Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2641-1768
Mini ReviewOpen Access
Juvenile Delinquency and It’s Psychological Implication-a Case Study of Pakistan Volume 4 - Issue 3
Muhammad Fahad Anwar1, Fatima Riaz2 and Mehran Idris Khan3*
- 1Assistant Professor, Department of Law, University of Sahiwal, Pakistan
- 2Assistant District Public Prosecutor, Pakistan
- 3Research Associate, School of Law, Dalian Maritime University, China
Received: August 01, 2020; Published: August 11, 2020
Corresponding author: Mehran Idris Khan, Research Associate, School of Law, Dalian Maritime University, Dalian 116026, Liaoning Province, China
DOI: 10.32474/SJPBS.2020.04.000186
Abstract
According to common law-the legal dispensation system used in most countries across the world, including Pakistan-two fundamental components are required to prove the commission of a crime: firstly, actus reus and secondly mens rea. In general, the first of these two-the actus reus-is the physical act (or omission) of committing the crime. The second-mens rea-is the necessary intent to prove that the alleged perpetrator wanted to commit the crime. Besides, these demonstrate potential psychological impacts over the societies across the world, which is focused on this study. The study adopts qualitative means to examine the psychological implications of Juvenile delinquency in Pakistan and provide insightful understanding for the readers.
Keywords:Juvenile; Psychological implication; Pakistan; Legal developments
Introduction
Human nature a complex topic since the earlier ages. Factors, conditions, circumstances, helping in the evolution of human nature. The different persons are acting differently in the same situation, making us wonder. The DNA composition of every man making us all perplexed. The same number of chromosomes millions of genes and genetic codes all contributing to the evolution and development of human psychology. Youngs, children, minors have always been the apple of the eye of the legislature. From the base of fundamental rights having a special place in principles of the policy of the supreme law of the land. “Doli incapax” the Latin term referring to the limelight fact inability of young to do the crime [1]. However, the question arises in societies like Pakistan, where we see young offenders involved in all sorts of crimes. Dealing with them, the legislature in Pakistan had to provide an act Juvenile Justice System Act, 2018 [2]. So now the hypothesis we can give is that the adolescent delinquency is mainly depending on the psychology of the offender. Factors contributing to it are Age, Social Status, Abusive Culture, Inequality and Partiality, Social Circle, Poor Education System, Social Factors, Economic Factors. The present study examines the juvenile delinquency and its psychological implication as a general and taking Pakistan as a case study. It presents the background and introduction of the subject matter in section one, provides an in-depth discussion in section two and concludes the discussion in section three with proactive findings with some appropriate suggestions.
Discussion
Keeping in focus the psychology is the heart of every juvenile case, so, following special procedure is introduced by the legislature in Juvenile Justice System Act, 2018:
a) Report about juvenile psychology/ economic and social
status by the probation officer.
b) Trial to be concluded in four months to prevent them from
the agony.
c) No trial with adults.
d) No arrest or detention in jail.
e) Special committee to formulate a reformative judgement
in a case where needed.
f) No fetters or capital punishment.
g) The expense of litigation with medical treatment by the
state.
h) Immunity of publication of name and facts of juvenile.
Furthermore, the height of delight is that the punishment awarded under this act will never act as conviction in case of jobs and future life of juvenile. It means an act done in the rage of hormones will not become repent/regret in future. Legislature wanted to secure the future of juveniles, but to the contrary, it is giving dirty minds of societies to get their work done without getting their hands dirty. The hands of the juvenile are tainted with the filth of crime; their minds are tortured with the agony of offences and trials; however, they are getting away easily. The upcoming decades will lead us to see the fact that all crimes will be done by juveniles making it impossible to track the real offenders as juveniles are never to be tortured for retraction of confession. Latest amendment sections 82 and 83 in Pakistan Penal Code, 1860, giving immunity to juvenile again the very nature was to safeguard the psychology of juveniles [3]. However, the honey of immunity and the general exception is attracting the thugs of society to attack the delicate minds and incorporate them with microchips of crimes, infecting their minds and softness.
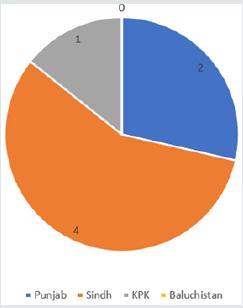
According to a Society for the Protection of the Rights of the Child (SPARC) report [4], published in 2012, in Pakistan 1500 to 2000, juveniles were imprisoned. This figure, however, excludes thousands of under trial juveniles whose numbers are unknown. Figure 1 presents an overview of the Juvenile detention facilities as provided by the governments of various provinces of Pakistan-it provides that Sindh province tops in the provision of such facilities, i.e. four centres; Punjab provinces adhere two centres; Khaybar Pakhtunkhwa (KPK) demonstrates one facilitation centre which is not functional; while Baluchistan province does not have any such facility [5].
Conclusion
Greater care is to be taken while dealing in such cases; penalties/ punishments/ reformations are to be awarded, keeping in view psychology of juvenile along with other factors of the case. Every case is to be dealt with individually keeping the facts in mind the future of juvenile can help us to determine the future of Pakistan.
Acknowledgement
Miss Fatima Riaz and Mr Fahad Anwar contributed with the writing up the initial draft. Dr Mehran Idris Khan contributed to the general guidelines, proofreads, revision, suggesting appropriate changes, and deals with the correspondence.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there no potential conflict of interest in this article among the authors.
References
- Rasool S (2014) A Justice that is Juvenile.
- (2019) Ministry of Law. The Juvenile Justice System.
- (2005) Ministry of Law Pakistan Penal Code (Act XLV of 1860).
- (2020) SPARC Confirmed cases below the age of 20 by gender.
- Farrukh A (2018) Pakistan’s Juvenile Justice System: The Deplorable Treatment of Juvenile Offenders.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...