Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-6695
Research Article(ISSN: 2637-6695) 
A Comparative Study on the Effect of Traditional Teaching Method with Multimedia Method in Learning the Lesson of Orthopedic Surgery Technique Students of Hamadan Medical Sciences Operating Room Volume 2 - Issue 3
Behzad Imani1*, Fatemeh Aghamohammadi2, Majid Ansari3, Zahra Azizi4
- 1Assistant professor, Department of Operating Room, School of Paramedicine, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran
- 2Student Operating Room, Student Research Committee, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran
- 3Master of Community Health Management, Faculty of Paramedicine, Hamedan University of Medical Sciences, Hamedan, Iran
- 4Operating Room Expert, Faculty of Paramedicine, Hamedan University of Medical Sciences, Hamedan, Iran
Received: October 12, 2019; Published: October 18, 2019
Corresponding author: Imani Behzad, Department of Operating Room, School of Paramedicine, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran
DOI: 10.32474/LOJNHC.2018.02.000136
Abstract
Introduction: Electronic education, including multimedia, is a new approach to providing learning-based learning environments. The benefits of using multimedia in educational settings include the use of multiple senses to learn, more practice to achieve mastery levels, facilitating participation to link concepts and facilitating lessons for re-use.
Methods: In this quasi-experimental study, 58 operative students (3 semester undergraduate students and 2 semester students of bachelor’s degree) were selected. At first, the first part of the topic was taught in the traditional way, and the second part was taught by the relevant teacher through the educational help software. After the end of the study, the effect of the two methods on the level of students’ learning was evaluated using questionnaires prepared by the faculty members of the Faculty of Paramedical Sciences of Hamedan University of Medical Sciences. SPSS23 software and descriptive and inferential statistics were used to analyze the data.
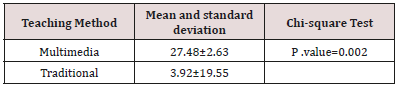
Results: According to independent t-test, two groups of traditional and multimedia training with p value: 0.000 showed significant differences. The results show that multimedia method is more effective than traditional method. Students are learning.
Conclusion: According to the performed studies, the designed educational software can be used as an effective educational strategy to improve the students’ learning of the operating room.
Keywords: Multimedia Education; Traditional Learning; Learning
Introduction
With the advent of information technology and the penetration of telecommunications deep into the community, educational tools and methods have also evolved, with the advent of technology using newer tools to transmit data [1]. Many institutions have been attracted by the opportunities provided by information and communication technologies [2]. Today, education as a key pillar in the transfer of concepts to learners has found a variety of ways, and the ever-expanding access to appropriate hardware and software for multimedia education has opened a new horizon for universities and training centers. It seems that using these facilities for training helps to realize some of the ideals that are referred to as quality education criteria. Multimedia education as a complementary education helps to improve the quality of learning. In Western countries, multimedia education has become increasingly popular and accepted as an educational style, with the problems of today’s life and the pressures of population growth, it has led people to this type of education [3,4]. Despite the fact that in nursing education most practitioners are using traditional methods in the education process, the reports of the articles indicate that traditional methods of education are now alone responding to the rapid movement of science and the learning needs of learners and the constant changing needs of communities Multimedia-based education is a response to the needs of today’s society, where it is almost impossible to provide all people in a class, at one time, with one method of learning for all. Multimedia is a response to different educational styles [5]. In many countries, including Iran, one of the challenges students face is learning theoretical topics and clinical skills [6]. In theory teaching, students learn a great deal of content and quickly forget it [7]. In traditional teaching, collaboration and intergroup relationships are poor and individual differences are overlooked. This is easy and costly compared to other methods, Scarce [8] with the increasing information in the present age and the development of educational and evolutionary patterns in the concept of learning, this transformation has been transformed with the transition from behaviorism to structuralism in recent decades and for the betterment of the education process has received worldwide accent [9]. Research shows that students understand the training they receive easier than others and that their skills will increase [10]. Software training will increase the speed of teaching and learning, and the student can engage in theoretical discussions. Access and review them on a number of occasions and provide a basis for evaluating their clinical skills [11].
Keeping in mind that learning using multimedia software and computers is an essential step in improving medical education systems. According to the results of some research, learning is an acceptable and useful way of learning clinical skills and its results are comparable to the usual methods [12]. Research shows that in traditional teaching methods, student-remembered content will last up to eight months and will be forgotten and will need to be repeated. Teaching a lesson as a lecturer will not be equivalent to teaching it by a student. One of the benefits of this approach is the active presence of the student in the teaching process, which shifts the teaching from teacher-centered and handwritten to studentcentered [5]. Multimedia, however, calls for the deployment of teachers to manage learning in new and innovative ways. Software, learners, and teachers are the three key variables in the discussion of multimedia, and we believe that the teacher plays a key role in using software to support children’s learning and integrate it into the curriculum [13]. The purpose of this study is to compare the multimedia teaching method with the traditional teaching method. We intend to develop multimedia simulator software including the concepts of anatomy training, familiarity with surgical instruments, and complete description of operations; we are looking at the impact of this software on student learning and which of these two methods will be preferred by student.
Method
The target population of this study was undergraduate students of Hamadan University of Medical Sciences who had completed the course “Orthopedic Surgery Technology”. The study was quasiexperimental, and the sampling was done by census method. All 60 undergraduate students who had opted for “Orthopedic Surgery Technology” course were asked to participate in the study if they wish. 58 students agreed to attend the test session and participated in the study as an example. Data gathering tool was a questionnaire to measure students ‘learning in orthopedic surgery technology lesson in both traditional and multimedia teaching methods. This questionnaire also included students’ educational level and gender. The face and content validity of the questionnaire was confirmed based on the opinions of ten operating room and nursing professors. According to the faculty members of the Medical School and according to the educational curriculum, the topics of orthopedic surgery technology were divided into two parts. Surgery, an introduction to surgical tools and anatomy, along with illustrations and animations related to each subject, were taught. At the end of the semester, evaluation of the effect of these two methods on students’ knowledge learning was done by using a written questionnaire with multiple choice questions. The scores of the two written tests were compared between the two groups in order to compare the learning of the two educational methods. SPSS 23 software and descriptive and inferential statistics were used for data analysis. Frequency distribution tables, central indices such as mean, median, and dispersion indices such as deviation and variance, etc. were used to describe the data. After using Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistical test for normality of sample distribution, t-test, binomial test, or bread parametric test (GPA) to compare learning of two educational methods, correlation tests Ray) was used according to the questionnaire.
Findings
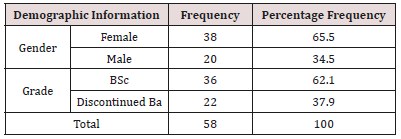
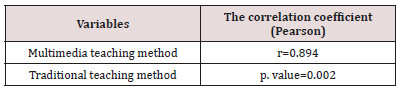
In this study, 58 students of the operating room of the Paramedical Faculty who were selected by the orthopedic surgery technology course in the academic year of 1397-97 were voluntarily participated. In this study 38 (65.5%) of the subjects were women and 20 (34.5%) were men and 22 (37.9%) undergraduates are discontinuous (Table 1). Multimedia teaching method has a positive and significant correlation with column teaching method. There is also a positive and significant correlation between multimedia teaching and traditional teaching with students’ educational level. The results for student scores are presented in Tables 2 & 3. The results of the following tables show that the multimedia teaching method has a positive and significant correlation with the column teaching method and a significant increase in the students’ average score in the multimedia teaching method indicates a positive effect of teaching in this way (Tables 1-3).
Discussion
The present study evaluated the impact of two traditional and multimedia teaching methods on learning of “Orthopedic Surgery Technology” course, operating room students of Hamadan University of Medical Sciences. The results show that there is a statistically significant difference between the rate of learning in the traditional and multimedia-based methods and the rate of learning in the multimedia-based method is higher than the traditional method. In this regard, the results of [14] study, which aimed to study the effect of designed educational software on practical nursing principles and techniques on learning practical skills of nursing students, showed that using educational software as an effective educational strategy can be effective. Improve nursing students’ practical skills, which is in line with the results of this study [15]. In a study aimed at investigating the effect of self-help and altruism training in two lecture and multimedia software packages on the knowledge of military combatant combatants, stated that if conditions were favorable When and where and with the availability of teaching aids, training with multimedia software packages can be more effective than increasing the level of knowledge of lecturers [15]. In the study by [16] The results indicate that the multimedia method improves the average or better sustainability of students’ knowledge, which is consistent with the results of this study [16] in another study by [17] The purpose of this study was to compare the effect of multimedia system with speech method on patients’ choice of prosthesis treatment. Results show that multimedia method is effective, and its application is recommended along with verbal method [17]. A Study by [18] with the aim of comparing the effect of triage training with lecture and multimedia software In addition to nurses’ learning, the results indicate the effectiveness of both lecture and multimedia software, but considering the features of virtual teaching, this method is recommended [18]. These findings are supported by findings from some research. It was different. Goode et al. In their study stated that CD and traditional education had a similar effect on learner learning [4].
Therefore, or noting the findings of this study, it can be stated that multimedia education is more effective than the traditional one and leads to improvement in the student average which can be due to the benefits of multimedia software. Such as taking advantage of audio and video facilities, being available at any time and place, becoming more attractive and understanding the content to enable and engage students in learning and make the learning environment more realistic. Also, by reusing the curriculum due to its reproducibility, it can be more effective in deepening the understanding of scientific content and promoting knowledge in the sustainable learning of working students. Although, in this study, the effectiveness of multimedia teaching compared to traditional teaching in the field of orthopedic surgery technology teaching has been identified, the limitations of this study with a group of students as well as the use of an educational topic make it possible to generalize the findings. Challenges to other topics. Therefore, it is suggested that more studies be conducted in other disciplines and disciplines to ensure greater effectiveness of multimedia teaching.
References
- Beyranland (2016) Comparison of the two Virtual and Traditional teaching methods in learning the course of the Introduction to Dental equipment and their maintenance for the students of the PhD General dentistry at Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences. AJRJoMS 23(143): 63-70.
- Banisi P, Shahrakipour H (2006) electronic education. peik noor. 15(4): 108-121.
- ASGARI A, Khaghanizadeh M (2010) Multimedia method of education.
- Khoobi M, Mohammadi N, Ahmadi Hedayat M, Ghiyasvandiyan S, Varaei S (2017) Comparison of the nursing students' learning in two teaching methods using CD and training through traditional method. JNE 5(6): 18-22.
- Fani MM, Mehravar S, Mehrabi M (2014) Level of learning and satisfaction through traditional methods and the use of multimedia: A comparative study. JIJoVLiMS 5(2): 72-78.
- Rafei lims P, Abdolzadeh S (2009) SJE 4(13): 35-43.
- Kordi M, Rashidi Fakari F, Mazlom R, Khadivarzadeh T, Akhlaghi F (2014) Comparison of web-based training, simulation and durability of traditional knowledge and skills in the management of postpartum hemorrhage midwifery students. JJOGI 16(89): 8-14.
- Mir Bagher Ajorpaz N, Sadat Z, MH (2014) Comparison of the Effect of Lecture Education and Multimedia Software on the Students' Learning and satisfaction in operating room in the course of Gastro-intestinal surgery Technology. Journal of social health 8(2): 47-55.
- Noorian A, Noorian A, EbnAhmadi A, AkbarzadeBaghban A, Khoshnevisan M (2012) Comparison of two methods of virtual and traditional education in the teaching of community-oriented dentistry course for general education students of shahidbeheshti Dental school 2010. Jornal of Dental school shahidBeheshti University of Medical sciences 30(3): 174-83.
- Kardong-Edgren SE, Oermann MH, Odom-Maryon T, Ha Y (2010) Comparison of two instructional modalities for nursing student CPR skill acquisition. JR 81(8): 1019-1024.
- Mohajeri S, Seyed M (2010) Simulation and virtual reality؛ A new method to improve the quality of medical education. JHMED 4(1): 1-6.
- Naseri M, Ahangari Z, Shantiaee Y, Rasekhi J, Kangarlou A (2013) JJoIDAoI 25(2): 141-147.
- Collins J, MHa, Wellington J (1997) Teaching and learning with multimedia.
- Khatooni M, Alimoradi Z, Samiei Seiboni F, Shafiei Z, Atashi V (2014) The impact of an educational software designed about fundamental of nursing skills on nursing students' learning of practical skills. Journal of Clinical Nursing and Midwifery 3(1): 9-16.
- Daneshmandi M, Asgari A, Tadrisi S, Ebadi A, Mokhtari Nouri J (2011) Effect of self-and buddy-aid education by lecture and multimedia software package methods on the knowledge level of personnel. JJMM 13(1): 7-10.
- Vahedparast H, Mohammadi B, RavaniPour M, Sadeghei T (2015) Comparing the Effects of Heart Dysrhythmia Training Through Both Lecture and Multimedia Software Approaches on the Knowledge Retention of Nursing Students. Educational Development of Jundishapur 6(2): 115-121.
- Shabestari Omati G, Vahid R, Ali Khasi M, Khojaste A, Baghai R (2010) Comparison of multimedia system and conventional method in patients selecting prosthetic treatment. Journal of Dental Medicine 23(3): 161-166.
- Tadrisi SD, Siavash Vahabi Y, Ghayem S, Ebadi A, Daneshmandi M, Saghafinia M (2011) Comparing the effect of triage education in lecture and multimedia software on nurses learning. Iranian Journal of Critical Care Nursing 4(1): 7-12.
Editorial Manager:
Email:

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...