Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2643-6760
Review Article(ISSN: 2643-6760) 
Disaster and Mass Casualty Management in Hospitals of Greece Volume 5 - Issue 4
Evangelia Michail Michailidou1,2,3,4*
- 1Intensive Medicine Department, Hippokration General Hospital, Greece
- 2Senior Student in the Department of Business Administration, University of Macedonia, Greece
- 3Masters Degree, International Medicine-Health Crisis Management, Greece
- 4Member of Health Response team to Crisis Situations of GHTHippokration, Greece
Received: August 25, 2020; Published: September 01, 2020
Corresponding author: Evangelia Michail Michailidou, Consultant, Anesthesiologist Intensivist, General Hospital Hippokratio of Thessaloniki, Konstantinoupoleos, Thessaloniki, Greece
DOI: 10.32474/SCSOAJ.2020.05.000220
Abstract
Preparing a hospital for a disaster is infinitely greater complex. Hospitals in most expansive populace centers are working at or close to full capacity. In numerous cities, healing centers and injury centers have issues, managing with a multiple-car thruway crash, much less the volume of patients likely to result from a large-scale accident. Amid crises, clinics can do a number of things to free up capacity and expand their assets. Studies demonstrate that the numbers of accessible beds, ventilators, confinement rooms, and pharmaceuticals may be efficient to care for casualties of a large-scale catastrophe. On the other hand, there are genuine physical impediments on this extension of their capabilities. The purpose of this research turned into to evaluate the information, hazard perception and mindset of the authorities, professionals, and employees at Greek hospitals to respond to terrorist attacks. A survey composed of 20 questions was being replied by 197 Healthcare Professionals and employees, using Google forms or tool in hard copy. However, numerous of the clinics do have at slightest a few of the basic components of readiness. Numerous of the healing centers do have archived and utilitarian readiness plans, give particular readiness education/training, and have fitting pharmaceutical strategies and supplies required within the occasion of an assault, including chemical or organic psychological militant operators. Tragically, agreeing to the answers of the participants most of healing centers might not increment their surge capacity or have symptomatic research facility administrations competent of analyzing, recognizing and confront biologic, chemical, nuclear, or explosive events.
Review Article
Disaster reaction entails many different network assetsfrom police and fireplace to clinical carriers, structural and environmental engineers, and transportation and hospitalizing specialists. The clinic performs a small but important role in this larger scene [1]. It is far the epicenter of medical care delivered to folks that are injured. Preparing a clinic for a disaster is infinitely greater complex. Planning for disasters includes a number of tough questions: For what varieties of disaster events have hospitals to prepare? Ought to every medical institution put together for disasters, or need to scientific reaction be rationalized? While reusing the extent of the catastrophe, who makes that decision, and how does a big, complex organization shift from habitual to disaster mode? How does a hospital defend itself and its personnel from biologic, chemical, nuclear, or explosive events caused of a terrorist attack, whilst patients are contaminated? Health facility employees, whilst as it should be organized and educated, are crucial for a powerful response to each natural and guy-made disasters, which include terrorist occasions. Consequently, it’s miles critical to assess the attitudes of employees in respect of risk discount and readiness for disaster control of terrorist assaults, as well as their willingness to go through normal training regarding safety approaches and reaction activities in the course of such occasions. The purpose of this research turned into to evaluate the information, hazard perception and mindset of the authorities, professionals and employees at Greek hospitals to respond to terrorist attacks. A survey composed of 20 questions was being replied by 227 Healthcare Professionals and employees, using Google forms or tool in hard copy [2].
Informatively we estate that in the future, new publications will follow with data and answers to the questionnaire from Europe and Saudi Arabia, as well as comparisons between countries. Disaster and mass casualties are a human and health tragedy, causes, consequences in big financial losses, causes devastating blows to improvement desires, and shakes social confidence. Medical institution catastrophe preparedness presents complicated scientific operation. It’s miles difficult philosophical mission. It is hard to decide how a whole lot of time, cash, and attempt should be spent in pre-paring for an event that might not occur. Health centers, whether hospitals have to be a source of electricity all through emergencies and screw ups. They need to be geared up to keep living and to keep providing vital emergencies and screw ups. This article investigates the hospital Disaster and mass casualty preparedness in Greece. The health facility represents an essential asset inside the occasion of a disaster, but it is also an inclined one. Hospitals could be damaged in the mass casualty event itself, as befell within the instances of earthquakes and terrorist attacks on abroad [3]. Obviously, each health center ought to delivery patients to alternative facilities in such situations. In addition, whilst a clinic shuts down, its personnel, automobiles, system, and supplies have to additionally be beneficial in emergencies and difficult conditions. Nearby disaster making plans ought to include plans to distribute this property as wanted through the network. Hospitals can be focused through terrorism at once or indirectly, and there has been little education for or maybe discussion of that opportunity. Hospitals need to plan for direct alternative procedures and establish plans for proscribing get right of entry to, securing perimeters, protecting water and electricity supplies, and sheltering personnel. A particular vulnerability, because of the statistics intensity of the clinic surroundings, is the medical institution’s publicity to cyber-attack. Such a procedure should have a profound impact on clinical operations, communications, telemetry, facts, and many different important functions. Hospitals are also at risk of an influx of catastrophe consequences [4]. Large numbers of victims descending on a hospital can be overwhelming and diminish its effectiveness in managing casualties. The endless larger part of the vast majority of terrorist events worldwide has included customary explosives and biohazards. Government investing on readiness has burdened intensely at the altar of the cost of other needs. Trauma frameworks to speak to a basic component of disaster reaction. Government bolsters for the advancement of these systems and their coordination with the other territorial disaster arranging endeavors does not show up to reflect acknowledgment of this truth [5].
Malpractice issues
It is lamentable, but true, that the primary reaction among some doctors these days who stand up to an emergent health crisis big’s scale in an open space is to dodge association. In terrorist attack coming about in mass casualties, there likely will be a deficiency of health professors. The above ascertainment makes the interest of Clinic Planning, Doctors, and Medical caretakers for a rapid response emergency team of volunteer specialists indeed more critical and imperative. Except of the organizing of the rapid response emergency team there should be training and simulation scenarios at regular periods. Patients suspected of exposure to chemicals or biohazards can completely close down a facility if they are not decontaminated properly earlier than getting into (the same applies to vehicles as well). Every clinic ought to have adequate decontamination showers and techniques for dealing with infected sufferers because experience has taught that many sufferers “self-evacuate” from the scene of a catastrophe, bypassing on the procedure of triage and decontamination. In extreme instances, the health center needs to be prepared to lock all the way down to save the access of infected sufferers who could otherwise disable the open manner wherein hospitals usually function [6].
Hospital training and drills
The unique components of disaster reaction require specialized education, each within the clinical control of catastrophe victims and in institutional strategies that can be pretty one-of-a-kind from those underneath normal operating conditions. There are sturdy elements that education is insufficient. Severe scientific and operational deficiencies, fragmentation, and absence of standardization exist throughout a huge spectrum of key professional personnel (nurses, physicians, paramedics, administrators etc.) in both character education and coordination of a team reaction. A concerted attempt to integrate catastrophe preparedness and education into mounted expert curricula, continuing schooling, and certification programs is the most affordable strategy to those shortcomings at this factor in time. therefore, to cope with the want for competency in catastrophe medicine throughout disciplines, the committee recommends that all institutions responsible for the education, continuing education, and credentialing and certification of specialists concerned in emergency care (together with remedy, nursing, emergency clinical services and medical institution management) comprise catastrophe preparedness schooling into their curricula and competency standards [7].
Some of the replies of participants by percentages
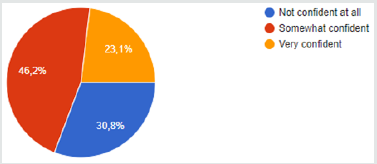
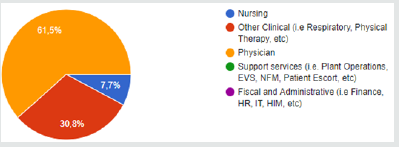
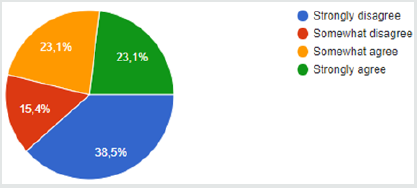
My level of confidence that my hospital will provide me with protective gear and take precautions to protect my safety during the encounter of terrorism attack (if the situation requires it) (Figure 1). What is your position in the hospital? (Figure 2). As a member of my department, i know what to do in the event of the encounter of terrorist attack (Figure 3).
Conclusion
Genuinely, primary efforts had been made to improve the
preparedness of hospitals in Greece, however, there are still terrific
gaps between those efforts and the preparedness status of hospitals
as evident from the findings. Consequently, health care executives
and policymakers should utilize the findings in this take a look
at to create a broader discussion board at the nearby, nation and
federal degrees for discussions about the important preparedness
problems going through hospitals; Interact in efforts to behavior
a full and thorough evaluation of terrorist threats to decide while
and in which the following attack will occur? What kind of weapon
could be used? How will the injuries/ailments and fatalities be
minimized? And what is the relative price of both preparing and
recovery? Further, health care officials need to be advocated to get
entry to and utilize the public investment for in preparedness to
boom surge capacity and acquire wished resources and gadget for
preparedness. The discoveries in this inquire about uncovering
that healing center by and large are not “truly” arranged to oversee
casualties of a fear based oppress or attack. However, numerous
of the clinics do have at slightest a few of the basic components of
readiness. Numerous of the healing centers do have archived and
utilitarian readiness plans, give particular readiness education/
training, and have fitting pharmaceutical strategies and supplies
required within the occasion of an assault, including biologic,
chemical, nuclear, or explosive events caused of a terrorist attack.
Tragically, agreeing to the answers of the participants most
of healing centers might not increment their surge capacity or
have symptomatic research facility administrations competent of
analyzing and recognizing biologic, chemical, nuclear, or explosive
events In addition, medical institution officers have to augment
their protection forces on the way to provide crowd manipulate
and facility command; Build federal alliances of public and
private authorities so that it will get entry to backup facilities;
enlarge preparedness schooling and exercise to include all stages
(physicians and indirect care carriers); and upgrade their diagnostic
laboratory capability to research and identify chemical or organic
factors. Ultimately, health facility officials and policymakers ought
to look at the modern effectiveness and appropriateness of public
policy associated with the preparedness against a possible terrorist
attack. Until now we did not have any case of a terrorist attack in
Greece, but we have to be ready for any possible scenario. Even
when we have backup processes in place to manage risk events, it
is very likely that they will not be able to serve our needs. We have
to understand that risk management in disaster and mass casualty
is efficient where comprehensive and timely input is given to health
professionals about all potential threats detected or shortcomings
in current control measures and all these in relaxed and daily
periods not inside the crisis.
References
- World Bank (2005) Hazards of Nature, Risks to Development.
- WHO (2004) World Health Report?
- CDC (2011) Post-Earthquake Injuries Treated at a Field Hospital-Haiti, 2010. MMWR 59: 1673-1677.
- Disaster Management Guidelines WHO.
- WHO (2007) Mass Casualty Management Systems: Strategies and guidelines for building health sector capacity?
- (2020) START (National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism), Global terrorism database. University of Maryland, Maryland, USA.
- Van Vactor JD (2012) Strategic health care logistics planning in emergency management. Disaster Prevention and Management 21(3): 299-309.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...