Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-4544
Case Report(ISSN: 2637-4544) 
Evaluation of Renal Rehabilitation Program for Cadaveric Renal Transplant Recipient- A Single Case Report Volume 2 - Issue 5
Kamalanathan P1*and Monisha RP2
- 1Associate Professor, SRM College of Physiotherapy, India
- 2Assistant Professor, SRM College of Physiotherapy, Kattankulathur, Tamil Nadu, India
Received: October 4, 2018; Published: October 10, 2018
Corresponding author: Kamalanathan P, Associate Professor, SRM College of Physiotherapy, Kattankulathur, Tamil Nadu, India
DOI: 10.32474/IGWHC.2018.02.000149
Abstract
To report a clinical case of Cadaveric renal transplant recipient 30 year old male reported to SRM Physiotherapy Department presented with complaints of difficulty in breathing, sitting, standing and independently walking. As clinical manifestations of post transplantation are wide, it leads to multidisciplinary approaches. Physiotherapy treatment protocol is important for early diagnosis of co morbidity and to provide initiation to renal rehabilitation program.
Keywords: Renal Rehabilitation; Cadaver Transplant; Renal Transplant
Introduction
Cadaveric renal transplant is a rare procedure, Renal recipient knowledge regarding post-transplant aspect is essential in terms of managing with short-term problems imposed by transplantation and the long-term outcome. This requires patient education programs that prepare patients and renal rehabilitation program that makes the patient to gain the functional independence to the greatest degree possible after returning back to daily activity with a new kidney [1]. The common manifestations related to renal transplantation are pain, difficulty in breathing, restriction in chest expansion and reduction in functional mobility. Manifestations related to cardio-vascular system are dysfunctional breathing. Aim of this single case study is to explore the post renal transplantation consequences and to highlight the need for renal rehabilitation program.
Case Report
A 30 year old male child reported to SRM Medical College, Physiotherapy Department with complaints of difficulty in breathing, sitting, standing, and walking independently. The past medical history revealed that he had chronic head ache and without any referral and prescription of drug he has been under medication for the past one year, He has been mentioning the tablet color as yellow, he doesn’t have the knowledge of the tablet name and the drug combinations. When enquiring history to his parents and wife, it is evident that he is a known case of alcoholic for the past 10 years. His first episode of headache was before 6month with pain lasting for a duration of 2 min. He had 5 episodes of abdominal pain. He was under regular drugs management for CKD- STAGE V diagnosed before a year on (20/2/2017). On observation, he has ECG leads in situ, follies catheter, oxygen mask delivering 6 liters of Oxygen and right inguinal incision is seen. He has difficulty in bed mobility, breathing dysfunction is the predominant symptom in him. On examination of higher mental function, he is conscious and oriented. On motor examination, he has normal muscle tone on the bilateral upper limb and lower limb segments. Deep tendon reflexes were normal. On a sensory examination, superficial sensation (assessed on body segments) was intact on the bilateral side of the upper limb and lower limb.
Renal Rehabilitation
Transplantation of Human Organs is one of the biggest medical breakthroughs of India. It has been initiated in the early 1970s. But, only relatively few Indian patients are benefitted from this medical advancement. Prevalence rate of CKD is increasingly common in this century, in India over 2, 22,000 people are diagnosed with End stage –GRADE V CKD, they were in need of renal transplantation and the majority of these patients are young, only through organ transplantation they can fulfill their hope to survive. Many patients lose their life mainly due to no availability of organs [2-4]. Even though the renal transplant procedure is becoming common, the co-morbidities faced by the individual in the post-transplant period is left unnoticed and there is no standardized treatment approach to deal with their kidneys at the post-operative period. In this single case study renal rehabilitation program has been initiated for the recipient of cadaveric kidney transplantation, his parents were accepted for cadaveric transplant according to their priority on the waiting list maintained at the University.
Renal rehabilitation is initiated on the day 0 on the day of transplant with breathing exercises; bed mobility exercise and sitting up in bed were done. On day 1- patient has been made to sit in a chair for four hours and asked to perform day 0 rehabilitation exercises. On day 2- he has been asked to transfer out of bed and made to sit in chair for at least eight hours in total, here the recipient has completed 2 short walks around the bed with oxygen support. On day 3- patient has been made to sit out of bed for most of the day and instructions were given to increase the distance and frequency of walks in a day, on day 4- primary emphasis has been given to walking without assistance and the total distance covered has to be increased, here the patients RPE should be assessed simultaneously. Based on the individual differences in outcome the post-operative treatment protocol used in renal rehabilitation can be varied [5-6]. Breathing exercises will help to re-expand lungs and helps to clear phlegm from the airways and therefore reduce the risk of chest infections. The patient has been asked to take four slow breaths and asked to maintain the holding time till 5 seconds and he has been advised to repeat the exercise every hour during the day. He is advised to practice this whenever he has the episodes of dyspnoea while walking. This patient had complaints of copious amount of purulent sputum production on day 2 following the post renal transplant and coughing was often be uncomfortable, but he has been asked to hold a rolled up towel or pillow against incision to provide some support [7].
He has been asked to practice bed mobility exercises three times a day, this will improve circulation and he was advised to sit upright in the bed as much as possible during the day to help prevent other complications. on day 0 of post-transplant procedure he is given instructions to perform Ankle pumps for one minute, alternate knee bends 15 times on each side. Straightening knee with a straight leg, he has been asked to push his knee down into the bed. He has been asked to Hold this for 5 seconds and repeat 15 times on each side. Leg raises –lift one leg up straight in the air, keeping your knee straight. Hold it up off the bed for five seconds and repeat 15 times on each side [8-10]. Renal Rehabilitation is a 12 week programme designed to help people with renal disease to start exercising regularly. This is a twice-weekly, hour long class involving a variety of exercises aimed at different ability levels, to find the individual differences in exercising ability, exercise dairy has been given to him.
Data Analysis
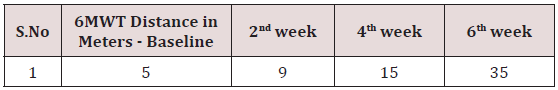
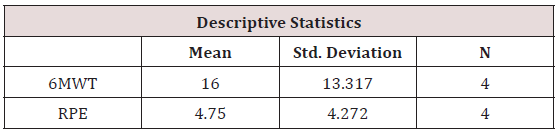
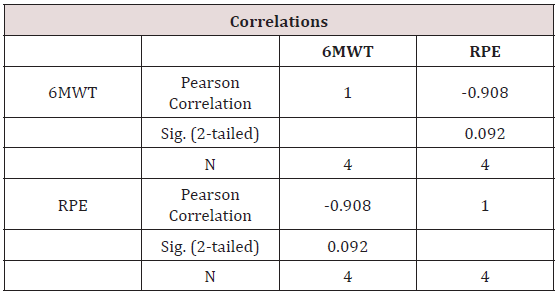
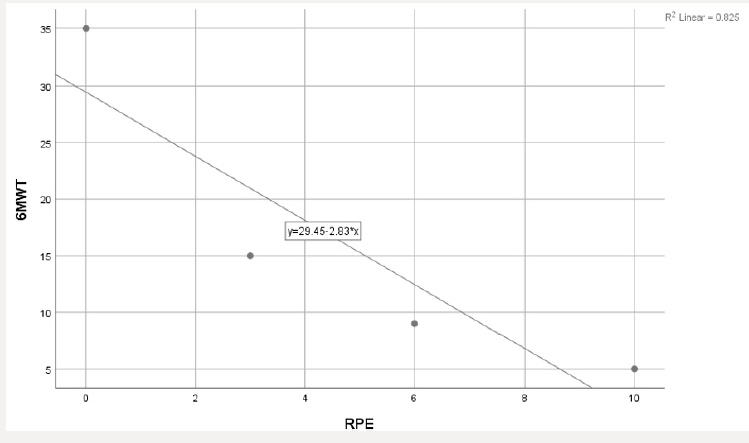
To analyze the beneficial effects of renal rehabilitation on posttransplant period, 6MWT and RPE scale has been used to monitor the treatment effects. After 6 weeks of renal rehabilitation, 6MWT has significant improvement and functional activity has been increased with marked reduction in RPE scale on compared to baseline (Tables 1-4) and (Figure 1).
Discussion
As cardio-respiratory and musculoskeletal dysfunction is common on the post transplantation period, there is a need for introducing the renal rehabilitation programme for the maintenance of functional capacity in this patient population. They are prone for reduction in functional exercise capacity as there is reduction in 6MWT distance and this study subject experiences perceived exertion even on a 2MWT on initial 1st to 3rd POD. He had a reduction in vital capacity and forced expiratory volume that can be assessed by bed side assessment tool of pulmonary function in snider match test and breath holding test. Early physiotherapy rehabilitation program emphasizing renal rehabilitation helps improving the patient functional capacity by improving the 6Minute walk Test distance and reducing the perceived exertion as measured by Borg’s rate of perceived Exertion. This early physiotherapy program during POD 0 for patient can prevent a reduction in respiratory muscle strength and increasing the functional capacity. There has been increased interest in providing exercise intervention for patient undergoing renal transplantation, but there is no standardized treatment protocol is evident. When he has diagnosed with CKD, lack of knowledge in exercise intervention has made him to be isolated and confined to the bed, that made him to acquire CKD STAGE V. During his waiting period for donor kidney, he had developed poor lung function and peripheral muscle de-conditioning. Little research and attention have been paid on to the effects of an exercise intervention after kidney transplantation, especially regarding the best time to start a program, how long to continue a program, and the level of intensity the activities should require to be accomplished. Pre-operative physiotherapy management will enhance the post-operative renal rehabilitation program participation, as the patients were aware of the treatment protocols in the patient education session; fear of participation in exercise session is minimized. But debate has been existing still now regarding the renal rehabilitation programs long term consequences and the advantages of incorporating physiotherapy management for post renal transplant patients were not wide spread enough. Lack of research findings in this patient population is still a limitation in finding a suitable treatment protocol in the management of patients with renal transplantation.
Conclusion
We conclude that early exercise intervention for patients undergoing renal transplantation is beneficial in improving the exercise capacity of patients and it has been proved that renal rehabilitation guidelines enhances the cardiovascular efficiency in the initial days of rehabilitation. Further research has been needed to find out the rehab guidelines that focus on the improvisation in renal parameters on post physiotherapy rehabilitation program.
References
- (2012) USRDS: 2012 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States, Bethesda, MD, US Renal Data System, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease.
- Venkataraman R, Sanderson B, Bittner V (2005) Outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing cardiac rehabilitation. Am Heart J 150(6): 1140-1146.
- Keith DS, Nichols GA, Gullion CM, Brown JB, Smith DH (2004) Longitudinal follow-up and outcomes among a population with chronic kidney disease in a large managed care organization. Arch Intern Med 164(6): 659-663.
- O’Hare AM, Tawney K, Bacchetti P, Johansen KL (2003) Decreased survival among sedentary patients undergoing dialysis: Results from the dialysis morbidity and mortality study wave 2. Am J Kidney Dis 41(2): 447-454.
- Witt BJ, Jacobsen SJ, Weston SA, Killian JM, Meverden RA, et al. (2004) Cardiac rehabilitation after myocardial infarction in the community. J Am Coll Cardiol 44(5): 988-996.
- Taylor RS, Brown A, Ebrahim S, Jolliffe J, Noorani H, et al. (2004) Exercise-based rehabilitation for patients with coronary heart disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Med 116(10): 682-692.
- Painter P, Carlson L, Carey S, Paul SM, Myll J (2000) Low-functioning hemodialysis patients improve with exercise training. Am J Kidney Dis 36(3): 600-608.
- Cheema BS, Singh MA (2005) Exercise training in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis: A systematic review of clinical trials. Am J Nephrol 25(4): 352-364.
- Johansen KL (2007) Exercise in the end-stage renal disease population. J Am Soc Nephrol 18(6): 1845-1854.
- Roshanravan B, Robinson-Cohen C, Patel KV, Ayers E, Littman AJ, et al. (2013) Association between physical performance and all-cause mortality in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 24(5): 822-830.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...