Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2641-1652
Review Article(ISSN: 2641-1652) 
Portal Hypertensive Gastric Polyps Volume 1 - Issue 5
Umadevi Malladi*
- Associate professor of Gastroenterology, India
Received: December 04, 2018; Published: December 11, 2018
*Corresponding author: Dr. M. Uma Devi, Associate professor Department of Gastroenterology Department of Gastroenterology, India
DOI: 10.32474/CTGH.2018.01.000123
Abstract
Portal hypertension is associated with an increased number of gastric polyps, hence the term portal hypertension-associated gastric polyps. Histopathological examination reveals mucosal hyperplasia and vascular proliferation. Formation may be due to mucosal injury that is vascular in nature. Their malignant potential has not been fully elucidated; however, lesions can grow to a large size. Patients with portal hypertension are at increased risk of post polypectomy bleeding and other complications of polypectomy. Surveillance is likely to be safer than multiple polypectomies, therefore in patients with portal hypertension it is essential that gastric polyps are photographed and biopsied during routine surveillance gastroscopies.
Introduction
Mucosal abnormalities of gastrointestinal tract are common in patients with portal hypertension. Upper gastrointestinal mucosal abnormalities are more common 65 % [1]. Gastric mucosal abnormalities are Fundal varices, gastric antral vascular ectasia and Portal hypertensive gastropathy and gastric polyps [1].
Gastric Polyps: Unlike polyps of the colon, Gastric polyps in general population are relatively uncommon, with an incidence of < 2-3%. The most common polyps are fundic gland and hyperplastic types, comprising 77% and 17%, respectively. Adenomas are relatively rare, making up < 1% of detected polyps.
Portal Hypertensive Polyps (PHP): Portal hypertension is associated with an increased number of gastric polyps, hence the term portal hypertension-associated gastric polyps. It is a recent entity, described in cirrhotic patients with portal hypertension, portal venous obstruction or antral vascular ectasia. These lesions are similar to hyperplastic polyps, but with subepithelial vascular alterations histological features. Its prevalence ranges from 1-3% [1-3] of gastric Polyps in Patients with portal Hypertension is 2.2% PHP. Till now few published reports of this entity. All pts are cirrhosis pts-100% and history of PPI therapy elicited in - 88% of pts. In Canada the incidence is about 0.1% only 12 cases are reported till now in 20years. Aravind et al from India reported [4] portal hypertensive polyps in a study duration of 11 months, stating that polyps may be more common in the Indian population [4]. Gastroduodenal polyps were far more frequent in their study; almost 10% of patients had gastric polyps, and 8% had duodenal polyps.
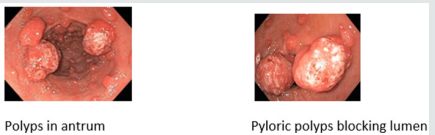
Historical Background: Zeitoun etal et al first described portal hyper tensive duodinal polyp-PHP in 2007 in GI bleed pt [5] Lam et al first described the histopathology - mucosal hyperplasia, extensive vascular proliferation, and granulation tissue. Location of Portal Hypertensive Polyps: The most common Gastric polyps are fundic gland and Hyperplastic types, comprising 77% and 17%, and Portal hypertensive Polyps < 2%. In a series by Amrapurkar Incidence gastric polyp in Portal Hypertension is 2.5 % (16 out of 631pts). of these 16, 9 (56.2%) are PHP, 6 (37.5%) Hyperplastic polyps, and one (6.25%) fundic gland polyp. Duodinal polyps were reported By Aravind et al. [4] and Boyed et al. [6] (Figure 1).
Etiopathogenesis: Exact etiology of Portal Hypertensive gastric Polyps is not known. Although they have a similar endoscopic appearance to hyperplastic polyps, they are believed to have a different etiology. Histopathological examination reveals mucosal hyperplasia and vascular proliferation. Their malignant potential has not been fully elucidated, however, the size of the polyps vary and can grow to a large size upto 3cms. Formation of PHPs may be initiated by mucosal injury that is vascular in nature. Several theories are proposed for the formation of polyps in an setting of portal Hypertension with Reactive changes in mucosa secondary to Increased vascularity in Portal hypertension.
a) PPI usage -in cirrhosis and portal Hypertension .H/O f PPI therapy elicited in 76% of pts [6]
b) H. Pylori infection - incidence of H.pylori In cirrhoisis is another proposed theory [6]
c) Mucosal injury - Following mucosal Injury there is ongoing healing and a reparative response in the form of foveolar hyperplasia. Resting Myofibroblasts in Muscularis propria are stimulated by mucosal injury, then they differentiate, proliferate, and migrate toward the site in injury. Hyperplastic tissue can either disappear (in 24.2% of cases) or persists, and progress to a Hyperplastic polyp. Hyperplastic polyp appears to be the result of over-vigorous regeneration that occurs in response to severe mucosal injury caused by penetration of the Muscularis propria. 55% of hyperplastic polyps with typical signs of PHP first arose or progressed following rubber band ligation. Baudet also reported a similar case, particularly implicating APC in the development of HP [7]. Macroscopically, portal hypertensive polyps cannot be distinguished from normal hyperplastic polyps but frequently present with small ulcerations [8,9].
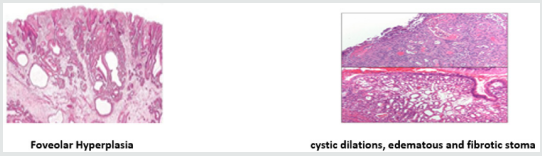
Histopathology of Portal Hypertensive Polyps: Lam et al -First described Typical Histopathological features [2]. The unique histological appearance of gastric hyperplastic polyps in patients with portal hypertension polyps is described. Marked Elongation tortuosity and dilatation of gastric foveolae with edema suggestive of foveolar hyperplasia with cystic dilations, edematous and fibrotic stoma scattered muscle bundles in surrounding stoma, a prominent capillary proliferation in the lamina propria, and scattered telangiectactic vessels . Numerous proliferating capillaries present in the sub epithelial tissue differentiating from Hyperplastic Polyps [4]. The histopathological examination of portal hypertensive polyps reveals mucosal hyperplasia and vascular proliferation with significantly higher vessel diameter of >50 μm and increased vascular density.
Morphometry: Amrapurkar etal studied Vessel density (mean vessel area/HPF) and diameter by using Morphometry lens. Foveolar Hyperplasia, with vascular proliferation Density and diameter of capillaries in the lamina propria were similar but more frequent. On immunohistochemistry, PH polyps and PH gastric mucosa had significantly higher vessel diameter of >50 μm, increased vascular density as compared to non-portal hypertensive polyps (PHP) and normal gastric mucosa [7].
Immunohistochemistry Staining: staining with CD 34 as a marker of vascular proliferation, proliferating capillaries indicating angiogenesis [7]. There are still no clear diagnostic criteria for portal hypertensive polyps [10]. However, typical features of portal hypertensive polyps reportedly include foveolar hyperplasia of the epithelium as well as proliferating, ectatic capillaries in the lamina propria. These features indicate their portal hypertensive nature and distinguishes them from inflammatory polyps (Figure 2).
Risk Factors for PHPs: The independent risk factors for PHP were identified. There are thrombocytopenia (platelet count < 130 × 103/μl), Child-Pugh score > 6, and MELD score > 16. The strongest risk factor for the development of these polyps was previous rubber band ligation. This may be because band ligation of the esophageal varices leads to increased formation of portosystemic shunts, including the gastric wall [11,12].
Natural History: Although there is an emerging evidence of the neoplastic potential of usual hyperplastic polyps, the natural history of portal hypertension-associated polyps is unknown. Identification and management of portal hypertension-associated gastric polyps present a particular dilemma, as these patients often have coagulopathies and vascular ectasias [13]. Therefore, the natural history and endoscopic features of gastric polyps arising in portal hypertensive patients warrants further exploration.
General Recommendations are
a) Portal Hypertensive Polyps-what is the Best way to Diagnose: Endoscopic features are Insufficient and indistinguishable from other polyps. Endoscopic ultra sound helps in assessing the vascularity of the polyp in special situations where there are obstructive symptoms with need for resection
b) Are mucosal Biopsies are Adequate? Or do we Need to Resect Polyp for Diagnosis?
Mucosal Biopsies are inadequate. Resection associated with high degree of bleeding (No increased Risk in colonic polypectomies) Reasonable approach should be to do mucosal biopsies initially and follow up the patients as these patients undergo upper endoscopy every 6months as per the protocol
c) What is the Risk of Turning into Malignancy?
As they resemble Hyperplastic polyps which are now considered to harbor risk of malignancy, these may be expected to behave similarly. However, there are No reports of Increased Gastric malignancy In Cirrhosis.
d) How Significant these Lesions to Practicing Clinician: Treatment has to be individualized
I. Neoplastic lesions need to be ruled out
II. Risk of continuing blood loss more in duodenal polyps
III. Polyp causing Obstructing symptoms by their location and sizes have to be removed after taking precautions
Surveillance: Hyperplastic polyps account for more than 50% of gastric polyps and are generally considered benign. Though their malignant potential is low, there is evidence supporting clonality and neoplastic potential of gastric HP particularly with polyps >5 mm is likely to be safer than multiple polypectomies, therefore in patients with portal hypertension it is essential that gastric polyps are photographed and biopsied during routine [14].
Conclusions
a) PHP are definite identifiable lesions in advanced cirrhosis pts with portal hypertension. Natural history and Pathogenesis of PHP is not known. May be related to angiogenesis following vascular mucosal injury after APC or band ligations
b) These PHP lesions are typically localized in the antrum of the stomach, are mostly multiple, and show typical microscopic findings.
c) Given the histological resemblance to Hyperplastic polyp which are now considered to harbor the risk of malignancy - potential to transform into malignancy cannot be undermined.
d) Diagnosis and Management of gastric Polyps in cirrhosis, Require further exploration
e) Surveillance is likely to be safer than multiple polypectomies Gastric polyps are photographed and biopsied during routine surveillance gastroscopies. Current recommendation is to restrict polypectomy only to those with specific reasons, symptoms or clear-cut risk of future malignancy.
References
- Cormack SW, Genta RM, Schuler CM (2009) The current spectrum of gastric polyps: a 1-year national study over 120,000 patients. Am J Gastroenterol 104: 1524-1532.
- Pai CG (2013) Portal hypertensive polyp - what is in a name? Indian J Gastroenterology 32: 163-164.
- Goddard AF, Badreldin R, Pritchard MD (2010) The management of gastric polyps. Gut 59: 1270-1276.
- Aravind C, Arul Murugan S, Sai Ravi Kiran B (2017) A study of portal hypertensive polyps. IJAM 4(1).
- Lam MC, Tha S, Owen D, Haque M, Chatur N (2011) Gastric polyps in patients with portal hypertension. Eur J Gastroenterology Hepatol 23(12): 1245-1249.
- R Boyd JT (2014) Portal hypertension-associated gastric polyps BMJ Case Rep.
- Amrapurkar D, Choksi M, Bhatt N, Amrapurkar P (2013) Portal hypertensive polyps: Distinct entity. Indian Journal of Gastroenterology 32(3): 195-199.
- Lee TH, Jang JY, Jeong SW, Jin SY (2013) Gastric polyposis associated with portal hypertension. Korean Journal of Internal Medicine 28(2): 261.
- Lemmers A, Evrard S, Demetter P (2014) Gastrointestinal polypoid lesions: a poorly known endoscopic feature of portal hypertension. United European Gastroenterology Journal 2(3): 189-196.
- Kimberly Kolkhorst, DO, Prasad Kulkarni (2015) Portal Hypertensive Polyposis: A Consequence of Esophageal Variceal Ligation? Case Rep J 2(3): 125-126.
- Sarwar S, Khan AA, Alam A (2006) Effect of band ligation on portal hypertensive gastropathy and development of fundal varices. J Ayyub Med Coll Abbottabad 18(1): 32-35.
- Nihar Shah, Yana Cavanagh, Dharmesh H Kaswala, Sohail (2015) Development of Hyperplastic polyps following argon plasma coagulation of gastric antral vascular ectasia. NSB 6(2): 479-482.
- Veronica Martín-Dominguez V, Diaz Mendez A, Santander C, Garcia Buey L (2016) Portal hypertensive polyps, a new entity? Revista Espanola de Enfermedades Digestivas 108(5): 279-280.
- Jason Timothy Boyd, Lennard Lee, Boyd JT (2014) Portal hypertension- associated gastric polyps, BMJ Case Rep.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...