Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2643-6736
Review article(ISSN: 2643-6736) 
Use of Renewable Energies in Uzbekistan Volume 2 - Issue 3
Yuldash Sobirov1* and Sirozhiddin Makhmudov2
- 1Institute of Materials Science, Academy of Sciences of Uzbekistan, Uzbekistan
- 2Tashkent State Technical University named after Islam Karimov, Uzbekistan
Received: January 31, 2020; Published: February 26, 2020
Corresponding author: Yuldash Sobirov, 1Institute of Materials Science, Academy of Sciences of Uzbekistan, Uzbekistan
DOI: 10.32474/ARME.2020.02.000137
Abstract
This chapter gives a small part of the work carried out in Uzbekistan on the use of solar and wind energy. It is, of course, impossible to list all the work performed in this area since the 1930s. Therefore, the author drew attention to the part that is associated with the author’s direct scientific and technical work. Here are the works related to the Big Solar Furnace of Uzbekistan, the operation of a modern automated weather station, the measurement and use of wind energy. The socio-economic development of the republic largely depends on a stable electricity supply. Renewable energy sources play an important role in this. In this sense, the construction of a wind power plant with a total capacity of 1,500 megawatts represents a change in the traditional energy system of the Republic of Uzbekistan, which has entered a new energy era.
Keywords: Large solar furnace; Concentrator; Eliostats; Solar radiant energy
Introduction
In Uzbekistan, the exploitation of renewable energies has increased in recent decades. different sources were used including solar energy and wind energy. Research on the use of solar energy in Uzbekistan was conducted back in the 1930s. In Tashkent, Samarkand, Bukhara and other cities of the republic, work was carried out in all areas of solar engineering: the creation of solar furnaces and their use for obtaining high temperatures, welding, cutting, refining and synthesis of refractory materials, the conversion of solar energy into electrical and mechanical, the creation of new solar materials, solar plants for domestic use, as well as for desalination plants, greenhouses, hotbeds, a solar thermal battery, etc. [1]. The institute of Material science is organized under initiative of AS RUz in 1993 on the basis of scientific laboratories of Physicotechnical institute and a skilled research-and-production complex of “Physics-Sun”-products of scientific and technical idea and architectural-engineering work and territorially located in Tashkent region in the structure of SPA “Physics-Sun” in area Parkent in 56kms from Tashkent. The general territorial area 0,74km2.
Characteristics of Big Solar Furnace, Capacity of 1000Kw
As it is known, the planet’s source of energy are limited, though
the world reserve on the various data are considered huge, but as it is forecasted by the end of the XXI century the problem of power
supply becomes most appreciable problem of the next century.
Optimistic and pessimistic propositions show that it is necessary
to find new energy resources or carry out the necessary actions on
developing the so-called alternative renewable energy resources.
The world energy reserve, especially fossil, for example, coal, oil
and wood as well per se are gathered under the action of the Solar
energy. Besides, in the near future, especially, if the development of
the near earth space begins, then the coming energy is the same of
that solar energy. Therefore, all energy of the future, in our opinion
will be substantially on the basis of the solar energy. Here exist two
main problems. The first, assemblage of the energy and the second,
conversion it into the most convenient form for consumption and
accumulation. If these problems will be solved as much that the
efficiency of using will be within the limits of those coefficients of
efficiency on which the modern resources work and in addition
the expenditures are below or at the same level, then mankind will
get rid of the danger of energy starvation, since the solar energy is
inexhaustible.
Moreover, the other vital and burning question turned out to be
that the reserves of uranium mines is not so big and on progressive
power consumption, as accounts of scientists show reserves
of uranium mines will be sufficient for 70 years. Therefore, the significance of assimilation ecologically pure that have no effect on
heat balance of the Earth and inexhaustible energy of the Sun is the
most reliable source. Besides, immense opportunities of using solar
energy is hidden on assimilation of cosmic space. Beginning from
the new millennium the perspectives of world power engineering
development cannot be considered in isolation from problems of
protection of the environment and related with the use of renewable
sources of energy among which the special place is taken by the
solar energy. Efforts are underway towards investigations in the
field of solar energy among countries are at the same level with
national programs designed for a long period.
By now quite a few various exploratory half-industrial
installations are operating in different countries and a big experience
is gained on accumulating the solar energy. In Uzbekistan scientific
researches on using the solar energy in national economy were
started in 1930s at institutes of higher education of Tashkent and
Samarkand. After organization of Academy of Sciences this work
obtained new bursts(impulses). By the early 70s interesting results
were already taken on high-temperature investigations. Specifically,
thermal physic properties of some materials were analyzed under
high temperatures, including thermal hit and first results are taken
on synthesis of new materials in the small solar furnaces. Carriedout
activities have shown that solar furnaces are not just scientific
instruments, but under determined conditions they can be halfindustrial
installation.
A big amount of work was done by the scientists of
physicotechnical institute of Academy of Sciences of the Republic
of Uzbekistan (PTI) on development of technology that receives
super-pure materials under their radiant heating. Adjustment of
technology of synthesis of new materials was carried out under
laboratory conditions on installations kind of “Uran” with the
artificial source of light and on small solar furnaces on a heliostat
field of PTI. Using the energy of the Sun in conformity to obtain
materials of high fire resistance initially were accomplished by
Japanese and French investigators. With this purpose in Japan
solar furnaces of little capacity and later on taking into account
this experience a Big Solar Furnace in France were built. The
results received by French investigators were interesting enough
and promising both with scientific and practical points of view.
In scientific plan oxide and non-metallic systems with the fluxing
temperature over 2000 degree Celsius in the oxidizing atmosphere
were studied and it is hard to fulfill using the traditional techniques.
By the results of the investigation the properties were revealed
indicating that as a result influence of the solar radiation mechanical,
optical characteristics and a whole series of other functional
parameters of materials significantly improves. In practical aspect
the opportunity of getting finished measure crucible products
by the centrifugal method was shown. From the point of view
technology of synthesis in melt the opportunity of implementation
of metastable conditions are challenging since it allows to control
phasic structure and accordingly, properties. Besides, it presents
considerable interest, an opportunity of obtaining superdispersed
particles by means of technology of ultraspeed quenching.
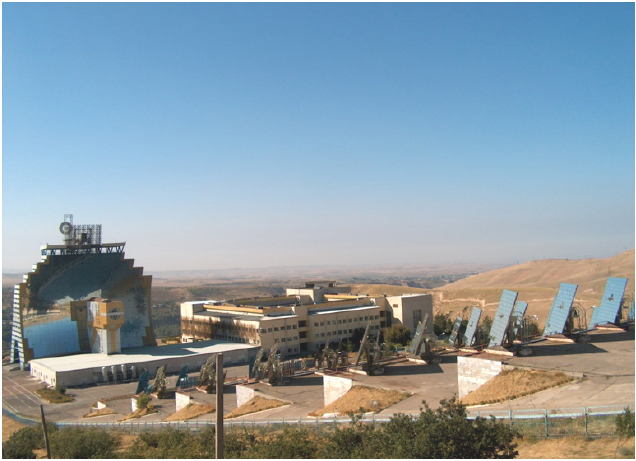
Considering all the advantages and perspectives in conformity
with our region, characterizing far from being lack of sunny days, a
Big Solar Furnace were created, and being the second installation in
the world with such a big capacity, namely, in the focus slightly less
than 1 m concentrates energy of 1000 kilowatt and temperature
about three thousand degrees Celsius is implemented. In creation
of the furnace the effort and work of many enterprises and
institutes of the former Soviet Union were put in and support at
all stages of the government of the Republic of Uzbekistan. Since
past 15 years systematic investigation of many-component oxide
system of the highest fire resistance was realized. In the series of
investigations combination and natural raw material, typical for our
region is included that is important from economical point of view.
Synthesized on the Big Solar Furnace (BSF) virtually all the groups of
materials of various classes-high oxide, glasses and glassceramics.
This allowed to discover features of influence of concentrated solar
radiation (CSR) on properties, and correspondingly take a step on
the way of directed synthesis.
First of all, to such peculiarities one should take changes of
such basic parameter as crystalline structure. As a rule, when
synthesizing under the influence of concentrated solar energy more
highly symmetrized structure stabilized. Accordingly, premises are
created for stability of materials on higher temperatures. Materials
are characterized by high purity-in melting cleanup takes place at
the expense of evaporation and diffusion in skull zone. Using the
technology of ultraspeed quenching showed the opportunity of
adjustment of formation process of required crystalline structure
and dispersion. Powders of size <5 micron, but ceramics on
their basis is characterized by unusual distinctive change of heat
resistance and mechanical durability.
By results of investigation of a class of such compounds as
titanates pellicles were obtained with refraction coefficient of more
than 2.4, that is challenging for use in systems of stabilization of
flying devices. In terms of groups of Al, Mg, Fe, having almost null
coefficient of thermal expansion ceramic components for engines
of internal combustion of adiabatic type. High temperature
conducting ceramics were obtained on the basis of zirconium oxide.
Superconductors are synthesized with the temperature of 900C. The
most vivid example of our elaborations in economy of the Republic
was series of work on creation of abrasives. It included technology
creation of abrasive synthesis of grain, structure development
of bundle on the basis of mineral raw material of the Republic of
Uzbekistan and concluding stage was creation of full-scale abrasive
circles, using at enterprises combined “ONIKS”. Amount saved
from their use (jeweler’s saw is replaced) comes to about 30%
from existing cost. Synthesis of new refractory oxide materials,
radial thermotreatment with the purpose of improvement of their
exploitative properties, thermalphysic determination, spectraloptical
characteristics, obtaining superpure materials, examination
on radial durability of bundles of new technology and etc. are
carried out under high temperatures. For solution of these tasks
along with lasers and furnaces with artificial sources concentrators
of solar energy are widely used, in addition their use is sometimes are the only method that gives answer to many abovementioned
tasks when powerful chromatic circuit stream of sufficiently big
size of different spectral composition are required. In these cases
the most appropriate ones could be large dimension concentrators
of solar energy, similar to Big Solar Furnace (BSF) with the power
of 1000 kilowatt Scientific-industrial association “Physics-Sun”
Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan.
Main directions of research
Basic researches
a. Research of processes of interaction of the concentrated
sunlight with substance.
b. Research of processes of synthesis of nonmetallic
materials with the set properties on the Big Solar Furnace.
Technical workings out
a. Working out of the big and small solar power installations,
expansion of functionality of the Big Solar Furnace.
b. Working out of technology of synthesis of ceramic fireresistant
materials and products from them for needs of medicine,
power, oil and gas branch, electronics and light industry.
Complex test: Knots of new technical and constructions design in the conditions of an irradiation the concentrated stream of a sun light of various capacity in pulse and continuous modes.
Unique scientific objects and manufacturing areas
a) The Institute operates a unique object-Big Solar Furnace
(BSF) with capacity of 1000kW.
b) BSF represents a difficult optical-mechanical complex
with the automatic control system consisting from heliostats
field and the parabolic concentrator, forming in a focal zone of
the concentrator (a technological tower) a radiant stationary
stream of high density.
c) Total area of reflecting surface of heliostats field -
3022,5m2, concentrator -1840m2.
For the oil and gas industry the elements of a ceramic pontoon
used in technological process of storage of oil and mineral oil for the
purpose of decrease of losses, connected with evaporation volatile
fractions are issued. Besides porcelain spheres for adsorbers of
zeolitic clearing of gas, and also skilled ceramic filters for clearing of
natural gas of various impurity are issued. For the textile industry
are issued more than 30 kinds thread drivers and thread to direct.
For the electro technical industry cases of safety locks of type PN-2
on 100, 250, 400А are made. Structures of high-voltage electro
technical porcelain are developed, experimental batches are made
and tests of cases of safety locks PKT-10 are conducted. On the basis
of the developed ceramic weights manufacture elements to electro
irons is debugged
Most a vivid example of the contribution of our creating out in
Republic economy was the cycle of works on creation of abrasives.
It included creation of technology of synthesis of abrasive grain, working out of structures of a sheaf on the basis of mineral raw
materials Republic of Uzbekistan and a finishing cycle there was a
creation of the natural abrasive circles used at enterprise “ONYX”.
The economy from their use (diamond circles are replaced)
makes about 30 % from the existing cost price. SPA “Physics-
Sun” particularly offers THEM synthesis by fusion on the solar
furnace composite materials of the set structure on a basis oxide of
aluminum, zirconium, the titan, magnesium, rare-earth elements,
etc., for manufacturing of constructional, heat-resistant, chemically
inert ceramics with certain electro physical properties.
The concentrator focuses reflected from heliostats solar beams
on a focal zone in diameter 1.5м, where is created high energy. The
focal area is located in a technological tower where special devices
are established and the equipment allowing to investigate the
physical and chemical processes proceeding at high temperature
influence on substances. On the basis of unique object international
projects STSU are carried out Р-3438. «Create out of ecologically
pure technology of creation of technical ceramics with solar
energy use» and Uzb-121 «Create out of optimum technology of
transformation of a solar energy in laser radiation»
Main results in fundamental research:
1) The phenomenon of threshold condensation streams
high-temperature materials in conditions of free cooling for
the first time is revealed and dependence of temperature of
condensation on modes of laser heating is revealed.
2) The phenomenon of multistage condensation streams
high-temperature materials in a mode of free cooling for the
first time is revealed.
3) Experimental data on spectral-optical properties of some
progressive materials widely used in modern industries for the
first time are received in the field of high temperatures, in a
liquid phase and in a zone of fusion.
Practical developments
The institute has an industrial line “Ceramics” where is made
on the basis of the materials developed and synthesized on the Big
Solar Furnace. These materials, possessing unique operational and
physical and chemical characteristics, such as the small factor of
thermal expansion, high durability and thermal stability in extreme
environments, have a wide scope. These ceramic materials can be
used to protect spaceships from overheating when they approach
the Sun, in blast furnaces, in glass melting furnaces, etc.
a. Multipurpose ceramics (high temperature heaters, thermo
coppers, transformers, gas burners, radiators for medicine).
b. thread drivers for textile industry.
c. Safety locks of type PN-2 on 100, 250, 400А and insulators
for the electrical power industry.
d. Ceramic pontoons for the oil and gas industry.
e. Ceramic balls for adsorbers of zeolitic clearing of gas of
the oil and gas industry
Developed and creating out installation for obtaining hydrogen, electrical power and high temperature streams simultaneously. Small solar furnaces by capacity 1500W which within the limits of the international contracts are developed and created for the Republics Egypt (Metallurgy institute in Cairo) and Indian institute of powder metallurgy. Flash of absorption of laser radiation for the first time is found experimentally out at laser heating sublimation refractory material. The new direction recognized in the world high-temperature spectral reflection meters - «a method of probing flash» is developed, allowing to carry out{spend} measurement of spectral-optical properties of modern materials with high accuracy in the field of high temperatures and in a zone of phase transitions where there is a sharp change indicatrices reflections of a researched surface. The technology of creation of ceramic materials with beforehand set properties a method of a radiating warming up on the Big Solar Furnace is created. On the basis of such technology materials with demanded properties, which scientifically - practical tests have passed are created necessary for needs of a national economy and medicine.
As a result of research of processes of interaction of the concentrated light stream with high-temperature materials the mechanism of formation of ultra-disperse particles in the field of the concentrated solar radiation is revealed. The mechanism has a basis of creation of technology of reception micro powders on the BSF. Development of the given direction can result to new and nonconventional methods in helio material sciences. On the basis of system Al2O3 - ZrO2 the mechanism of formation of a heterogeneous phase owing to diffusion of modifying additives in high-temperature ceramic materials is revealed. The mechanism allows to describe a condition of materials at influence of heats and mechanical loadings, and also to adjust their manufacture.
Since 2001 at the initiative of the President of Republic action for ignition of a torch of sports for pupils of high schools, colleges and students of University («Umid nihollari», «Barkamol avlod», “Universiada”) on focus of the BSF. Direct participation in of such actions of employees of the Device of the President, Academy of Sciences, the Ministry of the Higher Education and Olympic committee, the Society «Vatanparvar» has allowed to carry out these actions at high level.
Opportunities for Using the Resource of Wind Energy in Uzbekistan
It is known that in the future a characteristic feature of the
development of modern energy is the wide involvement of the
country’s energy balance of renewable energy sources (RES). In
a number of countries and regions, the share of electricity among
renewable energy generated by wind farms is a real competitor to
traditional energy [2]. Estimation of the global potential of wind
energy on the Earth’s surface is about 1200 TW. Wind power is
present in more than 79 countries, of which 24 countries have more
than 1GW of installed wind power in Denmark, 20% of electricity
is generated from wind energy, in Spain this figure has reached 8%,
in the Netherlands and the Northern Lands of Germany 10%. It is
expected that by 2020 the share of generated wind turbine energy alone will be 15% of the generated electricity, which is half of the
total forecast for the use of alternative sources [3].
To use the main energy resources of renewable energy sources
on a large industrial scale in Uzbekistan is solar, hydraulic and
wind energy. Their local use in autonomous power plants (sparsely
populated mountain and rural areas, remote small consumers, etc.)
are not considered in view of their small share in the balance of
electricity in the republic. By the condition of their effectiveness as
power plants, the Uzbek-Energo State Joint-Stock Company and the
volume of availability for the conditions and climate of Uzbekistan
that are connected to the electric network of the territorial
branches, the above RESs for electricity generation are located in
the indicated descending order.
The introduction of renewable energy is one of the most
important priorities for the transition of the economy of the
Republic of Uzbekistan to innovative rails and environmentally
friendly technologies. The relevance of this direction was once
again emphasized in the Decree of the President of Uzbekistan
Sh.M. Mirziyoyev dated May 26, 2017 No. PP-30-12 “On the Program
of Measures for the Further Development of Renewable Energy,
Increasing Energy Efficiency in the Economic and Social Spheres
for 2017-2021” The decree is aimed at conducting scientific and
practical research and developing a program of measures for the
further development of renewable energy, as well as at the practical
use of wind energy, taking into account the climatic characteristics
of the regions of Uzbekistan. The Decree’s implementation program
is intended to increase the generated renewable energy capacities
to 2021 by 1,003.9MW, of which hydroelectric capacity is 601.9MW,
solar energy by 300.0MW, wind energy by 102.0MW.
The main limiting factor for the widespread introduction of
wind energy in Uzbekistan is the lack of incentive measures for the
population and industrial consumers, characteristic of Germany,
Holland, Denmark, the USA and China and, as a result, high capital
investments that completely fall on the shoulders of the consumer.
Another significant problem is the lack of enterprises for the
production of wind generators of various capacities and components
based on the most modern technologies. Therefore, investors in
tendering projects of a wind power plant (wind farm) are guided
by the use of expensive imported wind turbines. This increases
the cost of electricity, inhibits the development of wind energy, the
necessary solutions to reduce wind farms are the production of
wind turbines in the country, using local raw materials.
The work [4- 6] studied the formation of wind flows over the
territory of Uzbekistan and their features, due to the orographic
parameters of the territory and synoptic processes in the
atmosphere, affecting the characteristics of wind flows. When
designing wind turbines, it is necessary to determine the wind
potential of the area where construction is planned. Wind farms
(wind farms) are being built in places where the wind speed is
higher than 4.5m/s. Currently, six modern meteorological stations
operate in different regions of Uzbekistan to study the solar and
wind cadaster. One of the six modern weather stations is shown in
Figure 1.
Figure 1: Big solar furnace with the power of 1000 kilowatt Scientific-industrial association “Physics-Sun” Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan.

In meteorology, anemometers are used to measure wind speed. According to the principle of action, mechanical anemometers are distinguished, in which the movement of gas rotates a cup wheel or impeller, thermal anemometers, the principle of which is based on measuring the decrease in temperature of a heated body (usually an incandescent wire), and the operation of ultrasonic anemometers is based on measuring the speed of sound in a flowing gas depending on its speed. A cup anemometer is the most common type of anemometer, which is installed at a standard height of 10m see Figure 2 for measuring wind speed. As a rule, the heads of small wind turbines are located at a height of 5 to 50m. To determine the velocity vz (at a height of z m) at these heights, the approximation formula (1) is often used, which includes the standard wind speed us measured at a height of 10 m, namely [7].
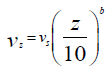 (1)
(1)where, vz is the average wind speed at an arbitrary height z, vs is the wind speed at a standard height.
Figure 2: A modern weather station installed in the Parkent region of Tashkent viloyat of Uzbekistan.

For open spaces, the parameter b = 1/7 = 0.14. The smaller the value of the parameter b, the less the loads experienced by the wind wheel blade in the lower and upper positions will differ. As you know, wind is a vector quantity, which, along with the average value of speed, is also characterized by an instantaneous value - a gust. That is, modern measuring instruments make it possible to measure not only the average wind speed values, but also the change in wind speed in a short time. In Figure 3 & 4 shows the results of experimental measurements of the gust and average wind speed at the Parkent weather station MHP MS4-12-1. They show the statistical nature of the change in these parameters over the course of a month, which should be taken into account when developing renewable energy sources.
Figure 3: Gust and hourly averaged wind speed values measured by the Parkent weather station MHP MS4-12-1 in the month of June 2013.
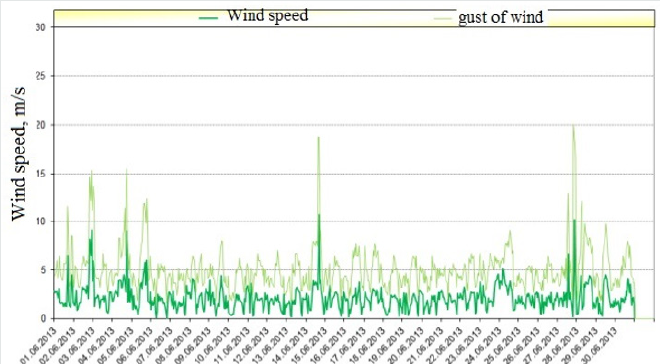
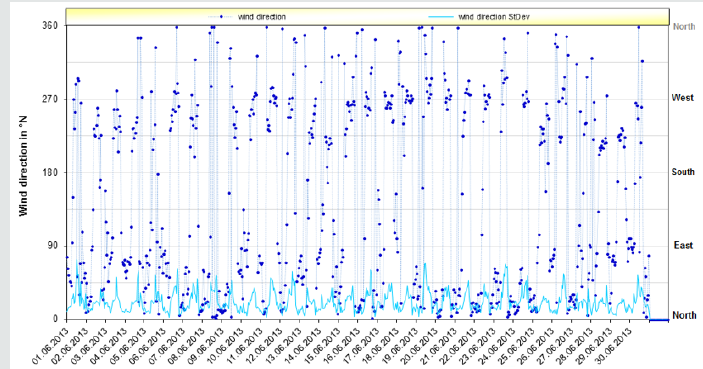
Figure 4: Wind directions measured by the Parkent weather station MHP MS4-12-1 in the month of June 2013 (wind direction - wind direction relative to the north, wind direction StDev - standard deviation of the change in wind direction within the measurement interval in degrees).
In 2010, to study the meteorological conditions at a selected site in the village of Yubileiny, Bostanlyksky district, a 52-meterhigh meteorological mast was installed. Anemometric devices for 1.5 years, recorded meteorological data around the clock with an interval of 10 minutes, which were subsequently processed in Germany according to a special program. As a result of the research, a pilot wind power plant with a capacity of 750kW was built in the village of Yubileiny, Bostanlyk district, Tashkent region (Figure 5). Based on the results of the data obtained, a project was developed, technical requirements for equipment were formulated, and an experimental wind turbine was built. The generated electric energy of wind turbines will be supplied to a single energy network.
To predict the generation of electricity from a grid or autonomous wind farm, it is necessary to assess the economic feasibility of wind farm efficiency. The basis for such estimates is the results of indicators of long-term monitoring obtained on the basis of real data. Wind turbine power generation data connected to the central network is recorded by a remote monitoring system. The monitoring results from October 2017 to October 2018 are shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6: Wind turbine electricity generation indicators with a capacity of 0.76MW (kW · h for months).
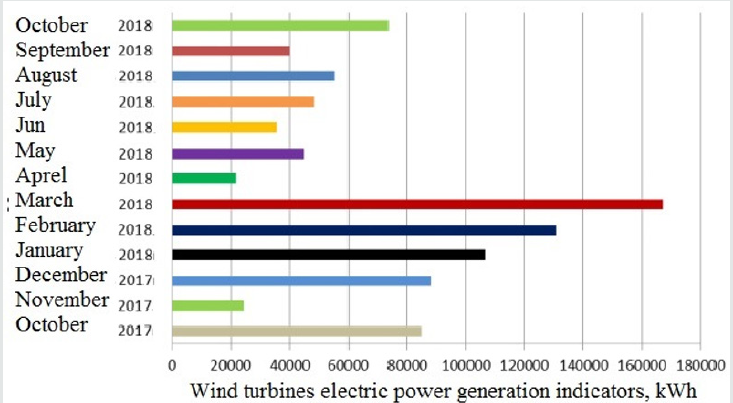
As can be seen from Figure 6, preserving the constancy of the
air flow rate, the generation of electricity increases. At the same
time, the analysis shows that the lower wind power generation is
explained as follows, if the wind speed is less than 4m/s, the wind
turbines will not generate electricity. At a wind speed of 14-15m/
s, a wind turbine generates 750kW of rated power. It should be
noted that in order to get a more complete picture of the station’s
operation, it is necessary to carry out at least one-year monitoring
of its operation.
The installation in the village of Yubileinaya, Bostanlyk
district of Tashkent region is the first experimental installation for
conducting research and monitoring wind turbine indicators, the
results obtained, which will be taken into account when designing
and constructing a wind farm in Uzbekistan. It is planned to build a wind power plant with a capacity of 200 megawatts (MW) worth
$1.8 billion at Kutchi pasture in the Gijduvan region of Bukhara
viloyat.
As part of this project, in September 2019, the ceremony of commissioning the wind speed meters of a huge object took place [8]. The foreign enterprise “Liaoning Leader Gijduvan Wayd Energy” has already collected 6,000 hectares of land for a major project in the area. The location of the selected area is considered optimal for sustained winds. This will play an important role in ensuring the high efficiency of devices that convert renewable energy into electricity. The masts of wind speed meters have a height of 120 meters. Upon completion of the study, several dozen masts will be built at this height at the first stage of the project with three large blades of 35 meters each. It is expected that the wind farm will be commissioned in the fall of 2020. The project cost is 240 million US dollars. It supplies electricity not only to Gijduvan, but also to some other areas.
Conclusions for the Chapter
In Uzbekistan, there are favorable conditions for the use of renewable types of energy, especially solar and wind energy [9]. A large solar furnace with a thermal power of 1000kW is operated here and small solar installations with concentrators of the type: parabola, parabolocylinder, Fresnel mirror concentrating system of various power are being built. In the Pap district of Namangan region, a photovoltaic station with a capacity of 130kW is operated in test mode. The efficiency of this FES is controlled by the staff of the International Institute of Solar Energy [10,11]. Much attention is paid to the use of wind energy in Uzbekistan. In test mode, a wind turbine with a horizontal axis of rotation with a power of 0.75MW is operated. Modern automatic weather stations have been installed in six regions of the country to determine the resources of solar and wind energy, as well as to predict the efficiency of solar and wind power plants [12].
References
- Arifov UA (1972) The development of solar technology in the USSR. Geliotexnika. p. 3-8.
- Krivtsov VS, Oleinikov AM (2003) Inexhaustible energy. Book 1. Wind power generators, Textbook, Kharkov: Nat. Aerocos University, “Kharkov Aviation Inst, Sevastopol: Sevast. Nat tech. Univ, Ukraine, pp. 400.
- Krivtsov VS, Oleinikov AM (2004) Inexhaustible energy. Book 2. Wind power generators, Textbook, Kharkov: Nat. Aerocos. University, “Kharkov Aviation. Inst, Sevastopol: Sevast. Nat tech. Univ, Ukraine, pp. 519.
- Daring VG (2010) Analytical forecast for the development of global wind energy. In: Derzky VG (Ed.), Energy and Electrification, №1, p. 53-56.
- Tazhiev UA, Kiseleva EI, Tajiev MU, Zakhidov RA (2014) Features of the formation of wind flows over the territory of Uzbekistan and the possibility of their use for electricity generation. Solar engineering p. 46-52.
- Zakhidov RA, Kremkov VM (2015) Potential of wind energy of Uzbekistan. Solar engineering Pp. 106-107.
- Zavarina MV (1971) Estimated wind speeds at altitudes of the lower atmosphere. Gidrometeoizdat p. 162.
- http://uza.uz/oz/society/zbekistondagi-ilk-yirik-shamol-elektrostantsiyasi-23-09-2019
- Faiziev Sh A, Sobirov Yu B (2017) Measurement of Solar Resources in Uzbekistan. Applied Solar Energy 53: 57-60.
- Matchanov HA, Avlokulov UA (2008) Development of draft national standards for satin energy in the Republic of Uzbekistan. Geliotexnika p. 73-74.
- Matchanov NA, Mirzabaev AM, Umarov BR, Malikov MA, Kamoldinov AU, et al. (2009) An experimental study of the characteristics of single-crystal and polycrystalline silicon photovoltaic modules in the climatic conditions of Tashkent. Geliotexnika p. 20-27.
- FaizievSh, Geder N, Lyupfert E (2013) Preliminary estimation of solar resources. ADB UZB TA 8008 Project Rep, Tashkent.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...






