Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2643-6760
Case Report(ISSN: 2643-6760) 
Testicular Fibro- Sarcoma in Pediatric Patient Volume 4 - Issue 2
Amani Saleh Hadi Saeed*
- Specialist of clinical oncology and nuclear medicine, Department of oncology, National oncolgy center-Aden, Yemen
Received: January 12, 2020; Published: January 24, 2020
Corresponding author: Amani Saleh Hadi Saeed, Department of oncology, National oncolgy center-Aden, Head of womencare unit for breast cancer, yemen
DOI: 10.32474/SCSOAJ.2020.04.000184
Abstract
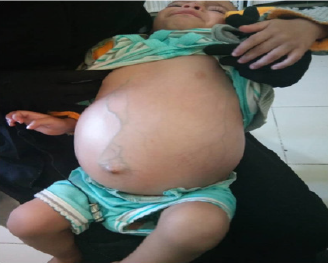
Sarcoma of the testis are extremely rare tumors, their incidence being difficult to assess accurately. a case of two-year-old male,
presented with painless scrotal swelling that increase in size insidiously within three months, send to urology, the examination
revealed left testicular swelling –hard, not tender and oval shape. scrotal US, show large mildly hyperechoic mass fat echogenicity
seen in the left inguinal canal and scrotum measuring about 84x41x44mm diameters. CT chest and abdomen were normal. Radical
orchidectomy was done through an inguinal approach, histopathology showed morphology constant with fibrosarcoma of gonadal
stromal origin. After 10 months, noticed reappearance of swelling in the left hemiscrotum.
CT scan abdomen and pelvic showed moderate to gross ascites with cystic lesion in the pelvis on the left side, these findings
are highly suggestion a of malignant ascites with possibility of metastatic cystic lesion. excision was done, Histopathology revealed
spindle cell sarcoma morphology favor fibrosarcoma of gonadal stromal origin. chemotherapy start for this case with ifosfamide+
doxorubcin protocol one cycle, his condition progress with hug ascites patient died. In conclusion, the recurrence rate of testicular
sarcoma is high following radical orchidectomy, prognosis is very poor.
Keywords: Testicular tumor, testicular fibrosarcoma, spindle cells, recurrent testicular sarcoma, prognosis
Introduction
Testicular cancer represents about 1.5% of male neoplasms and 5% genitourinary tumor. Most testicular tumor are diagnosed in 20th and 30th years of life. the histological type varies, although there is clear predominance (90-95%) of germ cell tumor. [1] infantile fibrosarcoma is rare in early childhood malignancy .it includes proximality 10% of all sarcoma in children [2]. Very little epidemiological data regarding soft tissue sarcoma and bone sarcomas from Yemen in general and Aden region in particular are available, one cross sectional study was carried out at Nation Oncology Center, Aden Yemen from 2009-2013 out of 107 new diagnosed patient 54 belonged to bone sarcoma and 53 to soft tissue sarcoma, the most common site of origin was lower extremities 55.1%. retroperitoneal 11.2%, trunk 10.3% and upper extremities 9.3% [3]. Furthermore, the rarity of primary fibrosarcoma in the further justifies the following report.
Case Report
a case of two-year-old male, presented with painless scrotal swelling that increase in size insidiously within three months, send to urology, the examination revealed left testicular swelling - hard, not tender and oval shape. Scrotal US show large mildly hyperechoic mass fat echogenicity seen in the left inguinal canal and scrotum measuring about 84x41x44mm diameters. CT chest and abdomen were normal. Radical orchidectomy was done through an inguinal approach ,12/1/2018 histopathology showed morphology constant with fibrosarcoma of gonadal stromal origin. Panel of immunostains is needed: vimentin, pankeratin, EMA, inhibin, CD99, S100, SMA. Desmin. but family patient neglected to do it. after 10 months, noticed reappearance of swelling in the left hemiscrotum.
Excision was done
11/11/2018 Histopathology revealed spindle cell sarcoma morphology favor fibrosarcoma of gonadal stromal origin Immunotoxins were done: the tumor cells are positive for CD 99 and negative for pankarrtin, vimentin, SAMA, S100, CD34 and BCL2.
Ct scan chest
12/11/2018:no significant pleuropulmonary or mediastinal abnormality CT scan abdomen and pelvic 12/11/2018: showed moderate to gross ascites with cystic lesion in the pelvis on the left side, these findings are highly suggestion a of malignant ascites with possibility of metastatic cystic lesion (Figure 1). Chemotherapy start for the case with Ifosfamide +doxorubicin protocol one cycle, his condition progressive with hug ascites patient died.
Discussion
Sarcoma of testis are extremely rare, when you review the
literature of published series of sarcoma they were distributed
as fellows: leiomyosarcoma 32%. Rhabdomyosarcoma RMS,24%
and liposarcoma 20% are the comments subtypes [4,5]. Gowing
and Morgan studied all mesenchymal tumors arising in testicular
tissues, and their relative rarity is apparent; the study consists of
22 sarcomas enrolled in a survey of around 1000 patients with
testicular neoplasm. The majority of the sarcomas in this study were
mesenchymal, that is fibrosarcoma, liposarcoma, myosarcoma,
rhabdomyosarcoma and leiomyosarcoma, or combinations [6]. The
sarcoma may present with a unilateral, painless scrotal swelling
with short duration as seen in this case report
The commonest way of metastasis is via lymphatic to internal
iliac and para -aortic lymph nodes. Distance metastasis to liver, lungs
and bone by hematogenous spread accounts for 20% of patients
in initial presentation [7]. Management of testicular fibrosarcoma
has shifted to multispecialty approach that improves the survival
chances up to80% by incorporating chemotherapeutic medication,
radiotherapy or surgical intervention [7,8]
In this case reported the radiological staging was N0M0, so
preferred fellow up after radical orchidectomy. inguinal approach
orchidectomy with ligation of spermatic cord at the internal ring
is the standard surgical intervention as seen in the case. The site of
tumor origin (, testicular-Para testicular), lymph node involvement,
distant metastasis, presence or absence of residual disease after
surgical resection will help in staging of testicular and the plan of
management of fibrosarcoma of testis. Gilbert, quoted by O’Brien
(1942), accepted seven cases of primary fibrosarcoma out of 91
malignant epididymal neoplasms in the literature. However, we do
not know the cases which he accepted or the criteria upon which he
judged them [9].
Catton et al. [10] mention 14% local recurrence in patients
who underwent wide local excision and /or radiotherapy after
original excision of testicular or paratesticular sarcomas. They
also suggested that orchidectomy alone is inadequate for testicular
sarcomas and recommended adjuvant wide hemiscrotum excision,
which may include inguinal lymph nodes for those managed
with orchidectomy or local excision. they found that there was
microscopic disease present in 27%, following wide excision in
patients with apparently completely excised tumors. In current
case, after 10 months there was noticed reappearance of swelling
in the left hemiscrotum, which made us to think of local recurrence,
and therefore the decision of re-exploration was made with wide
local excision of the swelling and the hemiscrotum. Histopathology
revealed spindle cell sarcoma morphology favor fibrosarcoma
of gonadal stromal origin Immunostains were done: the tumor
cells are positive for CD 99 and negative for pankarrtin, vimentin,
SAMA, S100, CD34 and BCL2. CT scan abdomen and pelvic showed
moderate to gross ascites with cystic lesion in the pelvis on the left
side, these findings are highly suggestion a of malignant ascites
with possibility of metastatic cystic chemotherapy start for the
case with Ifosfamide +doxorubcin protocol one cycle, his condition
progressive with hug ascites patient died.
The role of retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) in
testicular sarcomas remain controversial [11-13]. Catton et al [11].
Recommended RPLND in their earlies series of 21 patients, but in
their subsequent reported they noted that the patients with high
risk of nodal metastasis are also that at high risk of concurrent
or subsequent systemic disease; accordingly, they felt that those
patients would benefit from systemic rather than regional
treatment [10]. Other suggest that RPLND should be limited to
patients with suspicion of LN metastasis in the image [14]. Adjuvant
chemotherapy in testicular sarcomas is not fully established. in
pediatrics, with testicular sarcomas -especially rhabdomyosarcoma
(RMS)- adjuvant chemotherapy had good outcome on the overall
survival [15,16]. It uses in adult testicular sarcomas has not been
yet specially addressed in controlled study [17]. The use of post
-intervention chemotherapy for adult -grad testicular fibrosarcoma
is controversial meta-analysis of randomize trials of testicular
sarcomas at different centers showed that doxorubicin-based
adjuvant chemotherapy significantly improved the time to local and
distant failure [18].
Conclusion
Testicular fibrosarcoma is extremely rare testicular tumor, usually indolent course with potential for distant metastases. The diagnosis of pure fibrosarcoma should be made only after extensive sampling of the testicular tumor to rule out an associated germ cell component. the differential diagnosis also includes the fibroma of gonadal stroma origin and the unclassified sex cord -stromal tumor with predominance of spindle cells
References
- Albers P, Albrecht W, Algaba F, Bokemeyer C, Cohn-Cedermark G, et al. (2014) Guidelines on testicular cancer. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Testicular cancer.
- Schneider DT, Calaminus G, K0ch S, Teske C, Schmidt P, et al. (2004) Epidemiological analysis of 1442 children and adolescent registered in the German germ cell tumor protocols. Pediatric Blood cancer 42(2): 169-75.
- Gamal Abdul Hamid (2015) world Journal of pharmaceutical research. 4(10); 2786-2794.
- Soosy GN, Parkinson MC, Paradinas J (1996) Paratistucular sarcomas revisited review of cases in the British Testicular Tumor Panel and Registry. British Journal of urology 77(1): 143-146.
- Fagunds MA, Zietman AL, Althausen AF, Coen JJ, Shipley WU, et al. (1996) The management of spermatic cord sarcoma. Cancer 77(9): 1873-1876.
- Dowling KJ, Lieb HE (1985) fibrosarcoma of epididymis. Urology 26(3): 307-308.
- Resim, S, OKur N, Barkar SS, Ali Osman Kilic, Bulent Altunoluk, et al. (2009) paratesicular embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma: Report of a case. Iranian Journal of pediatric19(4): 430-434.
- Kumar R, Bharti S, Khosla D, Rakesh Kapoor (2012) Long-term survival in Para testicular rhabdomyosarcoma. Clinical cancer investigation Journal 1(1): 31-32.
- O'Brien MG (1942) Primary sarcoma of the epididymis: case report J Urol 47: 311-319.
- Catton CN, Jeweet M, O "Sullivan, l, Kandel R (1999) paratesticular sarcoma: Failure pattern after definitive local therapy journal of urology 161(6): 1844-18747.
- Catton CN, Cumming V, Fornasier B, O’SullivanI, QuirtD.Warr (1991) Adult paratesticular sarcomas: A review of 21 cases Journal of Urology 146(2): 342-345.
- Merimsky O, Terrier P, Bonvalot S, Cecile Le Pechoux, JeanPierre Delord, et al. (1999) Spermatic cord sarcoma in adults. Acta Oncologica 38(5): 635-638.
- Hermans BP, Foster RS, Bihrle R, Foster, Richardbihrle et al. (1998) Is retroperitoneal lymph node dissection necessary for adult paratesticular rhabdomyosarcoma? Journal of urology 160(6): 2074-2077.
- Goldfarb B, Khoury AE, Greenberg M, Bernard M ChurchillCharles, Smithet R, et.al. (1994) The role of retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy in localized paratesicular rhabdomyosarcoma. Journal of Urology 152(2): 785-787.
- Raney RB, Tefft M, Lawrence W, et al. (1987) paratesticular sarcoma in childhood and adolescence: A report from the intergroup rhabdomyosarcoma studies I and II ,1973-83. Cancer 60: 2337-2343.
- De Vries JD (1997) Paratesticular rhabdomyosarcoma. world Journal of Urology 13: 219-225.
- Anonymous (1997) Adjuvant chemotherapy for localized resectable soft-tissue sarcoma of adults: Meta-analysis of individual data. Sarcoma Meta-analysis collaboration. Lancet 350(9092): 1647-1654.
- Khoubehi B, Mishar V, Ali M, Motiwala H, Karim O (2002) Adult paratesticular tumors. BJU international 90(7): 707-715.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...