Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2641-1709
Research Article(ISSN: 2641-1709) 
Rare Causes for Foreign Body Sensation in Throat: When Old Outlook Meets New Novelty Volume 4 - Issue 4
Sphoorthi Basavannaiah*
- Department of ENT, Subbaiah Institute of Medical Sciences, India
Received:June 18, 2020; Published: July 02, 2020
Corresponding author: Sphoorthi Basavannaiah, Assistant Professor, Department of ENT, Subbaiah Institute of Medical Sciences, India
DOI: 10.32474/SJO.2020.04.000192
Abstract
Introduction: Foreign body sensation in throat is one of the commonest presentations in ENT. It can be simple & easy to treat but at times can be complex & alarming. Here, is a study exploring the uncommon causes of this symptom which is taking over the charts clinically in the routine mundane of life.
Aims & Objectives: To ascertain rare causes for foreign body sensation in throat in all possible mediums and how patient’s ideologies sum up to instilled seeds of cancer in their minds.
Methodology: 196 patients with rare causes for foreign body sensation in the throat over a year was clinically assessed, evaluated & treated after analyzing the source for the condition.
Results: Nearly 40% of new novelty causes i.e., GERD & “EpiConTon” superseded old outlook causes with female preponderance and stress topping the list of risk factor.
Conclusion: Time is said to heal things but life at times could throw on us new challenges & consequences in this present changing trends and lifestyle. People should crave only for a healthy living and happy state of mind in this taxing and thorny life.
Keywords: Globus pharyngeus; Eagle’s syndrome; EpiConTon; Laryngopharyngeal reflux; foreign body sensation
Introduction
Foreign body sensation in the throat is a vague symptom at times, but can be an alarming sign as well. There are different perspectives to this symptomatology which can range from a simple Globus sensation syndrome to complicated, malignant Laryngeal mass. Though it looks as a simple presentation, it has diverse branches in a variety of fields of medicine that is yet to be explored or in the process of being discovered. Usual causes for this symptom have been come across on day to day basis and are treated accordingly [1]. In this study, I have tried to bring to focus the uncommon causes for foreign body sensation of throat which these days have become common. Plus, also to highlight & emphasis on one of the finding/ cause which I have encountered in patients nowadays when rest of the ENT examination seems within normal limits particularly in my short practical experience and exposure so far, that is “EpiConTon”. As I have not come across any such study done so far in my review of literature for foreign body sensation in the throat.
Aims & Objectives
a) To list out rare causes for foreign body sensation in the
throat encountered at ENT OPD.
b) To group the rare causes based on which category they
belong to.
c) To look for if these causes have an association with the
neuropathic pain
d) To find out gender and age-group predilection of the
causes that lead to this symptom.
e) To categories the risk factors which have synergism with
these causes that lead to this symptom.
Objectives: To highlight the specifics and sometimes the “out of the box” approach for the various probable causes for foreign body sensation in the throat in Indian population as it is at times way beyond “mystery of malignancy”.
Materials & Methods
Study design: Descriptive study.
Place of study: This study was taken place at Subbaiah Institute of Medical Sciences (SUIMS), Shimoga, Karnataka which is a Tertiary Care Hospital.
Study period: 1 year (October 2018 to September 2019). Selection criteria: A random sample of 196 patients (pts) who consulted the ENT outpatient department with rare causes for foreign body sensation in the throat were clinically assessed and evaluated and a provisional diagnosis was made. Following which, necessary laboratory & radiological investigations were considered, based on which treatment protocols were executed in all the patients mainly conservatively.
Inclusion criteria
a) Only adults were considered for the study.
b) Age group included in this study was between 18 to 48 years.
Exclusion criteria
a) All usual causes for foreign body sensation in the throat were omitted from the study.
b) Age group excluded from the study were < 18 years & > 48 years of age.
c) Children were excluded from the study.
Procedure of the study
Over a period of 1 year, a random sample of 196 pts who consulted ENT OPD with rare causes for foreign body sensation in the throat were clinically evaluated after taking a detailed & thorough history as well as complete ENT Head & Neck examination. Foreign body sensation in the throat is one of the common symptomatology while presentation in ENT OPD. In this study, 4 rare causes for foreign body sensation in the throat were considered. They are Globus pharyngeus (GP), Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) or Gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD), Eagle’s syndrome (ES) or Styalgia and “EpiConTon”: It is Epiglottis touch/ Connect the base of Tongue.
Epi ConTon: Epiglottis is the leaf like projection or flap which is present at the base of tongue normally. It has a very important role in the physiology of deglutition. It prevents food from entering the windpipe and lungs. During breathing, it stands open allowing air into the larynx. This terminology was given by me in this study to address this condition. This is the new found endoscopic picture by me during laryngoscope examination. Patients with this clinical presentation are seen especially in females presenting with foreign body sensation in the throat, diffuse pain all along the posterior 1/3 of tongue. I have not across of this finding incidentally while on laryngoscope examination in patients with Throat and Head & Neck complaints. This clinical finding is not being addressed in literature data by far. After a thorough Ear, Nose, Throat with Head and Neck examination, a probable diagnosis was made. Following which, necessary laboratory & radiological investigations were considered, based on which treatment protocols were executed in all the patients mainly conservative line of treatment was apt in this study.
Globus pharyngeus/ globus sensation syndrome: It is the persistent feeling of something lodged in the throat. All patients with Globus pharyngeus showed no abnormality on ENT examination. A complete and in depth history was taken from the patient especially personal history. Usually in patients with Globus sensation, they tend to have a gross emotional intensity and their symptoms are more or so related to this outbreak. They were directed towards complete hemogram test. Based on the results, treatment was been advised. Mainly dietary implementation+ lifestyle modifications+ advisory counselling were given to these patients. In treatment, Haematinics along with Multivitamins were prescribed and before the start 1 dose of anthelminthic was also given. In this case, reassurance to the patient plays a major and a very crucial role.
Gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD)/ laryngopharyngeal reflux disease (LPR)/ Acid reflux disease: It is a chronic disease when the bile flows back into the esophagus that causes irritation of the mucosal lining and thereby leading to symptomatology. While in GERD pts, mainly lifestyle adaptations with dietary changes were advised and for temporary relief, antacids were given. Most of the patients were advised to follow a routine dietary course to stay free of reflux symptoms. The patients were also asked to follow these modifications on routine basis for wanting things beyond temporary relief in their symptomatology. “Dwell in the twelve”, I have put up 12 points that the patient has to follow in their routine basis to overcome GERD. Judicious follow of these points has been found useful for Migraine as well. The 12 points are mentioned below in the discussion.
Eagle’s syndrome/ Styalgia/ Styloid syndrome/Stylohyoid syndrome: It is a rare sudden, sharp nerve like pain in the jaw region, Temporomandibular joint region, back of throat, base of tongue and which is triggered by swallow, movement of jaw, turning the neck. In Eagle’s syndrome, when this elongated styloid process impinges in the tonsillar fossa, pt. complains of foreign body sensation in the throat with in some neuropathic pain. Patient is explained about the condition. For pain relief, drugs given with combination of analgesics with sedatives such as Gabapentin with Tramadol, Pregabalin & Tryptomer. The doses are calculated as per the weight of the patient/ day basis. They are also advised to take Multivitamins along with the treatment. These medications are only for temporary relief and should not be taken on continuous basis to avoid from its prolonged side effects. Tonsillo-styloidectomy is the surgical procedure done, but only gives relief to the impingement caused by the styloid process with no relief from the neuropathic pain point of view. Hence, mostly patients are not advised surgical management as it very gross and painful postoperatively. Similarly pts with EpiConTon, they present with foreign body sensation in the throat, neuralgic pain. As mentioned above, the same treatment is given for neuralgic pain which is temporary relief. Usually, I do not suggest surgical management for such neuralgic pain. Some pts have responded to Injection of local anaesthesia like Lignocaine at the root of the nerve origin at the base of anterior pillar and also all along it for pain relief done on OPD basis. Here, injection is given to block the plexus of Glossopharyngeal nerve that is spread all along the posterior 1/3 of tongue and posterior pharyngeal wall. Injection is given at the root of the nerve origin as mentioned above. On follow up, patients showed good response to treatment provided to them. Psychological factors play a major role in these conditions. Increased reporting of stressful life events prior to development of symptoms have an exacerbation of symptoms during times of emotional intensity. Informed written consent were taken from the patients during the study period. Institutional Ethics Committee has given clearance before the start of the study.
Results
The results of the study are depicted below Figures 1-7.
Figure 1: Video Laryngoscope (indirect) view of the larynx in the OPD showing the larynx and also the epiglottis is seen touching the base of tongue-“EpiConTon”.
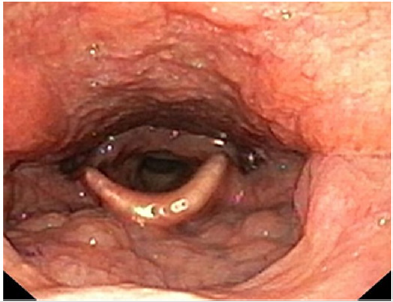
Figure 2: “Pie in 3D representation” showing encountered rare causes for foreign body sensation in the throat.
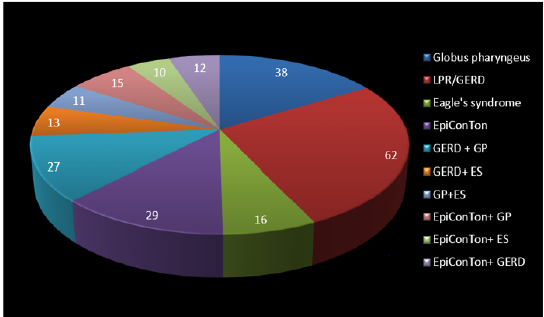
Figure 3: Showing the “3D cylinder depiction” of various categories represented for rare causes for foreign body sensation in the throat in this study. They are O+N: (GERD+ GP= 27, GERD+ES= 13, EpiConTon+ GP= 15, EpiConTon+ ES= 10), N+ N: (EpiConTon+ GERD= 12), O+O: (GP+ES= 11).
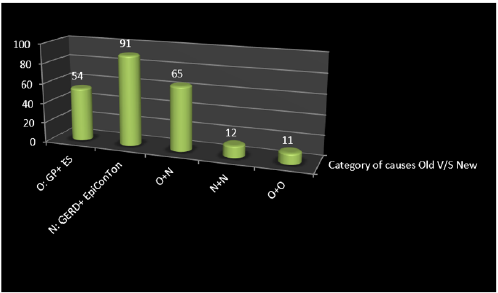
Figure 4: “Exploded doughnut depiction” shows if the rare causes considered in study for foreign body sensation in the throat are associated with the presence of neuropathic pain or not. “YES”: 106 (ES-16 + EpiConTon-29 + GERD with ES- 13 + GP with ES- 11 + EpiConTon with GP- 15 + EpiConTon with ES- 10 + EpiConTon with GERD- 12). “NO”: 127 (GP- 38 + GERD- 62 + GERD with GP- 27).
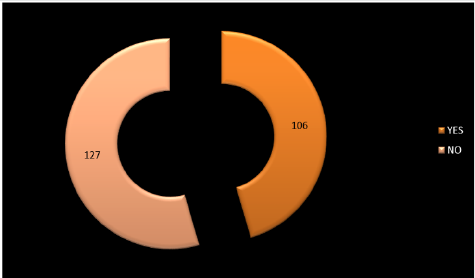
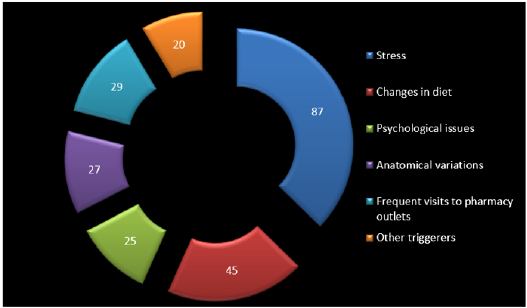
Figure 7: Exploded doughnut representation showing the probable risk factors that could be associated with foreign body sensation in the throat.
Discussion
Foreign body sensation in the throat is an ambiguous symptom at times, but can be an alarming as well. There are different perspectives to this symptomatology which ranges from a meek Globus sensation syndrome to malignant Laryngeal mass. Though it looks as simple the clinical presentation, it has diverse branches of presentations among population. There are many aspects for it source of symptomatology which are yet to be explored and are in the process of discovery [2]. Usual causes for this symptom have been a day to day encounter in the ENT OPD. In this study, I have tried to bring to focus the uncommon causes for foreign body sensation of throat which these days have become common. 4 such unusual causes that have been seen very common in the ENT outpatient department in the hospital so far is considered in this study. Based on history & examination, diagnosis of Globus pharyngeus is made. Patients should be asked for how long are they facing this feeling and to describe it. The presenting complaint may be described in various ways like a lump or ball in the throat, sticky sensation in the throat, some vague swelling moving up and down the throat etc. The symptoms often come by and go but constant or worsening symptoms are more of concern. The location of symptoms and the region involved for this feeling is central and suprasternal [3-5].
Pain on swallowing is not typical of globus. Note down if any reflux symptoms, throat clearing, cough or hoarseness of voice. Consider anxiety and ask about other symptoms of psychological distress including other physical symptoms such as palpitations, poor sleep and feelings of panic. Although cancer very rarely presents as globus pharyngeus. It is important to ask about red flag symptoms such as persistent hoarseness of voice, progressive dysphagia or dysphagia for solids, pain on swallowing, haemoptysis and weight loss [6-8]. Patients consuming alcohol or tobacco in excess leading to worsening of globus pharyngeus must be considered for referral to secondary care. As in every consultation the patient’s notions, apprehensions and prospects should be considered as most of them are worried about cancer. In general practice, a full examination of the head and neck is important [1]. The neck should be examined for thyroid gland and cervical lymph nodes. Oral cavity & oropharynx should be considered for any ulcerations or asymmetric features, which may suggest malignancy. Nose should be examined for any sort of inflamed mucosa, polyps or pus, any post-nasal discharge which has to be considered as a cause for globus pharyngeus. An abnormal neck or oral examination should prompt urgent referral to secondary care [9]. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)/ Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) occurs when contents from stomach frequently flows back into esophagus. The mucosal lining of the esophagus can get irritated and stimulated by the backlash or acid reflux of the gastric contents. It is also called acid regurgitation. It has now become the present day most common health concern in India due to urbane and deluxe lifestyle. It is very soon trending on the disease charts of occurrence due to the current regime picks [10,11].
Many people experience acid reflux from time and again these days. GERD is mild acid reflux that occurs weekly twice while moderate to severe acid reflux that occurs weekly once. Most people can manage the uneasiness of GERD with regime variations and over-the-counter medications. But few people with GERD may need stronger medical therapy to relieve them of their symptoms [12,13]. Common signs and symptoms: retrosternal sensation in the chest/ chest burn/ heartburn usually after eating, which might be worse at night, chest pain, dysphagia, reflux of gastric contents, sensation of lump in throat. If there is presence of acid reflux at night, then there may be: chronic cough, laryngitis, new or worsening asthma, disrupted sleep. Complications like esophageal stricture, esophageal ulcer, and Barrett’s oesophagus. All these patients have an increased risk of esophageal cancer [13]. GERD is found to be very common these days. In the present day, when minting money has become the prime focus, very often health takes a backseat which is ignored and neglected. Hence it is better to avoid the triggering factors as far as possible and provide relieving factors at the earliest. Adapting these lifestyle modifications or measures on day to day scenario, has brought in lots of health benefits which has indirectly brought in a positive impact in the way of living and improving the way of life [14,15]. Following this sincerely on routine basis, can withhold and minimize the necessity of any medications if required and this can help lead a healthy and fit life. The points that fall under “dwell in the twelve” [16,17] are:
a) Avoid certain food such as- dark chocolates, cheese,
caffeine, nicotine, egg whites, corn, sea food, citrus fruits,
onions, artificial sweeteners & food colorings, sugary foods,
red wine, alcohol, milk containing sweets, avocado, aerated
drinks, any kind of fast food. Prefer foods rich in dietary fibers
and natural sugars, all green & green leafy vegetables, cereals &
pulses, dates, apples, milk.
b) Use fresh fruits and vegetables (avoid frozen foods).
c) Intake of food either solids/ liquids at frequent intervals
in the form of small bites/ bouts with a gap of < 3 hours and eat
mints instead of chewing gum. Do not skip meals (as in fasting
/ dieting/ intermittent fasting). Have timely intake of food (4
times/ day: 9AM, 1PM, 4.30PM, 8PM)
d) Avoid eating or eat less of spicy/ sour/ oily/ cold/sweet
food stuff (do not use items directly out from fridge).
e) Do drink water before food (i.e. 15-20mins) is best and
important rather than after food. Drink least of 3-4 liters of
water / day.
f) Avoid /quit/ reduce smoke/ alcohol/ tobacco or gutka
chewing/ supari etc.
g) Avoid stress as much as possible. Whenever stress hinders
your path, try to change them if possible or else change the way
you react to stress or find an alternative to face it and get rid of
it in a nice way.
h) To relieve from stress- relax with meditation, guided
imaginary yoga and divert focus on one task at a time. Taking
up relaxing therapy to rejuvenate self and mind whenever
possible- activities such as massage, painting, listening to music
etc. (anything that makes you feel better and happy).
i) Reduce/ lose weight - either by hitting the gym or regular
exercises (run or brisk walk for 45 minutes- 1 hour / day).
Exercise 30 minutes 3 times a week to relieve distress/ stress
and also to maintain healthy weight and body. Cut down on
carbs and increase intake of proteins(less intake of rice and
prefer roti’s/chapattis instead).
j) Sleep for adequate of 7-8 hours (have a regimented sleep
pattern and do not lie down immediately post lunch or post
dinner and stay awake for a minimum of 2 hours before going
to bed or lying down especially during night times (when there
is less chances of body exertion or exercise). Provide head end
elevation of 15-30 degrees while asleep or during resting hours.
k) Try to avoid unnecessary intake of medications (as
pharmacy outlets have become a “mini” hospitals to provide
medications at their own will and wish).
l) Think and be positive in any possible situation, this is of
utmost importance to lead a peaceful and healthy life.
Eagle syndrome is a rare condition characterized with sudden, sharp, shooting nerve-like pain in the jaw region, around temporomandibular joint area, back of the throat, base of the tongue and around ear, neck and /or face. Impingement or entanglement are stimulated as nerve connections have to pass through neck which seems the bridge between brain and body. This condition is caused by an elongated styloid process and/or calcification of stylohyoid ligament that interferes with functioning of neighboring regions in the body giving rise to pain. About 4% of the population have styalgia among them around 4% will give rise to symptoms Hence, the incidence of this syndrome may be about 0.16%. Patients with this syndrome fall under 30 and 50 years of age with male: female ratio ~ 1:2 [18,19]. This condition is also accompanied by dysphagia, foreign body sensation in the throat, pain is triggered on chewing, swallowing, turning neck on one side, touching the back of throat and movement of jaw. There can be association of tinnitus sometimes. Its classic presentation, is only on one side but can rarely present on both the sides. It could either occur spontaneously or can arise after birth. Usually normal stylohyoid process is 2. 5–3 cm in length, but length if longer than 3 cm, it is classified as an elongated styloid process [20,21]. In vascular type of Eagle syndrome, elongated styloid process comes in contact with internal carotid artery. Here, turning the head can cause compression of artery or a tear inside the vessel restricting blood flow and can potentially lead to a transient ischemic attack or stroke. Sometimes, it can compress internal jugular vein that can lead to increased intracranial pressure [22].
Diagnosis is suspected when a patient presents with symptoms of classic form that is unilateral neck pain, sore throat or tinnitus. Sometimes, tip of styloid process is palpable in the tonsillar bed. The diagnosis of the vascular type is more difficult and requires expertise. They can be relieved by infiltration of lidocaine into tonsillar bed. Because of close proximity of vascular structures in this area, this procedure should not be considered with much care [20,23]. Imaging is the diagnostic for styalgia other than clinical palpation. Picturing styloid process on 3D reconstructed CT scan is the suggested imaging technique. The enlarged styloid process may be also visible on an orthopantogram (OPG) or lateral soft tissue X ray neck or X-Ray neck( Towne’ s view) [22,24]. Partial styloidectomy is the preferred approach for any form of styalgia. In case to prevent neurological complications, repair of a damaged carotid artery is essential. Regrowth of the styloid process as well as relapse being a common occurrence is controversial. Medical management may include the use of analgesics with sedatives and anti-inflammatory medications, antidepressants, and/ or corticosteroids. The success rate for treatment (medical or surgical) is about 80% [18,21]. Among the rare causes for foreign body sensation in the throat in 233 pts, the top 3 causes based on the frequency of occurrence in this study are: GERD in 62 pts that is 27%, Globus pharyngeus in 38 pts that is 16% and EpiConTon in 29 pts that is 12%. So, among them the tendency for new category of causes among these 3 is nearly 40% pts. With changing trends and lifestyle reforms, new category of rare causes for foreign body sensation in the throat is seen taking over in the present scenario of population [25].
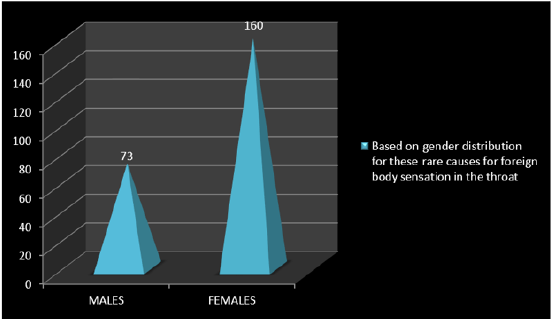
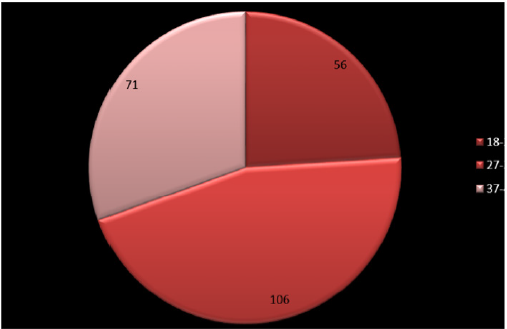
In this study, 5 different categories are formulated based on the rare causes for foreign body sensation in the throat. The 5 categories are: that is Old (O) and New (N).O (Globus pharyngeus (GP) & Eagle’s syndrome (ES), N (GERD & EpiConTon), O+N (GERD+ GP, GERD+ES, EpiConTon+ GP, EpiConTon+ ES), N+N (EpiConTon+ GERD) & O+O (GP+ES). Of which 91 pts belonged to New category that is in 39%, next is 65pts in O+N category that is in 28% and lastly 54 pts belong to Old category that is 23%. This shows that new category is having far more pts compared to the other category. This infers that the new generation outlook is making its way in this new aged modern era. Along with foreign body sensation in the throat, the next complaint was neuropathic pain. Neuropathic pain is continuous or episodic abnormal sensations from either a painful or non-painful stimuli that can occur as a result caused by the damage or disease affecting the somatosensory nervous system. It is different from neuralgia, as in it does not cause pain due to damaged or irritated nerve. In this study 45% showed presence of this pain among 106 pts and 55% showed no presence of pain among 55%. The ratio of yes: no for the presence of neuropathic pain is nearly 1:1. As there was no abnormality detected on ENT examination, except for these 2 complaints. Hence neuropathic pain presented as secondary symptom in this study. As only adults were considered for the study between age group of 18 to 48 years of age. Among them, 31% were males that is in 73 pts and 69% is females that is in 160 pts. The ratio of M: F is 1:2. Of the 3 categories of age group, 46% belonged to 28-38 years of age in 106 pts, 30% belonged to 38-48 years of age in 71 pts and 24% belonged to 18-28 years of age in 56 pts. The age group most affected is 28-38 years, where people are in the rat race to make money, leading a very stressful and unhealthy life, where in health is totally neglected and ignored.
Coming to the probable risk factors that could be encountered in this study where these reasons play a synergistic role that leads to this diagnosis. Among them, 37% showed stress to be the most probable risk factor in 87 pts. Next down the line are faulty and unhealthy eating habits/ dietary changes in 19% that is in 45 pts. While, the rest of the risk factors fall under < 13% of the total pts. These risk factors are additive in nature and always form the iceberg of any condition. Habitual consumption of spirit & smoke were purposely not accounted in the study, as actually it was not found to have any role to play in this study. As per literature search, I have not come across any such study which focuses on the rare causes for foreign body sensation in the throat. As apart from this, I have also come across “EpiConTon” in many of my patients which by far has not been reported in the data. This condition is one of a kind, as we all know that epiglottis which is normally present at the base of the tongue has its role in deglutition. But, epiglottis touching the posterior third of tongue not only stimulates the nerve pathway but has its effects that are not just limited to the base of tongue but also to posterior pharyngeal wall as well.
Conclusion
This study was mainly to introduce to the new encounter “EpiConTon” in my early practical experience in the field of medicine. This study was also to bring into light the uncommon causes of the common symptom “lump like” sensation in the throat which is taking the new plunge which is now presently encountered. To take out the notion from the minds of Indian population that even though there is no abnormality detected but still it is very essential to find the root cause for this symptom. It is not always “cancer” that is dreadful, but even this symptom can sometime be an alarming sign for some hidden critical situation. As the fact is known that Head and Neck cancer are one of the major reasons for mortality in India, due to which they end up with a consultation when this symptom is being encountered. Indian mentality is known to believe more of mouth to mouth bit over their self- experience. The only thing ticking in their minds is that while there is no compromise in their basic necessities in life such as respire, swallow and speech, then why is it still they are facing such a symptom. Plus, with the advent of science & technology, people prefer not just prefer “media popping”, “hospital hopping” along with “pharmacy shopping” till they are satisfied and convinced. So, these days along with the medications it is also become important to study the psychology of the patient and meet the needs of patient’s expectations over the experience & exposure that is actually attained by the health care takers.
References
- Foden N, Ellis M, Shepherd K, Joseph T (2014) A feeling of a lump in the throat. BMJ.
- Lee BE, Kim GH (2012) Globus pharyngeus: a review of its etiology, diagnosis and treatment. World J Gastroenterol 18(20): 2462-2471.
- Subramanya BT, Basavannaiah S (2018) Globus pharyngeus in women: Observations and Opinions. International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery 6: 1462-1467.
- Oridate N, Nishizawa N, Fukuda S (2008) The diagnosis and management of globus: a perspective from Japan. CurrOpinOtolaryngol Head Neck Surg 16(16): 498-502.
- Liu SH, Wang Y, Zhang RH (2005) Diagnosis and treatment of 23 cases with stylohyoid syndrome. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue 14: 223-226.
- Jones D, Prowse S (2015) Globus pharyngeus: an update for general practice. British Journal of General Practice 65(639): 554-555.
- Mitchell S, Olaleye O, Weller M (2012) Review: current trends in the diagnosis and management of globus pharyngeus. Int J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1(3):57-62.
- Hill J, Stuart RC, Fung HK (1997) Gastroesophageal reflux, motility disorders, and psychological profiles in the etiology of globus pharyngis. Laryngoscope 107: 1373-1377.
- Kortequee S, Karkos PD, Atkinson H (2013) Management of globus pharyngeus. Int J Otolaryngol.
- Siupsinskiene N, Adamonis K, Toohill RJ (2008) Predictors of response to short-term proton pump inhibitor treatment in laryngopharyngeal reflux patients. J LaryngolOtol 122: 1206-1212.
- Park KH, Choi SM, Kwon SU (2006) Diagnosis of laryngopharyngeal reflux among globus patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134: 81-85.
- Tokashiki R, Funato N, Suzuki M (2010) Globus sensation and increased upper esophageal sphincter pressure with distal esophageal acid perfusion. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 267: 737-741.
- Chevalier JM, Brossard E, Monnier P (2003) Globus sensation and gastroesophageal reflux. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 260: 273-276.
- Lee JW, Song CW, Kang CD (2000) Pharyngoesophageal motility in patients with globus sensation. Korean J Gastroenterol36:1-9.
- Moser G, Wenzel Abatzi TA, Stelzeneder M (1998) Globus sensation: pharyngoesophageal function, psychometric and psychiatric findings, and follow-up in 88 patients. Arch Intern Med 158(12): 1365-1373.
- Basavannaiah S (2017) Case study of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD) v/s Migraine: Do they mingle or it is a myth. International Journal of Advanced Research 9: 1051-1061.
- Cathcart R, Wilson JA (2008) Lump in the throat. ClinOtolaryngol 32(2): 108-110.
- Aydin E, Quliyev H, Cinar C (2018) Eagle Syndrome Presenting with Neurological Symptoms. Turk Neurosurg 28(2): 219-225.
- Ford CN (2005) Evaluation and management of laryngopharyngeal reflux. JAMA 294(12): 1534-1540.
- Malik JN, Monga S, Sharma AP (2018) Stylalgia Revisited: Clinical Profile and Management Iran J Otorhinolaryngol 30(101): 335-340.
- Petrović B, Radak D,Kostić V (2007) Styloid syndrome: a review of literature. SrpskiArhivZaCelokupnoLekarstvo 136 (11-12): 667-674.
- Saccomanno S, Greco F, De corso E (2018) Eagle’s Syndrome, from clinical presentation to diagnosis and surgical treatment: a case report. ActaOtorhinolaryngol Ital 38(2): 166-169.
- Ceylan A, Köybaşioğlu A, Çelenk F (2008) Surgical treatment of elongated styloid process: experience of 61 cases. Skull Base 18(5): 289-295.
- Yavuz H, Caylakli F, Yildiram T (2008) Angulation of the styloid process in Eagle’s syndrome. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 265: 1393-1396.
- Harar RP, Kumar S, Saeed MA (2004) Management of globus pharyngeus: review of 699 cases. J LaryngolOtol 118(7): 522-527.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...