Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-4544
Review Article(ISSN: 2637-4544) 
Major Issues Related to Women Health, Social, Cultural and Economic Development Volume 2 - Issue 5
Ravi Kant Upadhyay*
- Department of Zoology, Deen Dayal Upadhyay Gorakhpur University, Gorakhpur, India
Received: October 6, 2018; Published: October 15, 2018
Corresponding author: Ravi Kant Upadhyay, Department of Zoology, Deen Dayal Upadhyay Gorakhpur University, Gorakhpur, India
DOI: 10.32474/IGWHC.2018.02.000150
Abstract
Present article sketches out major issues related to health, social, cultural, and economic wellbeing of the women. Most prevailing problems are related to malnutrition, sociality, sanitation, shelter, education, and livelihood, cultural and economic development in modern human ecological system. In poor countries women are living at socio-demographic risk of reproductive health, sociality, and healthcare. Condition is worst as large percentage of women belong to poorest strata of demography with highest fertility rates, having no means to meet out their daily needs. Starting from child birth to motherhood they are living under huge plethora of problems and a miserable cursed life. There is no real time data available on reproductive health, sociality, and healthcare of pregnant mothers, house hold and working women at global level. Two major factors lack of education and early marriage/parenthood are more assessed threats to girl-child and women in developing countries. These factors directly affect their social, cultural and economic development. There is a dire need of assistance from international agencies, governments, policy and law makers and social community to find solution of these burning problems. There is an urgent need for development of community support system for welfare of women that can assist them in decision making, confidence building, skill development, social and cultural wellbeing and economic empowerment of women.
Keywords: Girl Child; Human Ecological System; Health, Social; Economic and Cultural Development
Introduction
From various surveys conducted by international organizations it is very much clear that condition of mother-child health is not satisfactory. For time bound improvement it will need quick efforts and support from national and international organizations. Questions have been raised on girl child health at global level as condition in Africa and Asia is not satisfactory. Important issues related to women health are malnutrition, gynecological, obstetrics, preterm birth and lack of post-partum care. It is hard truth that both in developing and under developed countries issues related to maternal Health Care are similar. Both in suburban and rural areas gynecological care is poor as routine checkup be required after conception till childbirth. It is well known that an undernourished mother inevitably gives birth to an undernourished baby, perpetuating an intergenerational cycle of under nutrition. Undernourished girls have a greater likelihood of becoming undernourished mothers. This cycle can be compounded further in young mothers, especially adolescent girls who begin childbearing before they have grown and developed enough. When mothers take only short intervals between pregnancies and have many children, this can exacerbate nutrition deficits, which are then passed on to their children. Because of low economic status, education and negligence of community support system pre-natal care is either unavailable or of low grade. There are 7 well defined rights of a girl child, i.e. freedom of cultural practices, health, physical and mental protection, sexuality and reproduction, protection from exploitation, early marriage, expression of opinion and equal rights to inheritance. This is abiding by rule that global administration should protect and seek their rights honestly. But it is a great question that sound efforts have not been made with full zeal and desire for improving health care, social safety and cultural and economic development of women mainly living in developing and underdeveloped countries. After screening reports and information available in database; though an improvement has been made in this direction, but more efforts are to be made for achieve the goal. This is much expected from society, community and people that they should pay due respect to the women and girl child. The Twenty Rights of Childbearing Women how many have been fulfilled is a subject of query at global level.
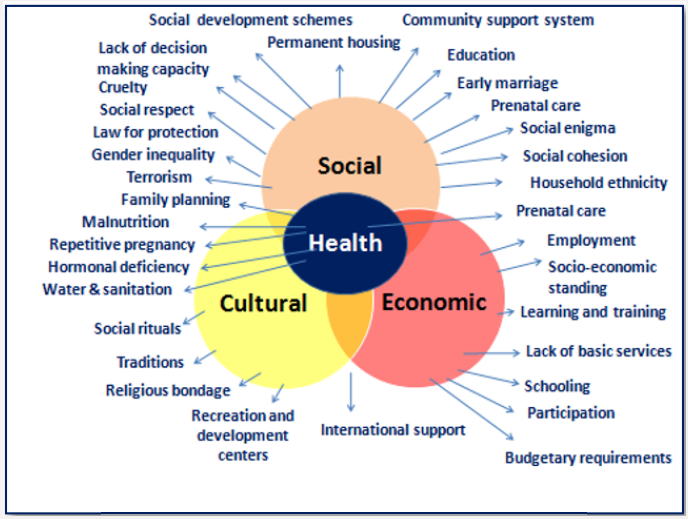
Despite of economic growth in India, India’s hunger is still worse than North Korea or Sudan. And a child raised in India is more likely to be malnourished than Somalia. Worst situation is in tribal dominated states such as Bihar, Orissa, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh. An all-round development be needed to fight against malnutrition. Approximately 620 million people in India did not have a toilet in their house and they use public toilet or just outside. Recently, in year 2016, Modi Government has started Swachh Bharart Abhiyan, Beti Bachao and Beti Paradho Abhiyan. Both sanitation and malnutrition are serious problems of Suburban and rural areas. Hence, present government has given due consideration to find quick solutions of health and sanitation problem and providing special attention to solve the problem of girl child and women. All four issues health, social, economic and cultural development have been decided by keeping the women health in centre. Problem of sanitation and malnutrition are not due to lack of economic problems, but social sectarianism and education are main factors. In 2012, UNICEF made a report that malnutrition is based entirely on lack of the food. But now, UNICEF and many charitable organizations are saying that poor sanitation is one of the biggest reasons of malnutrition. Currently, the India government is working to solve malnutrition problem by making more foods. There is no detailed report available on women population affected ith communicable diseases and noncommunicable diseases at global level. There is a rising trend of life style diseases in urban women due to non-functionality in rich society. Two trends in human population i.e. under nourished and over nourished are prevailing and both are harmful for society. There are three contributing factors poverty, malnutrition, and sanitation which are responsible for ill health. Lack of education is responsible for very low socio, economic and cultural development in country with majority of the population is living at or below the poverty line. Even after existence of all negative factors, fertility rate in low economic group is very high, with low socialization and cultural following. This signifies need of controlling factors such as family planning and generation of livelihood means to fight against hunger and poverty existing in sphere of women in society by excluding religious and social factors. Some of the major causes for malnutrition in India are economic inequality that can be finished only by making and implementing new education and housing policy, law for work and wages, legal system to provide equal rights to share resources, income, economy and development of a selfsustained self-governing system (Figure 1).
Issues Related to Women and Child Health
More especially in developed and under developed countries women mainly mothers are kept in un-represented groups of society and at high-risk for specific health problems. Major problem is malnutrition, gender inequality, education and social security in large section of society. There is a great anomaly that highest fertility rate exists in weakest economic section of the society. Women in poor countries facing problem of micronutrient deficiencies, and they are in great need of nutritional supplements to supply vitamin A, iron, iodine, zinc and folic acid. Iron deficiency is the most common micronutrient deficiency in children and pregnant women worldwide. Most susceptible iron deficient groups are infants, preschoolers, women of childbearing age, and pregnant women [1]. Women suffer from anemia because they do not have enough iron-rich foods. Moreover, a woman’s body loses iron because of menstrual blood flow and also during childbirth. Iron is required for the developing fetus, neonate, infant, and child. Its requirement increases during development period of life due to production of red blood cells and muscle cells as well as brain development. It is made available to neonates, infants, and children from dietary sources including breast milk (lactoferrin) and hemeand non-heme-containing foods. But mother require enough amount of lactoferrin in day’s meals during pregnancy [2]. Breast feeding improves the health of mothers and infants.
Micronutrients improve the health of mothers, protect their reproductive age, and provide strength to pregnant women to support growth and development of unborn children. These are not only required for the survival of the child but also assist in physical and mental development of children up to five years old. Folic acid supplementation, iodized salt, vitamin D, and A, iron and protein are main dietary requirements of pregnant women. After iron, vitamin A deficiency also prevails at global level as one in three preschool-aged children and one in six pregnant women are deficient in vitamin A due to inadequate dietary intake (1995–2005 data). Global evidence indicates that in regions where vitamin A deficiency is prevalent, vitamin A supplementation can reduce child mortality by an average 23 per cent. Vitamin A is necessary to support the response of the body’s immune system, and children who are deficient face a higher risk of dying from infectious diseases such as measles and diarrhea. Child and mother both need nutritive food during pregnancy and before pregnancy. It could make available by providing supplementary foods under the integrated child development services scheme. Due to lifelong malnourishment women always have low blood pressure. Woman of the house is usually the last one to eat the food. And many a times she is left with the smallest portion of food.
In poor countries women are at high socio-demographic risk for preterm birth [3]. This is due to early age marriages of young girls, it severely affect their maternal health. Young age mothers have more burdens to give birth to their child but they have no affordable means available for effectively managing maternity. Condition is so worst that they have no budget to buy sanitary napkins and safety pads to manage their menstrual flow. They are looking for government help for seeking maternal health care, antenatal care, institutional birth, and cesarean safe delivery. There is a load of repeated pregnancies that creates great problem of anemia. It results in birth infant deaths; hence, there should be long term strategies to end preventable maternal deaths. There is a need to ensuring marriage at/after legal age of 18 through awareness and ensuring a girl completes secondary education. It is a fact that young mothers, who are lacking good diet and intake low calorie food, face the incidence of low birth weight (LBW) of child. A third of women of reproductive age in India are undernourished with a body mass index (BMI) of less than 18.5kg/m2. Thus, both child and mother are affected due to malnutrition.
In economic sections of society there are two problems either under-nutrition or over-nutrition, both are due to unequal distribution of resources. One is responsible for low birth weight in infants, while second overweight, both situations are avoidable and need micro discrepancies in public supply. It was hard truth up to 1991 that more than one third of the world’s malnourished children live in India but in last fifteen years a significant improvement has been done not even in case of child and women but in other sections of society. The prevalence of underweight children in India is among the highest in the world and is nearly double that of Sub-Saharan Africa with dire consequences for mobility, mortality, productivity and economic growth [3,4]. Some of the major causes for malnutrition in India are Economic inequality. Due to the low social status of some population groups, their diet often lacks in both quality and quantity. Women who suffer malnutrition are less likely to have healthy babies. In India, mothers generally lack proper knowledge in feeding children. Consequently, new born infants are unable to get adequate amount of nutrition from their mothers.
According to Global Hunger Index 2017, India ranked 97th out of 118 countries. Though India is one of the fastest growing countries in terms of population and economics, sitting at a population of 1.342 billion and growing at 1.5%–1.7% annually (from 2001–2007) [5,6]. India’s Gross Domestic Product growth was 9.0% from 2007 to 2008; since Independence in 1947, its economic status has been classified as a low-income country with majority of the population at or below the poverty line [7]. Now in recent report it conditions in poverty alleviation has been improved from 67 to 35% in rural areas. Due to prevalence of poverty in geographically poor remote areas, there is delineation of people from national development. Its main causes are low education, forced child labor, and prevalence of child marriage. Population living below the National Poverty Line is in need of civic amenities, education, and employment for their economic development. It needs new policies on work force, wages, resource utilization and sharing of cost, and enhancement of rural productivity by supporting agriculture micro-industry sector.
Deficiencies in nutrition cause long-term damage to both individuals and society. Compared with their better-fed peers, nutrition-deficient individuals are more prone to infectious diseases such as pneumonia tuberculosis and other communicable diseases that results in higher mortality rate. In addition, nutritiondeficient individuals are less productive at work. Malnutrition during pregnancy causes the child to have increased risk of future diseases, physical retardation, and reduced cognitive abilities. It is very clear that low income groups show low productivity, that is not only gives them low pay but traps them in a vicious circle of undernutrition [8]. It also brings inefficiency to the society, especially in India where labor is a major input factor for economic production [9]. On the other hand, over-nutrition also has severe consequences such as obesity, cardiovascular, blood pressure and stroke. Obesity causes several non- communicable such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancers and chronic respiratory diseases. In India national obesity rates in 2010 were 14% for women and 18% for men with some urban areas having rates as high as 40% [10]. Based on employment and wages two groups of malnutrition undernutrition and over-nutrition has been emerged [11]. Many factors, including region, religion and caste affect the nutritional status of Indians. Living in rural areas also contributes to nutritional status.
First partnership has been established with the “Aaajevika” program of the India government’s National Rural Livelihood Mission to test whether women’s nutrition initiatives can be mainstreamed through women’s empowerment platforms under “Aaajevika”. Secondly, UNICEF in Andhra Pradesh and Telengana is technically supporting the state government to implement the One full meal scheme. The programme aims to improve the nutrient intake of pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers and reduce the prevalence and severity of maternal anemia. In Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, 5100 women federations, supported by Aajeevika and UNICEF, partner with State Governments to provide 895,000 pregnant and lactating mothers nutritious meals daily through ‘ONE FULL MEAL’ scheme, located in villages where under nutrition rates are high. One Full Meal entitles pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers to receive a free nutritious meal every day between 11am and 2pm at the village Anganwadi centre, 25 days a month. Each ICDS project gives a quarterly grant to the federations that are involved in the implementation of the programme. There must be a long-term program for mitigation of nutritional deficiency in women.
For management of health of economically poor women international agencies and civil society, government and local bodies should come forward to find timely solutions of problems related to gynecological, obstetrics, and maternal health. Women need full care and support starting from time of conception till childbirth, ensuring them to provide pre-natal care, management of pregnancy, and post-partum care. The menopause is a physiological event involving ovarian failure as a result of a loss of ovarian follicular activity, which leads to oestrogen deficiency, resulting in permanent cessation of menstruation and loss of reproductive function. Women become hormonal deficient (oestrogen deficiency) very easily. Efforts should be made to lower down avoidable risks for women and infants, including preterm birth, cardiometabolic risk factors, including waist circumference (WC), blood pressure, cholesterol level, and presence of type 2 diabetes. There should be an arrangement of nutritional food for adolescent girls who begin childbearing. It is well known that an undernourished mother inevitably gives birth to an undernourished baby, perpetuating an intergenerational cycle of under-nutrition. And all these deficiencies passed on to their children, and effect health of both child and mother.
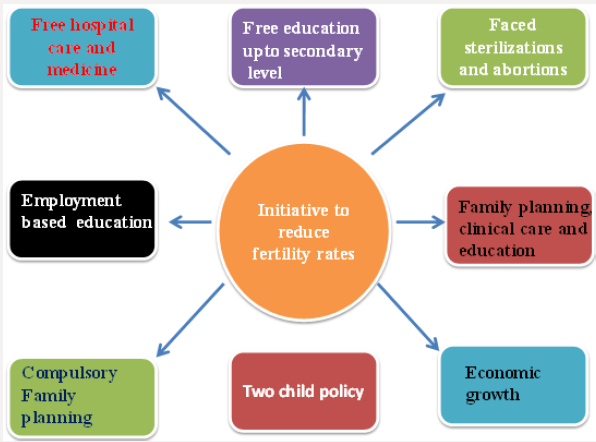
Awareness programs be launched to tell about safe use of contraceptives among all women including poor women both in urban and rural areas for control of child birth [12] (Figure 2). They should be abiding the benefits of one or two child policy. Awareness programs on women health can make significant change in nutritional behavior and reduce health related problems. Preterm birth is a disease of multi-factorial etiologies that has environmental, social, and maternal health components. However, for successful pregnancy outcome antenatal nutritional counseling is required for young mothers. Furthermore, enhancing nutritional support can ensure adequate weight gain during pregnancy may provide additional benefits especially for women with a history of child marriage. Long term effect of counseling will also assist in infant and young child feeding (IYCF) practice. Of total 1-2% of infants born preterm (<32 weeks of gestation) and have low birth weight (<1500 g) need adequate nutrition to ensure good health, growth and development. This category of infants’ needs incremental milk feeding that can provide them vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates and lipids. No additional resources will require implementing an optimal feeding strategy.
Issues Related to Social Well Being of Women
From various surveys conducted by international organizations condition of mother-child health is not satisfactory. There is high level insensitivity to the women during pregnancy, and post pregnancy. Questions have been raised on over all issues related to girl child health at global level. Despite of economic growth in India, India’s hunger is still worse than North Korea or Sudan. And a child raised in India is more likely to be malnourished than Somalia. Worse situation is in tribal dominated states such as Bihar, Orissa, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh. An all round development be needed to fight against malnutrition. Approximately 620 million people in India don’t have a toilet in their house and they use public toilet or just outside. Recently, in year 2016, Modi Government has started Swachh Bharart Abhiyan, Beti Bachao and Beti Paradho Abhiyan. Both sanitation and malnutrition are serious problems of Sub-urban and rural areas. Women have burden of family, sanitation and are facing problem of malnutrition and victims of social sectarianism. In 2012, UNICEF made a report that malnutrition is based entirely on lack of the food. But now, UNICEF and many charitable organizations are saying that poor sanitation is one of the biggest reasons of malnutrition. Currently, the with Indian government is working to solve malnutrition problem by making more foods. Two major factors lack of education and early marriage/parenthood are more assessed threats to girl-child and women. Girl child should provide traditional knowledge and cultural values during her school and pre-school period.
Traditional knowledge and practice of Indigenous Peoples related to their food use and well-being is a wealth of information for academic study and for public health nutrition. Despite unique long-evolved heritages of knowledge of ecosystem resources, Indigenous Peoples comprise 15% of the global poor, but only 5% of the world’s population, and they experience poverty, discrimination, and poor nutritional health at far greater rates than mainstream populations in their nations of residence [13]. Perinatal mental health is considered an important public health issue with health policy internationally identifying the importance of psychological support for women in the perinatal period. Midwives and primary care nurses are ideally positioned to detect mental distress early. There should be a fight against hunger and poverty existing in sphere of women in society (Figure 3). The government of India started a program called Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) in 1975. ICDS has been instrumental in improving the health of mothers and children under age 6 by providing health and nutrition education, health services, supplementary food, and pre-school education. The ICDS program is one of the largest in the world. It reaches more than 34 million children ages 0–6 years and 7 million pregnant and lactating mothers. Other programs impacting under-nutrition include the National Midday Meal Scheme, the National Rural Health Mission, and the Public distribution system. The challenge for these programs and schemes is how to increase efficiency, impact, and coverage. India is a signatory to the 27 survival and development goals lay down by the World Summit on children 1990.
In India National Rural Health Mission is working for rural people working with the goal to “improve the availability of and access to quality health care by people, especially for those residing in rural areas, the poor, women, and children. It has included the objectives to reduce infant mortality rate, launching public health services, prevention of communicable and non-communicable diseases mainly endemic disease like JE. It also kept attention to provide universal access to public health services, create population stabilization, as well as gender and demographic balance, revitalize local health traditions and mainstream and finally, to promote healthy life styles. Traditionally, UNICEF has been supporting India in a number of sectors like child development, women’s development, urban basic services, support for community based convergent services, health, education, nutrition, water & sanitation, childhood disability, children in especially difficult circumstances, information and communication, planning and program support. The Indian government started midday meal scheme on 15 August 1995. It serves millions of children with fresh cooked meals in almost all the government run schools or schools aided by the government fund.
ISKCON Food Relief Foundation run Annamrita, and Food for Life and Akashya patra Foundation are the world’s largest NGO which are running midday meal programs. The meals served by Food for Life Annamrita and Akshaya Patra complies with the nutritional norms given by the government of India and aims to eradicate malnutrition among children in India. Each of them are serving freshly cooked plant-based meals to over 1.3 million school children in government and government-aided schools in India. These programmes are conducted with part subsidies from the government and partly with donations from individuals and corporations. Food for Life Annamrita is the premier affiliate of Food for Life Global the world’s largest free food relief network, with projects in over 60 countries [14]. In order to implement these goals, the Department of Women & Child Development has formulated a National Plan of Action on Children. Kuposhan Mukta Bharat by Ministry of Social Welfare
Issues Related to Economic Well Being of Women
Economic inequality can be alleviated by providing good education, schooling, learning and training based business oriented programs to support women. Both in rural and urban sectors more micro-economic and handicraft training-based programs are required to provide initial employment for women self-standing. Most of the forest and agricultural products are used by industries for production of goods, small self-help groups and government loans can provide more employment to rural women. Sericulture, aquaculture, honey bee culture, pearl culture, mushroom culture, nurseries, energy plantation, agri-business, handicrafts, cloth designing, painting, art and other small-scale industries can support women economic empowerment. In next step for increasing their participation young women should allowed to join knowledge based personality development programs, for capacity building, generation of good workmanship and leadership in all different sectors of human life. Economic development is only possible through education, training, learning, skills and proficiency in work. It will need new development policies, plans and programs for raising issues related to welfare of women. Change in education policies, personality development and cultural mindsets can finish economic marginalization in women. It will support to build a positive force for social equality and economic development in all stratums of women in society. It will also important for selfmotivation freeness in thinking, relieve from bondage, decision making capability and for making women self-dependent. It is combined force be required economic, social and cultural development and safety of girl child. Recent economic growth of India has been increased due to participation of women as employee in various industrial, social, educational and information technology sectors. Both private partnerships and corporate and government sectors are considering more number of females due to their skill based learning and education.
Child marriage is a central stage issue that directly influences education, health, cultural, social and economic development of girl child. It is main obstacle to economic prosperity and development. It is a health hazard and barrier to girl child education. Child marriage is estimated to cost economies at least 1.7% of GDP. This lonely factor has largely disturbed socio-economic wellbeing of the women. In case of women working as labor they are facing more destitution and inequality in wages and other benefits. Condition is worst in case of migrant workers; child labor, forced labor, slavery and occupational health. There are many countries where there is discrimination in women transport services, passport services, vehicle driving, entertainment and communication. Behind all these odd situations lack of education and personal development of women are responsible factors. There are two sustainable development goals gender equality (SDGs 2030 no. 5) and decent work and economic growth (No. 8) also direct us for development of women without any discrimination in work, wedge, livelihood and living. Though there are many parameters of viewing economic development, but culture and its relationship can boost economic development in rural as well as in urban area.
For every girl child recurring deposit schemes are required during school age with insured money by government to assist the girl child in rural areas where there is no economic base is available to them. There should be school level program to keep a close watch on child marriage, because rural people think that girl child are burden on their shoulders, hence, choose un-lawful act of child marriage. It has high economic impact on economic development of girl child that results in higher fertility, severe prenatal and postnatal health problems, lower educational attainment and lower lifetime earnings, with other negative outputs. Child marriage is a part of the newly adopted sustainable development goals or agenda 2030. But despite a growing acknowledgement of the harms of child marriage, not nearly enough is being done to end this practice. If girls and women are discriminated against in accessing education and training, the country is denied of a skilled human capital needed otherwise to promote growth. Alternatively, investment in girls/ women education proved to be a more effective way of controlling the size of a population and improving child’s welfare.
Issues Related to Cultural Well Being of Women
For overall development of girl child, their participation in cultural activity and traditional rituals must be ascertained. From school level girl child should allow to join music art, theater, sculpturing, designing, forestry and agriculture for their over cultural development. Religion biased restriction and discrimination of women must be prohibited by making law. Deprivation of health and hygiene, education and recreation and cultural facilities weaken the social development of women. It severely affects country’s overall productivity, prosperity and economic development. For multicultural development of girl child, they should be allowed to join inter-religious, social and cultural activities and so that they can be benefited of cultural and ethnic diversity of contemporary society. They will get the ability to express and share their individual cultural heritage, including their language and religion. The influence of subcultures within their society based on shared characteristics such as religion, social class, special needs or sexuality, and their individual factors such as gender, education, experience and age. For cultural development ecological, agricultural, traditional, socio-geographical, historical, ethical and religious activities be solemnize with equal participation of women. They should not be prohibited from cultural and social rituals, religious pilgrimages. In ethnic world, it is very hard to equalize the value-based practices, because circumstantial uneasiness due to unavailability of possibilities and cultural objectives. All this happens due to nearsightedness, religious blindness, and mental agony and superiority of man that harm the cultural pluralism and its diversity.
In every society there are social rules, standards and regulations that will assist in formation of system of law-based governance. Formation of law, rules, policies, rights and values articulates democracy with social system. Both democracy and human society should promote cultural and economic development for sustainability of generation and ecological system. In human society culture is not developed in days but it is outcome of our long legacy of past, formed through shared and learned social norms, values, behaviors, education, rituals, customs and traditions and communication. It is main dimension of ecological development, international cooperation, and socio-economic inter-relationships among democratic countries. Cultural diversity is an important development factor that provides identity, exposure to long heritage, environmental and social wellbeing and human behavior in group. It is also related with internal development of society, resource sharing, and social networking. Cultural dimension of environmental management is widely concerned to world heritage, traditional knowledge, witnessing the gradual emergence of a universal, global culture with equal rights and values. It holds adherence to civil and human rights, gender equality, respect for property rights, favors the rule of law, acceptance of market forces as a mechanism for resource allocation. Due to rising trends of international communication on education, social structure and culture, it is quite necessary to prepare girl child for multicultural development. Girl child should provide knowledge of art and craft, customs dressing style, forms of address and relating to others are important as practical subjects. In addition, development of communication skills, language, behavior identity, non-verbal communication and interpretation of meaning is also essential. They also need knowledge of modern tools such as computer programming, visual methods, including photo voice, and participatory video, digital storytelling, creative writing, debate, adventures, fares, films, acting, designing, art, culture, games, focuses on identifying and addressing gendered violence in communities. For making family structure ideal they should be acquainted with kinship, leniency, morality, social norms, religion, decision making and self-reliant in economic development.
Conclusion
There is an urgent need to improvement of health and hygiene, education and social networking, recreation and cultural facilities for women. There should be new policies and programs be launched to upgrade the socioeconomic status of women. Among. The Twenty Rights of Childbearing Women how many have been fulfilled is a subject of query at global level. Therefore, rather than making critics and questions, more solutions be needed. There is a rising trend of life style diseases in urban women due to non-functionality in rich society. Contrary to this, women living in poor sanitation, in nutritionally vulnerable and deprived social areas, having no appropriate maternal diet; energy balance and protein intake in food are functional. Gender violence against women should be minimized. Understanding and developing prevention strategies and interventions for psychological or emotional abuse remain a major international challenge. One step ahead development should base on values, sociality, culture, behavioral harmony, should compatible with humanity’s moral development. It could only possible through by social acceptance, by selective elimination and by integration. Hence, there is a need to provide knowledge of geography, climate, and natural resources, access to new technologies, communication methods, cultural methods to transform the mind, body and soul of women for thinking at global level, make successful behaviors for increasing productivity, economic growth and prosperity. With international declarations such as the United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals including gender equality and women’s rights as central to national and global development, there is hope. Women should provide equal opportunity in education, entrepreneurship, social and religious activities, law making, external affairs, defense, and political decisions at regional and national policies. Social unjustice to women is great hurdle to building human humanity and overall societal development of man.
References
- Sermini CG, Acevedo MJ, Arredondo M (2017) Biomarkers of Metabolism and Iron Nutrition. Rev Peru Med Exp Salud Publica 34(4): 690-698.
- Mishra S, Goldman JD, Sahyoun NR, Moshfegh AJ (2018) Association between dietary protein intake and grip strength among adults aged 51 years and over: What We Eat in America, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2014. PLoS One 13(1): e0191368.
- Franck LS, McLemore MR, Cooper N, De Castro B, Gordon AY, et al. (2018) A Novel Method for Involving Women of Color at High Risk for Preterm Birth in Research Priority Setting. J Vis Exp (131).
- (2012) Turning the tide of malnutrition. World Health Organization.
- (2010) India in grip of obesity epidemic. The Times of India.
- (2009) World Bank Report on Malnutrition in India. World Bank Report.
- (2017) Global Hunger Index Report. International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI).
- World Development Indicators - Google Public Data Explorer.
- (2009) World Bank Development Report. Source: The World Bank 2009.
- Derek Yach, Corinna Hawkes, C Linn Gould, Karen J Hofman (2004) The global burden of chronic diseases. Journal of the American Medical Association. Source: JAMA.
- Benson A, Calhoun L, Corroon M, Gueye A, Guilkey D, et al. (2018) The Senegal Urban Reproductive Health Initiative: A Longitudinal Program Impact Evaluation. Contraception. 97(5): 439-444.
- Kuhnlein HV (2017) Gender roles, food system biodiversity, and food security in Indigenous Peoples’ communities. Matern Child Nutr 13(Suppl 3).
- Meenakshi JV (2016) Trends and patterns in the triple burden of malnutrition in India. Agricultural Economics 47(S1): 115-134.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...