 39(3): 241-247.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...