Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2644-1381
Research Article(ISSN: 2644-1381) 
Biostatistical Analysis on the Influence of Agricultural Structure Adjustment on Farmers’ Income during the Epidemic of Coronavirus Disease in China Volume 3 - Issue 1
Jilian Lu1, Huan Zhao1, Jinming Cao2 and Bin Zhao1*
- 1School of Science, Hubei University of Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
- 2School of Information and Mathematics, Yangtze University, Jingzhou, Hubei, China
Received: July 02, 2020; Published: July 09, 2020
*Corresponding author: Bin Zhao, School of Science, Hubei University of Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China.
DOI: 10.32474/CTBB.2020.03.000154
Abstract
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Relationship between Agricultural Industrial Structure and Farmers’ Income
- Suizhou’s Agricultural Industry Structure Status in the Past Five Years
- Summary
- The Impact of Agricultural Structure Adjustment on the Income of All Farmers
- Conclusion and Countermeasures
- Suggestions
- Conflict of interest
- Acknowledgment
- References
Agricultural structural adjustment is a significant policy formulated by the state based on agricultural development. The purpose is to promote the development of the local economy through reasonable agricultural structural adjustment and then to raise the income level of farmers. Hubei Province is a big agricultural province in China, and Suizhou City is the north gate of Hubei Province, opening to the outside world during the epidemic of Coronavirus Disease in China. Given the problem of the slow growth of farmers’ income, this paper uses the method of sampling survey and empirical analysis to study the effect of agricultural structural adjustment on the income of all farmers and low-income families in Suizhou city. It establishes a panel data model based on the results of model regression. In terms of the characteristics of the head of household, the age characteristics of the head of household have a significant positive impact on the per capita income of the family. The difference of the number of years of education of the head of household is small, and the impact on the per capita income of the family is not significant. Through the group regression of poor households and non-poor households, the variables reflecting the production structure have a significant positive effect on both poor and non-poor. Still, the positive of poor is significantly lower than that of non-poor. Based on the conclusion, it suggests that the structure of planting and animal husbandry should be adjusted, and then the scale of land and mechanization of production should be further realized; the investment of science and technology should be increased, and the practical training of farmers’ specialized skills should be carried out to raise the income level of farmers more effectively. More assistance should be given to lowincome families to actively participate in the restructuring of agriculture.
Keywords: Suizhou city; agricultural restructuring; panel data model; the farmers’ income
Introduction
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Relationship between Agricultural Industrial Structure and Farmers’ Income
- Suizhou’s Agricultural Industry Structure Status in the Past Five Years
- Summary
- The Impact of Agricultural Structure Adjustment on the Income of All Farmers
- Conclusion and Countermeasures
- Suggestions
- Conflict of interest
- Acknowledgment
- References
Purpose and significance of research
The adjustment of China’s agricultural structure has begun since the 1980s. With the continuous and rapid development of China’s agriculture, China’s agricultural industry structure has been improved compared with the past. Still, we can’t reduce the importance we attach to agricultural restructuring. Agricultural structural adjustment is an eternal topic and a dynamic process. It still needs to be continuously studied and frequently improved. At present, the development of agriculture, the opening up of agriculture to the outside world, the rational development and utilization of agricultural resources, and the improvement of farmers’ economic interests are all inseparable from the adjustment of the industry structure during the epidemic of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. The previous adjustment of the agricultural structure was more inclined to obtain more profits by enriching the types of products or raising the sales prices of products. Still from the current point of view, the effect of increasing farmers’ income through this method is minimal. Nowadays, with the continuous improvement of people’s living standard, the quality requirements of products are becoming higher and higher. To effectively increase the income of farmers, more high-quality agricultural products should be developed, and the investment of famous and particular new products should be encouraged. Satisfying the market’s demand for high-quality products and product diversification can also achieve the purpose of increasing farmers’ income and improve the economic efficiency of agriculture. The development of high-quality agricultural products through the adjustment of the agricultural structure is, of course, not achieved overnight. It requires overall planning and scientific arrangements. Each region has its characteristics, so the industry structure should not use a unified model. The market demand is constantly changing, so the structure should also be adjusted promptly. The situation in each region is different, and the adjustments should be targeted, using the regional advantages to improve agricultural productivity. China has been making efforts in the adjustment of agricultural industry structure. According to Chinese national conditions, there are four factors affecting China’s agricultural restructuring. First, market demand is a dynamic process of change, and it will inevitably require dynamic modulation of the geoponic industry structure. With the continuous progress of society development, the current supply and demand relationship of geoponic products has changed. It is no longer a seller’s market like the past, but a buyer’s market now. Today’s customers’ demand for consumption is more diversified and high-quality. Therefore, we can no longer rely on price increases and increase the number of products to increase revenue but should pay attention to both quality and quantity.
Secondly, the requirements for opening up agriculture to the outside world are rising. China is a country that is open to the outside world, and agriculture is increasingly entering the international market. Therefore, while agricultural production meets the needs of the domestic market, it must also meet the needs of foreign markets, thereby improving the competitiveness of China’s agriculture in the international market. Third, China’s agricultural resources are relatively scarce, and the overexploitation and utilization of land have led to irrational resource allocation. Therefore, the sustainable development of agriculture is particularly vital in structural adjustment. The last point is to improve the economic efficiency of agricultural production, through reasonable adjustments, identifying market demand, improving the quality of products, and realizing farmers’ desire to increase income. Generally speaking, China’s current industry structure has improved considerably compared with it at the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century. However, the gap with the developed countries is still distinct. To develop modern agriculture, we must continually optimize and perfect Chinese agriculture industrial structure. Since the adjustment of the agricultural structure requires a targeted adjustment plan for a decided area, most researchers are currently studying for a province, and few people specifically go to a city, especially some less developed cities, often Was ignored. Suizhou is the youngest prefecture-level city in Hubei Province and the northern gate of Hubei Province. Although the people in Suizhou and cadres at all levels have been making continuous efforts in the adjustment of the agricultural industry structure and have achieved superb results over the years, in fact, farmers have paid a lot for this, but they need to adjust at higher risk. For example, the price of agricultural products is often lower than the expected of farmers, agricultural products such as grain and cotton are under pressure, and some farming and breeding industries follow the trend of farming and breeding, resulting in some agricultural products appearing cold or hot. Once a product yields better, farmers will follow suit and eventually produce excess supply. Since the government has not intervened too much in the adjustment of the structure of Suizhou in recent years, farmers often followed the trend blindly, leading to many agricultural products in Suizhou are unusually popular, such as jujube, garlic, peach, silkworm, etc. Over the first few years, they had a good profit. But later on, due to the trend, it resulted in overproduction, low market prices, or making it difficult to sell, so they had to be destroyed, rotted, and chopped off. It was a wasteful phenomenon, and farmers’ income was also seriously lost. Faced with this situation, we need the government to assist farmers in rationally adjusting the structure of the agricultural industry to increase farmers’ income. This article will take Suizhou as an example to deeply explore the impact of Suizhou’s agricultural, industrial structure adjustment on farmers’ income.
Research status at home and abroad
At present, the research on the adjustment of agricultural structure in China is mainly carry out from two aspects. One is to study the internal structure of the agricultural industry, that is, to evaluate the strength of the overall relationship between the adjustment of a inevitable structure in agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery to farmers’ income. The second is to study the impact of the four major industrial structures within agriculture, that is, the overall adjustment of these four industrial structures on farmers’ income. Analyzed the impact of agricultural structural adjust on farmers’ income by constructing equations and using the maximum likelihood estimation method. The results show that there are very significant correlations between various industries within the agricultural structure and farmers’ income from different sources[1]. In [2] reviewed the evolution of China’s praedial restructuring since the reform and opening up. From the perspective of economics, it can conclude that agricultural restructuring can promote the improvement of the efficiency of resource allocation. Still, it has no overt effect on the increase of crop yields. [3]calculated the correlation between the agricultural structure of the Yangtze River Delta and household income through the gray correlation model and found that there is a correlation between the income of farmers and the output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery. [4] conducted a policyoriented analysis of the following three levels of agricultural industry structure adjustment in Gansu Province. One is a strategic leading industry, the other is a regional advantage industry, and the third is a local specialty product. The adjustment has played a role in increasing farmers’ income in Gansu. [5]used panel data from 2000 to 2014 in all regions of the country to analyze from two aspects: the net income per capita of farmers and the income gap of rural residents and concluded that there are significant regional differences in the degree of impact of agricultural structural adjustment on farmers’ income. [6]. Yonghui, and Huo Xuexi analyzed the survey data of farm households using a panel data regression model and concluded that the adjustment of the agricultural structure has a significant role in promoting the income of farm households. [7] studied the impact of the modulation of agricultural structure in Shaanxi Province on the increase of farmers’ income by using the cointegration measurement analysis method and concluded that the low per capita income of farmers in Shaanxi Province was caused by the unreasonable agricultural structure. [8] analyzed the impact of Chongqing’s georgic structure adjustment on farmers’ income using a multiple linear regression method and concluded that fisheries had a positive influence on Chongqing’s farmers’ income, while planting hurt farmers’ income. Forestry and animal husbandry had Farmers’ income has a little effect. At dawn in 2017, the vector autoregressive model was used to analyze the data related to agriculture in Guangxi from 1980 to 2015, and it was concluded that the forestry output value contributed the most to the net income of farmers in Guangxi [9].
At present, there has been a systematic study on the impact of agricultural structural adjustment on farmers’ income at home and abroad. Most scholars believe that agricultural restructuring has a significant influence on farmers’ income. However, we have found that there are still some deficiencies in the research on the influence of agricultural structural modulation on farmers’ income. For example, most scholars focusing on the influence of agricultural structural adjustment on farmers’ income have concentrated on empirical research in large regions such as the country or provinces. For a decided city and township, few scholars have studied and analyzed it. The impact of different levels of agricultural development on farmers’ incomes in different cities will also be disparate. Targeted research is needed. On the other hand, the existing literature is also a lack of discussion on poverty factors.
Research ideas and research methods
The concept of agricultural, industrial structure is explained, and the relationship between agricultural, industrial structure adjustment and farmers’ income is found. Then the current structure of each township in Suizhou is explained, and then the structure of Suizhou in the past five years. Statistical analysis of the data, and finally the use of sampling methods to build multiple panel data models for 2015, 2016, 2017 three years of data, find the most suitable model for analysis, find out the production structure and other influencing factors on farmers. The degree of income impact, combined with national policies and the international situation, puts forward a reasonable adjustment plan and proposes corresponding countermeasures and suggestions for possible problems.
Relationship between Agricultural Industrial Structure and Farmers’ Income
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Relationship between Agricultural Industrial Structure and Farmers’ Income
- Suizhou’s Agricultural Industry Structure Status in the Past Five Years
- Summary
- The Impact of Agricultural Structure Adjustment on the Income of All Farmers
- Conclusion and Countermeasures
- Suggestions
- Conflict of interest
- Acknowledgment
- References
The concept of agricultural industrial structure
The agricultural industrial structure can also be called the praedial production structure, which refers to the economic area of the countryside, the various economic sectors and categories to which it belongs, the combined form, the movement law, the proportional relationship of each production project, and the status function. The agricultural industry structure can be divided by the vertical stratification method or the horizontal division of labor method. The structure of the agricultural industry has the characteristics of integrity, multi-level, and dynamic. Agriculture is China’s primary industry, including four major agricultural structures: plantation, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery [10-15]. The economic benefits produced by different industrial structures will be diverse. On the one hand, the industrial structure can reflect the level of economic progress, on the other hand, it can continuously promote the transformation of the industrial structure to a higher level, and can also promote economic development. For the adjustment of agricultural structure, there is currently no unified measurement indicator in the academic community. According to the existing literature, the connotation of agricultural structure adjustment can summarize from four aspects: one is to adjust from the four major industrial structures of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishing, and the other is to amend from the agricultural industry structure, the third is to amend the quality of agricultural production, and the fourth is to adjust according to the part of production factors. The first kind of adjustment refers to the allocation of the four parts of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery. The second kind of adjustment refers to the more detailed change of the internal structure of one of the four parts of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and Fishery. The third kind of the main adjustment is to improve the quality of products through technical means. The elements of the fourth structural adjustment refer to agricultural production factors, which include factors, labor factors, capital factors, and so on. This article will make reasonable adjustments to the structure of Suizhou City by studying the production input of the planting industry, animal husbandry, forestry, fishery, and the impact of various agricultural production factors on farmers’ income.
Analysis framework of the relationship between agricultural industrial structure and farmers’ income
In the process of economic development, the agricultural industrial structure, and the level of economic progress are mutually reinforcing and interdependent. Economic development promotes the evolution of the industrial structure, and a complete industrial structure, in turn, promotes economic progress. Each economic development period corresponds to different agricultural industrial structures; disparate industrial structures can bring disparate economic benefits. Therefore, the adjustment of the industry structure will inevitably affect the corresponding changes in farmers’ income (Figure 1).
Suizhou’s Agricultural Industry Structure Status in the Past Five Years
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Relationship between Agricultural Industrial Structure and Farmers’ Income
- Suizhou’s Agricultural Industry Structure Status in the Past Five Years
- Summary
- The Impact of Agricultural Structure Adjustment on the Income of All Farmers
- Conclusion and Countermeasures
- Suggestions
- Conflict of interest
- Acknowledgment
- References
Agricultural resources
Suizhou is a prefecture-level city in the north of Hubei Province and the “North Gate” of Hubei Province. It is adjacent to Xiaogan in the east, undertaking Wuhan City, the capital city of Hubei Province, and Xiangyang City, the sub-central of the province, in the west. The north is adjacent to Nanyang City and Xinyang City in Henan Province, and the south is adjacent to Jingmen City. It is known as “Hanxiang Throat, North Hubei Pearl.” Suizhou City locates at the confluence of the Yangtze River Basin and the Huaihe River Basin. Therefore, the water flow is abundant, and its terrain is diverse. The terrain gradually
slopes from north to south to the middle. There are multiple terrains of mountains, hills, and plains. The total area of the city is 9636ki2, of which mountain area is 4285ki2, hill area is 2094ki2 , the plain area is 530ki2 , and the beach area is 80ki2 . Mountains and rivers are interlaced, and valleys and Slopes are connected, and the hills and flats correspond to the natural landscape. Therefore, Suizhou has the reputation of “one thousand mountains and one hundred springs.” At present, the actual cultivated area of Suizhou fluctuates slightly around 192.5 thousand hectares. The cultivated land in Suizhou is mainly paddy fields. Among them, the paddy field area is about 120 thousand hectares, and the dry land area is about 25,000 hectares. According to the labor force of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery, the per capita arable land area of Suizhou are approximately 0.17 hectares. The production of agricultural products in Suizhou mainly base on food crops. The area of grain crops for summer harvest is close to 250,000 hectares. The afforestation area in Suizhou has almost increased every year. In 2016, the afforestation area exceeded 20,000 hectares. According to statistics, at the end of 2018, Suizhou has a permanent population of nearly 2.2117 million, including rural areas. The population is 1.0613 million, and the labor force is 551,900, which is about half of the rural population. Suizhou locate in the middle of the mid-latitude monsoon circulation area. The climate is seasonally affected by solar radiation and monsoon circulation. The seasons are distinct, the summer is very torridity, and the winter is cold. It belongs to the north subtropical monsoon climate [16-20]. According to statistics, the mean annual precipitation in Suizhou is between 865mm and 1070mm. The rainfall is relatively sufficient, but in recent years, the plantation industry in Suizhou has been affected by drought. The total annual sunshine in Suizhou exceeds 2,000 hours; the average annual temperature is 15.5℃. Compared with Wuhan City, the capital city in Hubei Province, the daily temperature is 2℃- 3℃ lower. The frost-free period in Suizhou is about 220-240 days per year. Suizhou is rich in products, such as carmine red peach in Guangzhou, Suizhou bubble green, Suizhou nectarine, Indian rice, Suizhou red dates, Xujiahe silver fish, Suixian black fungus, Suizhou shiitake mushroom, Guangshui Bailing mushroom , Suizhou Hongmei Li and other agricultural and sideline products are famous at home and abroad. Suizhou is also the largest edible fungus distribution center and export base in Central and South China. It is known as the “home of Chinese mushrooms.” Suizhou is also known as the world’s largest ginkgo tribe Known as the “Hometown of Ancient Chinese Ginkgo,” it is favored by many people for its rich fragrance of Cymbidium and the pure fragrance of Cymbidium, and is known as the “Hometown of Cymbidium in China.”
Investigation on the adjustment of agricultural industrial structure in some towns Using forest resources to develop edible fungus industry
There are rich forest resources in mountainous towns and villages. Using their oak resources to vigorously develop edible fungus industries such as mushrooms and fungus, farmers’ income has increased significantly. Take Sanligang Town and Canadian Town as examples. Sanligang Town is an agricultural town in Suizhou City. The total cultivated area is 5052.87 hectares, the per capita cultivated area is 0.11 hectares, the foundational farmland area is up to 4193.58 hectares, and the general farmland area is 859.29 hectares. Therefore, there are characteristics of less land and more people. The government encourages farmers to diversify their operations and increase the protection of farmland. Sanligang Town is rich in natural resources, especially the forest resources are extremely fertile, so the use of oak trees can vigorously develop fungus and mushrooms. Due to the fertile oak resources, by modifying the mushroom ear forest to increase the production of mushrooms and fungus, the climate of Sanligang Town is very suitable for artificially cultivating shiitake mushrooms, the town has thus become an advanced unit for the production of edible mushrooms in the country. Canadian Town is also a main town for the production of edible fungi in Suizhou. Since the 1960s, Canadian Town has grown shiitake mushrooms, and its abundant mushrooms are well-known throughout the country. More than 6,000 farmers in the town are engaged in edible fungus cultivation all year round. The annual production of bag mushrooms can reach more than 30 million bags [21-24]. The annual output of dried mushrooms exceeds 10 million kilograms, and the yield of fungus can reach 1.2 million sticks. The annual output value is up to 300 million yuan. The three lines of production, processing, and sales of shiitake mushrooms bring high profits to local farmers and become a pillar industry for local farmers. Suizhou is therefore known as the “home of Chinese mushrooms.”
Utilizing climatic and geographical conditions to develop fruit planting and aquaculture
The unique soil slopes and climate conditions of the hilly hills are conducive to the growth of fruit trees and are also a superior place for breeding. Therefore, this advantage can be used to develop fruit and breeding industries to increase farmers’ income. For example, the Shenzhen Township Committee, the township government’s agricultural management, scientifically planning the industrial structure, formulating appropriate methods according to the specific circumstances of each place, and adopting typical demonstration methods, the purpose is to increase farmers’ income. The main line is to adhere to the adjustment of agricultural structure [25]. The ultimate goal is to develop Shanghai Town as a fruit town in northern Hubei. Shanghai Town has gradually formed a new pattern of featured agriculture, tourism agriculture, and modern agriculture with nectarine and grapes as the leading products. At present, the town’s nectarine planting area is 350,000 mu, the grape planting area is 150,000 mu, and the other fruit planting area is 100,000 mu, with a total area of 600,000 mu. The annual income of farmers in the city can reach one billion and five hundred million yuan, which has achieved the goal of a large fruit town in northern Hubei. The area of the plantation of forest fruits in Shangshi Town is 45,000 mu, and there are more than 8,000 farmers engaged in forest fruit production; the annual output of forest fruits exceeds 80,000 tons, and the output value exceeds 100 million yuan.This town has been praised as “ The Great Fruit Town in Suizhou.” When you walk into Shanghai Town, you can see the fruit trees all over the mountains and fields, and the fruity aroma is blowing in the wind.
Utilize water resources to develop aquaculture and tourism
Changling Town has always adhered to the development concept of “Tourist Town” and promoted all-round work. It has introduced several enterprises. The town currently has nine tourism receptionunits and has developed and built tourist attractions such as Crocodile Island and Folk Island. Seven farmhouses, including Muyu Lake and Yuntai Mountain Villa were constructed, and modern water Margin City, Shanghai New City Construction Investment Company, Agricultural Cultural Industrial Park, and Wanzhong Customs Industrial Park were introduced successively. Under the idea of “Promoting hill and water culture, taking a characteristic economy,” Changling Town began to promote peculiar breeding bases throughout the town. The base has ample water sources and a quiet environment. This unique condition is very suitable for aquaculture. Since 1997, the township has formulated preferential policies to vigorously help the special aquaculture industry. After several years of progress, the town has more than 200 special farming farmers, with an annual output value of more than 40 million yuan, and farmers have benefited a lot. Of course, there are some cities and towns that use natural human landscapes to develop eco- cultural tourism. For example, Hongshan Town has Biwa Lake in the east of the township, which is an ideal place for tourism [26-30]. It has also created five major tourist products, such as Linquan Ecological Park and Linquan Ecological Park. Luoyang Town in Suizhou has four distinct seasons and beautiful mountains and rivers. It has the largest ginkgo community in the world, as well as many scenic spots and historic sites. It is a classic tourist destination. Guangzhou city in Suizhou has two 4A-level scenic spots, namely Xujiahe and Santan, as well as two national forest parks, China Mountain and Dagui Temple. These townships regard tourism as their leading role, creating wealth for the people of the whole town and enhancing their reputation.
The current situation of Suizhou’s agricultural industry structure
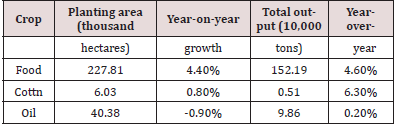
In 2018, the total output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery in Suizhou reached 25.793 billion yuan, an increase of 3.3% year-on-year in terms of comparable prices. See Table 1 for the current development status of primary crops. The current status of forestry development is also superb. The area of afforestation completed is 19.11 thousand hectares, sporadic tree planting has reached 23.688 million trees, and the amount of wood harvested is 56,100 i3 . The status of animal husbandry development is shown in Table 2. For fisheries, Suizhou’s aquatic product output reached 81,700 tons, a year-on-year increase of 1.9%. In 2018, rural power consumption in Suizhou was 532 million kWh, an increase of 3.1% year-on-year. The total power of agricultural machinery is 2.814 million kilowatts. The mechanization rate of main crop cultivation and harvesting is 74%. The application amount of chemical fertilizer was 156,600 tons, down 4.3% year-on-year.
Statistics of industrial structure adjustment in the past five years
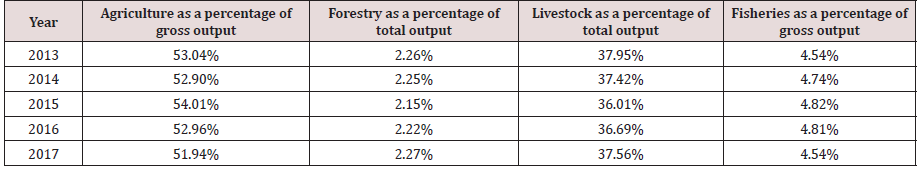
The following data is obtained by compiling the data of agriculture in Suizhou Statistical Yearbook from 2013 to 2017. In the following a, b, and d of (Figure 2) the orange curve represents the production value, and the blue line represents the area. In c of (Figure2) the orange curve represents the output value, and the blue line represents the number of slaughter. From the line chart, it can be seen that the area and output value of forestry and fishery have been rising steadily in the past five years. Although the number of agricultural planted areas and the number of slaughtered livestock have fluctuated, their output value has also been rising steadily. The growth rate of the output value of these four major industries is relatively similar, and the forestry has the fastest growth rate, with an increase of 28.44%. Secondly, the output value of fishery increased by 27.83%, the output value of animal husbandry increased by 26.46%, and the output value of agriculture increased by 25.11%. It can be seen from the above Table 3 that although the agricultural output value has increased in the past five years, the proportion of the total output value has slightly decreased. In 2015, the output value of forestry and animal husbandry was lower than that of the previous two years. The output value of Hehe Fishery in 2015 has been at its peak in the past five years. Overall, the ratio of agricultural output value to the total output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry ,and fishery has fluctuated within a small range without much change. The average disposable income of rural residents is shown in (Table 4) . It can be seen from the (Table 4) that the average disposable income of rural residents has increased from 2013 to 2017.Still, the growth rate has shown a linear downward trend, so it is imperative to increase Suizhou The growth rate of the average disposable income of rural residents in the city is necessary to adjust the agricultural structure.
Table 3: Proportion of output value of agricultural industries in the total output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery in the past five years.
Summary
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Relationship between Agricultural Industrial Structure and Farmers’ Income
- Suizhou’s Agricultural Industry Structure Status in the Past Five Years
- Summary
- The Impact of Agricultural Structure Adjustment on the Income of All Farmers
- Conclusion and Countermeasures
- Suggestions
- Conflict of interest
- Acknowledgment
- References
In the past five years, the output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery in Suizhou has increased. It is predicted that in the next few years, the output value of agriculture in Suizhou will continue to growth. Due to the drought in the past three years, the agricultural output value as a percentage of the total output value has decreased by 2.07%.Still, the total output value has increased from 13.21489 million yuan in 2015 to 137.8981 million yuan in 2017, an increase of 4.35%, which can obtain the benefits of agricultural restructuring [31]. However, in the past five years, the growth rate of the average disposable income of rural residents has continued to decline, so agricultural structural adjustment needs to be further improved.
The Impact of Agricultural Structure Adjustment on the Income of All Farmers
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Relationship between Agricultural Industrial Structure and Farmers’ Income
- Suizhou’s Agricultural Industry Structure Status in the Past Five Years
- Summary
- The Impact of Agricultural Structure Adjustment on the Income of All Farmers
- Conclusion and Countermeasures
- Suggestions
- Conflict of interest
- Acknowledgment
- References
Model setting
The advantage of using Panel Data to build a model is that the Panel Data Model can control individual differences (non-observed effects) by setting dummy variables, and has the heterogeneity of controlling individuals; secondly, the Panel Data Model can provide more information, increases the degree of freedom, and reduces the ollinearity between explanatory variables by the observation of combinations of different cross-sectional elements at different times, which can improve the validity of the estimation results; more importantly, the panel data model is a repeated observation of the same cross-section element set, which can better study the dynamic adjustment process and can construct a more complex behavior model. Therefore, this subject selects the panel data model for research. We construct the following model:

Farm household income per capita (inc), per capita productive asset value (asset) and household land area (land) I use the logarithmic form to reduce the effect of heteroscedasticity on the equation. In this model, α0 is the intercept term; αi is the individual fixed effect; ut is the time fixed effect, t is the year, i is the county; β1, β2 β3 β4 β5 β6 β7 and β8 are the parameters to be estimated, and εi is the random Disturbance term. Crop farm is the proportion of family farming income in total household income; graham is the proportion of animal husbandry income in the total household income; word is the proportion of wage income in household productive income; labor pop is used to indicate the abundance of labor resources in the family; hidage is the age of the head of the household, and he is the number of years of education of the head of the household. According to the previous analysis, the output value of plantation and animal husbandry in Suizhou City accounts for a much larger proportion of total output value than forestry and fishery. Therefore, the adjustment of the agricultural structure should focus on plantation and animal husbandry. Plantation accounts for the largest proportion. Therefore, crop farm is used as the first indicator to measure structural adjustment, followed by the proportion of animal husbandry, so graham is used as the second indicator to measure structural adjustment [32- 36]. Due to the increase in rural agricultural productivity, farmers are increasingly earning income from non agricultural labor activities. Therefore, wage income also affects the rural economic structure. We use word as the third indicator to measure structural adjustment. During the field investigation, we found that the input of household production factors accounted for a relatively large amount of total household expenditure and had a great impact on farmers’ income. Therefore, we introduced three variables, labor pop, land, and asset, to reflect the input of household factors. We also found that the characteristics of household heads also affect household income to a certain extent. We introduced two variables, age, and education to reflect the characteristics of household heads and study their impact on farmers’ income.
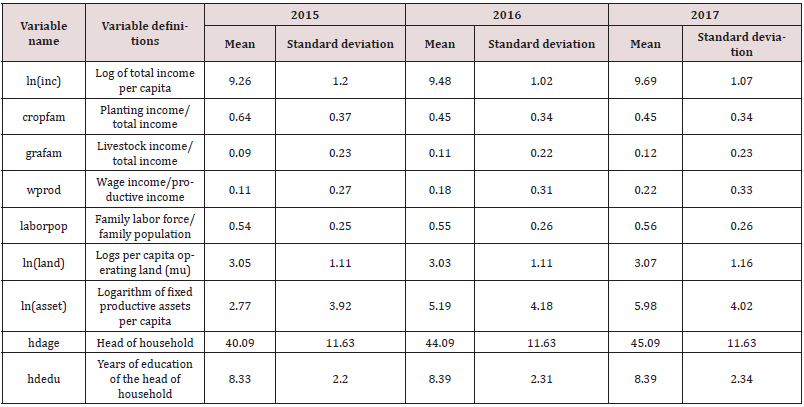
Statistical analysis of data and description
We selected data from 2015-2017 to analyze the impact of agricultural structural adjustment on farmers’ income. The data shows that the overall income of farmers in Suizhou is on the rise, and the proportion of planting income in total household income has declined slightly, but animal husbandry income. The proportion of total household income has increased. From a micro perspective, expanding the scale of animal husbandry will have a relatively significant positive impact on the increase in farmers’ income. On the whole, Suizhou’s fixed productive assets are on the rise, which shows that Suizhou has made remarkable achievements in the adjustment of agricultural structure in the past three years.
Empirical analysis
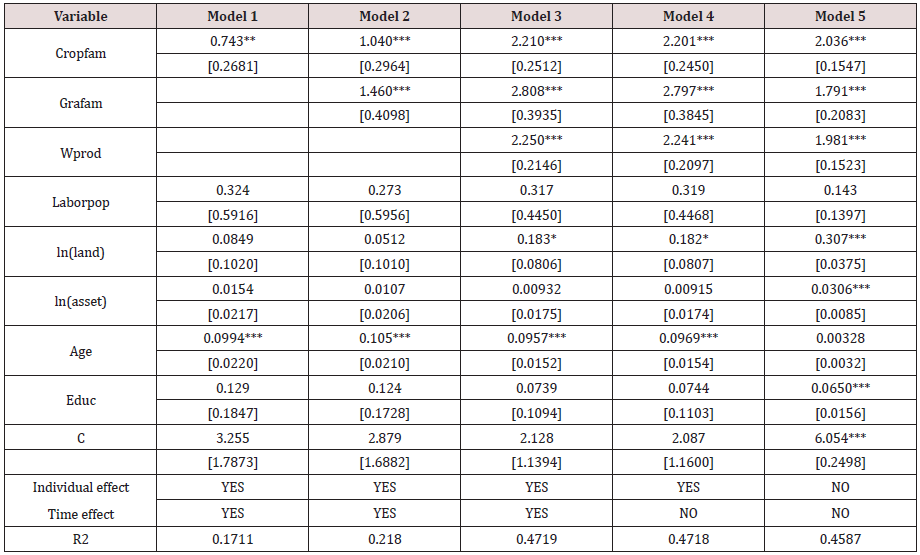
To make the results more reasonable and robust, we changed the number of production structural variables included in the model and constructed five-panel, regression models. Models 1 to 3 add variables in turn, using model 1 as the basic model, including only the production structure variable crop farm, namely:

First, the three models were tested by the likelihood ratio test. The results show that the sample data meets the requirements of the variable intercept model. The variable intercept model can be divided into two types, namely the fixed effect model and the random effect model, so the Hausman test must be carried out. According to the results of the Hausmann test, the W statistics of the three models are larger than the critical value, so a fixed-effect model is established. The results of the likelihood ratio test also found that the sample data has individual effects and time effects. Due to the differences between farmers, individual fixed effects need to be controlled and because agricultural development in different years is also affected by various aspects. Therefore, it is reasonable to control the time effect, so these three models all use the individual time point double fixed-effect model. Based on other regressions, model 4 and model 5 are established. The estimated results of the five models are shown in the following Table 5. Where *p<0.05,**p<0.01, ***p<0.001 Among the five models, the larger the R2 value, the better the fitting effect of the model. It can be seen that model 3 has the best fitting effect. Good, and Model 3 also meets the minimum criteria of AIC and SC. Comparing the differences in the influence of the significant coefficients of the five models, it can be found that Model 3 has the most stable influence direction and the influence difference is also small, which shows that the regression result of Model 3 is more robust, so We finally choose Model 3 for analysis and research. It can receive from the regression results of Model 3 that each production structure has a significant impact on farmers’ income. Among them, the share of planting earning in total earning and the share of animal husbandry income in total income have a significant positive effect on farmers’ income. Still, the positive effect of planting income in total income on farmers’ income is slightly lower than that of animal husbandry, mainly due to 2015-2017, the drought in Suizhou was severe, and the income from planting industry was affected, while the livestock industry was relatively less affected by natural disasters, so the income from animal husbandry was relatively stable. The regression results of Model 3 show that the structural adjustment of planting and animal husbandry in Suizhou is currently beneficial to the significant improvement of farmers’ income levels. Because agricultural production is affected by the seasons, the demand for agricultural labor is cyclical, and agricultural modernization is also advancing [37,38]. Agricultural production is gradually scaled up and mechanized, which makes labor productivity continue to increase. The regression results also show that the proportion of wage income to produce income in Household income per capita shows a significant positive effect. Therefore, in the future adjustment of agricultural structure, we should increase investment in science and technology, and promote the improvement of dynamic labor productivity, so that more labor can engage in nonagricultural labor, and thus increase overall income. In the input of family factors, the regression results show that land and productive capital and household income per capita have a significant positive impact. Still, the contribution of land to rural household income is greater than productive capital, so expanding the scale of land can reduce production costs and increase productivity. Regarding the characteristics of heads of household, age characteristics have a significant impact on the per capita income of the family, which is positively correlated. This is because the older the head is, the richer the farmer’s experience is in farming, and the decisions made on structural adjustment are more in line with expectations. Since the sample data collected, the difference in the years of education of the head of the household is small, and the impact on the per capita income of the family is not significant. Today’s agricultural production, elementary education does not affect the farmers’ earnings as much as the practical training of specialized skills. In general, structural adjustments to planting and animal husbandry can effectively increase farmers’ income levels. Second, land scale and production mechanization should be further realized, and investment in science and technology should be increased to enhance farmers’ income levels more effectively.
The impact of agricultural restructuring on the income of poor farmers
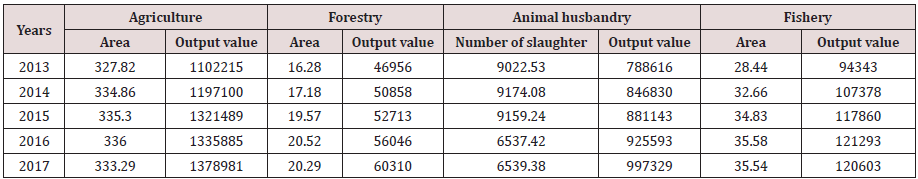
The Eighteenth National Congress of the Communist Party of China has clearly stated that by 2020, China must ensure the realization of the goal of a comprehensive well-off society, but today’s poverty problem still exists. Many rural families suffer from poverty due to illness, poverty due to marriage, and poverty due to education. The preceding analysis aims at all farmers in Suizhou. It does not distinguish between poor and non-poor families, but helps low-income families increase their income and achieve poverty alleviation, which is more conducive to social stability. In the following, we will make a regression analysis on the sample data of poor households and non-poor based on whether the households are poor, and compare the differences in the impact of various structural variables on the two, to make targeted adjustments. Where *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. The test steps are the same as the previous ones. The test results show that the poverty group and the non-poverty group are still building double fixed-effect models. From the regression results in Table 6 above, can analyze that the impact of each structural variable on poor households and non-poor households has a significant positive correlation, but the positive impact on poor households is significantly lower than that of non-poor households. Looking at the impact coefficients of each production variable on poor households separately, it can be found that the increase in labor input has the most significant positive impact on household income. Nevertheless, in the course of our investigation, we found that rural households in Suizhou City were mainly classified as low-income due to illness and poverty, resulting in a lack of effective labor in the households and poorer resistance to risks. Most of these farmers are still accustomed to the original production structure. Therefore, for these farmers, encouragement and assistance policies should be adopted actively to participate in the adjustment of agricultural structure (Tables 7&8).
Table 7: Statistics of industrial structure adjustment in the past five years Area (thousand hectares), the output value (ten thousand yuan), number of slaughtered livestock and poultry (ten thousand heads, ten thousand).
Conclusion and Countermeasures
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Relationship between Agricultural Industrial Structure and Farmers’ Income
- Suizhou’s Agricultural Industry Structure Status in the Past Five Years
- Summary
- The Impact of Agricultural Structure Adjustment on the Income of All Farmers
- Conclusion and Countermeasures
- Suggestions
- Conflict of interest
- Acknowledgment
- References
Main conclusion
This article takes Suizhou City as an example to analyze the impact of agricultural structure adjustment on the income of farmers and herdsmen in ethnic areas. The conversion coefficient of agricultural structure adjustment is used to obtain the law of the change of income of farmers and herdsmen with the adjustment of agricultural structure. Based on the current situation, from the macro-level and the micro-level based on the survey data, empirical research was conducted on the impact of agricultural structure adjustment, planting and animal husbandry internal structure adjustment on farmers’ income, and the corresponding conclusions and conclusions were drawn based on the analysis of empirical results. The relevant policy recommendations applicable to the adjustment of the agricultural structure of Suizhou City and the increase in income of farmers and herdsmen are as follows. The proportion of planting income and animal husbandry income in total income has a significant positive correlation with farmers’ income. Focusing on the structural adjustment of planting and animal husbandry can effectively increase farmers’ income. The proportion of wage income to produce income has a significant positive impact on household income per capita, so we should further realize the land scale and production mechanization; increase investment in science and technology; and provide practical training for farmers with specialized skills, so that they can more quickly raise the income level of farmers. In terms of the characteristics of the head of the household the age characteristics of the head of the household have a significant positive effect on the per capita income of the family. By grouping regression of poor and non-poor households, the variables reflecting the production structure have a significant positive impact on both poor and nonpoor households. Still, the positive influence of poor is significantly lower than that of non-poor, mainly because this part of the farmers themselves are more accustomed to the past production methods, we should provide more help to this part of the family so that they can actively participate in structural adjustment. On the whole, the adjustment of the agricultural structure has a positive impact on farmers’ income.
Suggestions
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Relationship between Agricultural Industrial Structure and Farmers’ Income
- Suizhou’s Agricultural Industry Structure Status in the Past Five Years
- Summary
- The Impact of Agricultural Structure Adjustment on the Income of All Farmers
- Conclusion and Countermeasures
- Suggestions
- Conflict of interest
- Acknowledgment
- References
The results of the study found that although the adjustment of the agricultural structure has a significant positive effect on farmers’ income, as the adjustment deepens, farmers’ income shows a trend of “inverted U” increasing first and then decreasing. For this phenomenon to occur as little as possible, the government should combine the actual situation to adjust it moderately, but not adjust it just for adjustment. The adjustment of the agricultural structure is actually to solve the problem that farmers’ income is not growing fast. To promote farmers’ income, we must not only see the shortterm benefits but also focus on the future and formulate a longterm construction system. Although the adjustment of planting and animal husbandry has a more significant impact on farmers’ income, it is also necessary to develop the potential of forestry and fishery structural adjustment to promote income growth. Suizhou has been affected by drought for many years, and the area of dry crops has expanded, resulting in an oversupply of dry crops on the market, resulting in price reductions, and farmers’ incomes have declined or even suffered losses. In response to this situation, we should actively develop Rice, rapeseed, and other advantageous industries. For agricultural restructuring to be implemented effectively, first of all, the government needs to have practical and feasible policy measures, such as improving financial services for rural areas, establishing a circulation mechanism, promoting agricultural industrialization, and helping to transfer agricultural surplus labor. Second, the government should accurately position and correctly perform functions, such as assisting farmers change their minds and ideas, helping guide farmers to introduce and promote new technologies and new varieties, and solve the problems that farmers do not want to adjust or do not know how to regulate. Third, the government should respect the wishes of farmers and farmers’ main status and avoid compulsory orders. Otherwise, it will cause irreparable economic losses, which will seriously affect farmers’ enthusiasm for adjustment. Fourth, the adjustment of the agricultural structure should be able to quickly adapt to changes in domestic and foreign markets. After China’s accession to the WTO (World Trade Organization), China’s market-oriented role has become increasingly stronger, high-tech has been independently applied, and characteristic industrial areas have become increasingly clear. Fifth, the adjustment of agricultural structure also requires an accurate grasp of the direction of adjustment. The entire Suizhou City cannot have only one adjustment mode. Each township has its advantages, and resources should be allocated scientifically and rationally during the adjustment process. Structural adjustment is also impossible not to change forever. It is a dynamic adjustment process, and adjustments should be made promptly according to market changes. Peasants can’t follow others all the time; their growing decides what we grow. We must look at market demand, the prices of agricultural products, and the changes in the macroeconomic environment, and decide what and how much to develop based on these factors.
Specifically, Suizhou should adjust from the following directions:
a. Vigorously develop “ecological” agriculture. With the
improvement of people’s quality of life and the enhancement
of environmental protection awareness, the adjustment of the
agricultural structure should focus on “ecotype” and pollution-free,
and vigorously develop green agriculture, sightseeing agriculture,
and tourism agriculture.
b. Increase the proportion of animal husbandry. Animal
husbandry is a crucial symbol of the urban agricultural
development level. With the increase of animal food in people’s
diet structure, animal husbandry has market potential. Therefore,
in the adjustment of agricultural structure, we must focus on the
development of animal husbandry and raise its proportion in
agriculture. It is necessary to actively breed excellent varieties,
develop high-quality feed, and adopt scientific breeding techniques.
c. Speed up the development of deep processing of
agricultural products. The product processing industry can not
only effectively increase the added value of primary agricultural
products, but also extend the agricultural industrial chain, promote
the value-added transformation of agricultural products for many times, and improve the overall efficiency of agriculture. Vigorously
developing the agricultural product processing industry is the need
to enhance competitiveness and promote the in-depth development
of the agricultural restructuring.
d. Optimize the layout of agricultural regions.For a product,
an enterprise, and a local economy, if there is no characteristic,
there is no advantage and vitality. By optimizing the layout and
regional division of labor, we should form major products and pillar
industries with district competitive advantages and scales, develop
characteristic agriculture, and transform from maximizing output
to maximizing benefits.
e. Vigorously develop rural non-agricultural industries
and small towns, and promote the transfer of surplus rural labor.
We must be market-oriented and accelerate the development of
rural secondary and tertiary industries, especially the processing
of agricultural products. Based on the transformation of existing
agricultural product processing capabilities, serval agricultural
product processing enterprises or enterprise groups should be
cultivated to raise the level of agricultural product processing.
Actively participate in the development of small
f.-town development plans, combining the development
of small towns with the development of township and village
enterprises, agricultural industrialization, and adjustment of the
agricultural structure during the epidemic of Coronavirus Disease.
Conflict of interest
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Relationship between Agricultural Industrial Structure and Farmers’ Income
- Suizhou’s Agricultural Industry Structure Status in the Past Five Years
- Summary
- The Impact of Agricultural Structure Adjustment on the Income of All Farmers
- Conclusion and Countermeasures
- Suggestions
- Conflict of interest
- Acknowledgment
- References
We have no conflict of interest to disclose, and the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors.
Acknowledgment
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Relationship between Agricultural Industrial Structure and Farmers’ Income
- Suizhou’s Agricultural Industry Structure Status in the Past Five Years
- Summary
- The Impact of Agricultural Structure Adjustment on the Income of All Farmers
- Conclusion and Countermeasures
- Suggestions
- Conflict of interest
- Acknowledgment
- References
This work was supported by the Philosophical and Social Sciences Research Project of Hubei Education Department (19Y049), and the Staring Research Foundation for the Ph.D. of Hubei University of Technology (BSQD2019054), Hubei Province, China.
References
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Relationship between Agricultural Industrial Structure and Farmers’ Income
- Suizhou’s Agricultural Industry Structure Status in the Past Five Years
- Summary
- The Impact of Agricultural Structure Adjustment on the Income of All Farmers
- Conclusion and Countermeasures
- Suggestions
- Conflict of interest
- Acknowledgment
- References
- Yang Ling (2017) Multiple linear regression analysis of the impact of agricultural, industrial structure on farmers' income. J Statistics and Decision(17): 118-120.
- Zhang Minglin, Huang Guoqin (2002) Economic thinking and analysis of agricultural structure adjustment. Journal of Jiangxi Agricultural University (Social Science Edition)(02): 11-14.
- Chen Kai (2011) Adjustment of agricultural structure, agricultural multi-functionality, and changes in farmers' incomesBased on the empirical research of Jiangsu, Zhejiang ,and Shanghai in the Yangtze River Delta. Economic Issues(11): 82- 86.
- Ma Yongxing (2014) A Study on the Adjustment of Regional Characteristic Agricultural Industrial Structure and Increasing Farmers’ Income in Gansu Province. Journal of Gansu Normal University19(01): 138-142.
- Tang Dan (2016) Regional differences in the impact of agricultural structural adjustment on farmers’ income in China. Exploration of Economic Problems(02): 180-184.
- Zhao Xiaofeng, Zhang Yonghui, Huo Xue xi (2012) An empirical analysis of the impact of agricultural structure adjustment on farmers’ household income. Journal of Zhongnan University of Economics and Law(05): 127-133+144.
- Zhang Xuqi (2016) Research on the Impact of Agricultural Structure Adjustment on Farmers' Income Increase in Shaanxi Province. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning37(08): 163-167+179.
- Liu Bofan (2013) Chongqing's agricultural industry structure adjustment and its impact on farmers' income. Chongqing Technology and Business University.
- Liming (2017) The effect of Guangxi agricultural industrial structure adjustment on farmers' income based on the VAR model. Tax Payment(23): 89-90.
- Peng Qinghai (2019) Combination of agricultural structural adjustment and industrial poverty alleviation [J]. Hunan Agriculture(12): 28.
- Miao Jiancheng (2019) Countermeasures for Shenyang’s agricultural structure adjustment. Heilongjiang Science 10(22): 162-164.
- Zhao Ningning (2019) To adjust agricultural structure in the new era to improve agricultural economic benefits. Office Automation24(16): 21-24.
- Chen Ming (2019) Research on the countermeasures for structural reform of the agricultural supply side in China. Shenyang University of Technology.
- Zhigang yu, Zhang, Liang (2018) Differences in farmers' willingness and behavior of planting structure adjustmentBased on a survey of 341 corn farmers in Heilongjiang Province [J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University (Social Science Edition)18(04): 137 -145+160.
- Huang Xiaofei (2018) Research on promoting the transformation and upgrading of the Hubei agricultural structure. Central China Normal University.
- Liu Cheng, Zhou Xiaoshi, Chen Shasha (2017) Analysis of the effect of Hubei Province agricultural structure adjustment on farmers’ income. Journal of China Agricultural University22(09): 201-211.
- Jiang Changyun, Zhixiong Du (2017) Thoughts on pushing forward the structural reform on the agricultural supply-side. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University (Social Science Edition)17(01): 1-10+144.643.
- Shengwei Tu (2016) The root cause of the imbalance of China's agricultural supply structure and the focus of reform. Economic Perspective(11): 108-113.
- Zhao Shuo (2019) Research on the impact of agricultural structure adjustment on farmers’ income in Gansu Province. Lanzhou University of Finance and Economics.
- Meng Xi (2019) Analysis of influencing factors of Jiamusi’s breeding structure and countermeasures. Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University.
- Haihua Ji (2019) Research on the pattern of regional agricultural production adjustment. Jiangxi University of Finance and Economics.
- Pengfei Li (2019) Research on the impact of agricultural structure adjustment on the income of farmers and herdsmen in ethnic areas. Inner Mongolia University.
- Zhang Zhibin (2019) Research on adjustment of agricultural water structure in Shandong Province. Shandong Agricultural University.
- Wang Yu (2018) Research on the adjustment and optimization of agricultural industry structure in Dingxi City in the new period . Gansu Agricultural University.
- Wang Chen (2018) Research on the adjustment of agricultural industry structure in Jixi City under the background of supply-side reform. Jilin University.
- Ding Liangjiao (2018) Development of "Internet + Agriculture" and its impact on agricultural structure adjustment. Zhejiang Technology and Business University.
- Sun Jianfeng (2018) Current situation and countermeasures of agricultural industry structure adjustment in Mumen Town. Sichuan Agricultural University.
- Hu Lei (2018) Research on the adjustment of agricultural industry structure in Tai’an City. Shandong Agricultural University.
- Wang Peiyi (2018) Research on the policy of agricultural structure adjustment in Shiyan City. Yanan University.
- Tianxiang Li (2017) Research on the impact of structural adjustment and technological progress on China’s grain production. Nanjing Agricultural University.
- Liang Jianlian (2016) The effect of Maoming’s agricultural, industrial structure adjustment on farmers’ income [D]. Zhongkai College of Agricultural Engineering.
- Yan Jun (2016) Research on Agricultural Structure Adjustment of Hunchun City. Yanbian University.
- Liu Wenzhong (2015) Research on Countermeasures of Agricultural Structure Adjustment in Wuwei City. Lanzhou University.
- Xinyuan Liang, Yangbing Li, Caihong Ran, Mingzhen Li, Hao Zhang (2020) Study on the transformed farmland landscape in rural areas of southwest China: A case study of Chongqing. Journal of Rural Studies (76): 272-285.
- Shiwei Liu, Pingyu Zhang, Wenxin Liu, Xiuli He (2019) Key Factors Affecting Farmers’ Choice of Corn Reduction under China’s New Agriculture Policy in the ‘Liandaowan’ Areas, Northeast China. Chinese Geographical Science 29(6): 1039-1051.
- Jin Minfeng, Ding Yongqian, Yu Hongfeng, Liu Haitao, Jiang Yizhuo, et al. (2017) Optimal Structure Design and Performance Tests of Seed metering Device with Fluted Rollers for Precision Wheat Seeding Machine. IFAC PapersOnLine 51(17): 509-514.
- Jamie M Sommer, John M Shandra, Michael Restivo (2017) The World Bank, contradictory lending, and forests: A cross-national analysis of organized hypocrisy. International Sociology 32(6): 707-730.
- Wenjun Jiao, Qingwen Min, Anthony M (2017) Fuller. Converting rice paddy to dry land farming in the Tai Lake Basin, China: toward an understanding of environmental and economic impacts. Paddy and Water Environment15(1): 171-179.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...