Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-4676
Research Article(ISSN: 2637-4676) 
Construction Of Elderberry Jam from the Bush And Berry Volume 10 - Issue 1
Ana Maria Castilla Sanchez1, Anggie Lisseth Salgado Sanchez1, Franklin Guillermo Montenegro Marín1 and Carlos Enrique Montenegro Marín2*
- 1Engineering Faculty, Universidad de Cundinamarca, Soacha, Colombia
- 2Engineering Faculty, Universidad Distrital Francisco José de Caldas, Fundación Universitaria International de la Rioja, Bogotá, Colombia
Received: March 01, 2022; Published: March 11, 2022
Corresponding author: Clara R Azzam, Cell Research Department, Field Crops Research Institute, Agricultural Research Center, Giza 12619, Egypt
DOI: 10.32474/CIACR.2022.10.000327
Abstract
The elder is a tree native to Europe that measures up to 6 meters, its flowers are white, and its fruits are purple. The fruits of this tree are produced throughout the year in cities such as Bogota, Colombia, and nowadays, the felling of this tree is increasing every day, and it is used as an ornamental tree and food for livestock. To use the residues in the treatment of this tree, this research seeks to design and manufacture an artisanal jam from elderberries. The main objective is to offer a healthy and wholesome food product that will help to promote the benefits of the tree and to increase its planting. The method used was divided into phases: gathering information about the shrub, elaboration of parameters for berry selection, process construction, pilot test for jam production, production adjustments, packaging selection and selection of additional components.
Keywords: Elderberry; logging; mitigate; pollution
Introduction
In Colombia, in the city of Bogotá and the municipalities of the Savannah there has been a constant logging of the elderberry bush, its most recognized use is ornamental because it mitigates air pollution generated by companies and communities[1], “the elderberry is planted in fences, boundaries, windbreaks and for protection against frost” (Rojas et al., [2]), subsequently it has medicinal uses for utopian treatments and the flower can be used for infusions to improve the respiratory system or act as an anti-flu, the fruit is used as food for cattle as a last resort to avoid wasting the berries. Currently in Colombia this shrub is distributed over a wide area of the Savannah due to its climatic conditions proliferate in harvest times of the berry (linden). This allows them to be catalogued as waste, since they do not have a constant purpose and are discarded. By means of the information obtained, an extensive research is carried out with the purpose of complementing the previously mentioned knowledge, allowing to analyze the taxonomy and to understand its wide properties established in different research worldwide, in which it is evidenced that: “The ripe fruits are rich in vitamins and minerals” (Pahlow, 1985), therefore, they are suitable for human consumption. Based on the above, the most appropriate way to transform the berry into a product that contributes to the reduction of this problem is being sought, thus allowing the use of linden as a raw material in the production of a natural and healthy product that can be marketed [3].
Methodology
Phase 1. Collecting information on the elderberry bush
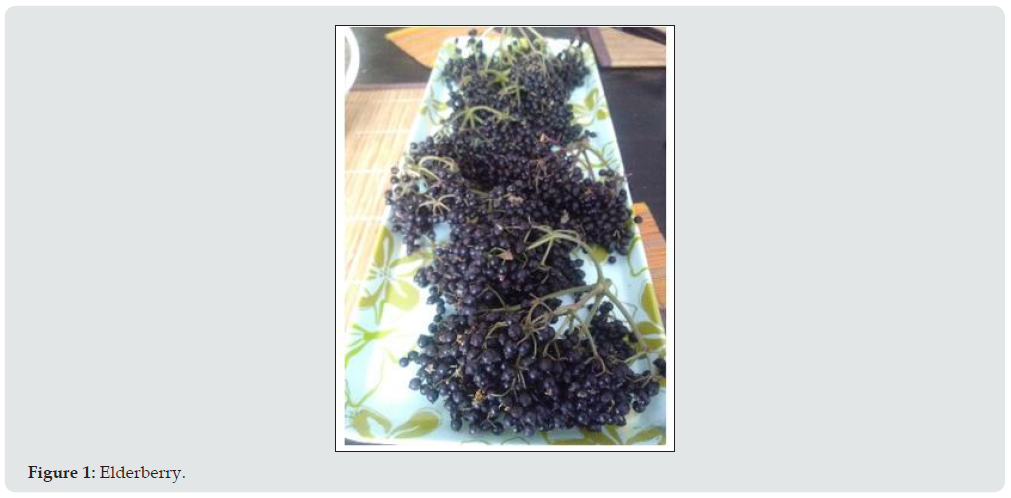
Initially, an investigation was carried out on the elderberry bush about its characteristics, benefits, conditions for its harvesting and handling. Recognizing that the berry must have a dark purple color with no green spots to be suitable for processing, then the berry In this way the linden is ready to start the production process.
Phase 2. Elaboration of the matrix for selecting additional components.
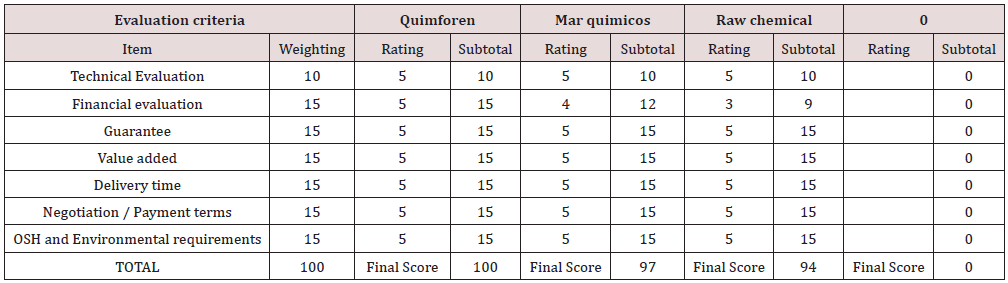
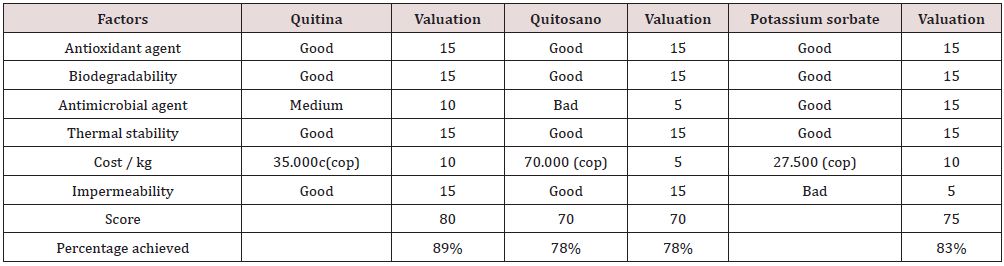
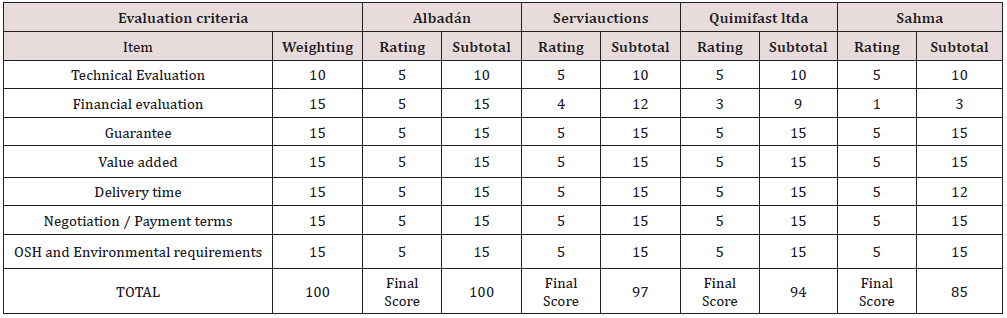
Based on the above information, different suppliers of pectin, sugar, elderberry, vinegar, citric acid, packaging, and labels were found, which were useful for the matrix of selection, where variables such as: costs, observations, guarantees, added values, etc. were evaluated. These were evaluated by means of a measurement score of 5 to 15, with 15 being good, 10, average and 5, bad. At the end, the components with the highest scores were selected [4].
Phase 3. Design and manufacture of elderberry jam prototype.
Only one type of jam was designed, each with a single component, the difference being the percentage of added sweetener: the manufacturing processes of the jams was also determined.
Elderberry jam making process
a) Note: The above procedure corresponds to the first jam test, of which there were more repetitions with different percentages of raw material, sweetener and pectin, in the first case 2 containers were obtained, the same happens in the second test and in the last test two containers of 230g and one of 110g were obtained [5].
Phase 4. Execution of pilot tests with the supplies
After performing several tests to find the most suitable amount of ingredients for the product, it is necessary to divide it in two: First, the adequate percentage of sugar is determined so that the jam obtains a low sweetness and is adequate for the product to be approved by the final consumer, therefore, tests were carried out with quantities of 100%, 75% and 50% sugar. Afterwards, pectin percentage tests are carried out for the right consistency and to make it easy for the consumer to handle, so tests were carried out with 100% sugar with 1% pectin; 75% sugar with 3% pectin; 50% sugar with 5% pectin [6] (Tables 1-3).
Results
Phase 1: Production of elderberry jam
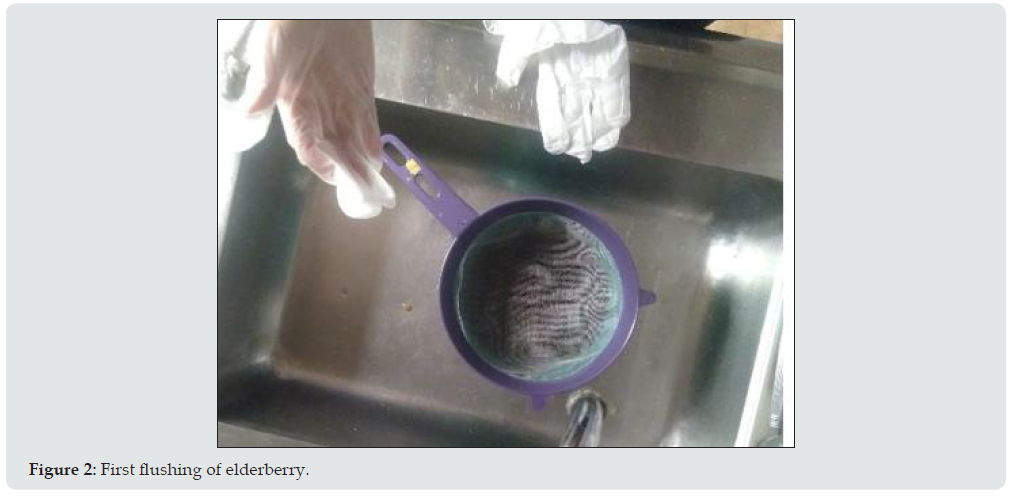
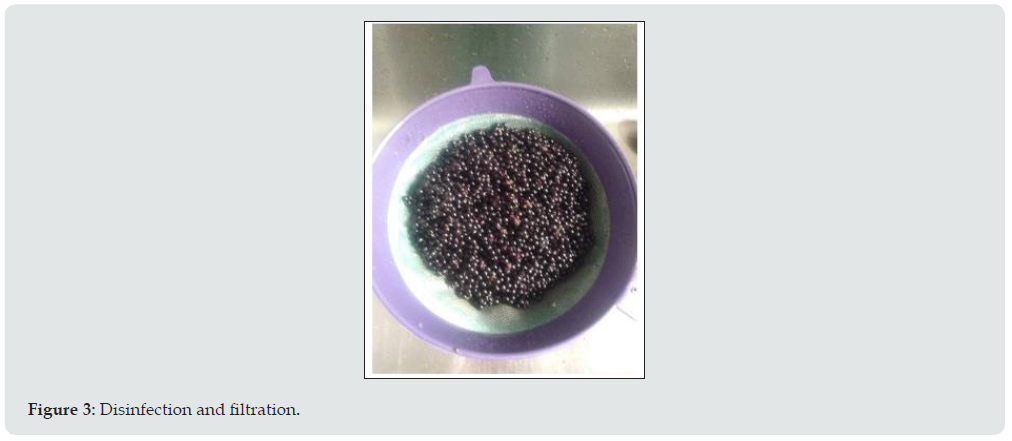
Initially, it is determined that the berry must be harvested at a suitable point of maturation, since it is then ready to be suitable for the transformation process; additionally, the need for rigorous washing and disinfection is determined. As it is an ornamental, a filter is implemented to remove excess water, since this affects the innocuousness and the percentages of the ingredients [7].
Phase 2: Elaboration of the matrix for the selection of additional components
Based on the list of suppliers that we find in the current market, we conclude to choose in accordance with the cost/benefit, that is meaning, that allows to obtain a product in good conditions with average costs assuring the quality and its purity percentages so that the jam is the optimal product when arriving to the final consumer (Tables 1-3). From the previous selection matrixes, it was found that the pectin and sugar providers that obtained the best scores were: Quimiforen for the pectin supplier and Albadan for the sugar supplier with a 100% score, respectively. The products of these brands will be used for the jam production process.
Phase 3: Design and manufacture of prototype trays
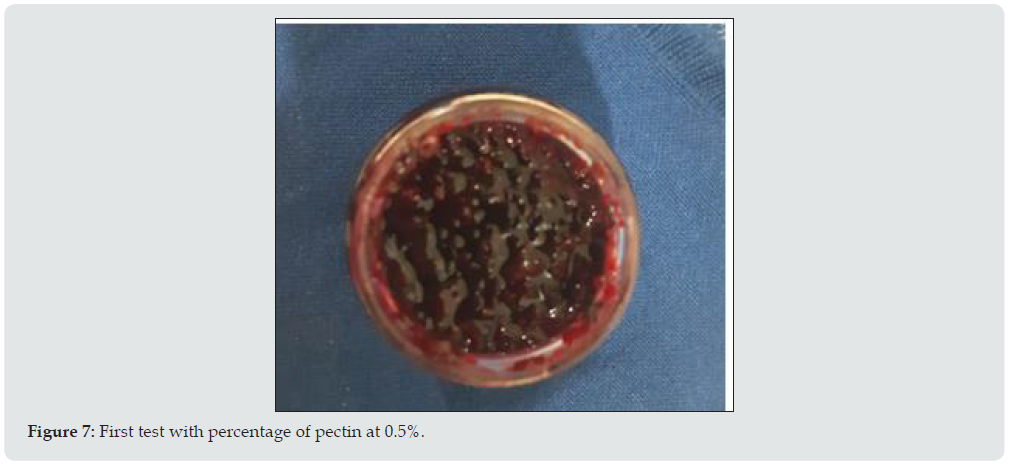
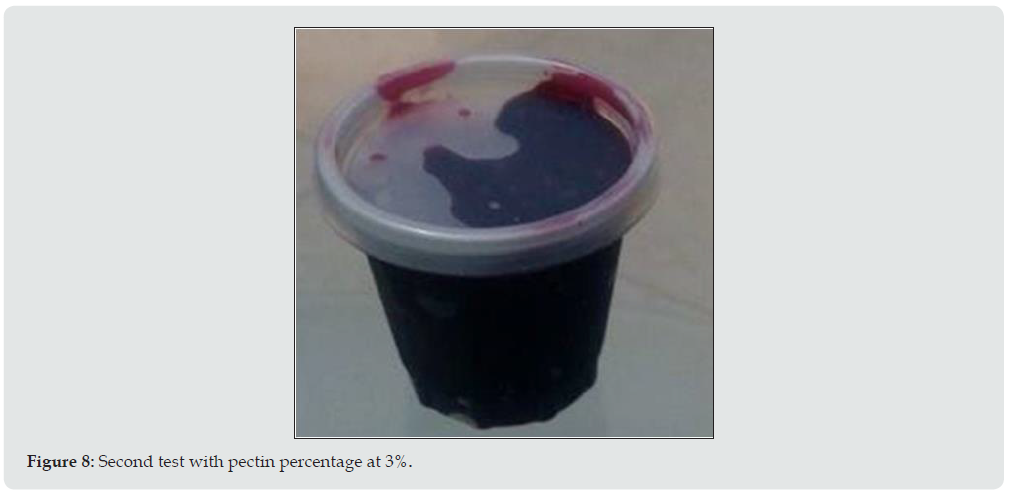
The jam prototypes with their respective percentages of inputs are shown below (Figure 7). As can be seen in (Figure 8), according to the percentage of the components, the texture of the jam is liquid due to its low percentage of pectin (Figure 8). As can be seen in Figure 9, according to the percentage of pectin components at 3%, a semi-liquid texture of the jam is obtained because the percentage of pectin must be adjusted. As can be seen in Figure 9, according to the percentage of pectin components at 5%, a thick texture of the jam is obtained because the percentage of pectin is adequate, allowing the consumer to have an easy handling due to its consistency [8,9].
Phase 4: Execution of mechanical tests
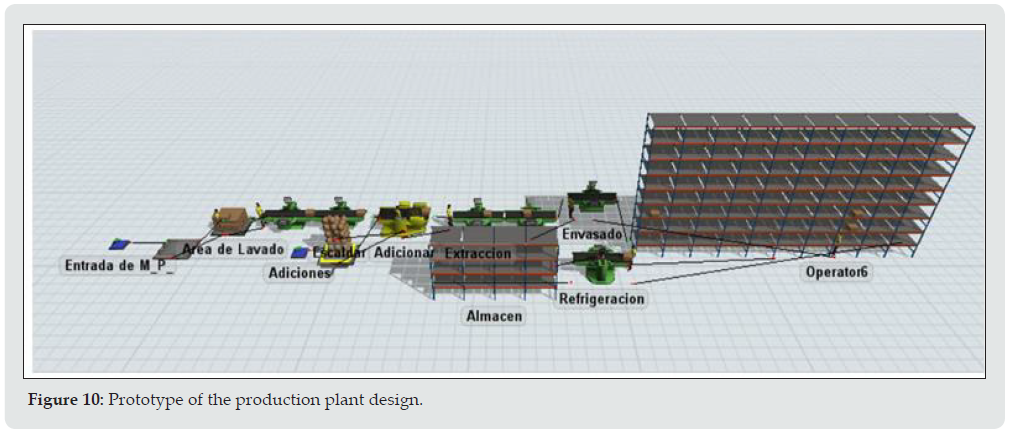
The sugar percentage changes according to the proportion of raw material (elderberry), as the higher the percentage of sugar the natural flavor of this berry is lost, for this reason, 3 subsequent experiments were conducted where the best option is to have this input at 50% as it allows the natural flavor to be preserved. Pectin influences the desired texture of the product, as this is a handmade product, the intention is that consumers can have the best experience with the jam, therefore [10], we use 5% of pectin so it is in a medium term and is not too liquid or too dense, at the time of handling (Figure 10).
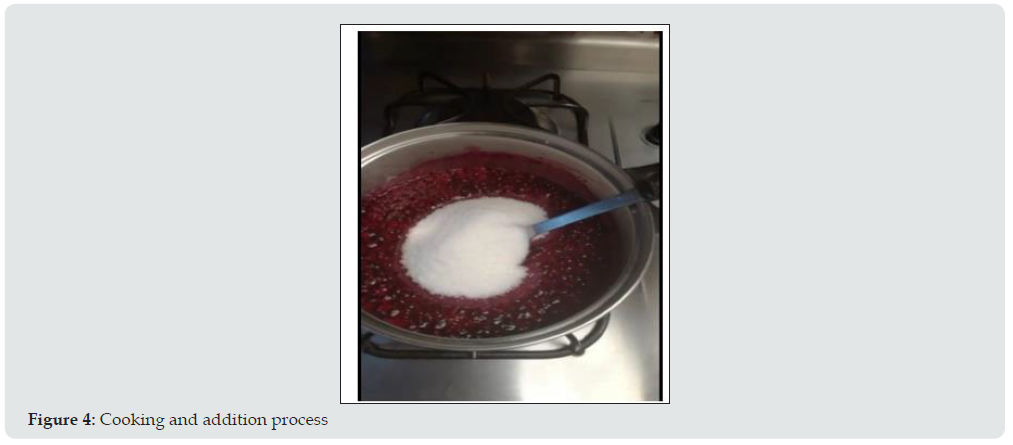
The processes were identified, as shown in Figure 10, which are as follows:
1. Receipt of raw materials
2. Washing
3. Disinfection
4. Cooking
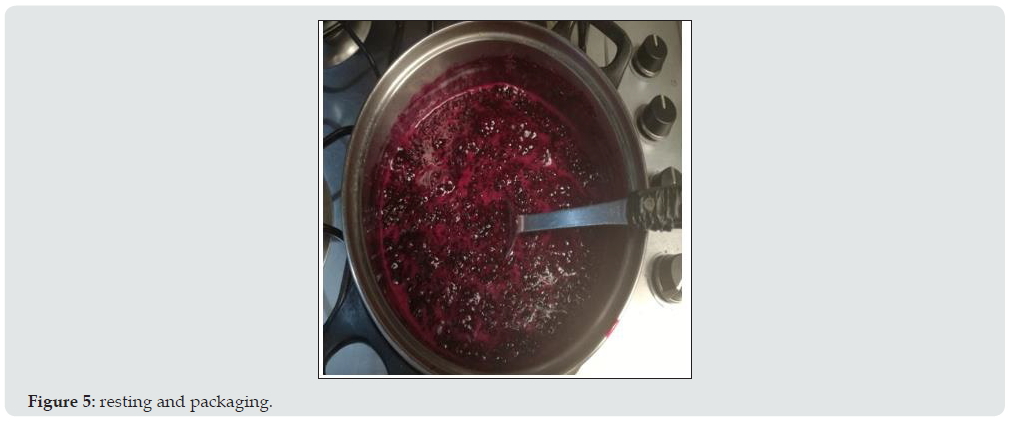
5. Packaging
6. Rest
7. Refrigeration
8. Warehouse
Conclusion
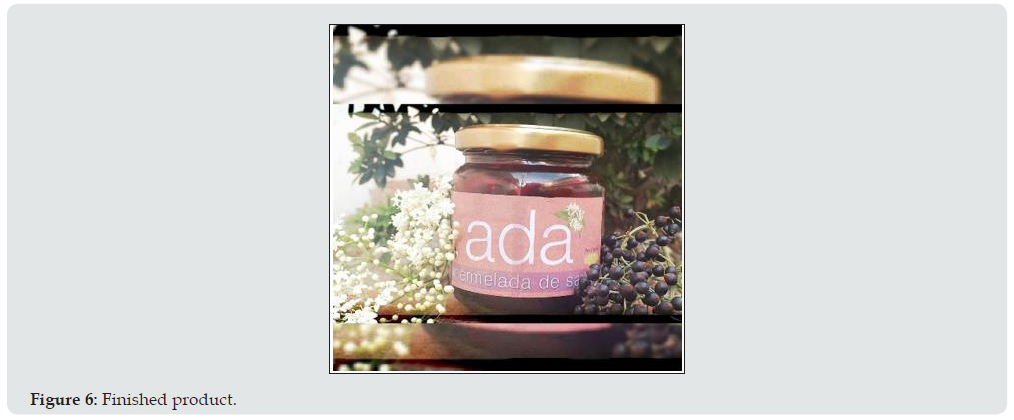
For the agro-industrial sector, it is possible to develop a market strategy with the objective of creating alliances, which will use the product as complementary additives, i.e., a stuffed cheese, a sauce, a yogurt and even in cookies. This allows to have a wider market reach and not to limit oneself. This product has a significant advantage corresponding to the use of elderberry that currently is intended to be discarded. This is important because it allowed us to look for alternative uses, creating an enterprise that contributes positively to the environmental impact and allows us to deliver a product to the population with low levels of sugar and high benefits because it has vitamins that help the immune system. The production of elderberry jam has had a good economic impact, since the raw material is easy to acquire because it is classified as waste, generating a unit cost of $8700 with a profitability of 30%. On the other hand, it has good commercial acceptance because its flavor is unique, it has a recyclable packaging, and its price suits the population’ s pocket.
Regarding the process of elaboration and production of the jam, we conclude:
a) Elderberry has unique properties in the manufacture of jam, however, it is necessary to add other components which allow us to obtain the desired texture and sweetness.
b) The addition of pectin provides the texture in the jam.
c) The lower the proportion of sweetener in the jam, the better the characteristic flavor is appreciated.
Recomendations
a. Use the elderberry when it is ripe, otherwise it is not suitable for human consumption.
b. It is recommended to eliminate the excess of water in the berry washing and disinfection process.
c. Use 100% natural pectin so that the process does not present setbacks when taking consistency.
d. Use an adequate amount of all inputs to avoid any rejection of the products by the public.
e. It is recommended to let the product rest before refrigerating as this may damage the product.
f. Labels should be placed in a visible manner, and its security seal.
References
- Bustamante GR (2019) Análisis de la cadena productiva de mermelada de sauco para la exportación a la ciudad de Miami, en el año 2019 (Tesis de licenciatura). Repositorio de la Universidad Privada del Norte. Recuperado de
- Salazar A, Oblitas J, Rojas E (2016) Reutilización del lactosuero ácido y dulce de las queserías de Cajamarca en la elaboración de una bebida con sabor a poro poro (Passiflora Mollisima) y sauco (Sambucus Peruviana). Agroindustrial Science 6(1): 45-51.
- Flores, Edilberto (2017) Extracción de Antioxidantes de las Bayas del Sauco (Sambucus nigra L. subsp. peruviana) con Ultrasonido, Microondas, Enzimas y Maceración para la obtención de Zumos Funcionales. Información tecnológica 28(1): 121-132.
- Ibarguen JO, Moreno Yd (2018) Implementación de una empresa productora de té a base de hierbas naturales y medicinales (sauco), en la comuna uno (1) de la ciudad de Quibdó – Chocó (FLAVORS. S.A.S). [Proyecto Aplicado o Tesis, Universidad Nacional Abierta y a Distancia UNAD]. Repositorio Institucional UNAD.
- Palomino C, Soria D (Elaboración de licor de sauco (sambucus nigra l.) en barricas de madera de castaño en el laboratorio de agroindustrias utea – abancay). (Universidad Tecnológica de los Andes)
- HSB (2018) Diabetes en Colombia en un 9% de la población adulta - HUSI en los medios - HUSI. Hospital universitario san Ignacio. Diabetes en Colombia en un 9% de la población adulta - HUSI en los medios - HUSI
- Gestarsalud (2021) Consumo de azúcar en Colombia: la radiografía de un problema de salud pública inminente. Gestarsalud. Consumo de azúcar en Colombia: la radiografía de un problema de salud pública inminente | Gestarsalud
- (Galvez. S (2019) Esencia de sauco para su uso en la repostería [Tesis profesional]
- https://www.larepublica.co/consumo/seis-de-cada-10-colombianos-no-saben-alimentarse-bien-2971569
- Clapé Laffita, Oneyda, Alfonso Castillo, Alfredo (2011) Caracterización fármaco-toxicológica de la planta medicinal Sambucus nigra subsp. canadensis (L). R Bolli Revista Cubana de Farmacia 45(4): 586-596.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...