Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2638-5945
Case Report(ISSN: 2638-5945) 
Identification of A Novel inv(2)(p13;q14) in Essential Thrombocythemia Volume 5 - Issue 1
Pier Paolo Piccaluga1-4*, Serah Kaggia3, Emily Rogena3, Nicholas A Abinya4, Shaymaa Khattab5, Ashraf Elghandour5, Manal Elsorady5, Nicoletta Testoni1, Giuseppe Visani6
- 1Department of Experimental, Diagnostic, and Specialty Medicine, University of Bologna School of Medicine, Institute of Hematology and Medical Oncology “L. and A. Seràgnoli”, Italy
- 2Istituto Euro-Mediterraneo di Scienza e Tecnologia (IEMEST) Palermo, Italy
- 3Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology, Juja, Kenya
- 4Nairobi Hospital and University of Nairobi, Nairobi, Kenya
- 5Hematology Unit, internal medicine department, Faculty of Medicine, Alexandria University, Egypt
- 6Hematology and Stem Cell Transplantation, AORMIN, Pesaro, Italy
Received: November 11, 2021 Published: December 2, 2021
Corresponding author: Pier Paolo Piccaluga, Department of Experimental, Diagnostic, and Specialty Medicine University of Bologna, Italy; Institute of Hematology and Medical Oncology “L&A Seràgnoli”, Via Massarenti, 9 -40138 Bologna, Italy
DOI: 10.32474/OAJOM.2021.05.000205
Introduction
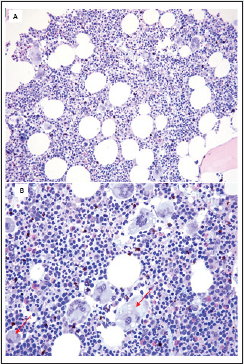
A 69-year-old man came at our observation for thrombocytosis. Peripheral blood counts showed: PLT, 805x109/L; hemoglobin 14.4 g/dl; WBC, 7x109/L (with 58% neutrophils, 27% lymphocytes, 12% monocytes, 2% eosinophils, and 1% basophils). Bone marrow examination at trephine biopsy showed a hypercellular marrow with an obvious megakaryocytopoiesis increase (Figure 1). Some of the megakaryocytes were small, with a reduced ploidy. The karyotype, assessed as previously described [8,9] showed an isolated inv(2)(p13;q14). The patient did not record any previous thrombosis or hemorrhage. Clinically, the disease remained stable, the PLT count being 750 x109/L, at the time of writing after 6 years of hydroxyurea treatment, at the daily dosage of 1000 mg p.o. No thrombotic or hemorrhagic event was reported during the follow-up. Some episodes of tinnitus were retailed after a period of 11 months since the date of diagnosis. This is the first time, to the best of our knowledge, that inv(2)(p13;q14) was recorded in ET. In anaplastic large cell lymphomas (ALCL) is rarely observed the inv(2)(p23q35). It involves ALK and ATIC genes, and the fusion protein has a cytoplasmic localization [10]. No other genetic aberrations involving the same chromosomal region are reported in hematological malignancies. Interestingly, however, the loci 2p13 and 2q14 do contain genes known to be involved in the pathogenesis of human cancer, such as MERTK (c-mer proto-oncogene tyrosine kinase), TGFA (transforming growth factor alpha), IL1A (interleukin-1 alpha), and, intriguingly, IL1B (interleukin-1 beta), known to enhance the megaryocyte proliferation in vitro [11]. In conclusion, though we cannot exclude that inv(2) was not strictly related to the neoplastic clone, we hypothesize that the herein described aberration is a newly acquired chromosomal abnormality in ET. Further studies are warranted to better define the exact prevalence and to definitively characterize the phenotypic and molecular features associated with this chromosomal aberration.
Figure 1: Bone marrow trephine biopsy. A) Hypercellular bone marrow with regular erythropoiesis and granulopoiesis. B) Megakaryocytes are increased in number and mature, with some evidence of dystrophy, and reduced size/ploidy (arrows).
Acknowledgment
Acknowledgment: This work was supported by AIL-Pesaro Onlus (Dr. Visani), BolognAIL (2020, Prof. Piccaluga), RFO DIMES (2018, Prof. Piccaluga), FIRB Futura 2011 RBFR12D1CB (Prof. Piccaluga).
References
- Thiele J, Tefferi A, Kvasnicka HM (2017) Essential thrombocythaemia. In WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues IARC, Lyon.
- Mitelman F, Johansson B, Mertens F (2021) Mitelman database of chromosome aberrations in cancer.
- Ganvat N, Tefferi A, Thanarajasingam G, Mrinal Patnaik, Susan Schwager, et al. (2009) Cytogenetic abnormalities in essential thrombocythemia:prevalence and prognostic significance. Europ J Haemat 83: 17-21.
- Sever M, Kantarjian H, Pierce S, Nitin Jain, Zeev Estrov, et al. (2009) Cytogenetic abnormalities in essential thrombocythemia at presentation and transformation. J Hematol 90(4): 522-525.
- Hsiao HH, Ito Y, Sashida G, Junko H Ohyashiki, Kazuma Ohyashiki, et al. (2005) De novo appearance of der(1;7)(q10;p10) is associated with leukemic transformation and unfavorable prognosis in essential thrombocythemia. Leuk Res 29(11): 1247-1252.
- Paz DL, Jouanneau-Courville R, Riou J, Jean-Christophe Ianotto, Françoise Boyer, et al. (2020) Leukemic evolution of polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: genomic profiles predict time to transformation. Blood Adv 4(19): 4887-4897.
- Wong KF (2004) A novel interstitial deletion of 3p in essential thrombocythemia. Cancer Genetics153(1): 84-85.
- Piccaluga PP, Luatti S, Ascani S, Michele Bianchini, Michele Malagola, et al. (2004) Identification of a novel t(1;9)(q11;q34) in acute myelocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 151(1): 85-86.
- Visani G, Bernasconi P, Boni M, G L Castoldi, S Ciolli, et al. (2001) The prognostic value of cytogenetics is reinforced by the kind of induction/consolidation therapy in influencing the outcome of acute myeloid leukemia--analysis of 848 patients. Leukemia 15(6): 903-909.
- Ma Z, Cools J, Marynen P, X Cui, R Siebert, et al. (2000) Inv(2)(p23q35) in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma induces constitutive anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) tyrosine kinase activation by fusion to ATIC, an enzyme involved in purine nucleotide biosynthesis. Blood 95: 2144-2149.
- Beaulieu LM, Lin E, Mick E (2014) Interleukin 1 Receptor 1 and Interleukin 1β Regulate Megakaryocyte Maturation, Platelet Activation, and Transcript Profile During Inflammation in Mice and Humans. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 34(3): 552-564.

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...




