Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2638-6062
Research Article(ISSN: 2638-6062) 
Blockchain Forensics in Policing and It’s Global Scenario Volume 4 - Issue 3
Hitesh Goyal1* and Beulah Shekhar2
- 1Assistant Professor of Criminology, Department of Criminology, School of Arts, Media and Management, Karunya Institute of Technology and Sciences (Deemed University), Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
- 2Chair Professor of Criminology, Department of Criminology, LNJN National Institute of Criminology, National Forensic Sciences University (NFSU), An Institution of National Importance, Under Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India.
Received: April 27, 2022; Published: May 25, 2022
*Corresponding author: Hitesh Goyal, Assistant Professor of Criminology, Department of Criminology, School of Arts, Media and Management, Karunya Institute of Technology and Sciences (Deemed University), Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
DOI: 10.32474/PRJFGS.2022.04.000189
Abstract
The blockchain forensics is an emerging domain in policing. It’s a one of the biggest challenges to law enforcement agencies now a days. The research paper addressed the need of digital forensics in policing and blockchain forensic across the world to combat with crimes in blockchain technology. It has reported that now technological era is shifting to its next advanced version that mainly based on blockchain technology concept. The study developed a framework of Digital Investigators. Also, the study has generated a theoretical framework based on routine activity theory. And suggested the legal framework to establish the certainty of punishment of its criminal intention.
Keywords: Blockchain Technology; Digital Forensic Investigators; Blockchain Forensics
Materials and Methods
Literature Review
No centralization of financial authority and no involvement of banks are some of the accountability threats in bitcoin and online cryptocurrencies revealed by [1] and raised the question that why bitcoin matters to bankers. Research paper consisted of the threats and the need for expert and advanced police to combat the virtual threats which are directly affected by the physical reality of society [2]. Also, he has considered that bitcoin and its frequent modifications are one of the biggest threats to the national economy and increment in crimes of money laundering and cyber terrorism. According to emerging threats in this growing technology based on blockchain [3] have generated the framework of IOTFC (Internet of things forensic chain) which ensures the adequate traceability of evidence on blockchain technology platforms. They also claimed that the digital forensic tool IOTFC offers forensic investigation with good authenticity, immutability, traceability, and track provenance of evidence items. The IOTFC and digital forensics can increase the trust in shreds of evidence of audit of blockchain technology platforms. But this method has not been standardized with all formats of blockchain. Still, there is a need to advance this digital skill to non-permissioned open blockchain formats to trace the manipulations. A group of researchers have initiated the process of implementation of digital forensic investigation in evidence management [4]. They also emphasized that there is a need for an effective framework to investigate the crimes on blockchain-based technology.
A scientist has expanded the use of the blockchain concept in the criminal investigation process and developed the tool to prevent illicit activities on dark webs and crimes [5]. As the blockchainbased technologies and internet of things (IOTs) have increased their market among its users and millions of people connecting themselves with this modern era technology it is becoming more challenging for the law enforcement agencies and states. The biggest challenge for the state is how to monitor and how catch the suspects in blockchain technology. Digital forensics and its framework to provide SOPs (Standard operating procedures) to the police officers and digital forensic investigators are going to be difficult tasks. A lot of social and scientific research is needed to address the issues of blockchain technology in a proper manner. There is still a lot of confusion existed on the use of blockchain technology in social sectors. This research study focused on the side of digital forensics and its investigators’ skills to combat the crimes on blockchain platforms.
Research Gaps
The existing literature is not enough and sequentially arranged to address the series of modifications in blockchain technology. Based on the literature review this study found that a standard operating procedure for the police officers needed and a framework required to build a digital forensic team or platform to combat these smart crimes.
In continuation of the need there are the following objectives addressed by this research paper:
Objectives
a. To assess the skills of digital forensic investigators on the Blockchain Technology Platforms.
b. To develop the digital investigation models.
c. To provide recommendations and suggestions to prevent crimes in Blockchain Technology Platforms.
Research Methodology
This research paper adopted a research approach qualitative analysis. The method for this study used the content analysis research method of existing literature to address the abovementioned objectives [6]. The existing literature and method frameworks will be reviewed to draw attention to building digital forensic support for law enforcement agencies and state monitoring systems. Also, there are few criminal cases that occurred based on blockchain technology. These cases were reviewed by the researchers and addressed the possible unsolved challenges.
Introduction
There are several innovations that occurred in virtual platforms and cyberspace. Also, simultaneously there are several cases that occurred from 2009 to till now in blockchain technology. The technologies become advanced and now in the competition of ensuring the trust of its users a new concept originated named Blockchain-based Internet of Things (IOTs) or devices. There are numerous myths associated with this technology and several trusts issues make it more controversial in the digital world. Blockchain technology is frequently changing its formats and exploring its applied areas. The technology is based on the concept of Blockchain which originated as a universal shared digital distributed ledger referred as to maintaining a record of transactions of tangible and intangible digital assets. In the year 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto a pseudo name came up with the idea of a decentralized electronic cash system by using a P2P (peer to peer) network [7]. The blockchain further advanced its format in permissioned chain and non-permission blockchain. it is exploring its advancement by its use in several public sectors in India and globally. Such as in India the concept of blockchain planning is to design the land structure maps online and non-changeable, followed by online finance, maintaining the record of healthcare and agriculture fields, etc (Niti Ayog Report 2020) [8]. This research paper is focused on challenging aspects of the blockchain technology platform for law enforcement agencies and state governments to monitor its activities. It has become a major challenge for government authorities to maintain peace in the digital world. Also, the paper has touched on the required skills for digital investigators to investigate the crimes associated with blockchain technology. Based on the required skills and needs of digital investigators a digital investigation model has been prescribed in this paper on the basis of existing literature and possible technological innovations. Last but not least this study has provided recommendations and suggestions to prevent crimes on blockchain technology platforms.
Concept of Blockchain Technology
(T. Sai) The blockchain concept changed the scenario of the traditional trading model to an advanced immutable digital ledger which makes it more comprehensively digitally advanced and trustworthy. Blockchain refers to a universal distributed ledger which stores every transaction of information in tangible and intangible digital assets. Every information record maintained in a block to enhance transparency, traceability, tracking, transferability, and trust. These blocks build a chain in chronological order of creation [9].
Three fundamental concepts of blockchain theory
a. Peer-to-peer (P2P) architecture.
b. Stores messages in a timestamp.
c. Consensus mechanisms with rules and security.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P)
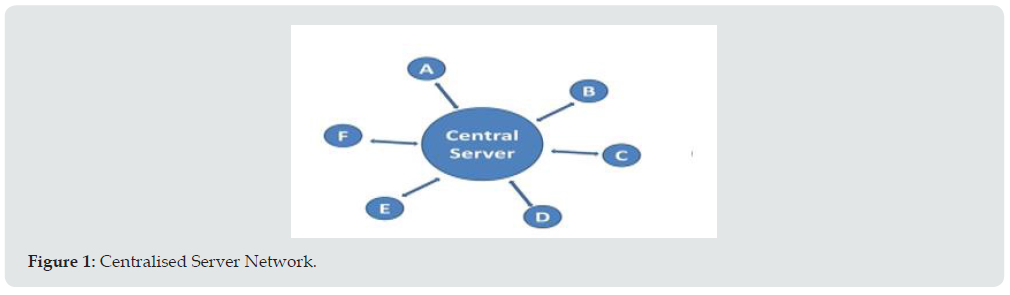
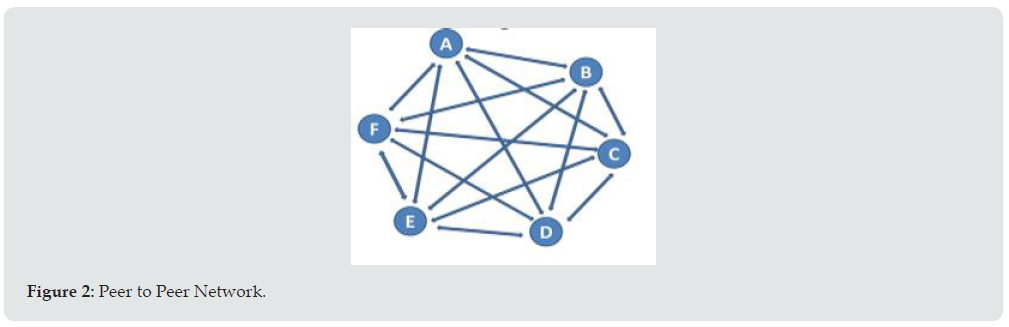
Blockchain-based technologies generate a network of connections between computers called nodes [7]. This network is built by members of nodes and operates over the internet. The feature of this network is the role and coordinates between the nodes. These nodes differentiate the type of network. The following figure demonstrates the peer-to-peer network and centralized network architecture. In a peer-to-peer network, the connected computer nodes are equal to peers. This nature of P2P makes it distributed network architecture. The nodes have equally distributed the tasks among the nodes. The data can be shared amongst the nodes without going via the central server (Figures 1 & 2).
Store Messages in Timestamp
Messages, data, or files add to the blocks attached to the information with a timestamp which ensures its credibility and transparency among the nodes.
Consensus Mechanisms with Rules and Security
All network participants of the blockchain agree on a state of decision collectively emphasizing the nature of the consensus mechanisms model. It is based on the consensus algorithm is a way to keep updating the nodes (members) synchronized in a network. Every algorithm has its own value of agreeing to a global agreement on a network update. So, it can be customized equally. This customization of nodes makes it vulnerable. The number of types available of consensus mechanisms based on the need such as Proof of Work, Proof of State, Delegated Proof of Stake, Proof of Importance, Proof of Capacity, Proof of Activity, Proof of Authority, and Proof of Burn, etc.
Assessing the Loopholes Respond to Unsolved Crimes
Technology paradigm shifting to the advanced version of its. Blockchain technology is one of the advanced platforms which ensures the safety of user data information precisely. But it has been reported that number of financial crimes based on NFTs (Non-fungible tokens), money laundering and other cybercrimes increasing in blockchain technology platforms gradually. Recently, FBI (Federal Beauru of Investigation) has established a new unit under their investigation agency named as National Cryptocurrency Enforcement Team (NCET). The purpose of this unit is to combat illicit abuse of cryptocurrencies and block technology. The NCET will monitor the digital asset seizure and blockchain-based lawbreaking. The unit has orientation of digital forensics and blockchain forensic Expertization [10]. The need of opening such kind of unique and most advanced cyber units shows the severity of such crimes. The many numbers of countries have not advanced infrastructure for their digitally oriented forensic labs and law enforcement agencies to combat with highly advanced crimes. The crimes based on blockchain technology is a very new orientation to the police officers in most of the developing countries. Even there are no proper policies designed to tackling with such crimes. There are number of cases based on the blockchain technology remain still unsolved and required an advanced skills and infrastructure. Here, some of the following such cases discussed the requirements for solving and finalizing the convictions.
Tax Evasion
This is one of the mostly noticed crimes in blockchain fraud. Before 2017, no guidance was available across the globe for preventing and monitoring these crimes. Taxes related to cryptocurrencies and their transactions being noticed in the several countries. Accordingly, now the polices and laws are strengthening. It has always been noticed that only developed countries can focused on such issues and Lend EDU conducted a survey on around 564 US-based bitcoin investors [11]. The output from survey was that approximately 36% of participants planned to knowingly avoid paying capital gains taxes in their 2018 tax filings. The situation is worst in the developing countries that still they don’t have structured policies to impose the tax on crypto transactions. Also, the more required thing is that lack of monitoring. Recently, Niti Ayog urges to the government in India to develop a framework for monitoring the blockchain technology transactions. India started a tax system on every transaction to stop the tax stealing crimes. According to the taxes imposed by the government on cryptocurrencies transactions in some cases, compliance can be useful for them who follow the tax paying regulations by avoiding going obvious consequences of jail time or fines. Again, here we want to emphasize that imposing the tax on transactions is a step to increase the threat of money laundering by legalizing the cryptocurrency.
Money Laundering
The nature of hiding the use of cryptocurrencies in dark web is one of the steps to launder the money in form of cryptocurrencies on a secrete blockchain. A secrete blockchain can be a permissioned one blockchain and manipulated as to hide the information from its other users. Based on the report released in Q2 2018 that cipher Trace, crypto criminals laundered around 1.2 billion dollars by the bitcoin tumblers and privacy coins in a one-year time during 2017-2018 [12]. Within a short period of time without having any extra efforts this motivates the criminal to commit crimes. In US the Financial Action Task Force – an intergovernmental organization formed to combat with the crypto threats to physical economy. This has now become the biggest threat to economy of every state across the globe. The major problem is here that no one has the safety monitoring system which can ensures the permanent solutions of these rising problems in blockchain technology. The lack of expertise, skills and infrastructure among the staff and government institutions can create a funding resource for terrorism sector. These pattern and process increases the terrorist fundings accordingly [13].
Terrorist Funding
All the transaction of money laundering and not to pay taxes might become a funding source to terrorism. As the Bank of England and other regulatory agencies had generated their warning guidelines towards the risk and threat of cryptocurrencies. The US lawmakers has recently inaugurated the homeland security assessment of terrorists’ use of virtual currencies Act around May 2017. Based on those other countries also has inaugurated the legislations but the skill and infrastructure are the same question. The blockchain enabled crimes can be solved by developing a blockchain digital forensic field. The venom can reduce its effects if an anti-dote made by that only [14].
The Development of Blockchain Enabled Solutions to Combat the Blockchain and Fraud
In the race of competition of earning the money without making efforts attracts criminals to put a simple digital algorithm and start a blockchain enabled businesses. It creates too many Ponzi schemes and people get loose their money after unknowingly investments. Like a smart contract blockchain enabled to trace and track. But if, a blockchain is permission less than, its monitors can’t check its inception and users [15]. In regarding of that smart contract and a permissioned one blockchain technology can help to the people not to get victimized by these crimes. Based on that only, an investigation model has generated for strengthening the investigation in crimes related to blockchain technology.
Strengthening the Investigation
The need of the strengthening the investigation in the cases of blockchain has now become a need of hour. A major problem in strengthening the investigation model is that lack of skilled people hand in handling the blockchain technology. A digital forensic investigation model has presented here with its five T model.
Digital Forensic Investigation Model
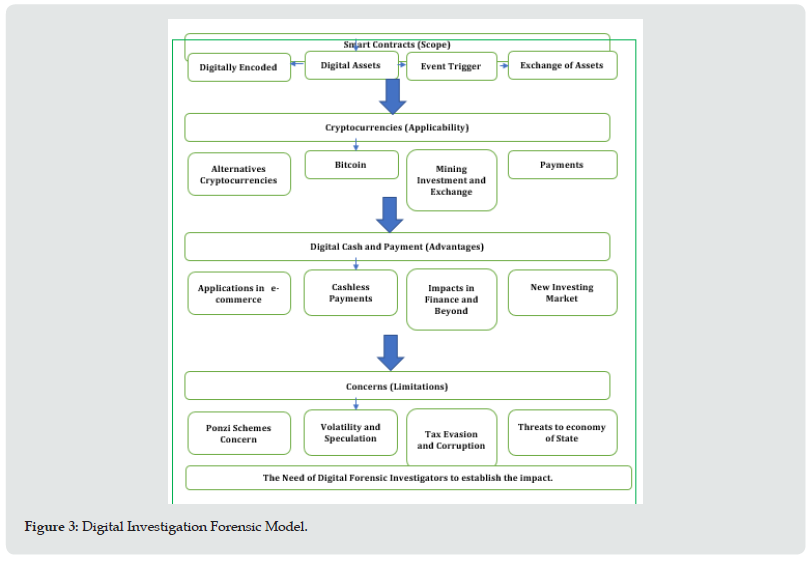
A digital forensic model can be an important asset for the law enforcement agencies to track the crimes. According to the model we must ensure that where a forensic expert to have looked at. There are two levels can we generate where it can apply. One is blockchain application in tracking the incident by enabling the smart contract concept and another one can be what technology aspect will go to combat with it [16]. The following figure explains about the digital forensic investigation model. This explains that where a digital forensic investigator must look out. The perspective of an investigator must be on the nature of smart contract. There are number of Ponzi Schemes available in digital market which ensures that invest your money in buying bitcoin and get your money doubled even tripled or ten, hundred times within a day or couple of day. The market of bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies is in demand because earlier there was no regulation to cash the money from online mode. But the scenario has changed, and a tax system imposed by government transactions of cryptocurrencies. Here, the threat of Ponzi Schemes increased. The concept of smart contract has given an opportunity to customize the blockchain and take off all the money of investors. Likewise, same occurs with the data chain also. These smart contracts are digitally encoded on digital assets, a lucrative scheme will be advertised, and people invested in that without checking the proper source of scheme. The model itself shows that a bogus event will occur, and people invest into that and come-up with a fraudulent complaint. The model has clearly stated the availability of threats. Here, a digital investigator shall take care of these steps and remove the technical barrier from the part of awareness to the people to not to involve in such activities. Whatever the concerns are there have been processed by one of the modus operandi. A digital investigator should look out at the technical aspects to find the inception of chain. Accordingly, a smart contract based blockchain technology can improved the investigation process and strengthen it (Figure 3).
Five T model
There are number of articles and literature available which ensures the transparency and immutability of blockchain technology. But it has noticed that a latent purpose of a blockchain based device, or a currency never revealed. It is clearly demonstrated by the digital investigation model. There is a five’ T’ model we proposed by this research study to ensure the effectivity of digital forensic approach i.e., Transparency, Traceability, Tracking, Transferability and Trust. Based on the monitoring policies of digital forensic investigators it better to ensure these five Ts in every scenario of blockchain based technology across the globe [17].
Transparency
The treatment given by the digital forensic investigator to the crime scenario shall be transparent and clear. Every blockchain based devices or event shall consider seriously and visible their all the smart contract conditions. Encoded smart contracts shall reveal the nature and purpose of blockchain event.
Traceability
The data on blockchain shall be created as a blockchain custody. So, the recorded data can easily trace the offender by his digital foot printings. Blockchain exist in a form of data structure that allows to create a data ledger in which all the data recorded with timestamp. The traceability will be easier to catch the offender.
Tracking
Digital forensic investigators can conduct a forensic accounting for cryptocurrency. The court law needs to ensure the facts and finding on fact-based research always. As per the expert view we can track the data based on wallet to wallet.
Transferability
There are number of permissions less blockchains are available where we can assure that a data transferability process shall be done under the supervision of digital forensic investigators or a monitor. Transferability also ensures that monitored the transactions of transfers.
Trust
According to the literature available the blockchain existed as an option with a lot of trust issues and confusion. Digital forensic Investigation Model established for a successful investigation.
Preventive Measures
Based on the model and theory of routine activity the research suggests a theoretical framework to prevent the frauds in blockchain technology. The implications of routine activity theory along with the safety measures covers the awareness aspects before using the blockchain technology.
Awareness to Public
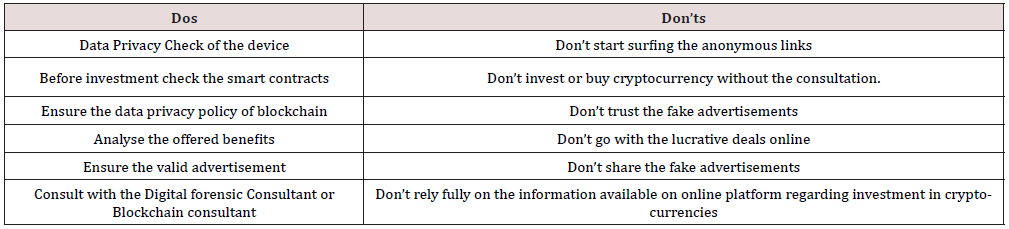
There number of gaming apps working in the blockchain technology. Apart that number of investment businesses via using the cryptocurrencies are available based on blockchain technology. It has been reviewed from the cases and articles relating to blockchain IOTs that people have not enough guidance and awareness to use these apps and internet of things devices. Due to the lack of awareness number of Ponzi Scheme crimes occurred. Based on the digital investigation forensic model a list of dos and don’ts discussed here to prevent the fraud and forgery (Table 1).
Theory of Routine Activity
The cases of fraudulent in blockchain technology increasing massively but not reporting in police stations. Because in most of the cases the money invested in these deals are part of black money. And the cases of Ponzi Schemes are reported in India and other countries are not purely based on blockchain technology, but fraud occurred via Ponzi Schemes in supporting to the blockchain based online gaming apps and other platforms. There is no model has been derived yet because there is no fixed modus operandi noticed in such cases. The Routine activity theory [18,19] provides a generalized format to be aware from indulging in the fraudulent activities on blockchain technology platforms [20].
Lack of Guardian
As model suggests that in most of the cases no identity is revealed yet. There is lack of guardianship found in most of the permissionless blockchains. Nobody is aware about the inception in this kind of blockchain and generally users indulged in fraud because of this guardian less non-accountable series of blockchain. And in terms of permissioned or blockchain based smart contracts the encoding of data and strategy is also a biggest challenge to ensure accountability on owners. There are lack of regulations and its monitoring authorities also makes it vulnerable to its users.
Suitable Target
People are having the lack of knowledge and using this technology becomes vulnerable targets. Having lack of understanding and or less understanding it makes more vulnerable.
Motivated Offender
No policies are ensured yet to monitor the full process of blockchain technology. Lack of guardianship in terms of lack of awareness and lack of regulations, laws, and easy targets to motivate the offender to conduct such crimes. Most of the offender used the information and personal data of users and extorted the money. Apart that in terms of Ponzi Schemes creates a forge event for its users. The theory generalises the idea of becoming a victim in blockchain world. The three important elements of its theory lack of guardianship, suitable target and motivated offender strategies the criminal intention.
Suggestive Framework for Awareness to General Public
Based on the theoretical framework list of Do’s and Don’ts provided above to beware from the fraudulent activities in blockchain enabled apps or devices. Also, the government should provide a extensive framework for users of blockchain IOTs. The regulation and a regulatory council can establish the role of blockchain in sectors. The limits have to be created for such highly encoded technologies.
Recommendation and Suggestions to Prevent Crimes in BCT Platform
Suggestions to Government Machineries
The national policy on blockchain technology and its uses shall be introduced with immediate effect. It is the matter of felt need. People having the less knowledge about how to use the blockchain technology makes them vulnerable to victimize. According to the theoretical framework the suggestion to introducing the national policies on blockchain enabled devices and technologies shall ensure the proper guardianship. By enforcing the digital forensic investigators or state enforcement agencies should monitor every series of blockchain technology. Implementing a proper guardianship can provide a better resolution to its misuses and its prevention too. Suitable target seeks a comprehensive guideline for using such blockchain technology platforms. A detailed guideline framework required to address every query of its users. A punishment provision shall be incorporate in the policy for them who make it or use it for fraud. A harsh and at least more than Simple Imprisonment sentencing shall impose by states on its criminals.
Simultaneously, a monetary punishment provision can address the severity of its crime. The punishment framework shall be certainty so, that state can prevent these criminals immediately to commit crimes. The following table addresses a suggested framework to prevent crimes in blockchain technology by legal punishments (Table 2).
Conclusion
Blockchain technology have wonderful benefits and technological advancements which can help us to combat with the threats and challenges of modernization. But simultaneously it can create a big non-reversable mess in society. Most of the Internet of things (IOTs) are on blockchain concepts and gradually shifting towards it. To monitoring and maintaining the peace in virtual block-chain world, we don’t have a strong guidance framework to prevent crimes in blockchain technology platforms. As the study came-up with a digital forensic investigation model and suggested the precautionary measurements to prevent the crime in blockchain technology platforms. The Routine Activity Theory has given a place to understand the loopholes in crimes in blockchain technology. On the seriousness and loopholes suggestive frameworks designed a pathway to the users of blockchain technology to beware from the frauds and crimes.
Limitations
The study itself limited to its legitimization use. An empirical case-based studies required to address its technical aspect.
References
- Hochstein M (2014) Why bitcoin matters for bankers. American Banker 124(2).
- Raj Rao G (2020) Pseudonymous not anonymous-The forensic and Investigative Aspect of Bitcoin Cryptocurrency. International Journal of Scientific Research & Engineering Trends 6(3): 1-4.
- Li S, Qin T , Min G (2019) Blockchain-based digital forensics investigation framework in the internet of things and social systems. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems 6(6): 1433-1441.
- Sathyaprakasan R, Govindan P, Alvi S, Sadath L, Philip S, et al. (2021) An Implementation of Blockchain Technology in Forensic Evidence Management. In 2021 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Knowledge Economy (ICCIKE) pp. 208-212.
- Tsai FC (2021) The Application of Blockchain of Custody in Criminal Investigation Process. Procedia Computer Science 192: 2779-2788.
- Mayring P (2015) Qualitative content analysis: Theoretical background and procedures. In Approaches to qualitative research in mathematics education pp. 365-380.
- Sultan K, Ruhi U, Lakhani R (2018) Conceptualizing blockchains: Characteristics & applications. arXiv 1806.03693.
- Kshetri N (2018) The Indian blockchain landscape: Regulations and policy measures. Asian Res. Policy 9(2): 56-71.
- Krishnan A (2020) Blockchain empowers social resistance and terrorism through decentralized autonomous organizations. Journal of Strategic Security 13(1): 41-58.
- Nofer M, Gomber P, Hinz O, Schiereck D (2017) Blockchain. Business & Information Systems Engineering 59(3): 183-187.
- Fang C and Wang L (2012) An effective shuffled frog-leaping algorithm for resource-constrained project scheduling problem. Computers & Operations Research 39(5): 890-901.
- Notheisen B, Hawlitschek F, Weinhardt C (2017) Breaking down the blockchain hype-towards a blockchain market engineering approach.
- Engeler SM, Balietti S (2021) Cryptocurrencies, Rational Choice, and Organized Crime.
- Deshmukh P, Kulkarni G, Meezan Shaikh VT, Thakare KS (2021) Digital India Digital Economy Using BCT. International Journal of Advance Scientific Research and Engineering Trends 6(6).
- Krishnan A (2020) Blockchain empowers social resistance and terrorism through decentralized autonomous organizations. Journal of Strategic Security 13(1): 41-58.
- Hyvärinen H, Risius M, Friis G (2017) A blockchain-based approach towards overcoming financial fraud in public sector services. Business & Information Systems Engineering 59(6): 441-456.
- Agbedanu P, Jurcut AD (2021) BLOFF: a blockchain-based forensic model in IoT. In Revolutionary Applications of Blockchain-Enabled Privacy and Access Control p. 59-73.
- Bertino E, Kundu A, Sura Z (2019) Data transparency with blockchain and AI ethics. Journal of Data and Information Quality (JDIQ) 11(4): 1-8.
- Miró F (2014) Routine activity theory. The encyclopaedia of theoretical criminology p. 1-7.
- Felson M (2016) The routine activity approach. In Environmental criminology and crime analysis pp. 106-116.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...