Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-4609
Research Article(ISSN: 2637-4609) 
Comparison of Biochemical Composition and Some Mineral Content between New and Old Fruits of Adansoniadigitata (Tabaldi) Volume 4 - Issue 4
Mahdi Abdelmageed Mohammed Ali1, Hisham Abd Almonem Mahmoud Ali2, Roba Mohammed Elhassan Ebrahim2 and Hatim MY Hamadnalla3*
- 1Department of biology & Technology (Botany) , University of Bahri, Sudan
- 2Department of food technology, University of Bahri, Sudan
- 3Department of Biochemistry College of Applied Sciences, University of Bahri, Sudan
Received: August 12, 2020; Published: August 25, 2020
*Corresponding author: Hatim M Y Hamadnalla, Department of Biochemistry College of Applied Sciences, University of Bahri, Sudan
DOI: 10.32474/AOICS.2020.04.000194
Abstract
This study was carried out in Khartoum state –Sudan, the aims of this study is to identifying the nutrient value of new (Adansonia,digitata) baobab fruit pulp and seed compared with old baobab fruit pulp and seed , To determine the proximate composition, mineral content and vitamin c .The fats and protein contents were determined by extraction and micro Kjeldahl method respectively, while Sodium, Potassium, magnesium and Calcium were determined by using flame photometer. The results obtained showed that the seeds contained high protein (18.83%), carbohydrate (48.93%), fat (8.40%), Ash (2.24%), crude fiber (12.65%), vitamin c (76.25) and moisture content (8.53%). The concentration of some minerals in milligram per hundred gram (mg/100g) in seed as present in the ash of baobab fruit pulp and seeds were: Na (52.84), K (488.75),mg (530.18) and Ca (392.08) this value is degreased infruit pulp except Na(51.64) decreased. The value of old fruit pulp and seed is decreased than new pulp and seed. The results showed that baobab fruit pulp could serve as a supplementary source of carbohydrate, mineral, protein and vitamin c and seed is good source of oil, fiber, carbohydrate, mineral, protein, and vitamin c and lose notional value during storage. Database of this study will contribute in improve the health and nutrition of population.
Keywords: Nutritional, Composition, Baobab fruits, Flame photometry and mineral analysis; biochemical composition
Introduction
Adansonia,digitate Baobab (Tabaldi)belong to the Malvceae family [1]. The Baobab tree is tolerant to high temperature and drought [2]. There are 8 species of baobab trees (6 native to Madagascar, one in Australia, and one in Africa). In Sudan, the Baobab is mostfrequently found on sandy soils and by seasonal streams ‘khors’ in short grass savannas. It forms belts in central Sudan, in Kordofan, Darfur, Blue Nile; It is often associated with the tamarind, Tamarindusindica L.[3]. The fruit of the species is a large, egg shaped capsule (often>120 mm), covered with yellowish brown hairs andconsists of a hard, woody outer shell with a dry, powdery substance inside that covers the hard, black kidneyshaped seeds[3].
The nutrient consist of pulpand seed of baobab fruit is documentedas a sources of vitamin C and high percentage of Ca more than milk and good source of carbohydrates , protein ,fat ,vitamins ,and mineral that may be deficient in common diet[4]. The dry Baobab fruit pulp has a slightly tart, refreshing taste and is very nutritious, with particularly high values for carbohydrates, energy, calcium, potassium (very high), and vitamin C[5].Fruit pulp is also acidic and this is due to the presence of organic acids including citric, tartaric, malic, succinic as well as ascorbic acid, when eaten raw, the pulp is a rich source of calcium and vitamins B and C,a high amount of carbohydrate, low protein[6].The objective of this study to identifying the nutrient value of new baobab fruit pulp and seed compared with old baobab fruit pulp and seed., To determine the proximate composition, mineral content and vitamin c .
Materials and Methods
Sample collection
5 kgof baobabfruits pulp and seeds were purchased and collected randomly from Khartoum markets
preparation of sample. The fruits were cracked using stones and placed in water for 24hours to soften the pulp. The soaked fruits were washed, and the seeds were separated from the pulp and rinsed with clean water, the seeds were dried under the sun for three days and pulverized by using a grinding machine.
Proximate analysis
The (Moisture ; Ash , Protein ; Crude fiber; oil and available Carbohydrate) Content were determined according to the method described by AOAC [7]with different formula as bellow ;but Mineral composition and vitamin C were determined according to AOAC [8] method.
Moisture content
The loss of weight was calculated as:
Moisture content% = (((wt1-wt2)×100))/((wt. of sample))
Where:
wt1=weight of sample +dish before oven dry.
wt2= weight of sample +dish after oven dry.
Wt.=weight of sample
Ash content
The ash content was calculated as follows:
Ash content (%) = (((w1-w2)×100))/((wt. of sample))
Where:
w1=weight of crucible with ash.
w2= weight of empty crucible.
Wt=wet of sample
Protein content
The total nitrogen and protein were calculated using the
formula:
Nitrogen[%]=(Volume of HCL×N×14×100))/((wt. of
sample)100)
Protein[%]= Nitrogen[%]×6.25×100)
Where:
Protein[%]=crude protein.
N=Normality of Hcl.
14=Equivalent weight of nitrogen.
Crude fiber
The fiber percentage was calculated as follows: Crude fiber % =(wt1-wt2×100)/(wt of sample) Where: Wt1=weight of sample and dish Wt2=weight of dish with ashed sample. WT = weight of sample
Oil content
Crude fat was determined according to the AOAC [7] method.
A 5g weight of sample was extracted with hexane using Soxhlet
apparatus. The solvent was evaporated, and the remaining crude
fat was determined.
Fat [%] = (wt2-wt1×100)/(wt of sample)
Where:
wt1= weight of empty flask.
wt1= weight of flask with oil.
Wt = weight of sample
Available Carbohydrate Content
Total Carbohydrate was calculated by difference according to
Pearson (1970) using the following formula:
Available Carbohydrate%=100-(moisture%+Crudefiber%+Cru
deFat%+Crude Protein%+Ash%).
Mineral composition
5 grams of the fruit pulp and seed flour was weighed into the crucible. The sample was ashedin a muffle furnace at 550oC until completely ashed. The ash was dissolved into 10% (V/V) HCl, heated to boiling, cooled and filtered and made up to 100 mL mark in a volumetric flask with deionized water and the mineral analysis was determined by Atomic Absorption Spectroscopic AOAC [8].
Vitamin C
Macerate 50 g of sample for 3 min in blender with 350 ml of 0.4% oxalic acid solution and filter. Obtain L1 as described above . To tube S, add 1 ml filtrate +9mldyeandrecord L2 after 15 second s.Calculated L1-L2 and obtain the concentration of ascorbic acid from the standard curve.
Result and Dissection
I. Proximate composition of Baobab
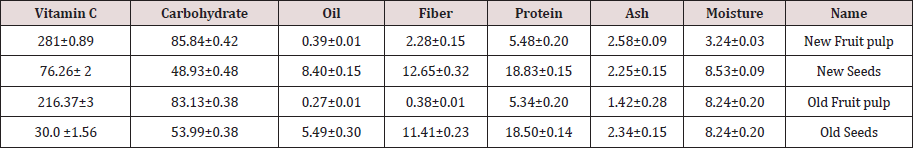
The proximate composition ofAdansoniadigitata fruit in this study include moisture content, ash content , crude protein ,cured fiber ,oil content and carbohydrate showed asin Table 1.
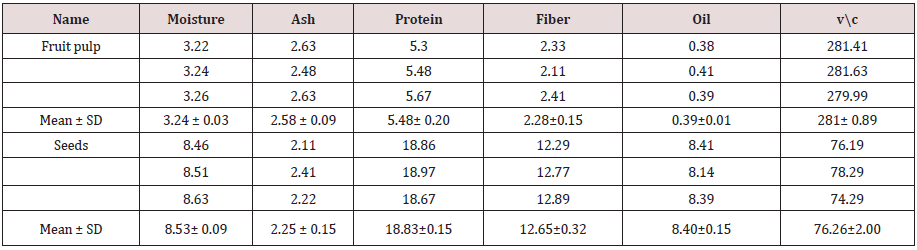
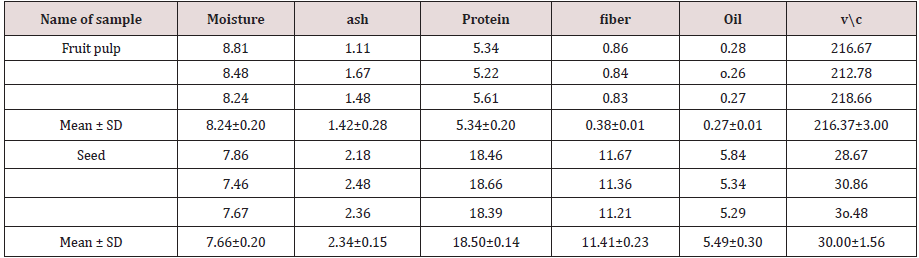
II. Moisture content
Moisture contents varied different from New fruit pulp, new seed, old fruit pulpand old seed(3.24c, 7.66b, 8.24aand8.53 a) respectively.The old pulp (8.24 a)is higher than new pulp (3.24 c) andold seed (8.53 a) is higher than value of new seed (7.66 b) these results can disagreed with Osman [9](10.4)Table 2.
III. Ash content
Ash contents varied different from New fruit pulp, new seed, old fruit pulpand old seed is (2.58a, 2.34b, 1.42c, 2.25 b) respectively. The new pulp value (2.58 a) is higher than old pulp (1.42 c) and new seed (2.34 b) is higher than old pulp (2.25 b). These results were disagreed with Murray [10](5.1)Table 3.
IV. Crude protein
Crude protein varied different from New fruit pulp, new seed, old fruit pulp and old seed is 5.48, 18.83, 5.34 and 18.50, respectively. The result value in new seed (18.83) is the higher than value of old seed ( 18.50) and the new pulp(5.48) is higher than old pulp(5.34). These results were similar to Obizoba and Amaechi[11]who report a very high protein contents in seed, (17 and 19.1) g/100 g.
V. Crude fiber
Crude fiber varied different from New fruit pulp, new seed, old fruit pulpand old seed is2.28c ,12.65a ,0.38 dand 11.41b respectively. The value of new seed (12.65a) is higher than old seed (11.41b) and new pulp (2.28c) is higher than old pulp(0.38 d) Table 4.
VI. Oil content
Oil content varying from New fruit pulp, new seed, old fruit pulp and old seed is( 0.39c ,8.40a ,0.27c, 5.49b) respectively. The value of new seed (8.40a) is higher than old seed (5.49b) and new pulp (0.39c) is higher than old pulp (0.27c) this result was disagreed with Lockett [12]2.1 g/100.
Carbohydrate
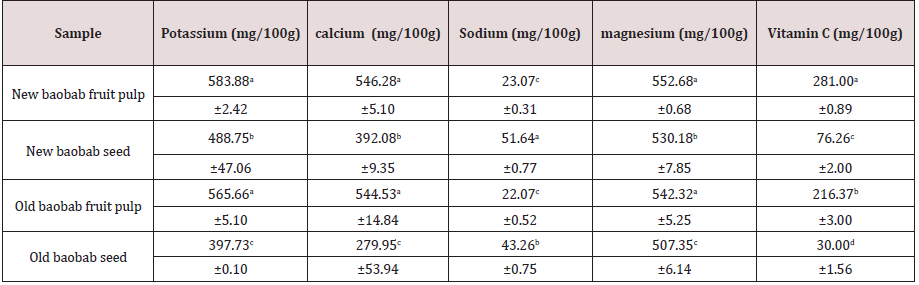
Carbohydrate varied different from new fruit pulp, new seed, old fruit pulp and old seed is (85.84a, 53.99c, 83.13b, 48.93d) respectively. The value of new pulp (85.84a)higher valuethan old pulp (83.13b) and the value of new seed (53.99c) is higher than old seed (48.93d) Carbohydrates represented more than 60% of the dry matter had high values, 71.7 and 60.8 % DM of fruit pulp, reported of seed from 26.1 to 43.9 %. The carbohydrate n seed content rangesfrom 22.1 g/100g dw (Ajayi et al., 2003) to 48.1 g/100 g dw[13].The mineral analysis show that the baobab Fruit pulp and seed contain high, Potassium, calcium , sodium and magnesium there for the fruit pulp and seed can be excellent source of Potassium, calcium and magnesium Table 5.
Potassium
Potassium varied different from New fruit pulp, new seed, old fruit pulp and old seed is (583,88a, 488.75b, 565.66a ) and (397.73c ) respectively. The value of new pulp (583,88a) is higher than old pulp (565.66a) and new seed (488.75b) is higher than old seed (397.73c) this result can disagreed with (Maha2016) which was cited (594.8 )
Calcium
Calcium varied different from New fruit pulp, new seed, old fruit pulpand old seed is(546.28a ,392.08b ,544.53a, 279.95c) respectively. Thevalue of new pulp (546.28a) is higher than old pulp (544.53a)in new seed andold seed (392.08b) is higher than old seed(279.95c). (Maha2016) reported that Ca contents was 558.5 in the Sudan because for the different of soil
Sodium
Sodium varied different from New fruit pulp, new seed, old fruit pulpand old seed is (23.07c ,51.64a ,22.07 c, 43.26b) respectively. The value ofnew seed is (51.64a) is higher than old seed(43.26b) and new pulp (23.07c)is higher than old pulp (22.07 c).
Magnesium
Magnesium varied different from New fruit pulp, new seed, old fruit pulpand old seed is 552.68a, 530.18b, 542.32a and 507.35c,respectively. Thevalue ofnew seed is (530.18b) is higher than old seed(507.35c) and new pulp (552.68a)is higher than old pulp (542.32 a), thisresultwas disagreed with (maha2016),(574.20).
Vitamin C
Varied different from New fruit pulp, new seed, old fruit pulpand old seed is (281.01a , 76.26 c, 216.37b )and (30.00d )respectively. The value of new pulpis (281.01a) is higher than old pulp (216.37 b) and new seed (76.27 c ) highervalue thanold seed (30 d).
Conclusion
The present results of this research recorded that the baobab pulp and seed have high economic value in terms of protein, fat, and carbohydrate contents. They were also good and cheap source of macro , micro elements, and vitamin c, and indicated that (Adansoniadigitata) pulp had low fat and protein content, fat, and moisture contents. It is also a good source of macronutrients, specially carbohydrate, crude fiber, and micronutrients especially Vitamin C.
Acknowledgement
Great thanks for natural research center for their cooperation and deep greetings to the Department of Biology and Technology- Faculty of Applied science and Technology and Industry-University of Bahri.
References
- Bremer B, Bremer K, Chase MW, Reveal JL, Soltis DE, and etal., (2003).
- El Amin HM (1990) Trees and Shrubs of the Sudan. Ithaca Press, UK, ISBN
- Kaboré D, Sawadogo-Lingani H, Diawara B, Compaoré CS, Dicko MH, and et al., (2011) A review of Baobab (Adansoniadigitata) products :Effect of processing techniques, medicinal roperties and uses. African Journal of Food Science 5(16): 833-844.
- Sidibe M, Williams JT (2002) Baobab. Adansoniadigitata. Fruits for the Future 4. International Centre for Underutilized Crops, Southampton.
- Emmy DC, Halamora K, Van Damme P (2010) Adonsoniadigitata L.: A review of traditional uses, photochemistry, and pharma cology. Africa Focus 23(1): 11-51.
- Abdalla AA, Mohammed MA, Mudaw HA I (2010) Production and Quality Assessment of Instant Baobab (AdansoniadigitataL.). Advance Journal of Food Science and Technology 2(2): 125-133.
- AOAC (2000) Official Methods of Analysis of Official Analytical Chemists, Maryland, USA.
- AOAC (2002) Official methods of analysis of the association of official’s analytical chemists, 17th edn. Association of official analytical chemists, Arlington, Virginia.
- Osman MA (2004) Chemical and Nutrient Analysis of Baobab Adansoniadigitata) Fruit and Seed Protein Solubility. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition 59(1): 29-33.
- Murray SS (2001) Nutritional Composition of some wild Plant Foods and Honey used by Hadza Forages of Tanzania. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 14(1): 3-13
- Obizoba IC, Amaechi NA (1993) The effect of processing methods on the chemical composition of Baobab (Adansoniadigitata L.) pulp and seed. Ecology Food and Nutrition 29: 199-205.
- Lockett C, Calvert C, Grivetti L (2000). Energy and micronutrient.
- Nnam NM, Obiakor PN (2003) Effect of fermentation on the utrient and antinutrient composition of baobab (Adansoniadigitata) seeds and rice (Oryza sativa) grains. Ecology of Food and Nutrition 42(4-5): 265-277.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...