Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-4579
Short Communication(ISSN: 2637-4579) 
Electro Elastic Actuator for Micro and Nano Surgical Repairs Volume 3 - Issue 2
Afonin SM*
- National Research University of Electronic Technology (MIET), Russia
Received: February 04, 2018; Published: February 13, 2019
*Corresponding author: Afonin Sergey Mikhailovich, National Research University of Electronic Technology (MIET), Moscow, Russia
DOI: 10.32474/OAJBEB.2019.03.000156
abstract
The structural scheme and the transfer functions, the characteristics of the electro elastic actuator for micro and nano surgical repairs are obtained. The transfer functions of the electro elastic actuator are described the characteristics of the actuator with regard to its physical parameters and external load.
Keywords: Electro elastic actuator; Piezo actuator; Structural scheme; Transfer function
Introduction
The electro elastic actuator on the piezoelectric, electrostriction effects is used in the mechatronics systems for the micro and nano surgical repairs, for the micro and nano robotics, for the micro and nano manipulators and injectors [1-6]. The mathematical model, the structural scheme and transfer functions of the electro elastic actuator are calculated for designing the control system for the micro and nano surgical repairs [4-11]. The structural scheme and transfer functions the electro elastic actuator based on the electro elasticity make it possible to describe the dynamic and static properties of the electro elastic actuator for the micro and nano surgical repairs with regard to its physical parameters and external load [12-23].
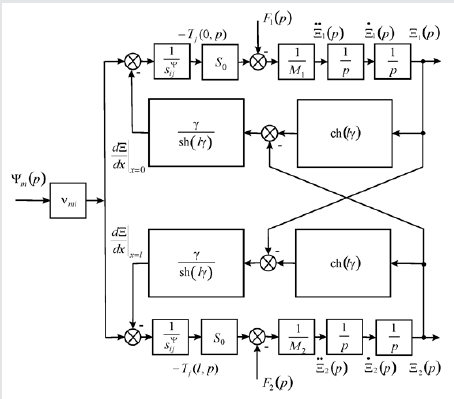
Structural Scheme Electro Elastic Actuator
The method of mathematical physics with Laplace transform is applied for the solution the wave equation. The structural scheme of the electro elastic actuator for the micro and nano surgical repairs is changed from Cady and Mason electrical equivalent circuits [7- 8]. The equation of the electro elasticity [6,8,12] has the following form
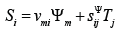
where Si is the relative displacement along axis i of the cross
section of the piezo actuator,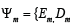 is the control parameter, Em, is the electric field strength for the voltage control along axis m, Dm is the electric induction for the current control along axis m,
Tj is the mechanical stress along axis j, νmi is the electro elastic
module, for example, the piezo module, ij sΨ is the elastic compliance
for the control parameter Ψ = const , and the indexes i= 1, 2, … ,
6; j = 1, 2, … , 6; m = 1, 2, 3. The main size along axis i for the electro
elastic actuator is determined us the working length l = {δ , h,b}
in form the thickness, the height or the width for the longitudinal,
transverse or shift piezo effect.
is the control parameter, Em, is the electric field strength for the voltage control along axis m, Dm is the electric induction for the current control along axis m,
Tj is the mechanical stress along axis j, νmi is the electro elastic
module, for example, the piezo module, ij sΨ is the elastic compliance
for the control parameter Ψ = const , and the indexes i= 1, 2, … ,
6; j = 1, 2, … , 6; m = 1, 2, 3. The main size along axis i for the electro
elastic actuator is determined us the working length l = {δ , h,b}
in form the thickness, the height or the width for the longitudinal,
transverse or shift piezo effect.
For the construction the structural scheme of the electro elastic actuator is used the wave equation [8,10,14] for the wave propagation in the long line with damping but without distortions. With using Laplace transform is obtained the linear ordinary second-order differential equation. The problem for the partial differential equation of hyperbolic type using the Laplace transform is reduced to the simpler problem [8,14] for the linear ordinary differential equation
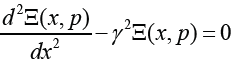
where Ξ(x, p) is the Laplace transform of the displacement
of the section of the electro elastic actuator 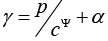 α Ψ = + is the
propagation coefficient, cΨ is the sound speed for the control
parameterΨ = const ,α is the damping coefficient.
α Ψ = + is the
propagation coefficient, cΨ is the sound speed for the control
parameterΨ = const ,α is the damping coefficient.
The mathematical model [6, 23] and the structural scheme of the electro elastic actuator for the micro and nano surgical repairs on Figure 1 are determined, using method of the mathematical physics for the solution of the wave equation, the boundary conditions and the equation of the electro elasticity, in the following form
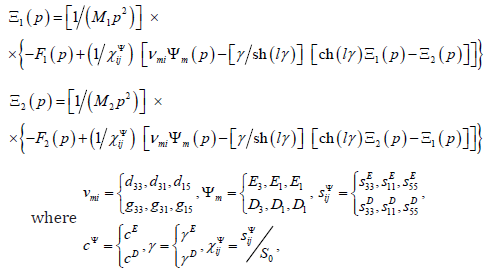
vmi is the electro elastic module, 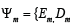 is the control
parameter, m E is the electric field strength for the voltage control
along axis m, m D is the electric induction for the current control
along axis m,
sΨij is the elastic compliance, dmi is the piezo module
at the voltage-controlled piezo actuator, gmi is the piezo module at
the current-controlled piezo actuator, S0 is the cross section area,
M1 , M2 are the mass of the load,
is the control
parameter, m E is the electric field strength for the voltage control
along axis m, m D is the electric induction for the current control
along axis m,
sΨij is the elastic compliance, dmi is the piezo module
at the voltage-controlled piezo actuator, gmi is the piezo module at
the current-controlled piezo actuator, S0 is the cross section area,
M1 , M2 are the mass of the load, 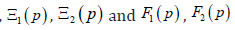 are
the Laplace transforms of the appropriate displacements and the
forces on the faces 1, 2. For the micro and nano surgical repairs the
structural schemes of the voltage-controlled or current-controlled
piezo actuator are obtained from its mathematical model.
are
the Laplace transforms of the appropriate displacements and the
forces on the faces 1, 2. For the micro and nano surgical repairs the
structural schemes of the voltage-controlled or current-controlled
piezo actuator are obtained from its mathematical model.
Transfer Function Electro Elastic Actuator
The matrix transfer function [6,18,21] of the electro elastic actuator for the micro and nano surgical repairs is derived from its mathematical model in the following form
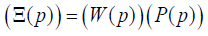
where (Ξ( p)) is the column-matrix of the Laplace transforms of the displacements for the faces 1, 2 of the electro elastic actuator, (W( p)) is the matrix transfer function, (P( p)) the column-matrix of the Laplace transforms of the control parameter and the forces for the faces 1, 2.
Conclusions
The structural scheme, the transfer functions of the electro elastic actuator for the micro and nano surgical repairs, for the micro and nano robotics, for the micro and nano manipulators and injectors are described the characteristics of the electro elastic actuator with regard to its physical parameters, external load.
References
- Schultz J, Ueda J, Asada H (2017) Cellular Actuators. Oxford: Butterworth- Heinemann Publisher, p. 382.
- Afonin SM (2006) Absolute stability conditions for a system controlling the deformation of an electro magnetoelastic transduser. Doklady Mathematics 74(3): 943-948.
- Przybylski J (2015) Static and dynamic analysis of a flextensional transducer with an axial piezoelectric actuation. Engineering Structures 84: 140-151.
- Afonin SM (2015) Block diagrams of a multilayer piezoelectric motor for nano- and microdisplacements based on the transverse piezoeffect. Journal of Computer and Systems Sciences International 54(3): 424-439.
- Afonin SM (2008) Structural parametric model of a piezoelectric nanodisplacement transduser. Doklady Physics 53(3): 137-143.
- Afonin SM (2006) Solution of the wave equation for the control of an elecromagnetoelastic transduser. Doklady Mathematics 73(2): 307-313.
- Cady WG (1946) Piezoelectricity: An Introduction to the Theory and Applications of Electromechancial Phenomena in Crystals. London: McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, p. 806.
- Mason W (1964) Physical Acoustics: Principles and Methods. Part A. Methods and Devices, Academic Press, New York 1: 515
- Zwillinger D (1989) Handbook of Differential Equations. Boston: Academic Press, p. 673.
- Afonin SM (2006) A generalized structural-parametric model of an elecromagnetoelastic converter for nano- and micrometric movement control systems: III. Transformation parametric structural circuits of an elecromagnetoelastic converter for nano- and micrometric movement control systems. Journal of Computer and Systems Sciences International 45(2): 317-325.
- Afonin SM (2016) Decision wave equation and block diagram of electromagnetoelastic actuator nano- and microdisplacement for communications systems. International Journal of Information and Communication Sciences 1(2): 22-29.
- Afonin SM (2015) Structural-parametric model and transfer functions of electroelastic actuator for nano- and microdisplacement. Chapter 9 in Piezoelectrics and Nanomaterials: Fundamentals, Developments and Applications. Parinov IA, editor, New York: Nova Science, pp. 225-242.
- Afonin SM (2017) A structural-parametric model of electroelastic actuator for nano- and microdisplacement of mechatronic system. Chapter 8 in Advances in Nanotechnology. Volume 19. Bartul Z, Trenor J, editors, New York: Nova Science, pp. 259-284.
- Afonin SM (2018) Electromagnetoelastic Nano- and Microactuators for Mechatronic Systems. Russian Engineering Research 38(12): 938-944.
- Afonin SM (2012) Nano- and micro-scale piezomotors. Russian Engineering Research 32(7-8): 519-522.
- Afonin SM (2007) Elastic compliances and mechanical and adjusting characteristics of composite piezoelectric transducers. Mechanics of Solid 42(1): 43-49.
- Afonin SM (2014) Stability of strain control systems of nano-and microdisplacement piezotransducers. Mechanics of Solids 49(2): 196- 207.
- Afonin SM (2017) Structural-parametric model electromagnetoelastic actuator nanodisplacement for mechatronics. International journal of Physics 5(1): 9-15.
- Afonin SM (2017) Structural-parametric model of piezoactuator nanoand microdisplacement for nanoscience. AASCIT Journal of Nanoscience 3(3): 12-18.
- Afonin SM (2016) Solution wave equation and parametric structural schematic diagrams of electromagnetoelastic actuators nano- and microdisplacement. International Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 3(4): 31-38.
- Afonin SM (2018) Structural-parametric model of electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanomechanics. Actuators 7(1): 1-9.
- Afonin SM (2016) Structural-parametric models and transfer functions of electromagnetoelastic actuators nano- and microdisplacement for mechatronic systems. International Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mathematics 2(2): 52-59.
- Afonin SM (2018) Structural-parametric model of electro elastic actuator for nanotechnology and biotechnology. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutics 5(1): 8-12.
Editorial Manager:
Email:
biomedicalengineering@lupinepublishers.com

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...