Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-4668
Research article(ISSN: 2637-4668) 
Phosphorus Transport Influenced by Exponential Homogeneous Dispersion Coefficient and Velocity of Flow in Eleme Stream Volume 4 - Issue 2
Ezeilo FE1* and Eluozo SN2
- 1Department of Civil Engineering, Rivers State University of Nkpolu Oroworukwo, Nigeria
- 2Department of Civil College of Engineering, Gregory University Uturu, Nigeria
Received: January 04, 2021 Published: January 21, 2021
Corresponding author: Ezeilo FE, Department of Civil Engineering, Rivers State University of Nkpolu Oroworukwo, Port Harcourt, Nigeria
DOI: 10.32474/TCEIA.2021.04.000181
Abstract
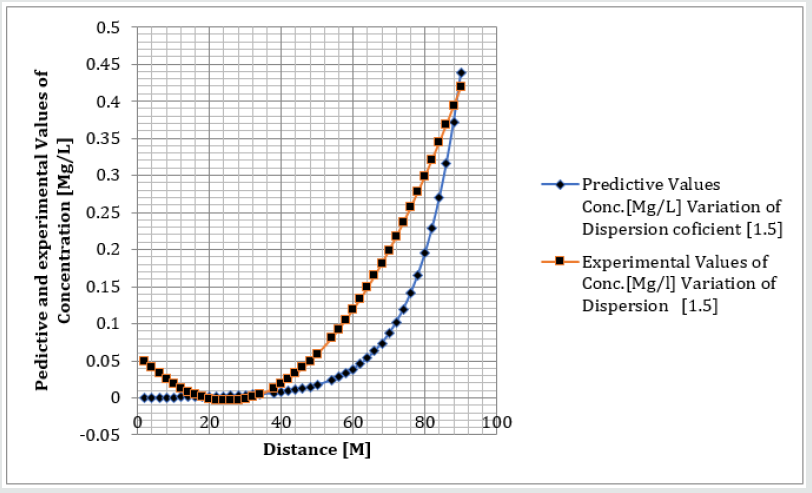
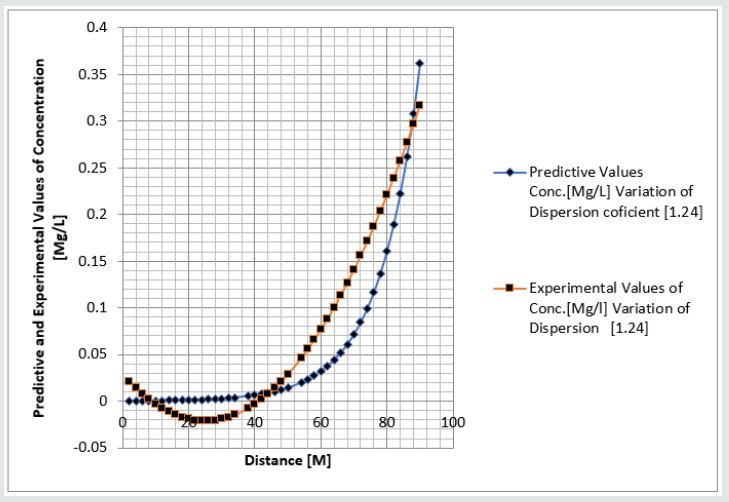
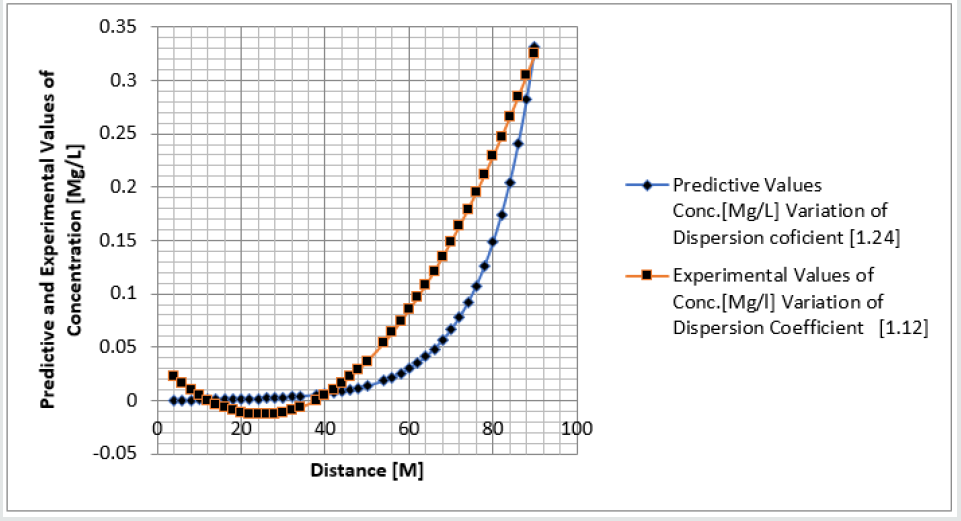
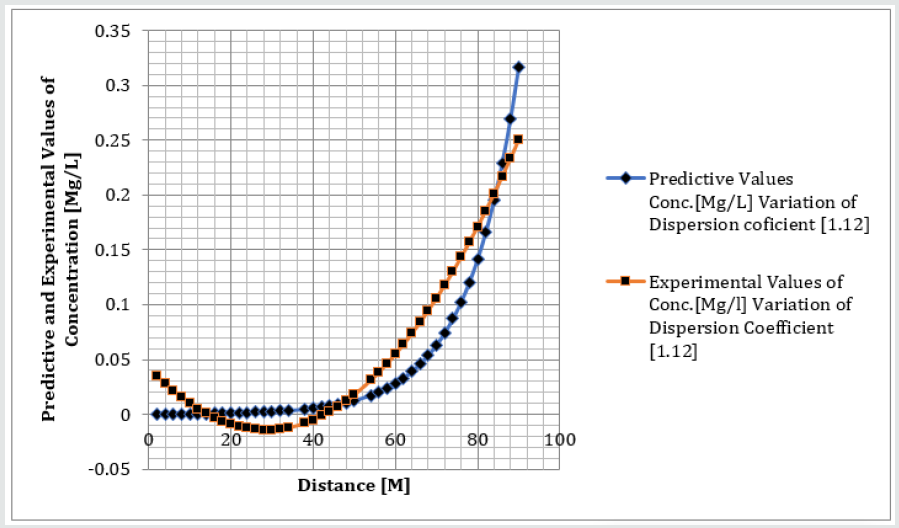
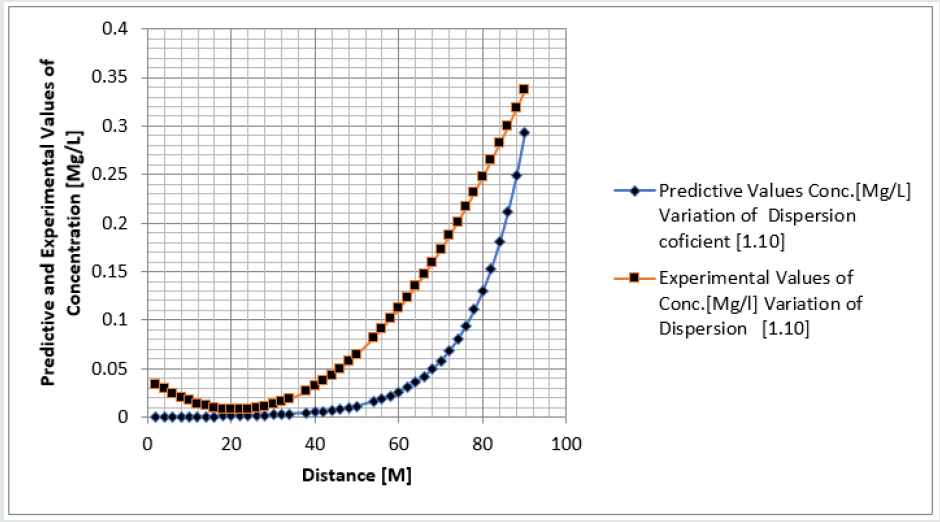
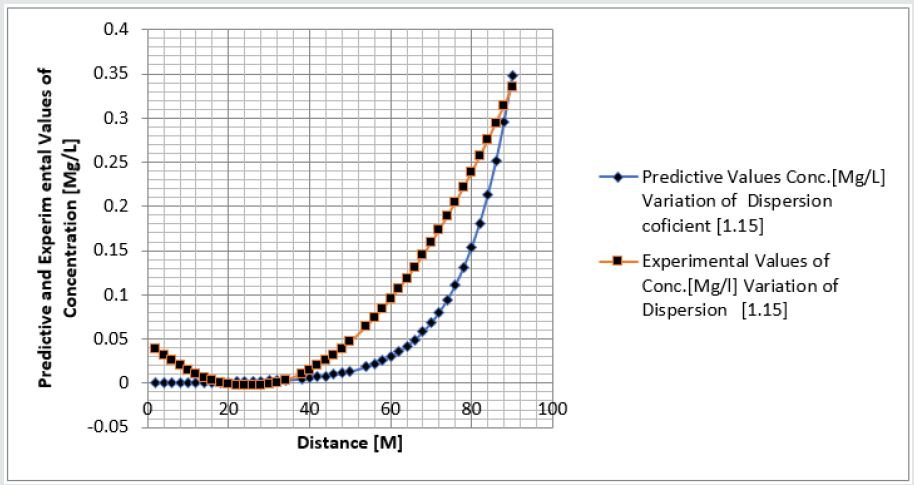
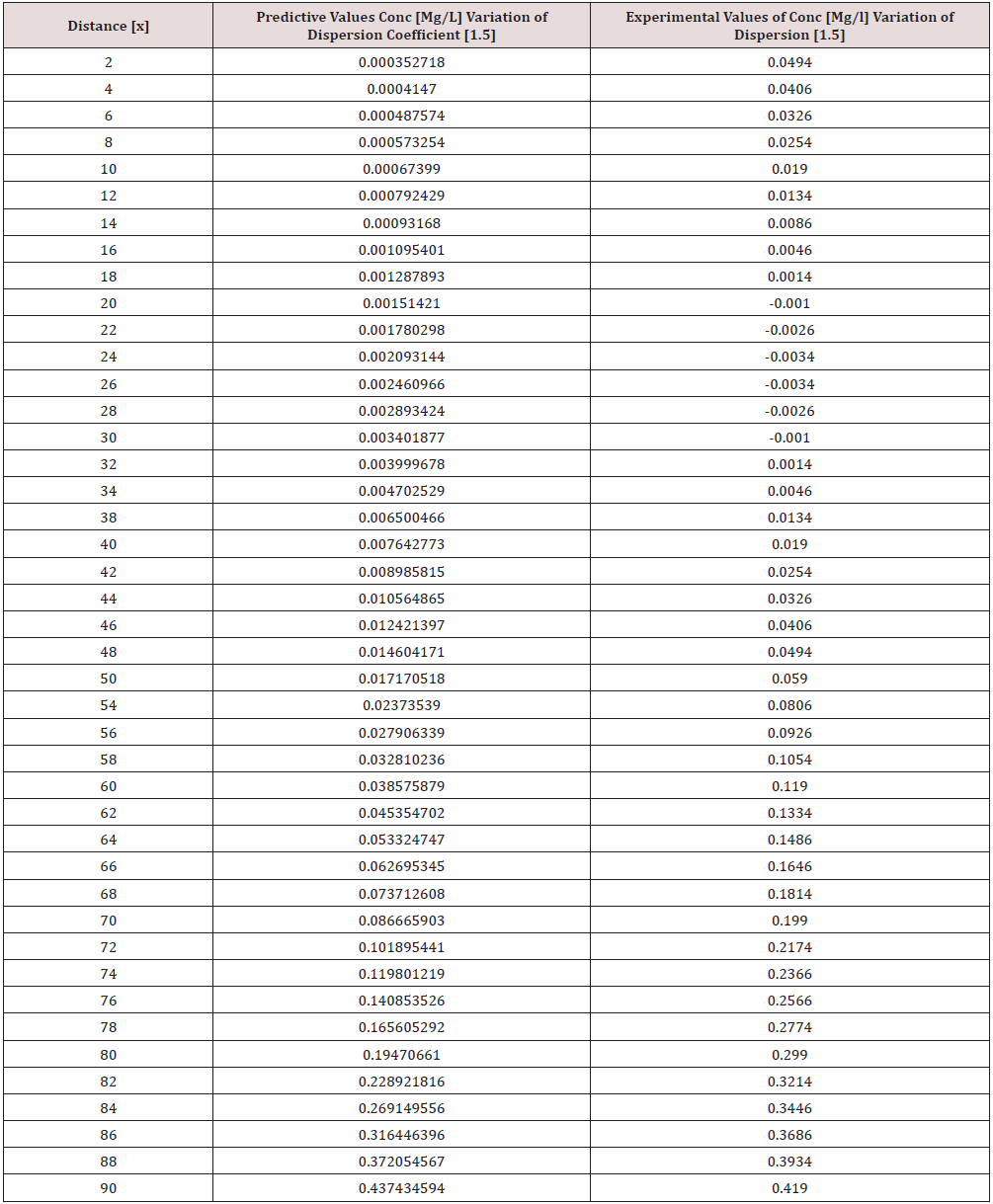
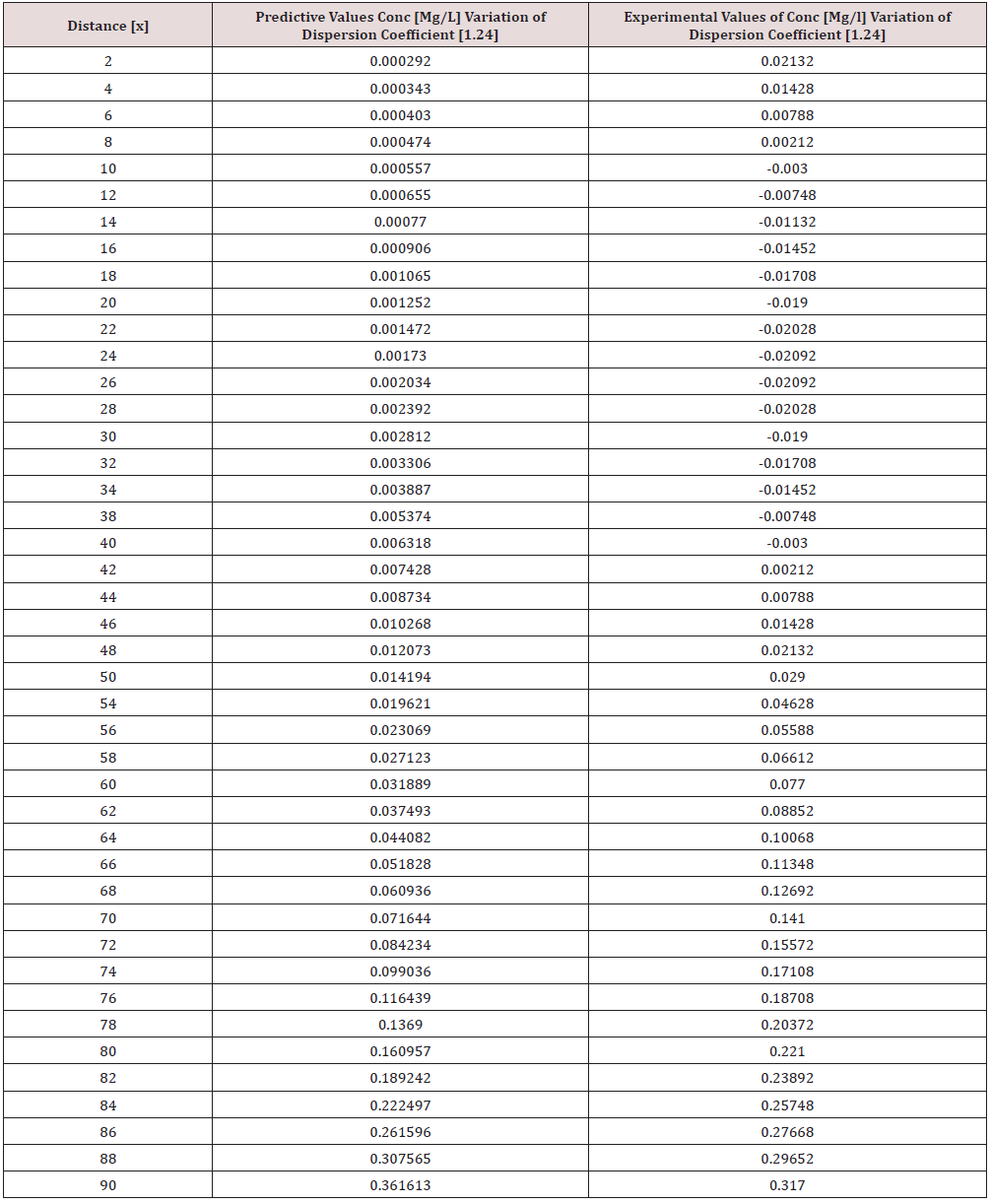
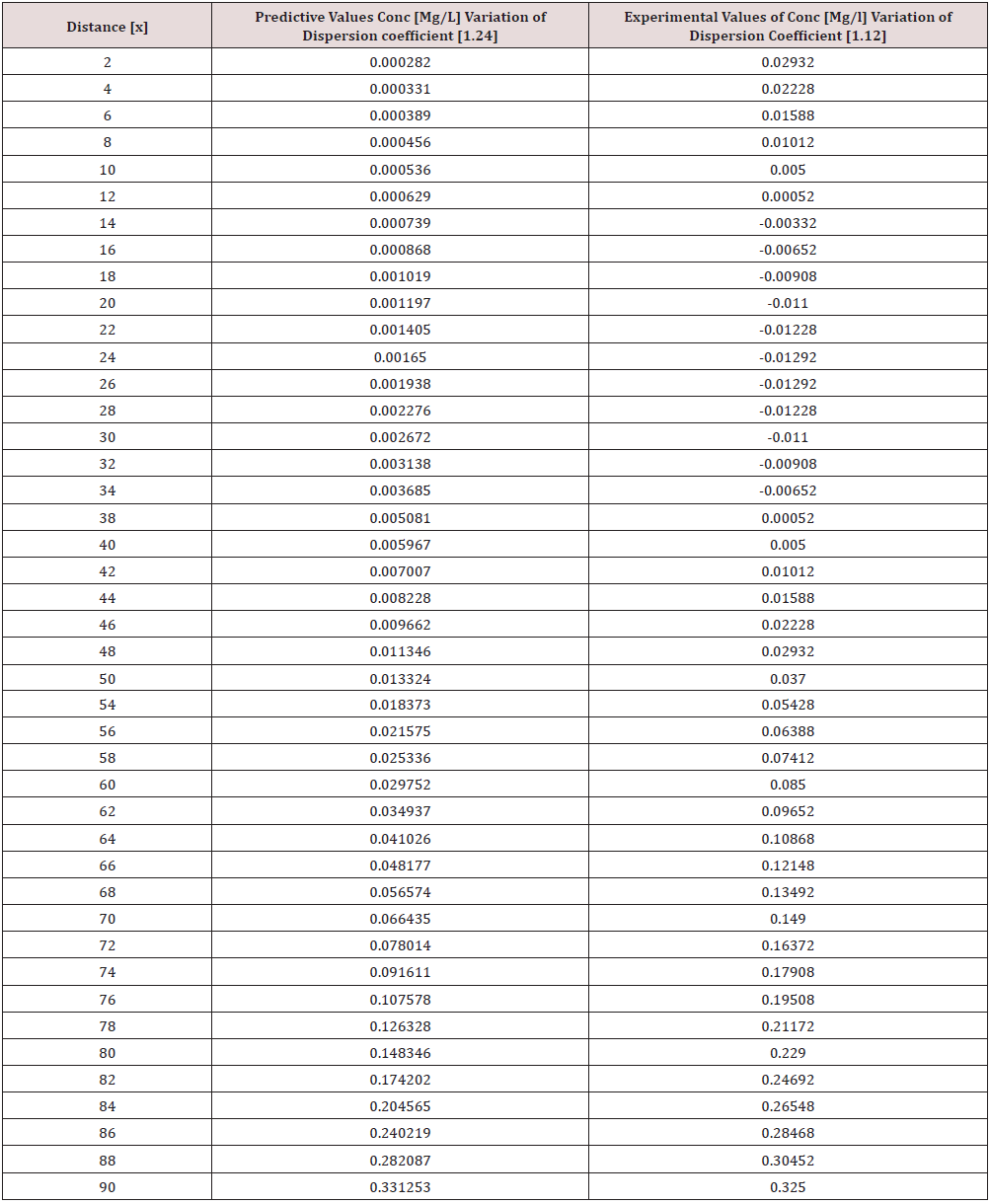
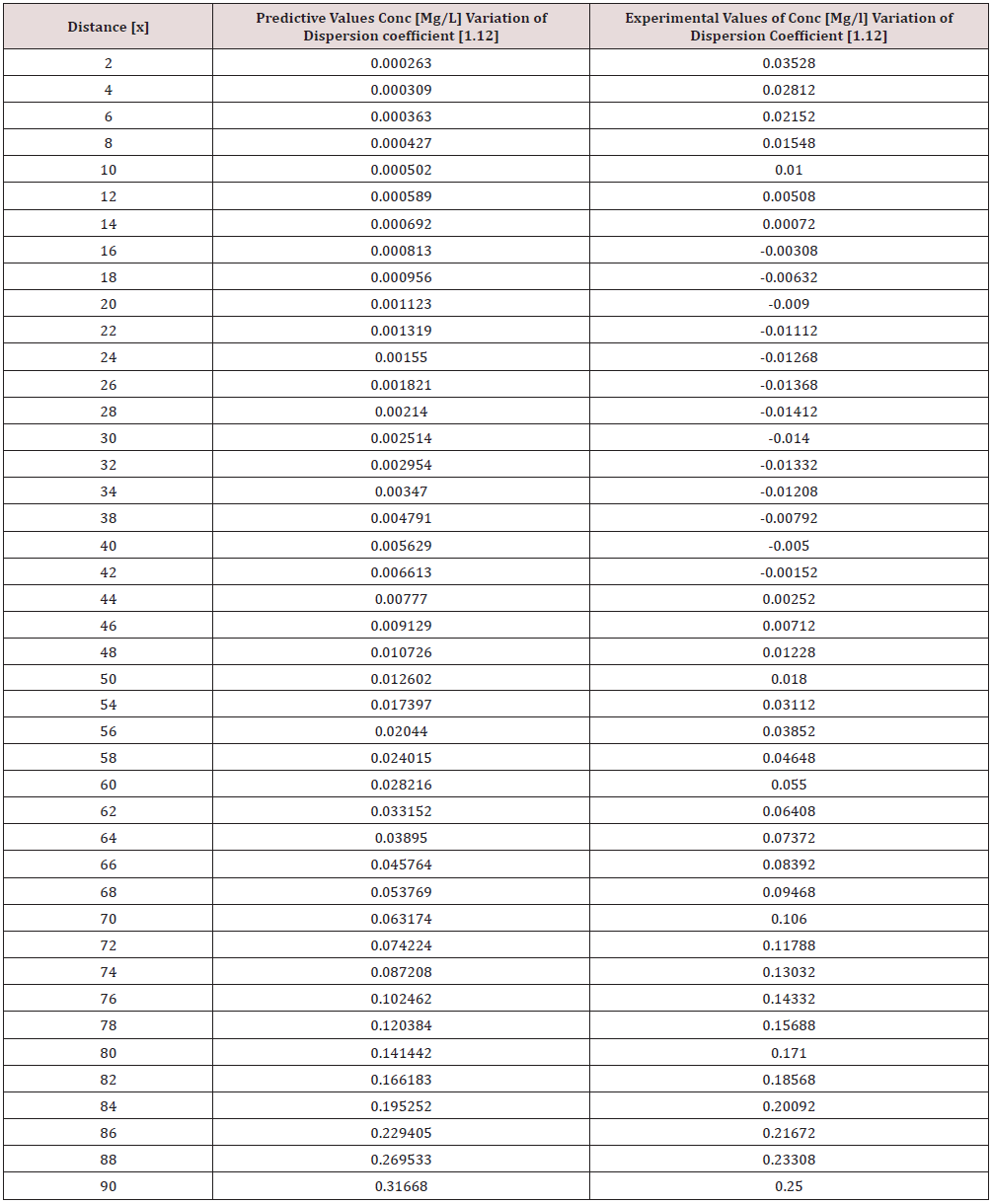
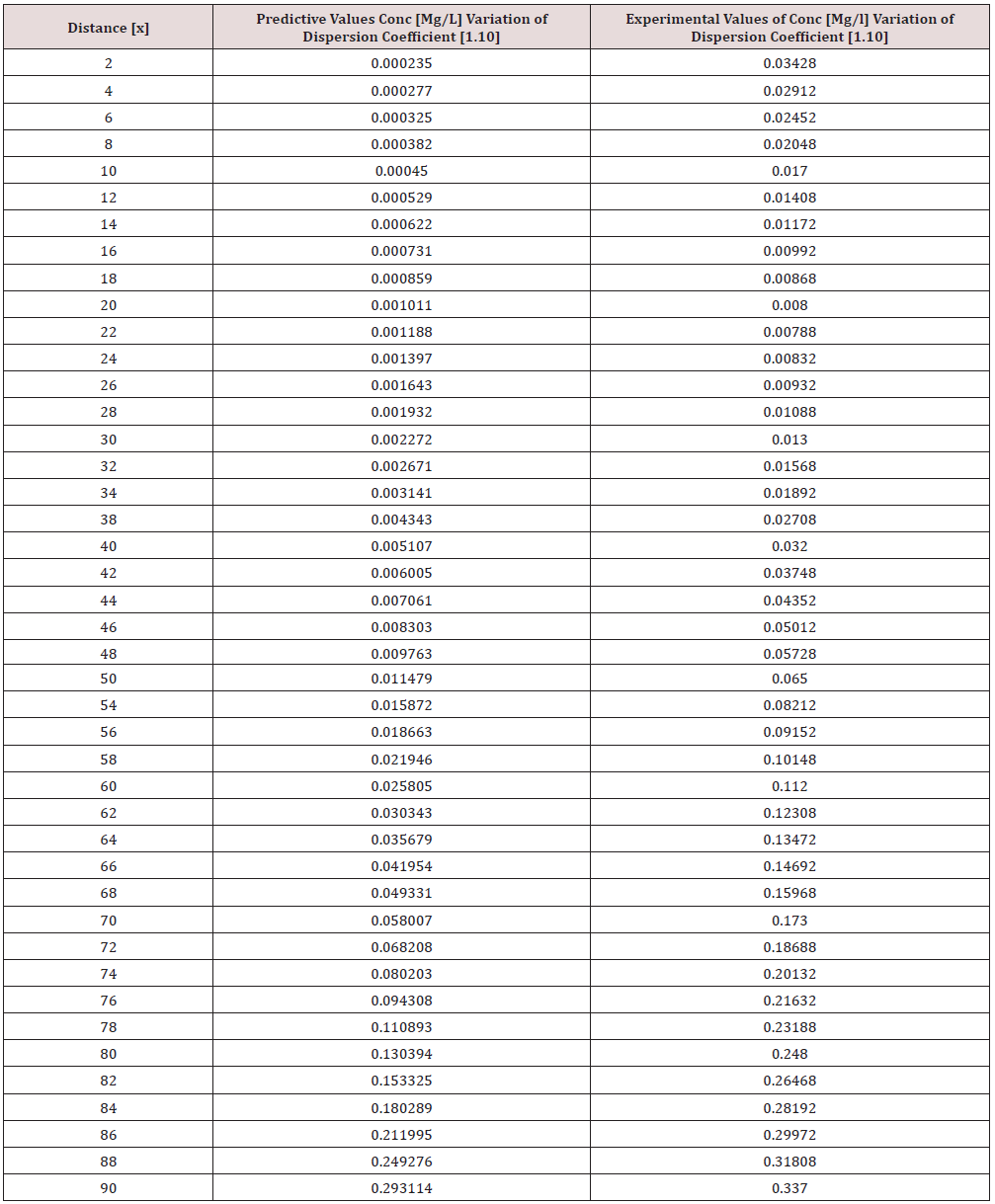
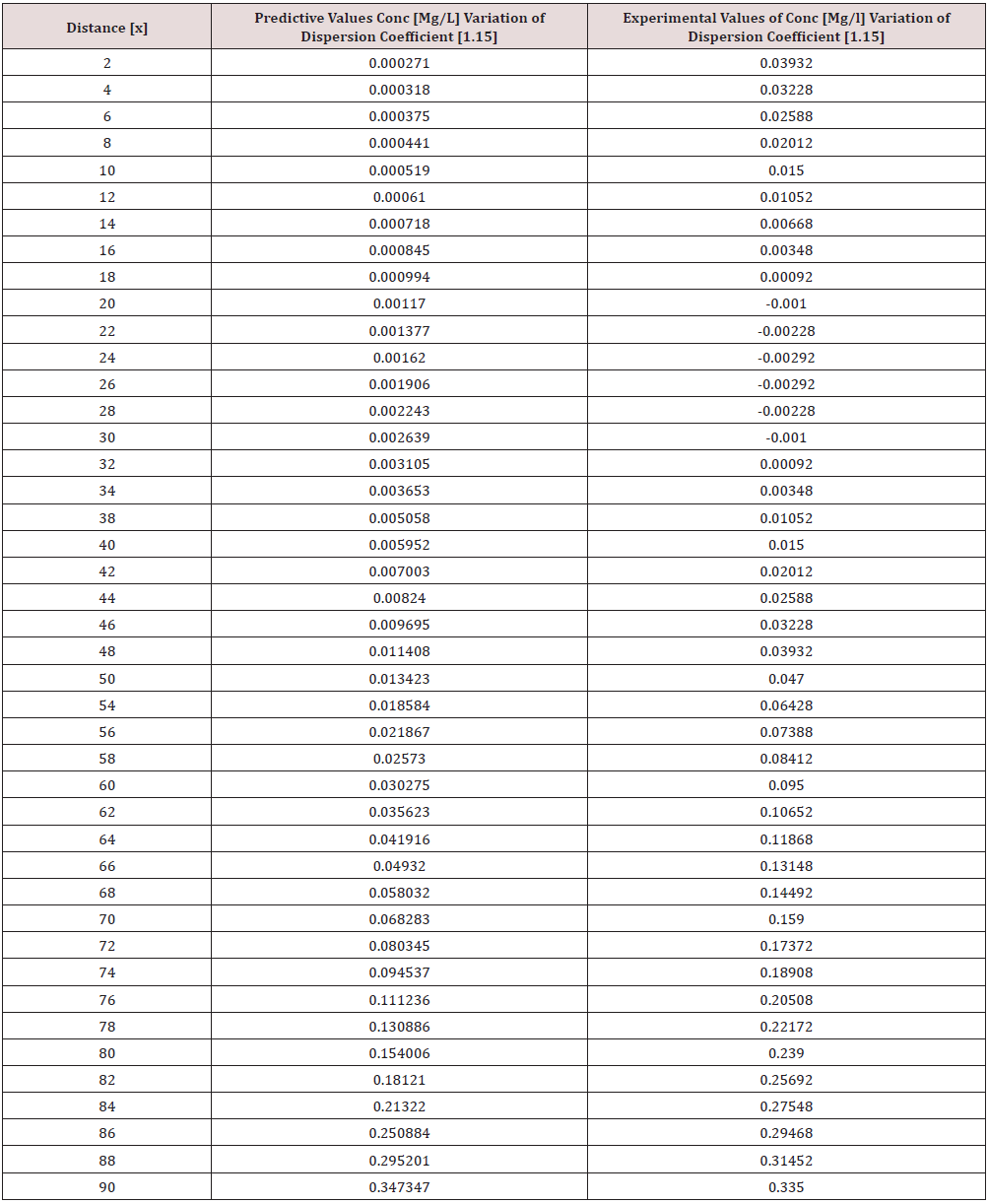
Phosphorus as one of the microelement was observed to predominantly deposit in the study environment, this were experienced from physiochemical investigation carried out in the stream, the examination observed the predominant deposition of increased phosphorus in different station point of discharge, this implies that there are some significant factors causing such increase of the contaminant in the stream, the evaluation generated other parameters that could influenced the exponential state of the contaminant, such condition call for serious concern, thus thorough examination of these parameters that affect the growth rate of phosphorus in the stream, the transport of this microelement experienced increase in all the figures based on the points source of discharge monitored, derived model were applied to monitor the behaviour of phosphorus in the stream, this were carried out through model and simulation, the system monitored other influential parameters that pressured the growth rate of the contaminant at different point source, gradual growth rate to the optimum level were experienced based on the continuity process of phosphorus substance discharged in the stream, the study also observed other effect from phosphorus deposition at high rate in the stream, the substance were observed in the stream to increase rapid rate of microbes in the stream, an increase of Eutrophication in the stream expressed high rate of phosphorus in the environment, there various rates of concentration ranged from 0.000352718-0.437434594,0.00029158-0.361612598,0.00028183-0.331253401, 0.000263182- 0.316679675, 0.000235172-0.293114139, 0.000270628- 0.347346913, the derived simulation values were compared with experimental data, and both parameters developed best fits correlation, the study is imperative because it has monitored various rate of velocity that influenced dispersion of phosphorus substance in the stream, it has also expressed the rate of homogeneous velocity of flows as it has been through evaluated.
Keywords: Phosphorus; Transport dispersion coefficient velocity and flow
Introduction
Preceding segments explain the pathogen pollution in various ambient water bodies and possible sources. Factors influencing pathogen continued existence and transport in ambient water bodies are of a huge interest Pathogen concentration in water bodies are influenced by many environmental factors. Scott et al. [1] several studies have been reviewed studies explaining the environmental factors impacts on pathogen survival are accessible Brookes et al. [2]; Fayer and Trout [3]; Gerba 4]; Hipsey et al. [5] Eluozo and Ezeilo [6]. The consequence of these factors has variation with season and these types of ambient water bodies Van Donsel et al. [7]; Gallagher and Spino [8]; Niemi [9] Eluozo and Ezeilo [10], Pandey [12]. Modeling In- Stream Escherichia coli Concentrations Graduate Dissertation Iowa state university pp 62-75. Other studies carried out such as for stream water, temperature is considered to be the governing factor in E. coli continued existence McFeters and Stuart [12] Eluozo and Ezeilo [13]; meanwhile, in the study of groundwater and reservoir, the existence of predators controls their survival Wcislo and Chrost [14]; Gordon and Toze [15]; John and Rose [16] Eluozo and Ezeilo [17], Eluozo and Amadi [18], Eluozo and Amadi [19]. In another development, solar radiation is considered to be the most significant factor that affect the survival of pathogens; more so, the effect may definitely vary with depth of water, including the of type water bodies, and type of pathogen Sinton et al. [20]. Sunlight For example, is an inactivation rates that definitely vary. These are from greatest to least, because they are: coliforms > enterococci > F-RNA phages > somatic coliphages Davies-Colley et al. [21]; Davies-Colley et al. [22]; Davies-Colley et al. [23] Eluozo and Afiibor [24] Eluozo and Afiibor [25]. Other research study carried out expressed the sunlight inactivation rate as: >enterococci > fecal coliforms > E. coli > somatic coliphages > F-RNA phages Sinton et al. [20], Eluozo [26].
Theoretical Background

Affordability
Nomenclatures
C = Concentration
B = Fluid Density
K = Dispersions
A= Velocity of flow
D = Distance
Multiplying the equation through by C[x], we have:
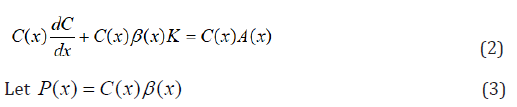
Then Equation (2), we have:
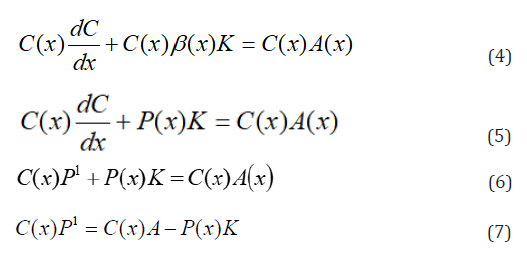
Differentiate 2nd term on the left-hand side of (6) with respect to x, we have
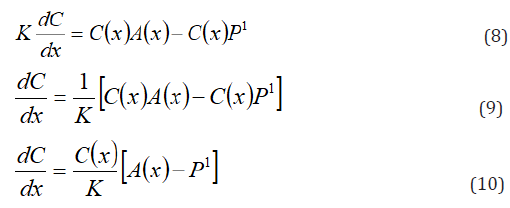
Applying separation of variables, by dividing through by C(x) and cross multiply by dx, gives:
Taking exponent of both side of the equation
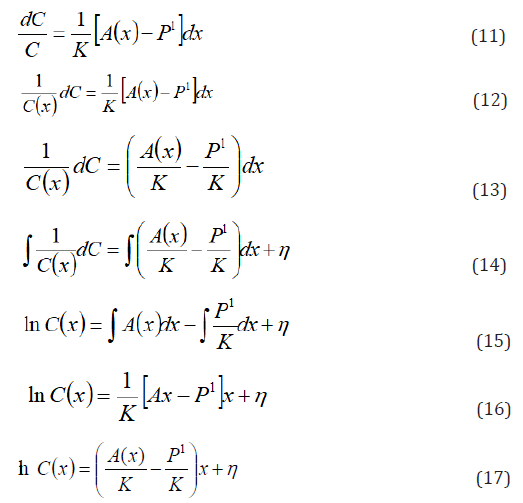
Materials and Method
Standard laboratory experiment where performed to monitor Phosphorus a using the standard method for the experiment at different sample at different station, the water sample were collected in sequences base on specification stipulated at different locations, this samples collected at different location generated variations at different distance producing different Phosphorus concentration through physiochemical analysis, the experimental result were compared with the theoretical values for model validation [27,28].
Results and Discussion
Table 1-6 and Figure 1-6 explained the behavior of the microelement growth rate in the stream, the figures shows exponential growth rate, this implies that the point source of the microelement discharging into the river are in continues process, the discharge from human settlers in the environment continue to increase, the concentration in the stream cause higher rate of increase from the point source of discharge, the trend gradual increase from the point source to optimum rate, such condition were monitor in the environment in other to determine the rate of it deposition at distance of ninety meters, because of the gradual increase in the stream, this condition implies that the system are influenced by other significant parameters that should be part of the transport system, the growth rate of both phosphorus are basically on the conditions observed in the study environment, the stream experienced heterogeneous velocity at different locations, the shape of the stream and other environmental factor were observed to influence the velocity of flow, but the trend monitored the dispersion coefficient effect on the stream, the growth rate of the microelement explained the rate of velocity of flows and the variation of dispersion coefficients in the transport process, based on this factors exponential phase of phosphorus were predominantly observed in the study area, the predictive and experimental values developed the gradual increase with higher percentage of best fits correlation.
Conclusion
Phosphorus deposition in Eleme stream were monitor at different locations, this were to evaluate the rate of its concentration at different station point of discharge in the stream, the study evaluate this microelement based on it exponential growth rate in the stream, this cause for thorough study in other to determine their various rate of increase at the stream, the rate of concentration in some location generated Eutrophication in the stream, the variations from velocity of flow were observed to influenced the rate dispersion of phosphorus in the study environment, this on physical process shows the rate water hyacinth on the stream, this condition implies that constant discharge of the microelement will definitely generate high increase of microbes in the river thus developed microbial increase from these points of discharge, the study has definitely express various rates of discharge and it level of concentration at different point, such study expressed thorough evaluation of the factor that cause the increase of phosphorus transport in the stream, the study has expressed the fundamentals causes of exponential growth rate of contaminant in the stream, the application of one dimensional flow transport system has express the variation effect of dispersion at various point source discharge locations in the study area. The predictive and experimental values developed best fits correlations.
References
- Scott TW, Takken W, Knols BGJ, Boete C (2002) The ecology of genetically modified mosquitoes. Science 298 (5591): 117-119.
- Brookes JD, Antenucci J, Hipsey M, Burch MD, Ashbolt NJ, et al. (2004) Fate and transport of pathogens in lakes and reservoirs. Environ Int 30(5): 741-759.
- Fayer R, Trout JM (2005) Oceans and Health: Pathogens in the Marine Environment, Springer US, pp. 143-163.
- Gerba CP, Smith J (2005) Sources of pathogenic microorganisms and their fate during land application of wastes. Journal of Environmental Quality 34(1): 42-48.
- Hipsey MR, Antenucci JP, Brookes JD (2008) A generic, process-based model of microbial pollution in aquatic systems. Water Resources Research 44(7).
- Eluozo SN, Ezeilo FE (2018) Numerical Modeling of Nocardia Migration Influenced Transport Pressured by Dispersion and Velocity in Fine Sand Formation in Wetland Environment. Journal of Water Resources Engineering and Management 5(1): 25-32.
- Van Donsel DJ, Geldreich EE, Clarke NA (1967) Seasonal variations in survival of indicator bacteria in soil and their contribution to storm-water pollution. Appl Microbiol 15(6): 1362-1370.
- Gallagher TP, Spino DF (1968) The significant of numbers of coliform bacteria as an indicator of enteric pathogens. Water Research 2: 169-175.
- Niemi M (1976) Survival of coli phage T7 in different water types. Water Research 10: 751-755.
- Eluozo SN, Ezeilo FE (2018) Modeling Heterogeneous Porosity in Alluvia Plain Deposition in Deltaic Formation. Recent Trend in Civil Engineering & Technology 8(2): 1-10.
- Pandey PK (2012) Modeling In- Stream Escherichia coli Concentrations Graduate Dissertation Iowa state university pp 62-75.
- McFeters GA, Stuart DG (1972) Survival of coliform bacteria in natural waters-field and laboratory studies with membrane-filter chambers. Appl Microbiol 24(5): 805-811.
- Ezeilo FE, Eluozo SN (2018) Dispersion and Storage Coefficient Influences on Accumulation of Frankia Transport in Heterogeneous Silty and Fine Sand Formation, Warri Delta State of Nigeria. International Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering 4(4): 1-16.
- Wcislo R, Chrost RJ (2000) Survival of Escherichia coli in freshwater. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies 9(3): 215-222.
- Gordon C, Toze S (2003) Influence of groundwater characteristics on the survival of enteric viruses. J Appl Microbiol 95(3): 536-544.
- John DE, Rose JB (2005) Review of factors affecting microbial survival in groundwater. Environment Science & Technology 39(19): 7345-7356.
- Eluozo SN, Ezeilo FE (2018) Predicting the Behaviour of Borrelia in Homogeneous Fine Sand in Coastal Area of Bakana Recent Trend in Civil Engineering & Technology 8(2): 1-19.
- Eluozo SN, Amadi CP (2019) Modeling and Simulation of Legionella Transport Influenced by Heterogeneous Velocity in Stream. Journal of Water Resource Engineering and Management 6(2): 25-31.
- Eluozo SN, Amadi CP (2019) Velocity and Oxygen Deficit Influence on the Transport of Francisela in Eleme Creek. Journal of Water Resource Engineering and Management 6(2): 43-48.
- Sinton LW, Hall CH, Lynch PA, Davies-Colley RJ (2002) Sunlight inactivation of fecal indicator bacteria and bacteriophages from waste stabilization pond effluent in fresh and saline waters. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 68: 3605-3613.
- Davies-Colley RJ, Donnison AM, Speed DJ, Ross CM, Nagels JW (1999) Inactivation of faecal indicator micro-organisms in waste stabilization ponds: Interactions of environmental factors with sunlight. Water Research 33(5): 1220-1230.
- Davies-Colley RJ, Bell RG, Donnison AM (1994) Sunlight inactivation of enterococci and fecal coliforms within sewage effluent diluted in seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol 60(6): 2049-2058.
- Davies C, Long Jah, Donald M, Ashbolt NJ (1995) Survival of fecal microorganisms in marine and freshwater sediments. Applied Environmental Microbiology 61(5): 1888-1896.
- Eluozo SN, Afiibor BB (2018) Dispersion and dynamics influences from phosphorus deposition on e-coli transport in coastal deltaic Lake. MOJ Applied Bionics and biomechanics 2(5).
- Eluozo SN, Afiibor BB (2019) Mathematical Model to Monitor the Transport of Bordetella Influenced by Heterogeneous Porosity in Homogeneous Gravel Depositions. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 6(1).
- Eluozo SN, Oba AL (2018) Modeling and simulation of cadmium transport influenced by high degree of saturation and porosity on homogeneous coarse depositions MOJ Civil Engineering 4(4).
- Ezeilo FE, Eluozo SN (2018) Linear Phase Velocity Effect on Accumulation of Zinc in Homogeneous Fine Sand Applying Predictive Model, International Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering 4(4): 17-32.
- Eluozo SN, Oba AL (2018) Predicting heterogeneous permeability coefficient pressured by heterogeneous seepage on coarse deposition MOJ Civil Engineering 4(4).

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...