Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2644-1381
Short Communication(ISSN: 2644-1381) 
E-Muser (Enhanced Multiple Sclerosis Expected Rate): A Technical Improvement Volume 1 - Issue 3
Davide Frumento*
- Department of Experimental Medicine, DIMES, University of Genoa, Genoa, Italy
Received: April 25, 2019; Published: April 30, 2019
*Corresponding author: Davide Frumento, Section of Biochemistry, Department of Experimental Medicine, Italy
DOI: 10.32474/CTBB.2018.01.000115
Abstract
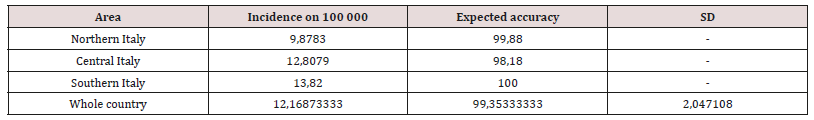
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an idiopathic chronic inflammatory disease that strikes the Central Nervous System (CNS). Moreover, it is the most diffused disabling neurologic disease, in fact about 12 * 103 new diagnoses/year arise in the United States alone. It is clear that the development of a MS predictive system is necessary, in order to have a reliable biostatistics tool to forecast the incidence value with a significant degree of accuracy in both time and space. Since the reached prevision time was equal to 1 year (namely 2019), the model was ameliorated by unpacking the considered and refined time period. The theoretical MS incidence for 2023 in Italy was calculated to be 12.17% (± 2.04), with a theoretical accuracy of 99.35% (± 1.02). It can be stated E-MuSER (Enhanced Multiple Sclerosis Expected Rate) could reach a higher dependability degree, as well as theoretical accuracy, with the respect to the previous model. Its efficiency will be assessed at the end of year 2023.
Introduction
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an idiopathic chronic inflammatory disease that strikes the Central Nervous System (CNS). Moreover, it is the most diffused disabling neurologic disease, in fact about 12 * 103 new diagnoses/year arise in the United States alone [1]. Interestingly, MS incidence was found to be directly proportional to the the distance from the equator [2-4] and it was also assessed that such a value is approximately twofold in women, if compared to men [5]. Some studies suggest that the above cited latitude distribution may be decreasing [6-8] and it was found that the sexual ratio (female vs male) could even be augmented over time [9-11]. Observing such a scenario, it becomes clear that the development of a MS predictive system is necessary, in order to have a reliable biostatistics tool to forecast the incidence value with a significant degree of accuracy in both time and space.
Rationale behind E-MuSER (Enhanced Multiple Sclerosis Expected Rate) Model
The model’s concept is based on a previous paper [12] in which a bran dew approach was proposed. It is the evolution of MuSER (Multiple Sclerosis Expected Rate) system [13], developed by analysing the Italian Multiple Sclerosis (MS) incidence within a 42-years long time period. Considering that Italy, as well as other Europeans countries, was proven to be ethnically homogeneous [14], it was taken as a starting area.
Methods & Results
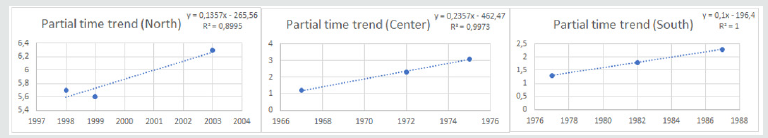
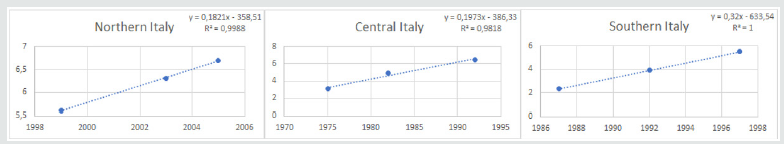
Italian MS annual incidence data, among 1965 and 2007 [15], were used in order to build three dispersion graphs, subdivided by geographic area (Northern, Central and Southern Italy). After setting tendency lines and calculating both equations and R2 coefficients. Since R2 accuracies were too low, outlier data were cancelled and R2 factors higher than 0.90 were obtained, conserving a minimum n=5. Since the reached prevision time was equal to 1 year (namely 2019), the model was ameliorated by unpacking the considered and refined time period (Figure 1) for each area (Northern, Central and Southern Italy). Since MuSER reached a theoretical accuracy of 93.76% (± 2.43), with a reliability range of 1 year in the future (namely 2019), and the unpacked set mean value is equal to 96.56% (± 5.73), it was decided to employ this kind of approach to reach 5 years in the future, up to 2023 (Figure 2). The theoretical MS incidence for 2023 (Table 1) in Italy was calculated to be 12.17% (± 2.04), with a theoretical accuracy of 99.35% (± 1.02).
Conclusion
It can be stated E-MuSER (Enhanced Multiple Sclerosis Expected Rate) could reach a higher dependability degree, as well as theoretical accuracy, with the respect to the previous model. Its efficiency will be assessed at the end of year 2023.
References
- Hirtz D, Thurman DJ, Gwinn Hardy K, Mohamed M (2007) How common are the “common” neurologic disorders? Neurology 68: 326-337.
- Acheson ED, Bachrach CA, Wright FM (1960) Some comments on the relationship of the distribution of multiple sclerosis to latitude, solar radiation, and other variables. Acta Psychiatr Scand 35: 132-147.
- Miller DH, Hammond SR, McLeod JG, Purdie G, Skegg D (1990) Multiple sclerosis in Australia and New Zealand: are the determinants genetic or environmental? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 53: 903-905.
- Kurtzke JF, Beebe GW, Norman JE (1979) Epidemiology of multiple sclerosis in US veterans: 1. Race, sex, and geographic distribution. Neurology 29: 1228-1235.
- Noseworthy JH, Lucchinetti C, Rodriguez M, Weinshenker BG (2000) Multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 343: 938-952.
- Hernán MA, Olek MJ, Ascherio A (1999) Geographic variation of multiple sclerosis incidence in two prospective studies of US women. Neurology 53: 1711-1718.
- Wallin MT, Page WF, Kurtzke JF (2004) Multiple sclerosis in US veterans of the Vietnam era and later military service: race, sex, and geography. Ann Neurol 55: 65-71.
- Ascherio A, Munger KL (2007) Environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis: part I: the role of infection. Ann Neurol 61: 288-299.
- Zivadinov R, Iona L, Monti-Bragadin L (2003) The use of standardized incidence and prevalence rates in epidemiological studies on multiple sclerosis. Neuroepidemiology 22: 65-74.
- Orton S-M, Herrera BN, Yee IM (2006) Sex ratio of multiple sclerosis in Canada: a longitudinal study. Lancet Neurol 5: 932-936.
- Cutter G, Yadavalli R, Marrie RA (2007) Changes in the sex ratio over time in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 68: A162.
- Frumento D (2019) Sarcoglycanopathies: a novel predictive approach. GSL J Public Health Epidemiol 2: 112.
- Frumento D (2019) MuSER (Multiple Sclerosis Expected Rate) predictive model development. Am J of Biom Sci & Res 2(2): 339-341.
- Lell TJ, Wallace DC (2000) The peopling of Europe from maternal and paternal perspectives. Am J Hum Genet 67(6): 1376-1381.
- Battaglia MA, Bezzini D (2017) Estimated prevalence of multiple sclerosis in Italy in 2015. Neurol Sci 38: 473-479.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...