Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2644-1373
Review ArticleOpen Access
A Brief Overview to TNF-a Inhibitors Therapy on Covid-19: Functions Inside Cell Cascades Volume 2 - Issue 1
Serife Yerlikaya*
- Istanbul Medipol University, Regenerative and Restorative Medicine Research Center (REMER), Turkey
Received: May 25, 2020; Published:June 02, 2020
Corresponding author: Serife Yerlikaya, Istanbul Medipol University, Regenerative and Restorative Medicine Research Center (REMER), Kavacik North Campus, Kavacik-Beykoz/ISTANBUL, Turkey
DOI: 10.32474/LOJPCR.2020.02.000129
Abstract
Viral Covid-19 has spreaded all over the World only in a few months and caused much deaths. Covid-19 is belong to coronavirus family (called also SARS-CoV-2). Virus entry into cell occurs by unification with membrane receptors by releasing viral capsids or by endocytosis. TNF inhibitors aim to block receptors that bind to intracellular pathways as soluble form or by membrane bounding. Some TNF-α inhibitors have been used on severe Covid-19 patients nowadays.
Keywords: Receptor; Cell; Covid-19; İnhibitors
Introduction
SARS-CoV-2, also named Covid-19, was emerged firstly in Wuhan, China at the end of November, 2019 and began to spread as a pandemic viral-infected illness all over the World. Originally, it is a type of coronoviruses. Coronaviruses are belong to Coronaviridae family and positive single stranded RNA viruses encircled with an envelope [1]. Generally they are divided into 4 groups as alpha (α), beta (β), gamma and delta (ᵟ) coronaviruses [2]. SARS-CoV (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus) is a type of the Alphacoronavirus genus [3] and emerged firsty in late 2002 in China as a characteristic pneumonia [4]. As reported previously, SARS viruses are mostly fatal therefore, highligthting of the pathological disorders of SARS is very important [4]. Apoptotic and MAPKs (Mitogen Activated Protein Kinases) activations play significiant role in SARS-CoV viral infections [4,5-7]. Several in vitro and in vivo studies showed that MAPK signal cascade may inhibit viral infections (SARS-CoV-infections) by involving in apoptosis or regulating extracellular cytokine activation [4]. Virus penetration inside cell takes place by fusion with membrane by releasing viral mirids or by endocytosis [8,9]. Recent studies showed that during transmission of human SARS-CoV viruses, Covid-19 (SARS-CoV-2) also uses the same receptor for angiotension converting enzyme (ACE2) [10]. This mini review targets to emphasize the importance of relationship between TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factors) inhibitors and intracellular signal transduction mechanism on Covid-19.
Tnf Inhibitors
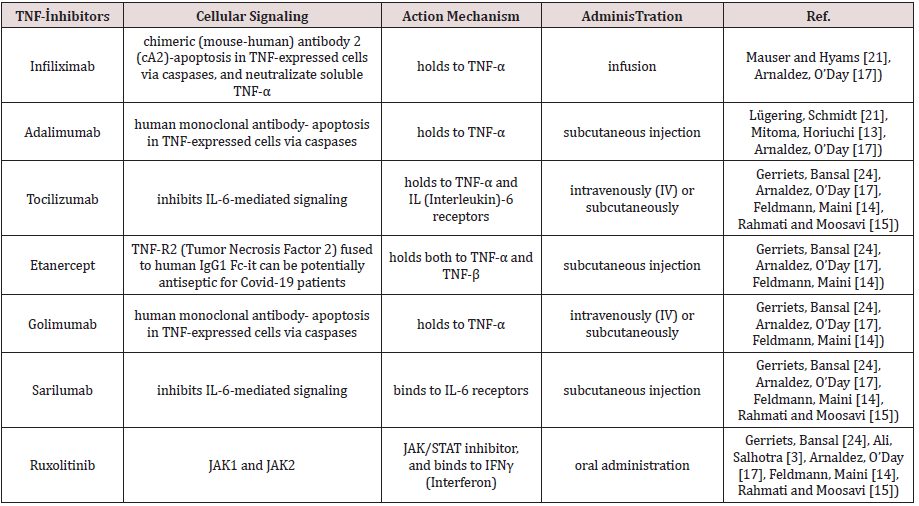
Tumor Necrosis Factors (TNF) are generally known as proteins that are responsible from killing malign cells; among them especially TNF-α and TNF-β are cytokines and have same receptors. They play important role on autoimmune diseases. Biological effects of TNF against disease depend on speed of stimuli in response [11]. Responses contain fever, shock, tissue and organ (especially lung in coronaviruses) injury, tumor necrosis, anorexia, induction of other cytokines and immunoregulatory molecules, cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis [11,12]. Also, TNFs are so important in initiation and enhancing imflammation on Covid-19 patients [6]. According to the latest studies, pathological disorders of lung of Covid-19 patients showed capillary fluids are ouflowed and immune-inflammatory lymphocytes, neutrophils, and macrophages are enlisted [13]. FDA approved some important TNF-inhibitors for treatment of inflammatory diseases about 20 years ago [14]. Therefore, clinical researchers are tend to search on novel TNF inhibitor molecules [14,15]. Some TNF inhibitor molecules was shown in Table 1 and a few of them are used thesedays for the treatment of Covid-19.
Among cytokines, IL-6 is the key receptor in severe Covid-19 patients. Coronavirus spike proteins contribute to increase of IL-6 production in immune and epithelial cells [2,16]. Tocilizumab and sarilumab block the activation of IL-6 receptor and under clinical phase studies. Turkey, China (21 severe trial), a case from France and Iran treat ICU (Intensive Care Unit) Covid-19 patients with tocilizumab and showed successful performance [17]. Fever and respiratory disorders began to improve in patients after a few days [12,15,18,19]. According to updated output number Covid-19 patients (on 22th May 2020) in Turkey, mortality rate has diminished vigorously (to 27) and also ICU and entubated patients are decreasing day by day. These data showed that treatment strategy was discovered successful in Turkey.
TNF-α can be in soluble or membrane bound form. Cell signaling of TNF-α in Covid-19 is complex and react with several tumor necrosis factor receptors [17]. Multiple signal cascades activate JAK (Janus kinase) and STAT (Signal transducer and activation of transcription). On account of this pathway activation PI3K activation initiates and destroyed cells begin to proliferate, survive, differentiate and pro-inflammatory transcription takes place. Ruxolitinib is a type of IL-6 receptor blocking molecule and ihibits JAK/STAT signaling pathway by binding to IFNγ [17]. It can be also potential molecule like other IL-6 inhibitor molecules for treatment of critical Covid-19 patients and also may be used as combinetherapy with other antiviral compounds [20-24].
Conclusion
Covid-19 has become a serious pandemi for months, there is no direct therapy for patients so clinical researchers need urgent treatment plan. Latest studies showed that TNF-α inhibitors could be potential candidate for spesific therapy, because mortality rate showed that cancer, diabetes and immunological disorders patients are tend to have more respiratory problems than the other. Some pathological problems cause sepsis into cell pathway. Therefore novel TNF-α inihibitors especially targetting apoptotic pathways (for elimination of destroyed cells) and IL-6 receptors (for blocking interleukins) could be potential candidate for the treatment of Covid-19. Highlighting the pathway mechanism behind virus penetration into cell is crucial in order to select correct drug for therapy.
Conflicts
There is no conflicts.
References
- Ciotti M, Angeletti S, Minieri M, Giovannetti M, Benvenuto D, et al. (2020) COVID-19 Outbreak: An Overview. Chemotherapy p:1-9.
- Shereen MA, Khan S, Kazmi A, Bashir N, Siddique S (2020) COVID-19 infection: origin, transmission, and characteristics of human coronaviruses. Journal of Advanced Research 24:91-98.
- Ali H, Salhotra A, Modi B, Nakamura R (2020) Ruxolitinib for the treatment of graft-versus-host disease. Expert Review of Clinical Immunology 16(4):347-359.
- Mizutani T (2007) Signal Transduction in SARS‐CoV‐Infected Cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1102(1):86-95.
- Whitmarsh TP, Johnson GL (1999) Organization and regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11(2):211-218.
- Whitmarsh AJ, Davis RJ (2000) A central control for cell growth. Nature 403(6767):255-256.
- Kyriakis JM, Avruch J (2001) Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 81(2):807-869.
- Marsh M, Helenius A (2006) Virus entry: open sesame. Cell 124(4):729-740.
- Chi PI, Liu HJ (2012) Molecular signaling and cellular pathways for virus entry. International Scholarly Research Notices 2013.
- Gabutti G, D’Anchera E, Sandri F, Savio M, Stefanati A (2020) Coronavirus: update related to the current outbreak of COVID-19. Infectious diseases and therapy p:1-13.
- Papadakis KA, Targan SR (2000) Tumor necrosis factor: biology and therapeutic inhibitors. Gastroenterology 119(4):1148-1157.
- Liu Zg, Hsu H, Goeddel DV, Karin M (1996) Dissection of TNF receptor 1 effector functions: JNK activation is not linked to apoptosis while NF-κB activation prevents cell death. Cell 87(3):565-576.
- Mitoma H, Horiuchi T, Hatta N, Tsukamoto H, Harashima SI, et al. (2005) Infliximab induces potent anti-inflammatory responses by outside-to-inside signals through transmembrane TNF-α. Gastroenterology 128(2):376-392.
- Feldmann M, Maini RN, Woody JN, Holgate ST, Winter G, et al. (2020) Trials of anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy for COVID-19 are urgently needed. Lancet 395(10234):1407-1409.
- Rahmati M, Moosavi MA (2020) Cytokine-Targeted Therapy in Severely ill COVID-19 Patients: Options and Cautions. Mortality pp:105954.
- Yoshikawa T, Hill T, Li K, Peters CJ, Tseng CTK (2009) Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus-induced lung epithelial cytokines exacerbate SARS pathogenesis by modulating intrinsic functions of monocyte-derived macrophages and dendritic cells. J Virol 83(7):3039-3048.
- Arnaldez FI, O'Day SJ, Drake CG, Fox BA, Fu B, et al. (2020) The Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer perspective on regulation of interleukin-6 signaling in COVID-19-related systemic inflammatory response. J immunother cancer 8(1):
- Cont P, Ronconi G, Caraffa A, Gallenga C, Ross R, et al. (2020) Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): anti-inflammatory strategies. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 34(2):1.
- Xu X, Han M, Li T, Sun W, Wang D, et al. (2020) Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117(20):10970-10975.
- Michot JM, Albiges L, Chaput N, Saada V, Pommeret F, et al. (2020) Tocilizumab, an anti-IL6 receptor antibody, to treat Covid-19-related respiratory failure: a case report. Anna Oncol.
- Mauser JF, Hyams JS (1999) Infliximab: a novel chimeric monoclonal antibody for the treatment of Crohn's disease. Clin Ther 21(6):932-942.
- Lügering A, Schmidt M, Lügering N, Pauels HG, Domschke W, et al. (2001) Infliximab induces apoptosis in monocytes from patients with chronic active Crohn's disease by using a caspase-dependent pathway. Gastroenterology 121(5):1145-1157.
- Liu J, Zheng X, Tong Q, Li W, Wang B, et al. (2020) Overlapping and discrete aspects of the pathology and pathogenesis of the emerging human pathogenic coronaviruses SARS‐CoV, MERS‐CoV, and 2019‐nCoV. J Med Virol 92(5):491-494.
- Gerriets V, Bansal P, Khaddour K (2019) Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors. Stat Pearls.