
Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2643-6760
Research Article(ISSN: 2643-6760) 
Astigmatism Control in Cataract Surgery by Phacoemulsification Volume 5 - Issue 4
Qiang Fu, Juan Raúl Hernández Silva*, Heidy Hernández Ramos, Meisy Ramos López and Wang Jiayue
- Cuban Institute of Ophthalmology Ramón Pando Ferrer. Havana. Cuba
Received: August 13, 2020; Published: August 20, 2020
Corresponding author: Juan Raúl Hernández Silva, Cuban Institute of Ophthalmology Ramón Pando Ferrer. Havana. Cuba
DOI: 10.32474/SCSOAJ.2020.05.000218
Summary
Cataract is a cause of visual deterioration in quantity and quality, surgery is the only solution to cure this disability. A prospective and analytical study of case series was carried out in 43 eyes of patients, diagnosed with cataract, operated by the phacoemulsification technique by Pre Chop with implantable intraocular folding lens, at the Cuban Institute of Ophthalmology Ramón Pando Ferrer since November 2018 until April 2020. Descriptive statistical techniques such as mean and standard deviation were used. In the non-compared results, the test used was the Chi square test, with a significance of 95%, a difference with a value of p <0.05 was considered statistically significant and the contingency coefficient to measure the strength of the relationship. The topographic and refractive changes of the cornea and their influence on the astigmatism induced after surgery were evaluated. The mean age was 69.4 ± 8.3 years, according to LOCS III 51.16% had NO3 hardness, the best visual acuity without correction in 76.75%, improved between 0.8 and 1.0, as well as the corrected vision with crystals in 93.02%; the mean keratometry pre vspost operative did not show statistically significant values (p> 0.05), the postoperative refractive cylinder in 72.09% was less than 0.5D; 51.17% of the eyes in the preoperative period had refractive astigmatism against the rule, 60.47% changed to astigmatism according to the rule one month after surgery. According to the FV-14 quality of life survey, 100% of patients had a very good quality of life one month after surgery. We conclude that with cataract surgery by personalized phacoemulsification, total efficiency is achieved in the correction of preoperative refractive defects.
Keywords: Astigmatism, Cataract, Phacoemulsification, Toric Intraocular Lenses, FV-14, Quality of life
Introduction
Cataract remains the leading cause of curable blindness in the
world, reaching 33% of blindness cases in general and its only
effective treatment is surgical, to date [1]. Surgery to remove the
cataract lens is maintained in constant perfection to restore the
vision of the patients with the highest quality and quantity, the
Phacoemulsification surgical technique has helped to gradually
improve the quality of the result.The pre-operative examination is
very important to guarantee the quality of the surgical result, and in
this consultation, astigmatism and its magnitude must be identified
to plan the surgery. Astigmatism is the refractive defect in which
the radius of curvature of any of the refractive surfaces of the eye
is not uniform, and may be present from birth, as a consequence of
some corneal disease or as a result of surgery performed on it [2-5].
Ferrer’s studies suggest that there is a prevalence of
approximately 70% of corneal astigmatism in the cataract
population. 64.4% of patients present with astigmatisms between
0.25 and 1.25 diopters (D) and 22.2% astigmatisms with 1.50 D or
greater[6]. In patients older than 65 years, the type of astigmatism
varies and 60% of them have astigmatism against the rule, with
values higher than 1.0 D [7]. The current objective of cataract
surgery is to achieve a refractive result, for this it is important to
carry out a detailed and personalized preoperative examination
to determine the most accurate eye measurements possible, to
plan the appropriate size and location of the main incision, the
selection of the intraocular lens that adjusts to the daily visual
needs of the patient and to the refractive defects of the patient and thus, with the result of the surgery, minimize astigmatism induced
by the procedure as much as possible.The preoperative diagnosis
of the amount and location of the patient’s corneal astigmatism
is determined by different preoperative studies to determine the
amount of preoperative corneal astigmatism and the location of the
most curved meridian, one of these tests is the keratometric study
that will allow us to determine the axis and cylinder power, with the
IOL master 700 (Zeiss) equipment and using corneal topography
the precision of these measurements is greater, in addition to having
information on any cornea site, elevation maps and anterior and
posterior surface of the cornea, through conventional surveyors
such as the Magella (Nidek) or high precision such as the Galilei,
the Pentacam (Oculus) and the OPD Scan [8].
The Pentacam surveyor (Oculus) is used to detect and
monitor patients with refractive defects and to assess topographic
irregularities, important in the detection of keratoconus and its
monitoring, determination of keratometric values and elevation
maps of the anterior and posterior face. of the cornea[8].After
diagnosing the amount and location of preoperative astigmatism,
we must evaluate the tools we have to eradicate it with surgery
or prevent it from increasing, in the first place, the location and
size of the main incision is important, since they are performed
on the temporal side and not greater than 3mm, valued in two or
three planes, have not shown an increase in the mean astigmatism
induced after surgery since the horizontal surface diameter of the
cornea is greater than the vertical, so that the temporal incisions
are further from the visual axis and, therefore, have less astigmatic
effect because they do not modify the curvature of the cornea,
resulting in a more stable refraction[9,10].
Other tools that we must take into account in surgical planning
that reduce corneal astigmatism between 0.50 and 4.00 D, are the
limbal relaxing incisions (IRL) adjusted by nomograms, which are
usually two arcuate incisions parallel to the corneo-scleral limbus
in the most curved meridian and in the flattest part of the cornea,
the opposite incisions in clear cornea (IOCC) placed symmetrically
along the curved axis of corneal astigmatism [1-13].When we
diagnose high astigmatism values in the preoperative examination,
toric IOLs, alone or combined with correction of near, intermediate
and distant vision, are effective in values between 1 to 4 D; For
values between 4.5 to 7 D, toric IOLs can be combined with IRL
in the most curved corneal meridian. Among the toric IOL models
we can point out the AcrysoftToric®, Rayner T-flexTM model 620
T or 623 T, and currently, diffractive trifocal toric lenses such as
the PanOptix-Toric (Alcon), FineVision-Pod F Toric have been
introduced (PhysIOL) and AT LISA 939 (Zeiss), for its calculation
it is recommended to use fourth generation formulas, such as Hill-
RBF, Barrett Universal II and Holladay II, in addition to taking into
account the posterior aspect of the cornea and new technologies for
this calculation[14,15].
Once cataract surgery is planned as a refractive lens surgery for
its excellent results, that is, in addition to removing the lens from
the patient, it is planned to emmetropise it, reducing as much as
possible its dependence on corrective glasses in the postoperative
period, it is necessary to mention the selection of the appropriate
surgical technique, where phacoemulsification is currently
considered the safest, most reproducible and excellent technique
due to the results of its use, which allows early visual gain and
high satisfaction for patients and families.The development of the
specialty applied to the surgery process to obtain these high results
of excellence, has developed the Cataract Refractive Suite Platform
(ALCON), to avoid intraoperative errors in the placement of toric
IOLs, since it integrates the phacoemulsification team Centurion®,
LuxORTM Ophthalmic Microscope, LenSx® Femtosecond Laser
and VERIONTM Image Guidance System, designed to add greater
precision and efficiency during surgery planning and execution.
Another technological innovation is the ORA® system
with VerifEye + ®, which provides a continuous evaluation of
intraoperative measurements of the eye, using the diagnosis of
wavefrontaberrometries and the AnalizOR TM database analyzer;
to obtain high-precision refractive measurements, data on anterior
and posterior corneal astigmatism, which allow reducing the
incidence of unwanted postoperative residual astigmatism and
perfecting the implantation of multifocal intraocular lenses, the
result will be a better expected spherical equivalent, with an error
less than 0.5D in 95% of cases[16,17].When all this planning fails
and refractive errors occur after cataract surgery, with moderate or
high cylinders, piggy back, IOL change and excimer laser-assisted
corneal refractive surgery can be performed, using LASIK or LASEK
techniques. a simple and effective solution or the Femtosecond
laser[18].At the Cuban Institute of Ophthalmology Ramón Pando
Ferrer, phacoemulsification techniques have been developed
with effective control of astigmatism induced by surgery, with
topographic control of the incision site, which will allow refractive
correction of cataract surgery. , according to the visual needs of the
patient, which translates into a more satisfied patient, who will
socially rejoin his tasks early[19].
Material and Methods
A prospective and analytical study of case series was carried
out in 48 eyes of patients, diagnosed with cataract, operated
by the technique of phacoemulsification by Pre Chop with
implantation of a foldable intraocular lens, which, once attended,
were included in the database of the Ocular Microsurgery Center
of the Cuban Institute of Ophthalmology Ramón Pando Ferrer from
November 2018 to April 2020, performed by the same surgeon.The
topographic and refractive changes of the cornea, its influence on
the astigmatism induced after cataract surgery, and its impact on
the visual and life quality of the studied patients were evaluated.
The universe was made up of all the patients operated on with the diagnosis of cataract, attended at the Ocular Microsurgery Center of
the Cuban Institute of Ophthalmology (ICO): “Ramón Pando Ferrer”,
in the consultation, during the period from November 2018 to April
2020; from which a sample of 48 patients was selected, operated
on by the Phe Chop Phacoemulsification surgical technique, with a
foldable intraocular lens implant, selected from the CMO database
of the Cuban Institute of Ophthalmology Ramón Pando Ferrer; who
fulfilled the inclusion criteria such as having a phacoemulsification
criterion, being over 50 years of age, having expressed their
willingness to participate in the research and having complete
information on the pre and postoperative examinations required
for the study.
Patients with general diseases such as: Collagenopathies
and immunological conditions, patients with eye diseases such
as: eyelid diseases (ectropion, entropion, eyelid ptosis), tear
disorders (dry eye), cornéal disorders (dystrophies, degenerations,
keratoconus, leucoma), traumatic, complicated and pathological
cataracts, glaucoma in any of its classifications, retinal and macular
degenerations if detected in the preoperative period, congenital
ocular abnormalities (microcornea, aniridia, persistence of the
hyperplastic primary vitreous)
Patients who decided to leave the study for medical and
/ or personal reasons left the study.To output the proposed
objectives, the following variables were analyzed: Age, Sex, Lens
hardness measured by the LOCSIII (Lens Opacities Classification
System) classification system [20], endothelial microscopy, to
determine endothelial cell density, hexagonality, coefficient of
variation, minimum cell size, maximum cell size, average cell
size and pachymetry.Phacodynamic parameters were studied:
effective ultrasound time (TEU) and power, provided by the
Phacoemulsification team (Revolution, OPTIKON), using the time
scale performed (minutes), representing the effective time it took
to emulsify the lens nucleus. , which was preset using a variable
value of less than 10% power, as the pedal is in position three.
The best visual acuity without correction (MAVSC) and the best
visual acuity with correction (MAVCC) were evaluated, measured
by the Snellen chart, the spherical equivalent (EE), mean induced
astigmatism (AMI), contrast sensitivity test, determined at through
the Pelli-Robson Primer, the aberometric study, carried out with the
OPD Scan II [21].
The index of variation of visual function VF-14 [22]was
calculated and its score was related to quality of life and was
grouped into poor quality of life (0-25), moderate quality of life
(26-50). ), good quality of life (51-75) and very good quality of life
(76-100).All the patients underwent a preoperative diagnostic line,
where after their diagnosis was defined, they explained what the
surgical technique consisted of, its risks and benefits, and after
surgery they were scheduled for consultation the following day, one
week. and one month.A diagnostic protocol was applied where the
patient and relatives were asked about their acceptance to perform
the surgical procedure, through informed consent, living conditions,
hygiene and habits, intellectual level and profession; in addition
to conducting a comprehensive preoperative ophthalmological
examination and by trained personnel.
To calculate the power of the IOL, the Carl Zeiss IOL Master 700
equipment was used, where Keratometry (K), White - White (White
to White, WTW), Anterior Chamber Depth (ACD), Pupillometry,
Thickness of the Crystalline, Pachymetry and Biometry, with these
data the IOL calculation formula was applied according to their
measurements, the 3rd generation formulas used were SRK-T for
emmetropic and myopic patients, as well as Hoffer Q for hyperopic
patients, for the IOL calculation for its high precision since they are
based on the effective position of the lens with respect to the plane
of the cornea (ELP) to increase its accuracy.
The surgery was performed following the protocol for the
prevention of post-surgical infections, with the implementation
of security measures for the surgical procedure and all patients
received antibiotic treatment with Ciprofloxacin 0.3% (eye drops)
every four hours two days before surgery. On the day of surgery we
used Prednisolona and Ciprofloxacin 0.3% every three hours before
surgery, pupillary dilation was performed with Phenylephrine and
1% Tropicamide eye drops.
Asepsis was carried out by applying Povidone Iodine 10% on
skin of the eyelids and appendages, and Povidone Iodine diluted 5%
in both eyes, about three to five minutes before surgery in both eyes.
The preparation of the surgical field always included the isolation of
the palpebral edge (eyelashes and Meibomian Glands) by means of a
sterile surgical field with transparent adhesive that is drilled for the
placement of the blepharostat. Anesthetic lidocaine eye drops were
placed, after three minutes the surgery was performed, which was
performed by phacoemulsification with the OPTIKON Revolution
equipment, with constant irrigation of Balanced Saline Solution
(BSS) for intraocular and ocular surface irrigation, aswell as the
memory foam at 4 °C. The main incision was made in the clear cornea
by the most curved meridian according to corneal topography (in
98% of the patients it corresponded to the temporal side in both
eyes), using a 2.7mm bevelled blade and a 1mm accessory. The
continued circular capsulorhexis was 5mm, somewhat smaller
than the lens to be implanted. Hydrodissection released the capsule
cortex to perform the bimanual phacofragmentation technique or
Pre Chop, with two Nagahara choppers, to emulsify the crystalline
nucleus and aspirate the cortex and its remnants with the Buratto
bimanual system.
Regarding the ultrasound mode used, the multi-burst or multibursts,
providing us with 80 milliseconds of long bursts linked to
an ultrasound power, was preset at less than 10%, through a linear
control of the pedal at the beginning, the impulses are separated by
spaces of 2.5 seconds and so on, the bursts increase as we depress
the pedal until reaching the figure of four bursts per second, in this way we avoid unnecessarily administering ultrasonic energy
to the eye with the consequent protection of the tissues, being the
mode ideal for Chopping or fracturing techniques. The vacuum was
prefixed at 400 mmHg, in 5 mmHg steps and a suction flow of 30
ml / min.
After aspiration of the cortical remains, the foldable intraocular
lens of hydrophilic acrylic of the Ocuflex brand, model RYCF, was
introduced to proceed with the final washing of the remains of the
viscoelastic material. No suture was performed, the wound lips
were closed by hydrating the lips using a syringe with Balanced
Saline Solution (BSS), then an antibiotic (Cefuroxime 750mg- 1mg
in 0.1ml) was diluted in BSS to inject it in the anterior chamber at the
end of surgery, according to doses recommended by the European
Society for Cataract and Refractive Surgery (ESCRS). At the end of
the surgery of the first eye, the blepharostat was removed, and the
surgical field was cleaned with sterile gauze moistened with BSS
and Povidone-Iodine-stained skin of the operated eye; applying
topical antibiotic therapy with Ciprofloxacin 0.3%.
The ocular occlusion after surgery depended on the surgeon’s
criteria and only for the transfer of the patient to the home, although
most of them were not occluded.Treatment was started with topical
antibiotics with Ciprofloxacin eye drops 0.3%, and steroidal antiinflammatory
drugs (Prednisolone 0.5% or Dexamethasone 0.1%),
every two hours, respecting sleep for the first 24 hours and then
every four hours, the topical antibiotic was suspended after ten days
and the steroidal anti-inflammatory drug was maintained for four
weeks after surgery.They were evaluated after surgery at 24 hours,
one week, 15 days and six weeks, where the parameters taken into
account in the pre-operative examination were evaluated to decide
the medical discharge.
The data collection was carried out using forms and they were
poured into a database prepared in SPSS version 15.0 previously
prepared by the author of the research where the variables under
study were included.Descriptive statistical techniques such as
mean and standard deviation were used. In the non-compared
results, the test used was the Chi square test (of independence or
with yacht correction as appropriate), with a significance of 95%,
a difference with a value of p <0.05 was considered statistically
significant and the contingency coefficient to measure the strength
of the relationship.From an ethical point of view, the investigation
was justified since it was carried out in accordance with the
provisions of the National Health System and provided for in Law
No. 41 of the Ministry of Public Health (MINSAP).The patient and
their relatives were offered an explanation of the research, its
importance, benefits and drawbacks, as it was a non-aggressive
and not mandatory study. Informed consent was obtained from the
people who participated and their approval was verified by signing
these individuals.
Results
In the present study, females were more frequent, who represented more than 60% of the total, as well as those over 70 years of age, who occupied 62.79%. The mean age was 69.4 ± 8.3 years, with a range between 49-84 years.51.16% of the patients had NO3 hardness according to LOCSIII.Regarding the best visual acuity without correction, at the start of the study more than 65% were in the group with vision <0.3; however, after seven days of evolution, only two patients remained with this condition, while 76.75% were in the group between 0.8 and 1.0. In relation to the MAVCC, 93.02% were in this last group.When analyzing the visual acuity means obtained with and without correction, a highly significant increase was observed in both between preoperative and 30 days postoperative, with differences of 0.59D for MAVSC and 0.29D for MAVCC (Table 1).
Table 1: Comparison between the MAVSC and MAVCC means between each evaluation moment.
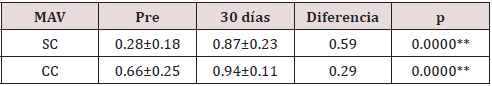
Source: Database. [**: highly significant (Values are expressed as Mean ± SD; DS: standard deviation of the mean)]
The Pre vs. Post Mean Keratometry showed a difference of 0.08 between the beginning and 30 days after the operation, finding that it was not statistically significant (p> 0.05), therefore, astigmatism was not induced with surgery(Table 2). Most of the patients had a refractive cylinder initially 0.75D or more, who represented 74.42%, however after seven days of evolution 72.09% had less than 0.5D.The mean refractive cylinder (Table 3) at the beginning of the study was -1.10 ± 0.86D, which had a highly significant variation in 0.55D (p <0.01), measured thirty days after surgery.As can be seen in Figure 1, the refractive cylinder and the mean postsurgery keratometric do not have a linear correlation (r = - 0.07). The mean keratometric cylinder values range between 42 and 47 independently of the refractive cylinder values. High and low order corneal aberrations, as observed in Table 4, experienced significant increases in the order of 0.21 and 0.17; respectively, while when comparing the means of the totals, a significant reduction of 0.15 was observed.
Table 2: keratometry comparison between the means of each evaluation moment.
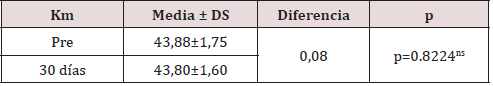
Source: Database. [ns: not significant; DS: standard deviation of the mean].
Figure 1: Scatter diagram of the relationship between the refractive and keratometric cylinder (r: Pearson’s correlation coefficient). Source: Database.
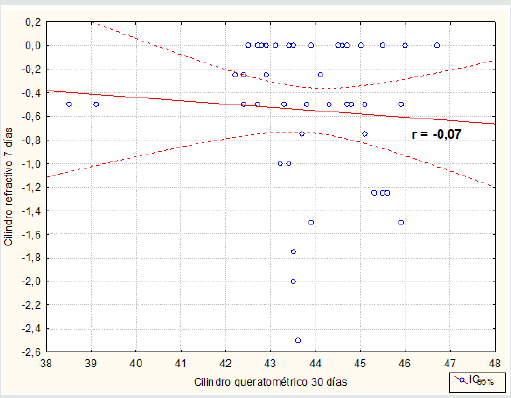
Table 3: keratometry comparison between the means of each evaluation moment.
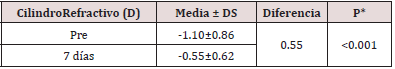
Source: Database.* associated with T-test for paired data
Table 4: Corneal aberrations comparison in each evaluation moment.
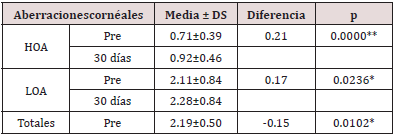
Source: Database. [**: highly significant; DS: standard deviation of the mean]
The values of the Pearson correlation coefficients calculated for
the interaction between the values of the high order pre and post
aberrations with respect to those of the refractive cylinder and the
mean keratometric pre vs post are very low, which denotes that
there is no relationship between these variables. Only a positive
relationship was found between the post-surgery high order
aberrations values with respect to the refractive cylinder measured
on the seventh day.51.17% of the eyes in the pre-operative period
had refractive astigmatism against the rule, a situation that changed
one month after the operation and 60.47% of the patients changed
to astigmatism according to the rule.The preoperative refractive
defect 46.53% of the cases had mixed astigmatism and 39.53%
compound myopic astigmatism, and one month after surgery
27.91% had simple myopic astigmatism and 23.26% compound
myopic astigmatism.
The preoperative quality of life was good in 90.69% and very
good in 9.31%; According to the FV-14 survey, it was observed that
the activities in which they manifested a degree of considerable
difficulty were those related to near vision in terms of reading small
printed letters, such as those in the telephone directory, on drug
labels ( Question 1) as well as reading newspaper and magazine
articles (Question 2), they also referred this qualification for
performing fine manual work (Question 7) and filling checks or
filling forms (Question 8). Regarding distance vision, they rated the
activity related to watching TV quite difficult (Question 12). %; one
month after surgery, it was found that 100% of the patients had
very good visual quality.
Discussion
The study of the relationship of astigmatism with visual quality as a result of cataract surgery by phacoemulsification, when analyzing its demographic data, showed that females were more frequent, who represented more than 60% of the total, as well as those over 70 years of age, who occupied 62.79%. The mean age was 69.4 ± 8.3 years, with a range between 49-84 years. Nieves López C.J. and cols reported in their study an average patient age of 66.1 ± 12.4 years and 58.92% were women [23]; Mateo Garbas J. reported an average of 73.1 ± 9.6 years and 73.3% were women [24] , Castillejos Santos A. studied patients with an overall average age of 74.25 years, with the female sex also predominant [25]; Pico Garcia A. found in his research 61.19% of patients over 60 years of age and women also represented 51% of the sample [26], all these data reaffirm that the elderly is a growing group due to the increased life expectancy of the population, who need health services that, among other aspects, guarantee ophthalmological care, and within it cataract surgery.
The cataract has different degrees of hardness according to the LOCS III classification, and for this study 51.16% of the patients had NO3 hardness, Castillejos Santos A. reported that the subjects operated on in their study presented corticonuclear cataract (CN) in a 68.18 % [25]; Hernandez Silva JR., Reported in her study significant results in the staging of LOCS III in the group of nuclear opalescence and nuclear color 2 and 3 with a value of 30.0 and 22.5%, respectively [27].In the vision analysis regarding the best visual acuity without correction, at the beginning of the study more than 65% were in the group with vision <0.3; however, after 30 days of evolution, vision in 76.75% improved between 0.8 to 1.0, this analysis in relation to MAVCC, 93.02% of patients improved between 0.8 to 1, 0; therefore, a highly significant increase in vision is observed between pre-operative and 30 days post-operatively. Nieves López C.J. et al., report that 82.14% of patients reached less than 0.1 in their AVSC and after surgery 53.57% reached vision greater than 0.6, in their AVMC [23], Mateo Garbas J. reports that the mean value of far VA without correction was 0.2 and for far VA with the best correction, the mean value was 0.45 in the study group similar to that of this investigation [24]; Pico García A., in his study, reported a mean preoperative AVSC of 0.12, which improved to 0.32 a week, and when corrected with crystals, went from 0.33 in the preoperative period to 0.56 a week after surgery [26], all these reports correspond to the results of this work.
The Pre vs. Post Mean Keratometry, for this investigation, did not show statistically significant values (p> 0.05) between the beginning and one month after the operation, so astigmatism was not induced with surgery; the refractive cylinder was initially 0.75D or more, in 74.42% of cases, and after seven days of evolution 72.09% of them had less than 0.5D. The mean of the induced keratometric astigmatism was 0.45 D due to phacoemulsification in the study by Hernández Silva JR. et al [19]; Nieves López C.J. et al. found that the total number of patients with astigmatism increased between the pre and postoperative period (89.28% to 98.28%), with respective variation from 1.43D ± 0.79 to 2.20D ± 0.99 diopters, an increase average of 0.78D (p = 0.000) and induction of astigmatism in 9.09% of the operated [23]; Mateo Garbas J., found in his work that refractive astigmatism decreased significantly with surgery <0.001) [24]; Castillejos Santos A., reported that the total cylinder decreases markedly from the preoperative one week after surgery, possibly due to the extraction of the opacified lens that induces unwanted astigmatisms [25]; Pico García A., in his research, found a mean preoperative astigmatism of 0.77D (SD 0.55), range 0.05 to 2.99, which showed values of 0.75D a week and a mean of 0.02. (SD 0.56) range 0.00 to 3.00, which were not significant P = 0.646; and at the end of the study the mean astigmatism was 0.67D with a mean of 0.08D, which represents a significance of P = 0.011 [26]. The mean of the induced keratometric astigmatism was 0.61 diopters one month after surgery, according to González Peña A. et al. [28], in their study; for his part, Hernández Ramos H. in his research found that there was a significant reduction in the mean astigmatism induced between the pre and postoperative period, parameters that evaluate the quality of the process and its results [29,30].
The values of the Pearson correlation coefficients calculated for the interaction between the values of the high order pre and post aberrations with respect to those of the refractive cylinder and the mean keratometric pre vs post for this investigation are very low, which denotes that it does not exist relationship between these variables, only a positive relationship was found between the values of high-order aberrations after surgery with respect to the refractive cylinder measured on the seventh day by the immediate changes in corneal curvature and transient corneal edema after cataract surgery by phacoemulsification , with incisions less than three millimeters in the most curved corneal meridian.51.17% of the eyes in this investigation in the pre-operative period had refractive astigmatism against the rule, a situation that changed one month after the operation and 60.47% of the patients changed to astigmatism according to the rule. Pico García A. reports that 38% of the cases in his study had corneal astigmatism according to the rule, 45% corneal astigmatism against the rule and 17% oblique astigmatism in the preoperative period [26].
The classification of the refractive defect in this study showed in the preoperative period that 46.53% of the cases had mixed astigmatism and 39.53% compound myopic astigmatism, and one month after surgery 27.91% had simple myopic astigmatism. and 23.26% compound myopic astigmatism when we speak of astigmatism in patients with cataract.All the previously analyzed studies, closely related to each other due to their results, reaffirm the idea that when studying a patient for cataract surgery by phacoemulsification, an exhaustive pre-operative examination is essential to optimize the surgical result, taking into account that approximately 40% of cataract patients have astigmatism higher than diopter1, and pseudophakic patients show post-surgical astigmatism higher than 0.75 D, the results of which decrease visual acuity in quantity and quality, resulting in a deterioration in quality of life of these patients.
According to the FV-14 quality of life survey, in the preoperative period it was good in 90.69% and one month after surgery it increased to 100% of the patients. Hernández Ramos H. reports in the pre-operative period more than 60% of his cases with poor visa quality, which improved to more than 98.3% of the cases that reported good or very good quality of life in the postoperative period [29]; meanwhile Luján Paredes S. [30] concludes that the use of questionnaires allows an adequate measurement of the results of the surgery, knowing the clinical response and the degree of patient satisfaction, which leads to a better quality of life Harrer A&MilanésArmengol AR [31-33]observed a significant improvement in visual acuity represented in visual recovery and quality of life, according to the FV-14 visual function index, with a high degree of validity, results that coincide with this research. Research related to quality of life and cataract surgery have been carried out in Cuba by Trujillo Fonseca & Rodríguez Suárez B. [34- 36], which coincide with the results of this study.
The current lifestyle dynamics that brings with it very specific
visual needs to drive, read, consult the cell phone and work with
the computer machine, patients seek a definitive refractive solution
with cataract surgery, so they meet The objective of greater vision
in quantity and quality includes evaluating the corneal curvature,
and then deciding the lens to be implanted in the model and power,
according to the personalized visual needs of each patient.In this
preoperative study, we must take into account the prognostic
factor and we must evaluate other aspects that may negatively
influence the result expected by the patient after cataract surgery,
which is why it is important to evaluate the tear film, optic nerve
and taint.The analysis of the results shown in this study and those
consulted showed that, to control the induction of astigmatism
in cataract surgery, in the preoperative study it is necessary to
consider the evaluation of corneal curvature and toricity, we must
perform a corneal topography and an optical biometry, evaluate
the anterior and posterior corneal surface and use the intraocular
lens calculators with the appropriate information and the use of
the latest generation calculation formulas, and as a result of this
analysis find the correct decision for each case.
Currently, in addition to the correction options for astigmatism
related to the incisions typical of cataract surgery due to
phacoemulsification in the most curved meridian, corneal incisions
for major astigmatisms; The toric lens is the option that offers the
best predictability in the correction of astigmatism in patients
who present with cataract, and although there are no studies that
demonstrate full efficacy in correction, if pre, intra and postsurgical
risk factors are controlled, may improve the accuracy of the results
of phacoemulsification cataract surgery.
References
- Bourne RRA, Flaxman SR, Braithwaite T, Cicinelli MV, Das A, et al. (2017) Vision Loss Expert Group. Magnitude, temporal trends, and projections of the global prevalence of blindness and distance and near vision impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health 5(9): 888-897.
- Sathar A, Abbas S, Nujum ZT, Benson JL, Sreedevi GP, et al. (2019) Visual Outcome of Preterm Infants Screened in a Tertiary Care Hospital Middle East Afr. J Ophthalmol 26(3): 158-162.
- Uprety S, Morjaria P, Shrestha JB, Shrestha GS, Khanal S (2017) Refractive Status in Nepalese Pre-Term and Full-Term Infants Early in Life. Optom Vis Sci 94(10): 957-964.
- Gordon-Shaag A, Millodot M, Shneor E, Liu Y (2015) The genetic and environmental factors for keratoconus. Biomed Res Int pp. 795738.
- Lake JC, Victor G, Clare G, Porfírio GJ, Kernohan A, et al. (2019) Toric intraocular lens versus limbal relaxing incisions for corneal astigmatism after phacoemulsification. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 12: CD012801.
- Ferrer T, Montés R, Peixoto S (2009) Prevalence of corneal astigmatism before cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 35(1): 70-75.
- Daponte P (2002) Cirugía refractiva de catarata. Médico Oftalmólogo 15(1): 1.
- Freydell H (2007) Astigmatismo en cirugía de cataratas. En: Centurión V, Nicoli C, Villar-Kouri J (editores). El Cristalino de las Amé Sao Paulo: Livraria Santos pp. 811-817.
- Ramos Pereira Y, Medina Perdomo JC, Hernández Silva JR, Rodríguez Suárez B, Pérez Candelaria EC, et al. (2020) Diagnóstico y control del astigmatismo en la cirugía del cristalino. Rev Cubana Oftalmol. 2015[citado 23 de abril de 28: 2.
- Nikose AS, Saha D, Laddha PM, Patil M (2018) Surgically induced astigmatism after phacoemulsification by temporal clear corneal and superior clear corneal approach: a comparison 12: 65-70.
- Amarilis Mariel PA (2019) Defectos refractivos en post operados de catarata senil Hospital Alberto Sabogal Sologuren. 2016. Universidad Nacional Federico Villarrea 58: 03Z.
- Hayashi K, Sato T, Yoshida M (2019) Corneal shape changes of the total and posterior cornea after temporal versus nasal clear corneal incision cataract surgery. British Journal of Ophthalmology 103: 181-185.
- Sonmez S, Karaca C (2020) The effect of tunnel length and position on postoperative corneal astigmatism: An optical coherence tomographic study. Eur J Ophthalmol 30(1): 104-111.
- Hashemi H, Khabazkhoob M, Soroush S, Shariati R, Miraftab M, et al. (2016) The location of incision in cataract surgery and its impact on induced astigmatism. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 27(1): 58-64.
- Tamez Peña A, Nava García JA, Zaldívar Orta EL, Lozano Ramírez JF, Cadena Garza CL, et al. (2015) Efecto clínico de la rotación postoperatoria de los lentes intraoculares tó Revista Mexicana de Oftalmología 8(4): 219-224.
- Castillo Cabrera J, Pucha Ortiz N, Pinos Velez E, Ipanque W, Chacón CL (2019) Proposal for a Tool for the Calculation of Toric Intraocular Lens Using Multivariate Regression. Springer.
- Albin Relucio (2019) Using ORA SYSTEM® Technology with AnalyzOR™ Technology to Optimize Refractive Cataract Outcomes: Normal to Complex Cases, Simultaneous Innovations.
- Cionni, Robert J (2018) “A Large Retrospective Database Analysis Comparing Outcomes of Intraoperative Aberrometry with Conventional Preoperative Planning.” Journal of Cataract & Refractive Surgery 4(10): 1230-1235.
- Hernández Silva JR, Ramos López M, Curbelo Cunill L, Fernández Vásquez G, Rio Torres M, et al. (2012) Astigmatismo posquirúrgico en la facoemulsificación según el lugar de la incisió Rev Cubana Oftalmol 25(1): 2-11.
- Hernández Silva JR, Barroso Cruz M, Ramos López M, Nafeh Mengual N, Hernández Ramos H, et al. (2013) Estudio densitométrico del cristalino y su relación con el sistema LOCS III. Revista Cubana Oftalmología 26(2):191-7.
- Lara del Castillo M, Torres A, Gonzáles L (2015) Trabajo Final de Grado en Óptica y Optometrí Facultad de Óptica Y optometría de Terrassa. Barcelona: Universidad Politécnica de Cataluña.
- Valderas JM, Rue M, Guyatt G, Alonso J (2005) Systematic Use of Quality of Life Measures in the Clinical Practice Working Group. The impact of the VF-14 index, a perceived visual function measure, in the routine management of cataract patients. Qual Life Res 14(7): 1743-1753.
- Nieves López CJ, Álvarez Díaz MC, Triana Casado I, Martínez Legón ZC, Morell Ochoa Z (2013) Caracterización del astigmatismo post-cirugía de catarata con técnica de Blumenthal. Centro Oftalmológico “Eloy Alfaro” de Ecuador, 2010. MEDICIEGO 19: 2.
- Mateo Garbas J (2013) Tratamiento del astigmatismo moderado en pacientes con cataratas. Tesis doctoral. Universidad de Zaragoza. Facultad de medicina .Departamento de Cirugía, Ginecología y Obstetricia.
- Castillejos Santos A (2015) Variación del astigmatismo corneal inducido por cirugía de catarata en función de la incisión lí Trabajo final de Máster Universitario en Optometría y Ciencias de la Visión. Facultad de Óptica y Optometría de Terrassa. Universidad Politécnica de Cataluña.
- Pico García A (2007) El astigmatismo en la cirugía de la catarata con incisión pequeña: análisis de la evolución queratométrica y refractiva en la sonofacoaspiració Tesis para opta al grado de Doctor en Medicina y cirugía. Universidad Autónoma de Barcelona. Facultad de Medicina. Departamento de Cirugía. Barcelona, Spain.
- Hernández Silva JR, Hernández Ramos H, Duperet Carvajal D, Ramos López M, Perera Miniet E, et al. (2016) Cirugía bilateral secuencial inmediata del cristalino por Facoemulsificació Revista Cubana de Oftalmología 29: 3.
- González Peña A, Ortega Díaz L, Pérez Candelaria E (2011) Astigmatismo inducido en la cirugía de catarata por técnica de Facoemulsificació Revista Cubana de Oftalmología 24: 1.
- Hernández Ramos H, Hernández Silva JR, Ramos López M, Fundora Nieto Y (2019) Calidad de vida y visual en pacientes operados de catarata por Facoemulsificación bilateral simultánea con implante de lente intraocular. Revista Cubana de Oftalmología 32: 2.
- Hernández Ramos H, Hernández Silva JR, Ramos López M, Padilla Gonzales CM, Perera Miniet E, et al. (2019) Evaluación de la efectividad en la cirugía de catarata por Facoemulsificación bilateral simultánea versus Facoemulsificación bilateral secuencial. Revista Cubana de Oftalmología 32: 2.
- Luján Paredes S, Pizanguo Maqiz O, Alburquerque Duglio M, Valenzuela Tito M, Mayta-Tristan P. (2014) Calidad de vida y función visual post cirugía de Catarata. Revista Mexicana Oftalmología 88(4): 176-181.
- Harrer A, Gerstmeyer K, Hirnschall N, Pesudovs K, Lundström M, et al. (2013) Impact of bilateral cataract surgery on vision-related activity limitations. J Cataract Refract Surg 39(5): 680-685.
- Milanés Armengol AR, Molina Castellanos K, Zamora Galindo I, González Díaz A, Jackson Villalpando Rodríguez J, et al. (2012) Cirugía de catarata en pacientes longevos: repercusión sobre su calidad de vida y funcionabilidad. Medisur 10(5): 386-392.
- Trujillo Fonseca KM, Valdés Carracedo G, Hormigó Puertas IF, Arrieta García H, Cuan Aguilar Y, et al. (2019) Calidad visual y calidad de vida en pacientes operados de catarata mediante Facoemulsificació Revista Cubana Oftalmología 32: 1.
- Rodríguez Suárez B, Ramos Pereira Y, Montero Díaz E, Cárdenas Díaz T, Pérez Candelaria EC, et al. (2018) Calidad de vida según la escala NEI VFQ-25 en la cirugía facorrefractiva de pacientes hipermétropes pré Revista Cubana Oftalmología 31: 2.
- Rodríguez Suárez B, Ferro Hernández D, González Medina J, Machado Forzate I, Medina Pastrana M, et al. (2019) Calidad de vida relativa a la visión según estudios psicofísicos en pacientes hipermétropes con cirugía facorrefractiva. Revista Cubana Oftalmologí 31: 2.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...




