Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2638-5945
Case Report(ISSN: 2638-5945) 
A Good Long-Term Outcome of Early Telemedicine for a SARS-CoV-2 Patient in Wuhan China Volume 4 - Issue 2
Wei Chen1,2*, Victoria J Wang3, Zhibin Zhang4, Ruizhen Xu5, Jinjun Qiu6, Guoping Sun1, and Shi V Liu7*
- 1Department of Radiology, Pingshan District People’s Hospital, Pingshan General Hospital of Southern Medical University, Shenzhen, China
- 2Department of Radiology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 3Department of Nephrology, Tufts Medical Center, Boston, USA
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Pingshan District People’s Hospital, Pingshan General Hospital of Southern Medical University, Shenzhen, China
- 5Outpatient Department, Pingshan District People’s Hospital, Pingshan General Hospital of Southern Medical University, Shenzhen, China
- 6Department of Community Health, Pingshan District People’s Hospital, Pingshan General Hospital of Southern Medical University, Shenzhen, China
- 7Eagle Institute of Molecular Medicine, Apex, NC, USA
Received: December 07, 2020 Published: December 16, 2020
Corresponding author: Dr. Wei Chen, Department of Radiology, Pingshan District People’s Hospital, Pingshan General Hospital of
Southern Medical University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518118, China, Email;1530831809@qq.com;
Dr. Shi Liu, Eagle Institute of Molecular Medicine, Apex, NC, USA, Email:svl8epa@gmail.com
DOI: 10.32474/OAJOM.2020.04.000183
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease 2019(COVID-19) still continues its threat to more and more people in even wider area. Many challenges remain as to how to efficiently manage the health risk and effectively reduce the social disturbance of this ongoing pandemic.
Methods: A 45-year-old COVID-19 woman living in Wuhan China, the initial epicenter of this global pandemic, isolate-at-home by herself, was given an early individual-based, situation and disease condition, as well as symptom-specific telemedicine.
Results: The patients who had abnormal pulmonary CT findings was effectively treated with timely telemedicine composed of multiple approaches. Up to now, the patient feels normal on all aspects and her family members have been remained infection-free as well.
Conclusions: The low dose of exposure and the early proper treatment and rehabilitation might helped overcome the disease without any lasting damage. Primary care physicians who knew their patients very well can work with radiologists and other specialists in a telemedicine mode to provide a safe, trusted, high quality professional health care and a cost-effective, situation-and disease condition, as well as symptom-specific medical treatment for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 , COVID-19, Telemedicine, Integrative medicine, Rehabilitation, Exposure control, Digital Record
Introduction
The infection by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus
2 (SARS-CoV-2) has now become a global pandemic with over
27486960 confirmed cases and resulted in 894983 deaths [1] since
its first report in January 2020 [2]. World-wide efforts are being
made in finding better ways for controlling the infection and treating
the disease formally called as COVID-19 (Coronavirus Disease 2019)
[3]. However, many challenges remain as to how to efficiently
manage the health risk and effectively reduce the social disturbance
of this ongoing pandemic. We would like to share our experience
in successfully treating a patient infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the
early time of the outbreak of this disease in Wuhan, China though
telemedicine while the patient was self-isolated at home. We believe
that this mode of medical treatment of SARS-CoV-2 may play a more important role in future for efficient containment of the infection
and for convenient treatment of the patients.
Our patient is a 45-year-old woman living in Wuhan China,
the initial epicenter of this global pandemic. She did not have
underlying health problems but routinely wore facial mask during
the peak time of SARS-CoV-2 infection outbreak in Wuhan because
she had a minor facial cosmetic surgery. She took off facial mask in
the public place only once when she attended a dinner on Jan. 20,
2000 with two of her close girlfriends in a small restaurant. She
normally took vitamin C and zinc supplement on daily basis. As a
precaution, she also took moxifloxacin hydrochloride tablets from
January 18 to 23, 2020 before she felt any symptom.
Figure 1: Time course of disease and treatment.
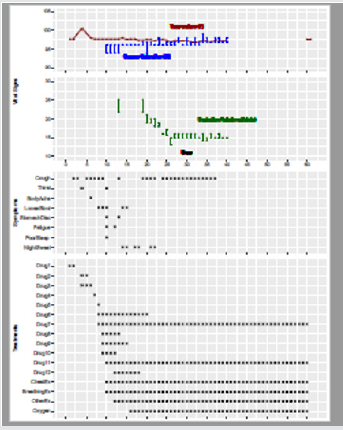
Patient’s vital signs such as body temperature, blood oxygen saturation and respiration rate and symptoms such as cough,
body-ache, fatigue etc. are plotted along with the various treatments which include taking medicines (see details listed below),
breathing in oxygen, and performing chest and breathing exercise.
Drug 1: EVE quick pain killer; drug 2: cold capsule; drug 3: ofloxacin; drug 4: cephalosporin; drug 5: moxifloxacin hydrochloride
iv; drug 6: arbidol hydrochloride; drug 7: Chinese medicine “LiKeJun” for raising white blood cell counts; drug 8: Chinese
medicine “Lianhuaqingwen exerts” claimed of having anti-viral effects and reducing cytokine secretion; drug 9: human
immune globin; drug 10: moxifloxacin hydrochloride tablet; drug 11: nutritional and supplementary treatments; drug 12:
azithromycin.
Note: The patient felt just headache on day 1 and took an over-the -counter (OTC) “pain killer”. She had occasional dry cough
from day 2 and low fever from day 3 for which she took an OTC “cold capsule”, and ofloxacin, from day 4 to day 6. On day 7
she took cephalosporin tablet. We instructed the patient took arbidol hydrochloride tablet and “LiKeJun” from day 8 to day
20. Meanwhile, from day 8 to day 11, moxifloxacin hydrochloride tablets were taken again because our patients complained
myalgia, fatigue, stomach pain and loose bowel movement. These medicines were replaced with azithromycin between day
12 and 18. Human immune globin was given between day 9 and 14. Beginning on day 1 our patient was able to self-monitor
her blood oxygen level which ranged between 93 and 96%. Her blood oxygen level was prevented from going down when a
portable oxygen generator was purchased and placed into use on day 10. She breathed in oxygen three times a day for 2-3 min
each time. Then she did chest and respiratory exercise according to our direction after each oxygen treatment.
The patient began to feel headache on January 24, 2020 which was the Eve of Chinese New Year. Two days later she began to have low fever and some dry cough. Because Wuhan was already placed under a lockdown on January 23 and normal medical treatment was extremely difficult to seek, the patient decided to isolate-athome by herself and found a way to obtain telemedicine from us for her treatment. Considering the outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Wuhan we speculated that our patient might be a victim of this virus’ attack. Since we also believed that COVID-19 was more like a repeated outbreak of SARS [4] we thus borrowed many experiences from past SARS treatment. We closely monitored our patient’s symptoms and signs, carefully analyzed her lab tests and imaging results, and gave situation-and symptom-specific treatment. We coded and quantified them in a figure for the convenient observation (Figure 1). The patient was formally diagnosed with a pneumonia on day 8 January 31, 2020 when her CT image showed a pneumonia sign with an obvious patchy consolidation shadows of exudative lesions in the left inferior lobe of her lung, and her blood test showed the total number of leukocytes decreased with lowered lymphocyte and neutrophil count and increased monocytes percentage, as well as C-reactive protein and hypersensitive c-reactive protein increased. Therefore, on day 8 she was given moxifloxacin hydrochloride via iv and arbidol hydrochloride tablets, as well as Leucogen Tablets which has been claimed with an effect of raising white blood cell counts [5] and whose Chinese name was called “LiKe Jun” (Figure 1). Due to limitations resulted from lockdown of Wuhan, our patient could took only four laboratory tests on day 8, 11 ,12and 14 and three CT examinations on day 8, 14 and 61 over the course of the treatment (Figure 2). On day 11, her hypersensitive c-reactive protein still increased, but her C-reactive protein was back to the normal. On day 12, her lymphocyte count increased and reached to the bottom line of the normal range, her total number of leukocytes also increased, but still lower than the bottom line of the normal range, meanwhile, her hypersensitive c-reactive protein still increased. On day 14, her blood test showed lymphocyte and leukocytes count increased than the ones on day 12, and total number of leukocytes was back to bottom line of the normal range, her hypersensitive c-reactive protein decreased to the normal range, however, the percentage of lymphocyte count still lower than the bottom line of the normal range on day14, her CT still showed a pneumonia sign with less inflammation than the one on day 8. We evaluated patient’s lab test results and made instant adjustments of our treatment. From day 9 we added another Chinese medicine called “Lianhuaqingwen exerts” and kept it in the treatment regime until day 14. We selected this particular Chinese medicine because of its known antiviral effect from the traditional Chinese medicine [6]. At the time of our writing this manuscript, we learnt that a very recent publication even showed its anti-viral effect directly on SARS-CoV-2 and showed suppression of cytokine secretion by SARS-CoV-2 infected cells [7]. After all the above treatments and the recovery from illness, our patient found an opportunity to test her blood for antibody against SARS-CoV-2 on March 24, 2020. Her blood test showed presence of IgG against SARS-CoV-2, indicating that she was indeed infected with SARSCoV- 2.
Figure 2: CT images showing patient’s progressive lung recovery from infection damages.
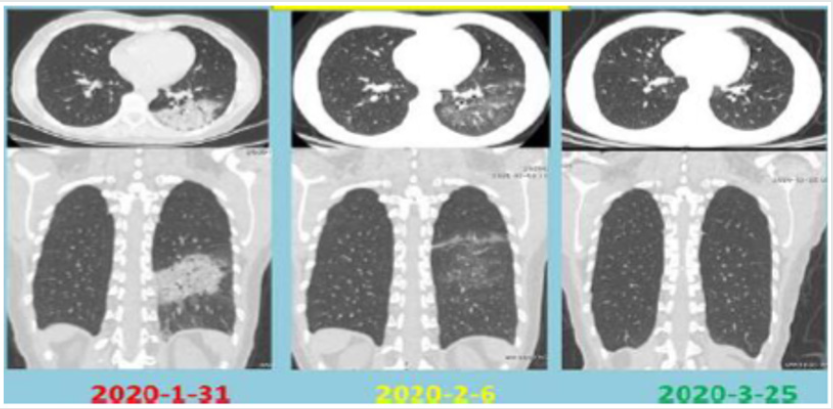
We witnessed the improvement of our patients’ symptoms following our treatment. Her second CT image done on day 14 of February 6, 2020 began to show a great improvement. Her third CT examination on March 25, 2020 confirmed complete recovery from earlier lung damage 61th day post her illness.
We maintained contact with our patient even up to now. The
patient feels normal on all aspects and her family members have
been remained infection-free as well. Thus, we had effectively
treated a patient suffering a pneumonia caused by SARS-CoV-2
infection via telemedicine. We believe that our success was mainly
contributed by our individual-based and situation-adjusted
treatment regime that matches well with patient’s health status
and catches up with dynamic disease progression.
We realized that pulmonary inflammation might be a great
contributor for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and
thus paid special attention in utilizing a combination of medicines for suppressing this pathogenesis and for preventing potential
cytokine storm. These measures might have helped the patient
from slipping into severe stages that are difficult to treat even with
advanced medical equipment and techniques in hospital-settings.
We also feel that a most important point in managing SARS-CoV-2
infection is limiting the exposure to the virus.
Our patient was unlucky to be infected when she took off
her facial mast to have a dinner with her close friends as one
of them was suffering COVID -19 without obvious symptoms.
The low dose of exposure and the early proper treatment and
physical rehabilitation might help the better cure. One thing that
may be worthy of mention is that our patient took vitamin C and
zinc routinely. Some studies suggest that zinc may be useful for
prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19 [8].
As the COVID-19 pandemic is still continuing its threat to more
and more people in even wider area, we believe that telemedicine
should become an important route for safe and cost-effective
rendering of patient’s situation-specific treatment. We strongly
believe that primary care physicians who knew their patients very
well can work with radiologists and other specialist in a telemedicine
mode to provide a safe, trusted, high quality professional health
care and a cost-effective, situation-and disease condition, as well
as symptom-specific medical treatment for SARS-CoV-2 infection,
which promotes the integrated care and rehabilitation medicine in
the face of acute infectious disease. Meanwhile, the integrated digital
recording and displaying of medical histories, including patient’s
symptoms, vital signs, as well as others aspects such as treatment
approaches may shed some light on the future medical records
augmented with some new techniques. This digital medical history
recoding of patients doesn’t only facilitate practice of telemedicine,
but also promotes exchanges of information and consolidation of
big data. It provides a basis for introducing machine learning (ML)
and artificial intelligence (AI) to play a big role in global efforts on
fighting a daunting pandemic which threatens human lives around
the world and causes massive social disturbance in human societies.
References

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...




