Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2644-1403
Case Report(ISSN: 2644-1403) 
Manipulation to Treat Superior Cluneal Nerve Entrapment Volume 4 - Issue 1
Wang Jun1, Yin Jichao2*, Hu Xing lV3 and Lei Chengxiang1
- 1Shanxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
- 2Shan’xi Xi’an Health School, China
- 3Xi’an Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, China
Received:March 01, 2021; Published: March 11, 2021
Corresponding author: Yin Jichao, Xi’an Health School, Beilin District, Xi’an City, Shaanxi Province, China
DOI: 10.32474/GJAPM.2021.04.000182
Abstract
Background and objectives: Superior cluneal nerve entrapment syndrome is one of the causes of low back pain. Explore new treatment methods for the treatment of Superior cluneal nerve entrapment syndrome.
Case Report: A 44-year-old man with severe pain in the right lower waist for 3 days, pain in the right iliac crest, accompanied by throbbing pain in the right hip, restricted waist movement, increased pain during forward bending and rotation his straight-legraising tests were negative on both sides. Check the sacroiliac joints and spine without obvious abnormalities.
Result: Manipulative therapy can relax the tension of the waist and hip muscles, and comprehensively obtain better treatment results for the compression of the buttock epithelial nerve; ultrasound examination can well describe the damage of the buttock epithelial nerve.
Keywords: Superior cluneal nerve entrapment syndrome; manual therapy; low back pain
Introduction
According to reports, the lower back pain caused by the Superior cluneal nerve entrapment syndrome is about 1.6%-12% [1,2] of the patients with lower back pain, and the bilateral incidence is about 20%-33% [3]. Research on gender It shows that the incidence of women is higher than that of men [4], and manual workers have a higher incidence [5]. Superior cluneal nerve entrapment syndrome is well known to cause lower back pain, but it is rarely diagnosed. We have 1 case of low back pain, which is believed to be caused by entrapment of the Superior cluneal nerve.
Case Report
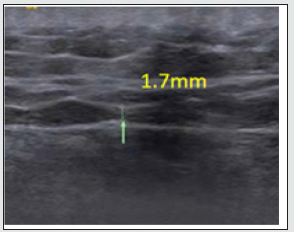
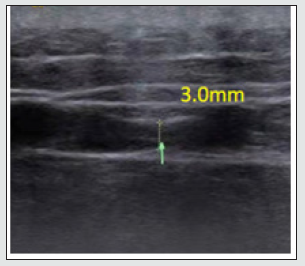
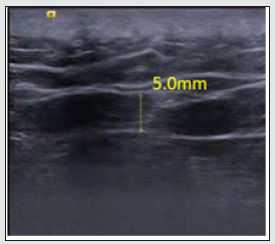
Male, 44 years old, 75kg. Severe pain in the right lower waist for 3 days, pain in the right iliac crest, and throbbing pain in the right hip, came to the orthopedics clinic. The pain was not responsive to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Inquiring about the medical history and physical examination, the patient complained that he had difficulty in turning over and walking after sitting for a long time 3 days ago, and his living ability was seriously affected. On physical examination, it was found that the waist movement was limited, the pain increased during forward bending and rotation, and his straight-leg-raising tests were negative on both sides. Check the sacroiliac joints and spine without obvious abnormalities. However, there is severe tenderness in the iliac crest. According to the visual analog pain score, the patient’s pain score is 7-8 points, with a maximum score of 10. According to the strong [6] diagnostic criteria, we consider the gluteal epithelial nerve compression syndrome. It is recommended to perform musculoskeletal ultrasound examination. The results of the examination revealed that the gluteal epithelial nerve narrowed in the iliac crest tunnel (Figure 1). Based on the patient’s symptoms, physical examination, and musculoskeletal ultrasound results, we diagnosed the compression of the gluteal epithelial nerve and gave manual treatment. After the manual treatment, the musculoskeletal ultrasound examination found that the tunnel at the iliac crest had the original 1.7mm changed to 3.0mm (Figure 2). After 1 week, a reexamination revealed that the tunnel at the iliac crest became 5.0mm (Figure 3), and the patient’s symptoms disappeared completely.
Technology
When the patient was brought into the treatment, lying prone on the treatment bed, a therapist performed relaxation treatment for the patient’s waist and hip muscles and fascia for about 10 minutes. The patient takes a sitting position, the surgery is located on the back of the patient, and the thumbs of both hands are placed on the painful part of the patient’s iliac crest, and there will be a noticeable depression. Instruct the patient to try his best to stretch the upper limbs of the affected side over the top of the head, stretch the body of the affected side, and make the patient do chest-lifting and waistup exercises. The surgeon uses the thumb to push the tissue toward the depression, reset and smooth. The local depression is smoother than the front, indicating successful reduction.
Discuss
The Superior cluneal nerve consist of fibers from L1-L3 [7]. The entrapment of the Superior cluneal nerve is closely related to the fragility of its surrounding anatomy. It often occurs when the peripheral nerve passes through the opening of the fibrous tissue or the bone fiber tube [8]. A general physical examination of a patient cannot make a diagnosis, so it is often easy to be misdiagnosed. Ultrasound can better describe the gluteal epithelial nerve, which can reduce the misdiagnosis rate of gluteal epithelial nerve compression [9]. On the other hand, by comparing the ultrasound data before and after, it objectively reflects the changes before and after treatment. We believe that the uneven force of the lower waist muscles and fascia is an important reason for the overall entrapment of the Superior cluneal nerve. The unbalanced force on the lower waist and local traction caused the tissue position at the iliac crest to shift. Through manual treatment, the dislocated tissue can be restored to its original position, which relieves the tension of the local muscle fascia and reduces The traction on the iliac crest can achieve the therapeutic effect.
Conflict of Interest
The authors have nothing to disclose.
References
- Maigne JY, Doursounian L (1997) Entrapment neuropathy of the medial superior cluneal nerve. Nineteen cases surgically treated, with a minimum of 2 years’ follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 22: 1156-1159.
- Kuniya H, Aota Y, Nakamura N, Kawai T, Tanabe H, et al. (2011) Low back pain patients with suspected entrapment of the superior cluneal nerve. J Spine Res 2: 1032-1035.
- Takayama T, Utsumi T (1961) Superior cluneal syndrome as a cause of low back pain. Surgery 23: 885-900.
- Kuniya H, Aota Y, Kawai T, Kaneko K, Konno T, et al. (2014) Prospective study of superior cluneal nerve disorder as a potential cause of low back pain and leg symptoms. J Orthop Surg Res 9: 139
- Feng Tianyou (2002) Clinical research on the treatment of soft tissue injury with integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine. China Science and Technology Publishing,
- Strong EK, Davila JC (1957) The cluneal nerve syndrome; a distinct type of low back pain. Ind Med Surg 26(9): 417-429.
- Maigne JY, Lazareth JP, Guerin Surville H, Maigne R (1989) The lateral cutaneous branches of the dorsal rami of the thoraco-lumbar junction. an anatomical study on 37 dissections. Surg Radiol Anat 11(4): 289-293.
- Talu GK, Ozyalçin S, Talu U (2000) Superior cluneal nerve entrapment. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 25(6): 648-650.
- Thomas DN, Moriggl B, Barchman J, Jensen JM, Soballe K, et al. (2019) Randomized trial of ultrasound-guided superior cluneal nerve block. Reg Anesth Pain Med.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...