Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-4609
Short Communication(ISSN: 2637-4609) 
Comparison between a Biochemical Pathway and Organic Chemical Synthesis Volume 2 - Issue 2
Josep J Centelles*
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biomedicine, Barcelona University, Spain
Received: March 09, 2018; Published: March 15, 2018
*Corresponding author: Josep J Centelles, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biomedicine, Barcelona University, Spain
DOI: 10.32474/AOICS.2018.02.000132
Introduction
The first reaction of biochemical degradation pathway from L-phenylalanine to L-tyrosine (para-hydroxy-L-phenylalanine) is compared with organic chemical synthesis of ortho-hydroxy-L- phenylalanine, meta-hydroxy-L-phenylalanine and para-hydroxy- L-phenylalanine. Enzymatic reaction is specific for the para- isomer, is a quicker reaction and shows higher yield than non enzymatic reactions.
Biochemical Synthesis of L-tyrosin
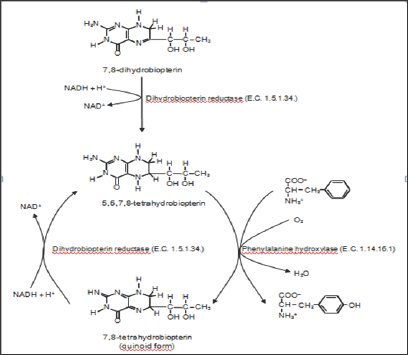
L-Tyrosine (Tyr or Y), or 4-hydroxy L-phenylalanine (para- hydroxy-L-phenylalanine) is one of the 20 standard amino acids used in protein synthesis. In humans, L-phenylalanine is an indispensable dietary amino acid. Nevertheless, L-tyrosine is not considered an indispensable dietary amino acid for humans, as it can be synthesized from L-phenylalanine in the first reaction of L-phenylalanine degradation. This reaction is enzymatically catalyzed by phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase (E.C. 1.14.16.1.), and this enzyme is located in the cytosol and expressed predominantly in the liver and kidney [1]. Mammalian phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase uses (6R)-tetrahydrobiopterin as a cofactor [2] in a reaction mechanism shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: First reaction of degradation of L-phenylalanine to L-tyrosine.
L-phenylalanine hydroxylase (E.C. 1.14.16.1.) catalyzes the degradation of L-phenilalanine to L-tyrosine. This enzyme requires oxygen and 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin for reaction.
In mammals, L-tyrosine is precursor of neurotransmitters and hormones. In dopaminergic cells in brain this amino acid is converted to L-DOPA (3,4-dihydroxy L-phenylalanine) and dopamine (3,4-dihydroxy phenethylamine) and furthermore to cathecolamines, such as noradrenaline (norepinephrine) and adrenaline (epinephrine). Thyroid hormones derived from L-tyrosine are triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). L-tyrosine is also precursor of alkaloids in plants (including morphine and mescaline), natural phenols derived from p-coumaric acid, pigments (including melanin) and the benzoquinone structure of coenzyme Q.
Thus, due to the interest of L-tyrosine as precursor of the previous described compounds, industrial synthesis of L-tyrosine and its derivatives has been performed. L-DOPA, melanin, phenylpropanoids and others compounds are used in pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements and food additives. Biochemical pathways consist in metabolic transformations to obtain a final product. Enzymes are chiral molecules, as they are formed from L-amino acids. Thus, they can catalyze organic reactions allowing generation of chiral compounds.
Non Enzymatic Chemical Synthesis of L-Tyrosine. Comparison with Ortho- and meta-tyrosine
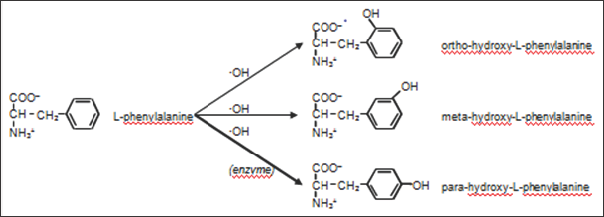
Although the amino acid L-tyrosine is the para isomer, the ortho-L-tyrosine (2-hydroxy-L-phenylalanine) and meta-L-tyrosine (3-hydroxy-L-phenylalanine) have been used for treatment of several abiotic diseases (such as Parkinson [3] and Alzheimer [4] ), arthritis [5] or several pancreatic disorders [6]. Due to this interest, several studies have been performed to organic synthesis of these compounds [6,7]. As it has been described above, L-phenylalanine is converted to para-hydroxy-L-phenylalanine (L-tyrosine) by the action of the L-phenylalanine hydrolase enzyme. No other tyrosine isomer is formed in this enzymatic reaction. Nevertheless, in the presence of a hydroxyl free radical (oOH), phenylalanine can be hydroxylated in para, meta and ortho positions (Figure 2). Thus, it is observed that chemical synthesis yields several compounds whereas enzymatic reaction is more effective and yields only one specific isomer. Molnar et al. [7] studied the presence of ortho-L- tyrosine and para-L-tyrosine in serum and in urinary excretion of some healthy people and patients.
Figure 2: Position isomers from hydroxy-L-phenylalanine.
Although L-tyrosine (para-hydroxy-L-phenilalanine) is the only position isomer obtained enzymatically, a mixture of ortho- hydroxy-L-phenylalanine, meta- hydroxy-L-phenylalanine and para- hydroxy-L-phenylalanine is chemically obtained.
They observed in serum, for the control group a concentration of 56|imol/L for para-L-tyrosine and 22nmol/L for ortho-L- tyrosine. Ishimitsu et al. [8] obtained also similar results in serum for healthy people (52|imol/L for para-L-tyrosine and 17nmol/L for ortho-L-tyrosine). These results indicate that enzymatic reaction is more than 3000 times more effective that non enzymatic reaction. To study the organic synthesis of L-tyrosine and to compare with the enzymatic synthesis, the paper from Humphrey et al. [6] was consulted. These authors analyzed several methods to obtain meta-L-tyrosine and developed a new enzymatic method, which complements to asymmetric hydrogenation. Although those authors did not prepare meta-L-tyrosine from L-phenylalanine, the overall yield for their optimized two-step synthesis was comparable with the usually used six-step synthesis at 68%. Thus, it can be observed that, although an enzyme step is also used for this synthesis, a good method of organic synthesis yields less product than the enzymatic reaction, that yields 100% product.
Conclusion
a) Enzymatic reactions are specific and yield only one product, whereas non enzymatic chemical synthesis reactions yield several stereoisomers.
b) Enzymatic reactions yield products in a quicker way than non enzymatic chemical synthesis reactions.
c) Enzymatic reactions yield more product than chemical synthesis reactions.
References
- Moller N, Meek S, Bigelow M, Andrews J, Nair KS (2000) The kidney is an important site for in vivo phenylalanine-to-tyrosine conversion in adults humans: A metabolic role of the kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(3): 1242-1246.
- Andersen OA, Flatmark T, Hough E (2002) Crystal structure of the ternary complex of the catalytic domain of human penylalanine hydroxylase with tetrahydrobiopterin and 3-(2-thienyl)-L-alanine, and its implications for the mechanism of catalysis and substrate activation. J Mol Biol 320(5): 1095-1108.
- Ungerstedt U, Fuxe K, Goldstein M, Battista A, Ogawa M, Anagnoste B (1973) Action of m-tyrosine in experimental models: Evidence for possible antiparkinsonian activity. European Journal of Pharmacology 21(2): 230-237.
- Coburn CA, Stachel SJ, Vacca JP (2008) Macrocyclic (3-secretase inhibidors for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. US Patent 7,371,853.
- Archibald SC, Head JC, Gozzard N, Howat DW, Parton TAH, Porter JR, Robinson M.K, Shock A, Warreblow GJ, Abraham WM (2000) Discovery and evaluation of potent, tyrosine-based a401 integrin antagonists. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters 10(9): 997-999.
- Humphrey CE, Furegati M, Laumen K, La Vecchia L, Leutert T, Millor- Hartouirg JCD, Vogtle M (2007) Optimized synthesis of L-m-tyrosine suitable for chemical scale-up. Organic Process Research & Development 11(6): 1069-1075.
- Molnar GE, Wagner Z, Marko L, Koszegi T, Mohas M, Kocsis B,Matus Z, Wagner L, Tamasko M, Mazek I, Laczy B, Nagy B (2005) Urinary orthotyrosine excretion in diabetis mellitus and renal failure: Evidence for hydroxyl radical production. Kidney International 68(5): 2281-2287.
- Ishimitsu S, Fujimoto S, Ohara A (1986) Determination of m-tyrosine and o-tyrosine in human serum by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection. J Chromatogr 378: 222-225.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...