Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2638-6003
Review Article(ISSN: 2638-6003) 
The Role Effectiveness of Physical Activities on Mental Disorders in Students with Low Mobility Using General Health Questionnaire (Ghq) Volume 1 - Issue 2
Vahid Bakhshalipour1* and Siavash Khodaparast Sareshkeh2
- 1Sama technical and vocational training college, Islamic Azad University, Lahijan Branch, Siyahkal, Iran
- 2Department of Physical Education and Sport Science, Lahijan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Guilan, Lahijan, Iran
Received: April 24, 2018; Published: May 02, 2018
Corresponding author: Vahid Bakhshalipour, Sama technical and vocational training college, Islamic Azad University, Lahijan Branch, Siyahkal, Iran
DOI: 10.32474/OSMOAJ.2018.01.000107
Abstract
Today, the emergence and growth of mental disorders are more noticeable in the student population due to the changes in health conditions of the world. Therefore, the purpose of this study was examining the role effectiveness of physical activities on mental disorders in students with low mobility using General Health Questionnaire (GHQ). The study was a causal-comparative research and has been conducted through the field method. The instrument was included the General Health Questionnaire-28 (GHQ-28). The statistical sample was included 430 male and female physical education and non-physical education students. The collected data was analyzed by descriptive and inferential statistical methods and analytical tests. The results showed that there was a significant difference between athlete and non-athlete students in all variable components of this study in two groups (P<0.05). It seems that regular physical activity can play an important role in students’ physical and mental health and students who participated in fitness and exercise programs have reported that their attitude and efficiency had a good state. Therefore, the increase of motivation through culture and the promotion of public awareness about the benefits of physical activity can be considered as one of the options for the development of the student sport.
Keywords: Anxiety; Social Function; Physical Problems; Depression; Physical Activities
Introduction
Today, the poor movement that has been created as a result of tremendous improvements in technology and mechanization of life and different jobs affects lifestyle in human societies. These very serious changes have had profound effects on human relationships at different levels of family and relationships with friends [1]. If we look at human’s physical construction, we will realize that human need naturally different kinds of physical activities for his/her entire development and evolution and the lack of adequate mobility and the lack of proper physical activities will disrupt different body systems. This great development in terms of health and well-being is one of the most important problems of today’s human [2]. This is very important for students, especially for students who are studying in a Master’s degree. Students should have a physical and mental health due to their role in social, cultural, and economic structures and their preparation to participate in social activities [3]. Today, the World Health Organization (WHO) considers a multidimensional concept for the concept of health multi-dimension and knows it as a positive concept based on the interests of individual and social sources and physical abilities. The WHO expresses that health is the welfare state and mental, physical, and social well-being and it is not only the lack of disease or body defects [4]. According to the definition of this organization, Health have physical, social, mental, emotional, and spiritual components. All five components have the interaction with each other for a healthy and strong person, so that if we give up one of them, we will be out of balance and our health will suffer in all domains [5, 6]. Therefore, dimensions of this definition (mental, physical, and social wellbeing and not merely the lack of disease) have the interaction with each other and these dimensions cannot be distinguished with a clear boundary [7]. There are indicators for the physical health and social welfare in many countries that those are reviewed and revised every few years, but the complexity and difficulty of definition often leads to neglect and ignore this in mental health [8]. The lack of mental health causes that a person suffers pains and physical and emotional symptoms such as isolation, headache, worry, anxiety, difficulty in falling asleep, and daily dysfunction [9]. Studies show that one of every two people will be prone to depression, so studies about improvement of mental health and its related factors are the most important studies in psychology [10]. In past decade’s huge changes were in the industrial world and considerably surround the lifestyle of many human communities. This has caused people to reduce physical activities, and have problems and diseases such as obesity, muscle weakness, cardiovascular and respiratory disease [11].
However, due to developments on the world health situation there is less risks to face this kind of problems. The considerable problem is emergence and growth of mental disorders .Purpose of mental health is the certain aspects such as human intelligence, mind and thought. According to Kameo someone has mental health, that who has no symptoms of anxiety and disability, able to establish communication with others and able to deal with the pressures of life [12]. We can found that the need for research in field of mental health and the survey of the effective factors on it is necessary with a look at the implications of urban lifestyle, apartment house, and the mechanization of societies in recent years and its negative effects especially on individuals’ mental health in a society and unresolved challenges [13]. The participation in sport activities as a scientific approach can increase individuals’ happiness and mental health. The various studies have shown that sport activities have psychological, emotional, and social benefits in addition to physical benefits, for example, the reduction of anxiety and depression, the increasing of sleep duration and better social relationships have been reported in different studies [14]. If a human has not enough calm to draw lost physical and personal resources and exposed to these severe psychological pressures repeatedly, the process of destruction will begin and then he/she will be sensitive to the disease especially psychosomatic diseases. Therefore, a human finds him/herself in anxiety without justification, fatigue, depression or feelings of dissatisfaction, and aimless, and he/she will hurt to relationships between individuals in the same way. One of the ways that psychologists introduce for the prevention and treatment of mental health problems is the role of physical activities in mental health, because the industrialization of societies and the reduction of physical activity in individuals have been revealed the need of sport more than ever and an extensive attention has been paid to exercise especially the role of exercise in psychological issues.
Research evidence show some environmental controversies that affect students’ mental health such as the desire for different social entertainments against willingness to study, the desire for physical superiority against organ limitations, the need to the lessons development against the feel of incompetence, the fear of personality expression against the desire for self-esteem, and job selection [15,17]. According to researchers’ idea who has mental health is a person that is distant from anxiety and disability symptoms and she/he can establish a constructive relationship with others, and is able to cope with life stresses [18]. On the other hand, conducted studies in the field of psychology and exercise have shown that exercise and physical activities are one of the effective methods for the prevention and treatment of mental illnesses [16,19]. Scientific evidences have shown that the participation in physical activities and the increasing of cardiovascular fitness are considered as an important factor in the improvement of mental health and mood. Nine factors are important in the creation of happiness and mental health that the participation in physical activities and exercise is one of the most important factors studied psychological and physical indexes in women that they concluded that aerobic activities and trainings had many benefits for behaviour and mood. Also, they stated that physical activities s were associated with the reduction of stress, tension, and the increasing of self-esteem [19].
Mental health is very importance for students in every community, because they are the future of any society. Mental disorders can lead to academic failure or the dropout. Students due to the specific conditions of students such as far away from family, getting into large and stressful collections, Economic problems and Lack of sufficient income, high volume courses, and intense competitions are prone to lose their mental health. They need an appropriate intervention for coping with such stressful situations. Regular physical activity at a moderate level course is one of strategies that scholars and researchers recommend to maintain and promote mental health [11,12] mental health (physical symptoms, anxiety, depression and dysfunction) of students in individual and team athletes with non-athletic and found out the amount of social dysfunction of team sports athletes than individual athletes and non-athletic and depression in non-athletes was more than two other groups. Also comparing each of the subscales between boys and girls athletes found that boys mean depression was more than girls [20].
Research results from Wang et al shows that any form of physical activity can protect and provide mental health. Sport in creating positive change, satisfaction with their sense of competence and efficiency play important role that are the component of mental health [14]. In his study concluded that following physical exercises, characters such as anxiety, depression and self-esteem varies to improvement that without regard to types of exercise activities that classified as aerobic have the most effects in terms of physiological and psychological.
Anxiety and depression are considered as trends and common mental disorders. So that Ghaffari (1384) studies results shows that non-athletes depression is less than professional and nonprofessional athletes. Studies suggests that physical activity and exercise has effect in promoting mental health, reducing depression,increasing welfare, mental and social health, self-confidence, self-belief and self-discovery. This study has compared male and female athlete and non-athlete students’ mental health, since many researchers have emphasized the role of physical activity and exercise as an instrument for the prevention of diseases and mental disorders and due to the existence of significant differences in men and women’s physiological characteristics. According to the findings of this study and differences of effectiveness in students due to studied different factors, we hope that can provide more effective and coherent programs for more participation in sports activities of different groups with an attention to these differences to improve students’ dimensions of mental health and the reduction of mental and psychological stresses in addition to the improvement of their physical abilities with the participation in sports activities.
Methods
This descriptive-analysis study was conducted on the causalcomparative method. The instruments of this study were included Goldberg’s General Health Questionnaire-28 (GHQ-28) and a demographic questionnaire that its validity and reliability have been proven in different studies. Goldberg’s General Health Questionnaire measures four categories of non-psychotic disorders such as somatic symptoms, anxiety and insomnia, social dysfunction and depression. Likert’s scoring method (0 to 3) was used for each case. The scoring criteria were the intensity of the evaluated symptoms and a higher score indicated a high intensity of the symptoms. According to this, a person with a score of 23 and lower score was considered as a healthy person and with a score of 24 and higher score was considered as suspected person who had a disorder. The statistical population of this study was all male and female physical education and non-physical education students in Universities Azad Islamic Branch of Gilan province. The statistical sample of this study was included 430 students that they were selected by randomized multi-stage cluster sampling. Athlete students were individuals who participated at least 3 times a week in sports programs and activities and non-athlete students were individuals who in this study did not have any physical activity or who their activities were limited to daily routine of life and education. The collected data were classified by descriptive statistical methods and were analyzed by dependent T-test. The SPSS software (version 21) was used for data analysis (α≤0.05).
Results
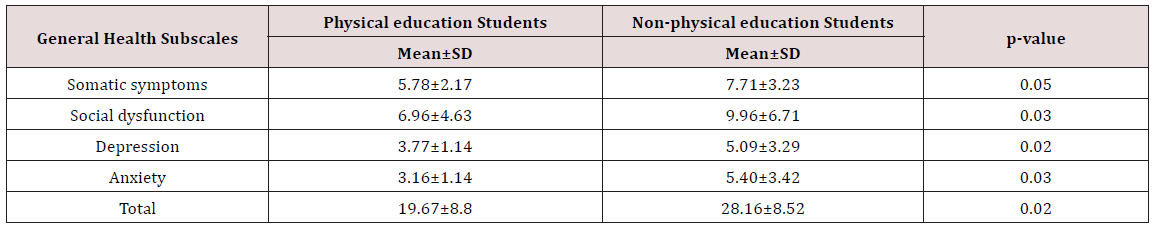
According to the results of the statistical analysis of this study, the status of general health indicators among physical education and sport sciences students was in the range of 19.68% that 27.11% was abnormal and 72.89% was normal in terms of general health status. Also, the results of statistical analyzes on the general health status among non-physical education students was in the range of 8.21%) that 42.17% was statistically abnormal and 57.83% was a good status. The male subjects’ age mean was 26 ± 3 and female subjects’ age mean was 24±7 in this study. The subjects’ age distribution was 63.17% in the age range of 20-30 years and 36.83% in the age range of over 30 years. 48.72% of physical education and sport sciences students were male students and 51.28% of them were female students. 56.11% of non-physical education students were male students and 43.89% of them were female students. The results in (Tables 1-3) showed that there was a significant difference between physical education and nonphysical education students (P<0.05).
Table 1: The results of independent T-test in the relationship with female Students’ General health subscales.
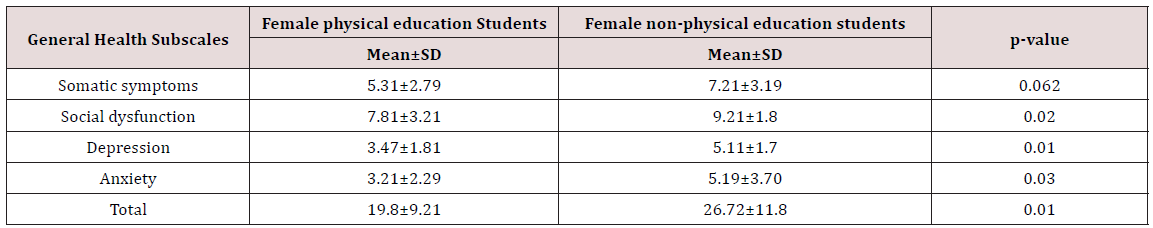
Table 2: The results of independent T-test in the relationship with male Students’ General health subscales.
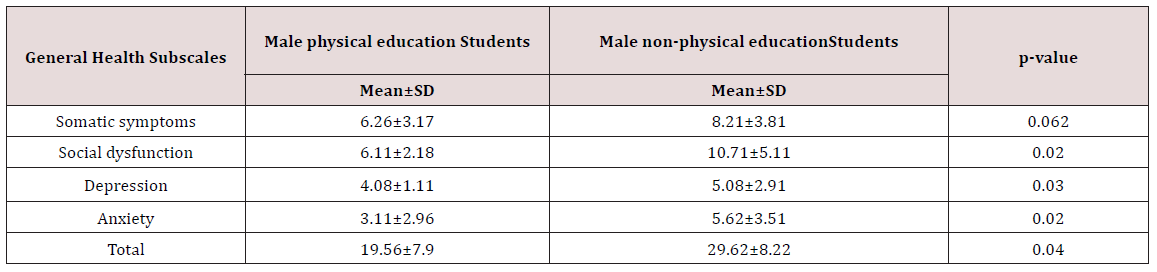
Table 3: The results of independent T-test in the relationship with physical education and non-physical education Students’ mental health subscales.
Discussion
the purpose of this study was examine the role effectiveness of physical activities on mental disorders in students with low mobility using General Health Questionnaire (GHQ).The results of this study showed that there was a significant difference between physical education and non-physical education teachers in mental health (P<0.05). It means that physical education teachers had a higher mental health score in comparison with non-physical education teachers. This result is consistent with the results of Hamer Rass and Hayes, Anonymous, Narimani, Ahmadi and Pirhayti and Nariman’s study [21-23].
Undoubtedly, the establishment of a healthy and happy society depends on the physical and mental health of the members in the society and needs to efforts of healthy, efficient, and thoughtful human forces. In this regard, the human and specialist resources in education that often have acceptable scientific and practical knowledge and abilities need to be able to overcome threatening factors of general health by the management of their organizations. Otherwise, the reduction of their capability will be inevitable. In this regard, the highest harm will be for students who are trained and the educational goals will encounter with serious problems. On the other hand, teachers will be aware of harmful problems and resources in their profession with the cognition of these factors and will use coping methods to deal with its undesirable effects.
The results of this study are consistent with the results of Bakhshalipour et al that they examined the effect of aerobic training on non-athlete postmenopausal women’s mental health. On the other hand, the difference in mean of mental health in the comparison of male and female athlete and non-athlete students did not show a significant difference in any of the subscales, but it was significant in all subscales with the comparison of male athlete and non-athlete students. So that male athlete students’ mental health had better condition than the male non-athlete students. This results is consistent with the results of study. They stated that male athlete students who participate regularly in physical activities such as walking, jogging, swimming, aerobics, or playing in sports teams can be able to do boring tasks in a longer period than inactive male students that this can be due to adaptive responses in a body as a result of regular exercise. There is a lot of evidence about the benefits of regular physical activity for general health. Studies show that intense and regular exercise is associated with less stress and anxiety. Also, people who participate in fitness and exercise programs report that their attitudes and efficiency are better at work; for example, they make fewer mistakes. It seems that exercise can play an important role in students’ physical and mental health due to all subjects are students who study at master’s level and they do many research works, and modern life conditions that have physical abnormalities such as back pain, joint damage, and diseases such as obesity and cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, the increasing of motivation through culture and the promotion of general knowledge about the benefits of physical activity can be considered as one of the options for the improvement of student sport. A program that may not have been seriously considered so far. According to the results of these findings, it seems that one of the factors that cause student athletes have better mental health than non-athletic students is their participating in healthy activities such as sport activities. Tuckers research results Showed, that physical fitness significantly reduces mental disorders in people.
Conclusion
Generally, Athletes that, participate different sports field based on personal interests and tastes the exposure groups and sports cooperation and cooperation with them and enjoy the new friendships. This may be cause removing such feelings and dissociable and helps create collective spirit, while non-athletic students deprived this opportunity
Reference
- Maller C, Townsend M, Pryor A, Brown P, Leger L (2006) Healthy nature healthy people: contact with nature as an upstream health promotion intervention for populations. Health Promot Int 21(1): 45-54.
- Pretty J, Peacock J, Sellens M, Griffin M (2005) The mental and physical health outcomes of green exercise. International Journal of Environmental Health Research 15(5): 319-337.
- Ahmadi T, Pirhayti S (2012) The effect of the selected exercise on male students` happiness and mental health. Procedia- Social and Behaviral Sciences 46: 2702- 2705
- Nasab SMHM, Taghavi SMR, Mohammadi N (2006) Optimism and Stress Appraisal: Evaluation of Two TheoreticalModels in Prediction of Psychological Adjustment. J Kerman Uni Med Sci 13(2): 111-120.
- Blanchard C, Rodgers W, Spence J, Courneya K (2001) Feeling state responses to acute exercise of high andlow intensity. J Sci Med Sport 4(1): 30-38.
- Feyer A, Herbison P, Williamson A, de Silva I, Mandryk J, et al. (2000) The role of physical andpsychological factors in occupational low back pain: A prospective cohort study. Occup Environ Med 57(2): 116-120.
- Thompson Coon J, Boddy K, Whear R, Barton J, Depledge MH (2011) Does participating in physical activity in outdoor natural environments have a greater effect on physical and mental wellbeing than physical activity indoors? A systematic review. Environmental Science & Technology 45(5): 1761-1772.
- Noorbala AA, Mohammad K, Bagheri Yazdi SA, Yasemi MT (2001) Looking for visage mental health inthe Iran. Research project Red Crescent Society.
- Macmahon JR (1990) The psychological benefits of exercise and the treatment of delinguent adolescents Sports Med 9(6): 344-351.
- Oweis P, Spinks W (2001) Bio psychological, affective and cognitive responses to acute physical activity. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 41(4): 528-538.
- Tasai Eva (2005) A cross cultural study of the influence of perceived positive outcome participation in regular active recreation: Hong Kong and Australian University Students. Leisure Sci 27(5): 385-404.
- Katrien Wijndaelea, Lynn Mattonb, Nathalie Duvigneaudc, Johan Lefevreb, Ilse De Bourdeaudhuija, et al. (2007) Association between leisure time physical activity and stress, social support and coping: A cluster-analytical approach. Psychology of Sport and Exercise 8(4): 425- 440.
- Bakhshalipour V, Sanatkaran A, Rezaei Soufi M (2015) The effects of 4-week of aerobic exercise training on non-athlete male students sleep and life quality. IJBPAS 4(12): 103-118.
- Zarkhah M (2009) The leisure time in Mellat Bank employees of Tehran and the needs assessment of recreational and sports programs. MA thesis, Islamic Azad University Central Tehran Branch, Iran.
- Farahbakhsh S, Gholamrezaee S Nikpey I (2007) The survey of students’ mental health in relationship with educational factors. Journal of Fundamentals of Mental Health 9(33-34): 61-66.
- Hansmann R, Hug SM, See land K (2007) Restoration and stress relief through physical activities in forestsand parks. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening 6(4): 213-225.
- Mitchell R (2012) Is physical activity in natural environments better for mental health than physical activity inother environments? Social Science & Medicine 1-5.
- Macmahon JR (1990) The psychological benefits of exercise and the treatment of delinguent adolescents Sports Med 9(6): 344-351.
- Bakhshalipour V, Sanatkaran A, Khodaparast Sareshkeh S, Zivdar Z, Azizi B (2017) The effectiveness of selected aerobic training on the mental health in non- athlete postmenopausal women. Sport Scientific and Practical Aspects. Sport SPA 14(1): 5-10.
- Narimani M (2006) The comparison of general health in athlete and non-athlete students. The Third National Conference on Mental Health in students, Iran University of Science and Technology pp. 360-364.
- Blair SN, Morris JN (2009) Healthy hearts and the universal benefits of being physical activity and health. Annals Epidemiology 19(4): 253-256.
- Rass JE, Hayes D (2008) Exercise and psychological well- being in the community. American Journal of Epidemiology 127(4): 762-771.
- Anonymous R (2005) Burnout in Texas Division 4A and 5A High School Athletic Trainers Form a Reversal Theory Perspective 76(1): 92-72.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...