Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-4544
Research Article(ISSN: 2637-4544) 
Sycp-3 Gene Mutation and DNA Copy Number Variation Increase Genetic Susceptibility in the Cases of Non- Obstructive Azoospermia Volume 5 - Issue 1
Ajit Kumar Saxena1*, Mukta Agarwal2, Meenakshi Tiwari1, Ujjwal Kumar1, Shailendra Kumar1, Lovely Sinha1 and Chandan Kumar Singh1
- 1Human Molecular Genetics Laboratory, Department of Pathology/Lab Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna, India
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna, India
Received:November 25, 2021Published: December 06, 2021
Corresponding author: Ajit K Saxena, Human Molecular Genetics Laboratory, Department of Pathology/Laboratory Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna, Bihar, India, Email: draksaxenal@rediffmail.com
DOI: 10.32474/IGWHC.2021.05.000203
Abstract
Background: In the human, infertility is a serious reproductive health problem in the world, and more than 15% couples are
infertile. Male infertility is a highly complex phenomenon involving large number of factors including endocrine dysfunction, socioeconomic,
life- style, use of alcohol, drugs, exposure with radiations, chemical (pesticides) and automobile fumes. The genetic
factors like complex chromosome rearrangements (CCRs), microdeletion of Y-chromosome (AZF regions) and genes assigned on
autosomal region of the chromosomes are also associated with male infertility.
Objective: The role of synaptonemal complex protein-3 (Sycp-3) gene mutation in male infertile patients is not clear in Indian
population. Therefore, the present study has been designed to evaluate the percentage frequency of Sycp-3 gene mutation and
simultaneously also assess the frequency of DNA copy number variations in nonobstructive azoospermia non obstructive azoospermic
(NOA) cases.
Materials and Methods: Genomic DNA was isolated followed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using two different sets of up
and down stream amplicons, both from clinically diagnosed cases of NOA and controls of the same age group.
Results: The present study mainly categorized, three type of Sycp-3 gene mutations - the complete disappearance bands (absent),
over expression and under expression. Interestingly, significant (p<0.05) individual variations were observed in the frequency
(%) of complete disappearance (null) of 173bp (8.33%) and 568 bp (12.5%) amplicon followed by calculated value of odd ratio
6.45 and 5.00 with confidence interval varies (C.I) at 95% interval 0.76-55.04 and 1.04-24.02, respectively in the cases of NOA when
compared with controls. Similarly, the frequency of over expression (up regulation) in 173bp (5.55%) and 568bp (2.77%) amplicons
were also showing significant variations (p<0.05). Further study was extended to calculate the DNA copy number variations,
which again shows statistically significant differences (p<0.05) between NOA cases and controls.
Conclusions: The present findings of Sycp-3 gene mutation using two different amplicons in cases of NOA concluded significant
variations of Sycp-3 gene mutation of 568 bp amplicon along with DNA CNVs showing negative impact on spermatogenesis determining
to causative factor of male infertility.
Keywords: Sycp-3 gene mutation, Copy Number Variation, Non Obstructive Azoospermic
Introduction
Reproductive health is a serious and mounting problem in the
world, where several factors including climate changes such as
global warming resulting in change in sperm quantity according
to world health organization [1]. The pathogenicity of infertility is
highly complex phenomenon affecting approximately 1:20 males
during reproductive age due to unknown genetic and epigenetic
factors [2,3]. The role of complex chromosomal rearrangement
(CCRs) and high incidence of mosaicism are well known in
azoospermic patients [4]. More than 20% of de novo mutations of
USP9Y and PCDH11Y genes were observed in both heterozygous
and homozygous conditions that encodes amino acid arginine
guanine, isoleucine and leucine modulates early transcription
factor such as Sox9 gene in non-obstructive azoospermic (NOA)
cases. Similarly, Sox9 gene expression is essential for the normal differentiation of Sertoli cells and DNA CNVs interfere in germ
cell proliferation inside the seminiferous tubule of the testes
[5-7]. The study of whole genome sequencing (WES) in male
infertility explore new knowledge between the positive interaction
to several gene like melatonin receptor1B (MTNR1B), sentrinspecific
protease-3 (SENP3), a-kinase anchoring protein3(AKAP3),
Procollagen-Lysine,2-Oxoglutrate 5-Dioxygenase 3 (PLOD3) genes
assigned on autosomes 11q14.3, 17p13.1, 12p13.3, 11p13.4,
respectively, modulates sequential transcriptional activity followed
by translational. These events are mechanism either due to changes
in function of amino acid or loss of binding capacity to the ligand
(receptor) during differentiating germ cells in the testis [8,9]. In
spite of the fact, still, more than 17% couples fall under the category
of unexplained cause of infertility and becomes a major challenge
to the scientist as well as for the clinicians to explore the underlying
cause.
In reproductive medicine, male counterpart is an active
and dominant part of the society and testis is highly sensitive
towards the exposure of environmental teratogens followed by
uninterrupted supply of mature and healthy spermatocytes or
sperms in male gonads.
Synaptonemal complex (SC) is a protein structure develop
during the pairing between two homologous chromosomes
after linkage and crossing over, where the exchange of gametes
information take place in zygotene stage of meiosis I of celldivision.
Synaptonemal complex-3 (Sycp-3) gene is mapped on
chromosome -12 (12q23.2) and consists of 9 exons, spanning 10.5
kb DNA and present outside the AZF region of Y- chromosome
[10,11]. However, there is scanty in literature on the functioning of
Sycp-3 protein and their association to the meiotic arrest during
spermatogenesis [12]. It has been observed earlier that there is
a reported a loss of DNA (>1bp) at 643delA, resulting in origin of
truncated sycp3 protein due to the presence of premature stop
codon; however, debatable findings regarding loss of Sycp-3 gene
expression or its restriction to germ cells in azoospermic has been
reported earlier [10].. Therefore, a present study has been designed
with the aim to assess the frequency (%) of Sycp-3 gene mutation
using two different specific set of primers and the same study was
further extended to evaluate the frequency of (CNVs) to determine
genomic instability in the cases of NOA and compare with controls
of the same age group to validate the significance after statistical
analysis of the study.
Materials and Methods
Subjects
In the present study, clinically diagnosed cases of NOA were included (n=72) and the finding were compared with control group. The study was approved by Institute Ethical Committee and Institutional Research Committee of All India Institute of Medical Sciences Patna. Written informed consent was taken from the patients.
Isolation of Genomic DNA and RNA
Genomic DNA and RNA was isolated from 1.0 ml whole blood samples using protocol of kit (Promega, USA), quantified by nanodrop spectrophotometer and quality was checked on 1.5 % agarose gel electrophoresis and DNA or RNA bands were visualized after staining with ethidium bromide by Gel Doc system (Bio Rad, USA). The cDNA was prepared by using reverse transcriptase with Oligo (dT) primer and complementary products were stored at -20°C till further analysis.
RT-qPCR analysis for the amplification of Sycp-3 gene mutation
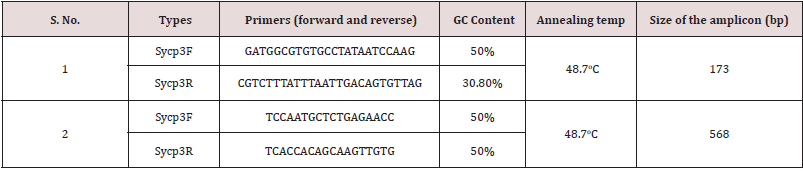
In the present study, Sycp-3 gene mutation and copy number variations (CNVs) were assessed using specific set of forward and reverse primers to amplify the desired regions of exons after confirmation of sequences from NCBI (BLAST/http://blast.ncbi. nlm.nih.gov./Blast.cgi) as documented by [13]. For the study of Sycp-3 gene expression RT qPCR-based analysis were carried out using SYBR® Green (10μl) as fluorescence dye, 1μg cDNA with specific primer in 20μl reaction mixture. The amplification was accomplished with a 25 μl reaction mixture containing 50 ng DNA, 1 μl each of 10 pmol of Sycp-3 primer (forward / reverse), 5x Green GoTaq PCR reaction buffer, dNTPs Mix (10 mM) and 0.2μl of Go Taq DNA polymerase (5U/μl). PCR program for Sycp-3 was as follows: initial denaturation 95°C for 5 minutes, 35 cycles for denaturation at 94°C for 45 seconds, annealing at 48.7°C for 30 seconds, elongation at 72°C for 1 minute, followed by final extension at 72°C for 8 minutes as depicted in table 1. The amplified products were analyzed on 1.5% agarose gel, bands were visualized and characterized on a Gel Doc system (Bio rad, USA), after ethidium bromide staining.
Table 1: Sycp-3 gene mutation were analyzed by using two different sets of amplicons (upstream / downstream) in non-obstructive azoospermic cases.
DNA Copy Number Analysis of Sycp3 gene
The DNA CNVs of Sycp-3 gene analysis were carried out using Image lab software 5.1 in Gel Doc system (Bio Rad, USA) by performing densitometry of individual bands (173 & 568 bp) for two different amplicons. The frequency of CNVs of Sycp-3 gene correlate genomic instability after statistical analysis between the cases of NOA and their respective controls.
Statistical Analysis
To find out the level of significant difference between cases of NOA and their respective controls, p-value (P<0.05) calculated using two tailed chi-square test and compared with controls of the same age groups.
Results
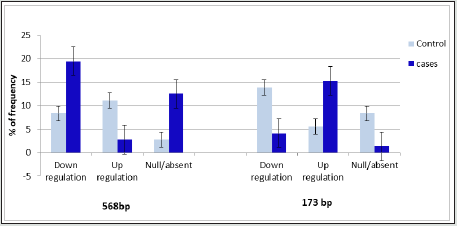
The Sycp-3 gene is mapped on the long arm of chromosome-12 (12q23.2) and encodes the (Sycp-3). The findings of RT qPCR-based analysis of Sycp-3 gene mutations presented in three different forms-1) the complete disappearance of band 173 and 568 bp, 2) over expression or up regulation and 3) under expression or down regulation using specific forward and reverse set of primers in NOA cases and the same compare with control groups as documented in figures 1A & 1B. Interestingly, the findings of Sycp- 3 gene mutations were assessed between NOA cases and controls as details were documented in table 2. The significant variations (p<0.05) were observed in Sycp-3 gene mutation of 173bp band (complete disappeared) and calculated value of O.R 6.45 with confidence interval (C.I) at 95% varies from 0.76 to 55.04, while for Sycp-3 gene (568bp) showing significant difference (p <0.05) with calculated odd ratio (5.00) and C.I. at 95% varying from 1.04-24.02, although, the mutation frequency (12.5 %) was observed higher in Sycp-3 568 bp than band 173 bp in Sycp-3 (8.33%). However, significant variations (p<0.05) were also observed in both down/ up regulation (over expression) using two different set of Sycp-3 primers 568 and 173bp in the cases of NOA when compared with controls group. Apparently, bar diagram showing lack of definite pattern of mutational frequency after using two different set of amplicons 568bp and 173 bp of Sycp-3 gene - null (absent), over expression or down regulation, but after statistical evaluation significant association (p<0.05) were observed when compared with controls (Figure 2).
Table 2: PCR based analysis of Sycp-3 gene mutations using two different set of amplicons (173 & 568bp) in the cases of NOA and their respective controls.
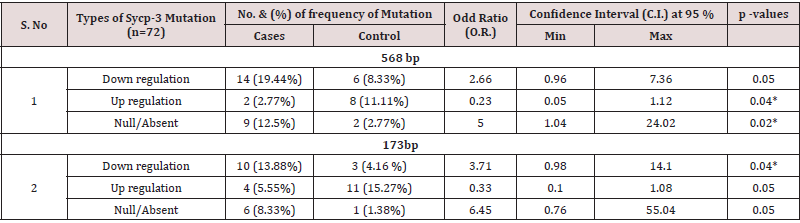
*Significant differences (p<0.05) were observed using x2-test.
Figures 1A & 1B: PCR based analysis of Sycp-3 gene mutation in NOA cases of male infertility using two sets of forward and reverse primers belong to 568 bp and 173 bp respectively, visualize on 1.5 % agarose gel after staining with ethidium bromide (A) and compare with respective controls (B). M= molecular weight marker (100 - bp DNA ladder), lane 1, 3 & 7-cases. (Arrow red) showing complete disappearance (null) of 568 bp bands and lane-3 also showing disappearance of band belong to 173 bp while lane-7 showing down regulation.
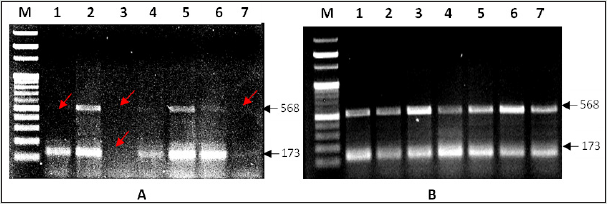
Figure 2: Bar diagram showing Sycp3 gene regulation over expression (up regulation) / under expression (down regulation) /complete disappearance of band (null) in two different set of primers in the cases of non-obstructive azoospermic with respect to controls.
The DNA CNVs has been associated with several complex diseases due to genetic susceptibility followed by changes in the behavior of either exons or introns involving deletions or duplications of DNA segments >1 kb during germ cell differentiation in testes. Figure 3 showing significant association of CNVs of Sycp-3 gene between cases and controls after using two set of forward and reverse primers. The DNA CNVs of Sycp-3 play an important role to determine genomic instability either at leptotene or zygotene stage of meiosis I during crossing over and synapse formation resulting formation of millions of mature and healthy sperm cells through a complex process of spermatogenesis. Sycp-3 (568 bp) showing observed mean and s.d values 1595.8 ±1030.37 in NOA cases, while 2067.8 ±188.23 in controls. Similarly, the mean and s.d. values 1730.5 ±920.34 in the cases and in control is 2508.7 ±76.76 for Sycp-3 (173 bp). Apparently, bar diagram (Figure 3) showing highly significant (p<0.01) differences in 173 bp of Sycp-3 gene with respect to controls between two different amplicons. Although, the detailed p-values after statistical evaluation of DNA CNVs between two sets of amplicons (173 bp or 568 bp) are documented in table 3.
Figure 3: Bar diagram showing mean values of Sycp3 gene between cases and controls in two different set of amplicons belong to 568 bp (Bar1) and 173 bp (Bar 2).
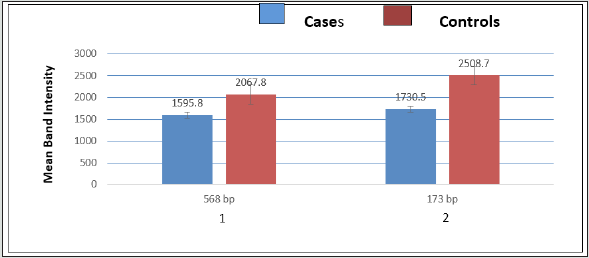
Table 3: Statistical analysis showing DNA Copy Number Variations using two set of amplicons between Cases and Controls.
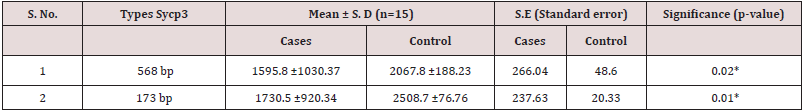
*Significant differences (p<0.05) were observed after using x2 -test.
Discussion
During crossing over, synapse is formed where the exchange
of genetic information takes place between maternal and paternal
homologous chromosomes. Synapse is highly complex and
sensitive structure consist of several proteins. However, the Sycp-3
play an important role at zygotene stage of cell - division during
spermatogenesis. Sycp-3 is a prominent DNA-binding protein that
encodes an essential component of the axial or lateral filament
during formation of synaptonemal complex in gametogenesis.
In the human, the role of Sycp-3 protein is highly debatable in
male infertility due to scanty of literature and different views by
the different group of the scientists. Hence, curiosity has been
developed to assess the role of Sycp-3 gene mutation in terms of
either complete disappearance (absent/null) or over expression
(up regulation) or under expression (down regulation) along
with the DNA copy number variations using two different set of
amplicons (173 bp & 568 bp) in the cases of NOA. Although, the
present study also showing the deletion of Sycp-3 gene belongs
to 568 bp amplicon significantly but lacking in 173 bp the same
cases of NOA with respect to controls, suggesting either sycp3
protein have different isoforms or different physiological identity
during meiotic I arrest at zygotene stage of cell division. Further,
authors suggested that the discrepancy of Sycp-3 gene mutation
frequency is either due to germ cell susceptibility during synapse
formation at crossing over in two different set of amplicons or
individual’s genetic susceptibility in the cases of NOA. However,
the controversial findings have been reported earlier by several
authors regarding the role of Sycp-3 gene mutation or expression
during meiosis in germ cells. However, the authors hypothesized
that such mutations (meiotic errors at spermiogenesis) may lead to
cause chromosomal translocation resulting spermatogenic arrest,
DNA CNVs and origin of aneuploid gametes due to non - disjunction
event during germ cell differentiation [10-13].
Genes affected by DNA CNVs are excellent candidates for
reproductive research in diseased conditions associated genetic
susceptibility and risk factor. In human, the role of Sycp-3 gene is
highly ambiguous during spermatogenesis and becomes relevant to
extend in the present study to assess the frequency of CNVs shows
statistically significant in the cases of NOA. The CNVs are structural
changes in DNA consisting of deletions or duplications of segments
larger than 1bp as compared to reference genome. Because CNVs
have shown to be associated with several complex diseases and
ubiquitous reports have also been documented both in normal and
diseased populations, including diseases like male infertility [3-
15]. Present study shows significant association in the frequency
of Sycp-3 gene mutation and DNA CNVs to determine “risk factors”
of the disease when compare with controls, suggesting penetrance
of mutated Sycp3 gene in to probands either from parents or de
novo mutation. Although, there is no direct evidence exist in the
literature to correlate CNVs and Sycp-3 gene mutation in male
infertility. Earlier study has shown that there is large number gene
such as arylsulphatase D (ARSD) polymorphism and cullinring
ubiquitin ligase4B (Cul4B) genes has also been associated with
male infertility due to non-frame shift mutation (deletion at position
1761-1766 of GGAGGA nucleotide sequences) in homozygous
condition, result loss of non-essential amino acid glycine in the cases
of male infertility [16,17]. Beside this, folate metabolism associated
MTHFR C677T gene polymorphism is also associated to increase
“risk factor” by modulating hormonal dysfunction (2). Similarly, the
role of Nanog and Sox9, the early transcription factor also plays an
important role to maintain pluripotency during organogenesis of
male gonad (testis)), sex reversal cases i.e., XX male or XY-female
and male infertility [18-19].
Conclusion
The present study concludes that Sycp-3 gene mutations play an important role in the cases of NOA either as independent factor or in association with DNA CNVs at early leptotene or zygotene stage of meiosis I during synapse formation. Further, out of different amplicons of Sycp-3, the frequency of amplicon of 568 bp showed higher susceptibility towards mutations leading to male infertility. Such study warned to determine the role of Sycp-3 in cases of male infertility. Further such study warned to determine the role of Sycp- 3 in cases of male infertility as an established diagnostic marker and determine its role in clinical management in Indian population.
Acknowledgement
AKS thankfully acknowledge the financial support from Indian Council of Medical Research (5/10/FR/13/2019-RBMCH), Govt. of India. AKS also thankfully acknowledge to the patients who participate to the study.
Conflict of Interest
Authors states no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization (1999) WHO laboratory manual for the examination of human semen and semen-cervical mucus interaction. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, USA.
- Saxena AK, Agarwal M, Kumar A, Singh CK (2020) Genetic heterogenicity of MTHFR C677T allele modulate hormonal dysfunction associated risk factors in the cases of male infertility. International Journal of Development Research 10(12): 42700-42705.
- Eggers S, DeBoer KD, van den Bergen J, Gordon L, White SJ, et al. (2015) Copy number variation associated with meiotic arrest in idiopathic male infertility. Fertil Steril 103(1): 214-219.
- Saxena AK, Kumar A (2019) Microdeletion of the AZFc locus with high frequency of mosaicism 46, XY/47XYY in cases of non-obstructive azoospermia in eastern population of India. Genetics and Molecular Research 18 (2): 18349.
- Saxena AK, Tiwari M, Kumar A (2019) Penetrance of de novo mutation of USP9Y and PCDH11Y gene in AZF regions of non-obstructive Azoospermic population in India. International Journal of Current Research 11(2): 1373-1379.
- Saxena AK, Tiwari M, Kumar R, Aprajita Kumar A, Singh K, et al. (2020) Impact of the Y-chromosome gene on SOX9 stem cell expression in non-obstructive azoospermic cases. Genetics and Molecular Research 19 (1): 18464.
- Chaboissier MC, Ko bayashi A, Vidal VI, Lutzkendorf S (2004) Functional analysis of Sox8 and Sox9 during sex determination in the mouse. Development 131(9): 1891-901.
- Aprajita AK, Tiwari M, Saxena AK (2019) Impact of MTNR1B and SENP3 Gene on Male Infertility: Prediction of 3D Structural Modeling of Protein and Drug Interaction during Spermatogenesis. J Mol Genet 2(1): 1-8.
- Saxena A K, Tiwari M, Agarwal M, Aprajita, Kumar A (2019) Prediction of 3D Protein Structure Based on The Mutation of AKAP3 and PLOD3 Genes in The Case of Non-Obstructive Azoospermia. International Journal of Fertility & Sterility 14(2): 102-109
- Aarabi M, Modarressi MH, Soltanghoraee H, Behjati R, Amirjannati N, et al. (2006) Testicular expression of synaptonemal complex protein 3 (SYCP3) messenger ribonucleic acid in 110 patients with nonobstructive azoospermia. Fertil Steril 86(2): 325-331.
- Yuan L, Liu JG, Zhao J, Brundell E, Daneholt B, et al. (2000) The murine SCP3 gene is required for synaptonemal complex assembly, chromosome synapsis, and male fertility. Mol Cell 5(1):73-83.
- Miyamoto T, Hasuike S, Yogev L, Maduro MR, Ishikawa M, et al. (2003) Azoospermia in patients heterozygous for a mutation in SYCP3. Lancet 362(9397): 1714-1719.
- Mizutani E, Suzumori N, Ozaki Y, Oseto K, Yamada Namikawa C, et al. (2011) SYCP3 mutation may not be associated with recurrent miscarriage caused by aneuploidy. Hum Reprod 26(5): 1259-1266.
- Dong Y, Pan Y, Wang R, Zhang Z, Xi Q, et al. (2015) Copy number variations in spermatogenic failure patients with chromosomal abnormalities and unexplained azoospermia. Genet Mol Res 14(4): 16041-16049.
- Colaco S, Modi D (2018) Genetics of the human Y chromosome and its association with male infertility. Reproductive biology and Endocrinology 16(1): 1-24.
- Saxena AK, Tiwari M, Agarwal M (2018) Single nucleotide polymorphism of Arylsulfatase D gene (ASRD) and their association with male infertility. J Clin Gen Genomics, 1(2): 11-13.
- Saxena AK, Agarwal M, Kumar R, Kumar A, Singh C K (2020) Human X-linked CUL4B Gene Mutation Mediated Changes in Function during Development of Testis after Prediction of 3D Structure. Perception in Reproductive Medicine 4(1): 278-283.
- Saxena AK, Rastogi A (2015) Impairment of Nanog 3 Stem Cell Dysregulation Associate with Male Infertility in Human. Hereditary Genetics 4(144): 2161-1041.
- Saxena AK, Kumar A (2019) Genes and Male Infertility in Human. Published by Index of Sciences. Chapter-5, London¸UK pp: 119-127.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...