Lupine Publishers Group
Lupine Publishers
Menu
ISSN: 2637-4668
Research article(ISSN: 2637-4668) 
Mathematical Modeling of Dispersion Coefficient and Particle Density Bacterial Influence on Campylobacter spp Transport In Surface Water Environment Volume 4 - Issue 2
Ezeilo FE1* and Eluozo SN2
- 1Department of Civil Engineering, Rivers State University of Nkpolu Oroworukwo, Port Harcourt
- 2Department of Civil College of Engineering, Gregory University Uturu Abia State
Received: January 04, 2021 Published: January 22, 2021
Corresponding author: Ezeilo FE, Department of Civil Engineering, Rivers State University of Nkpolu Oroworukwo, Port Harcourt, Nigeria
DOI: 10.32474/TCEIA.2021.04.000182
Abstract
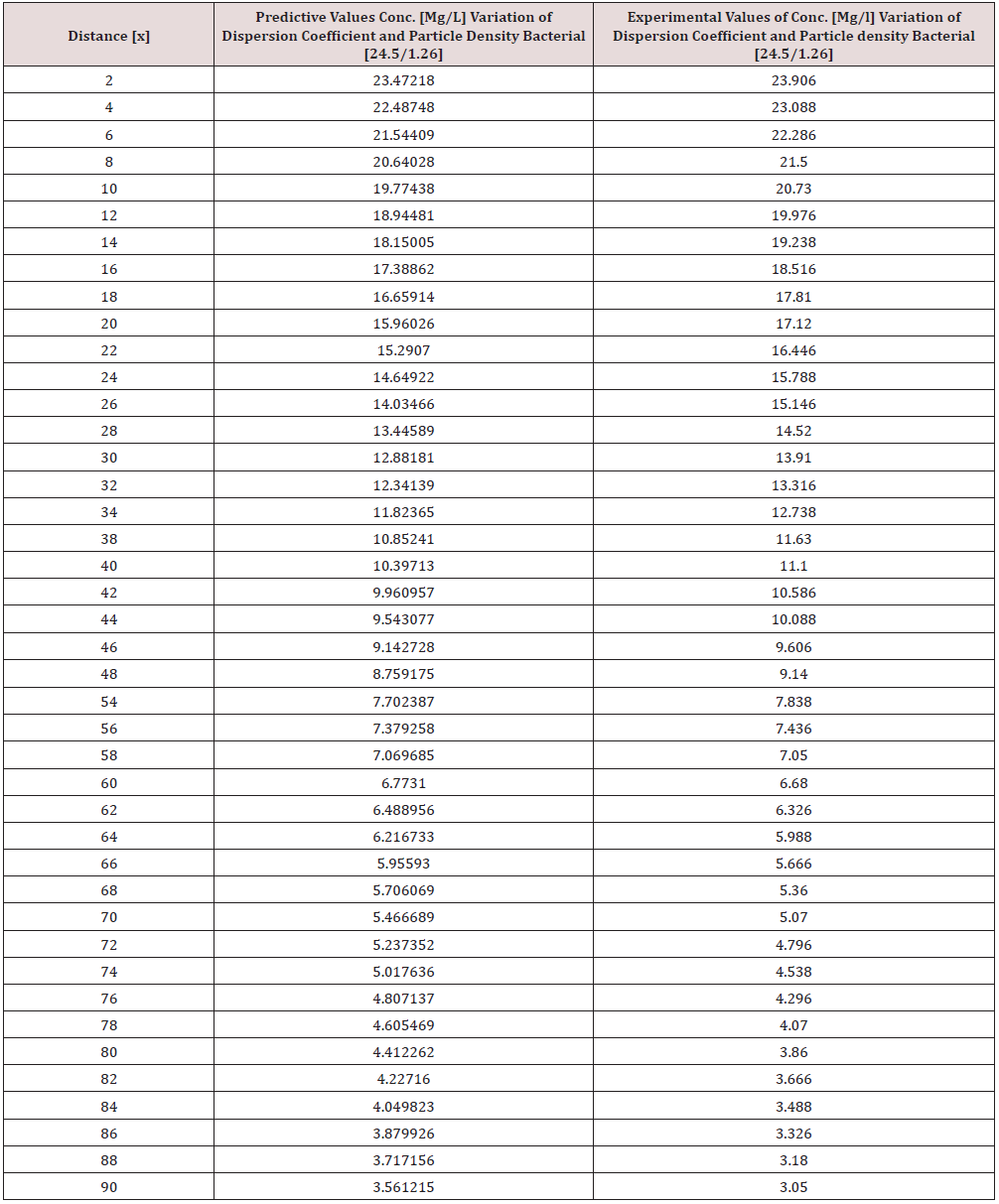
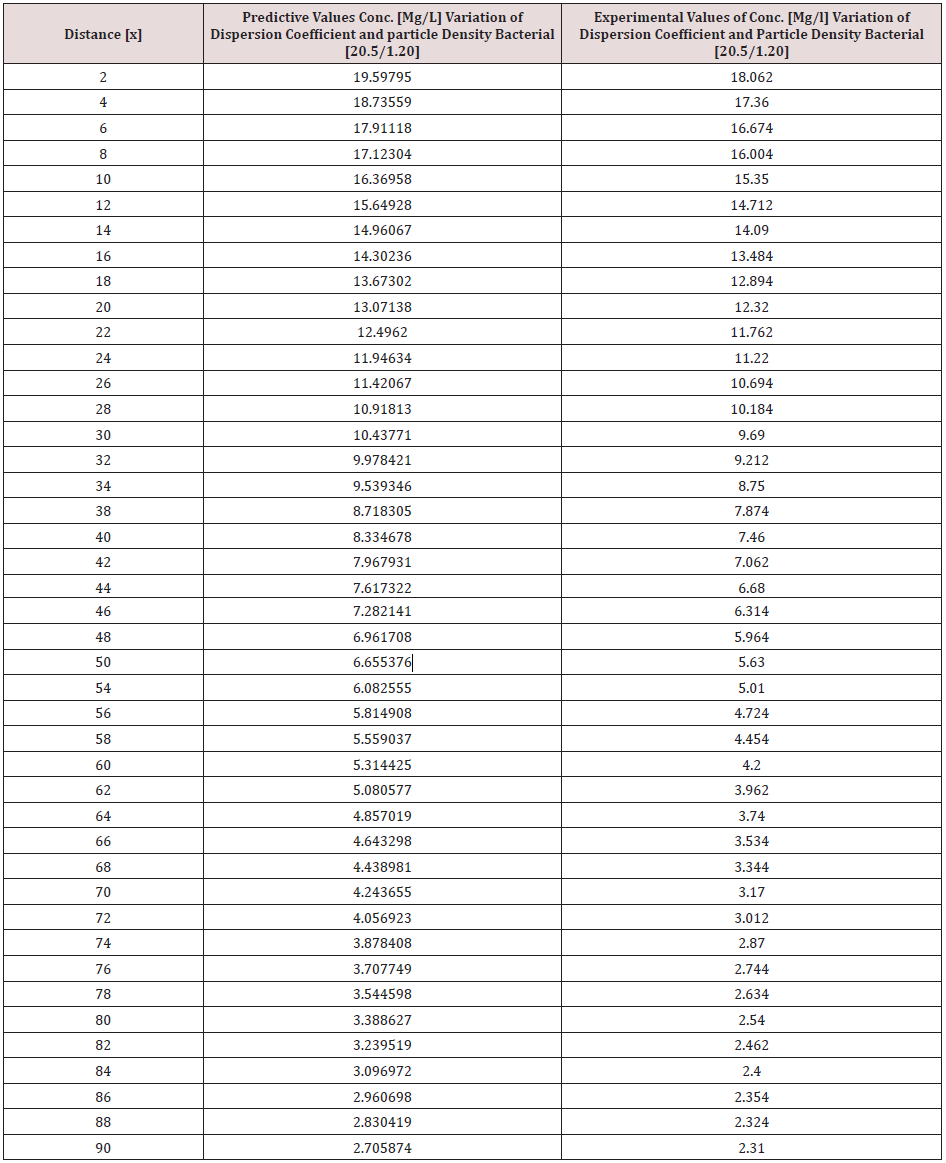
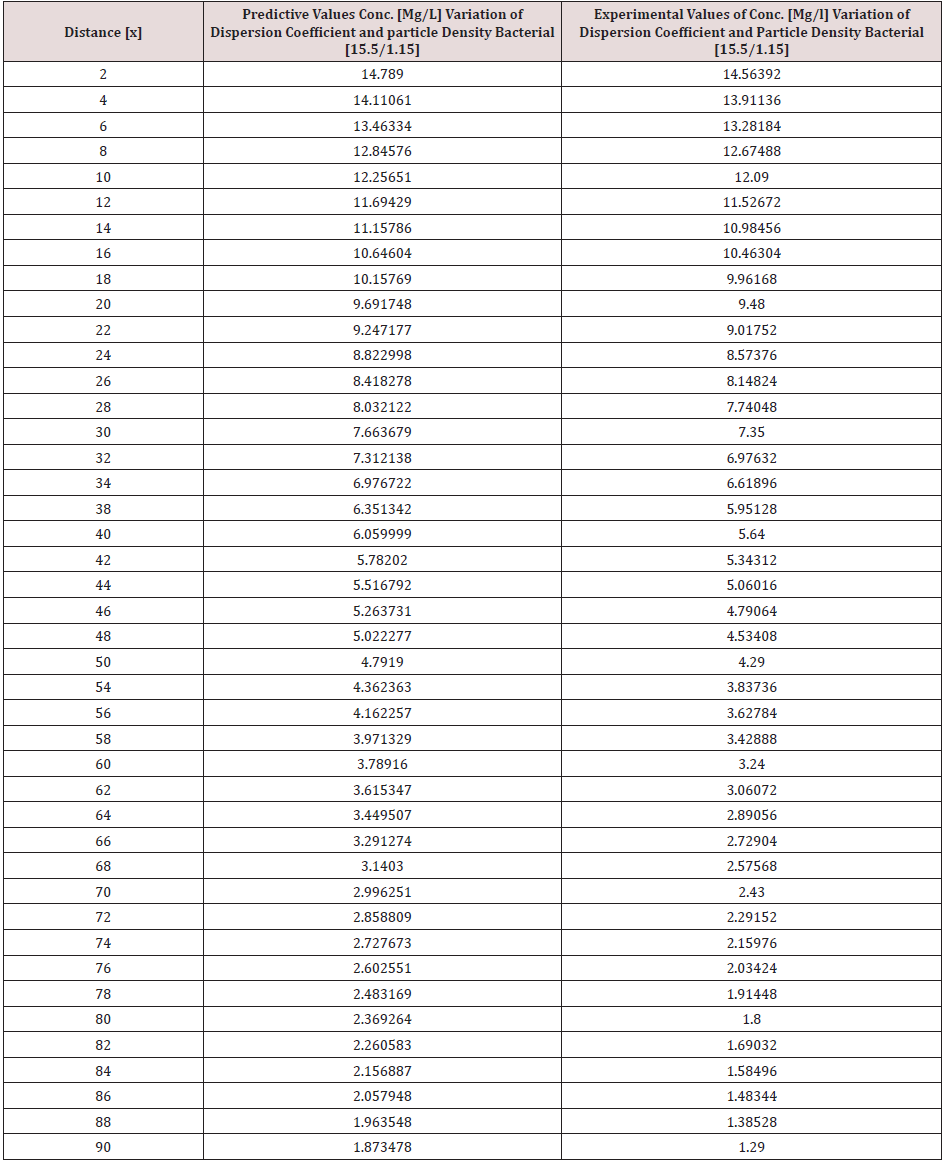
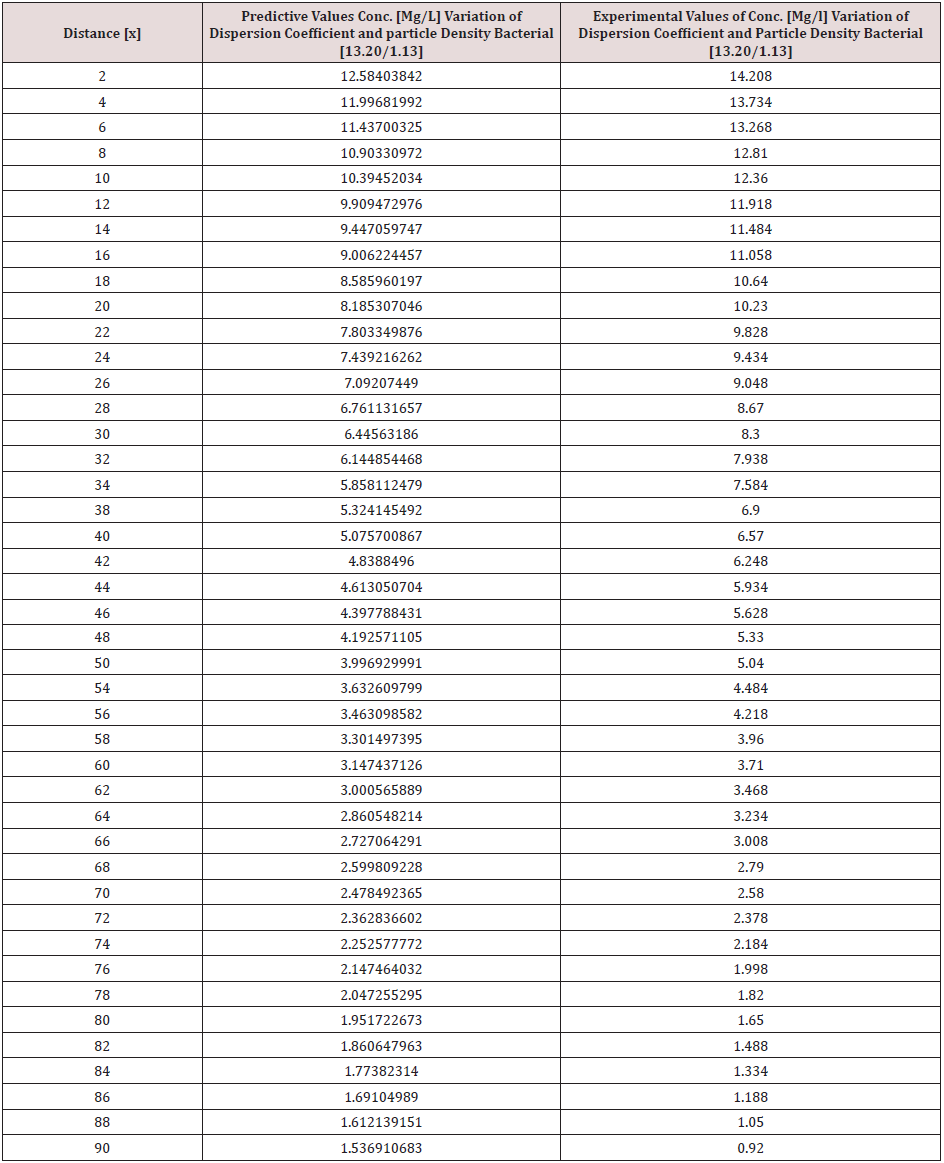
Particle density bacterial and dispersions of Campylobacter deposition was monitor in surface water environment, the transport of these microbes were observed to decrease with respect to change in distance at various monitored locations, dispersion of the contaminant at initial point of discharge were examined in the study environment, this was influenced through the migration of the contaminant at various station point of discharge, it was based on the heterogeneous velocity in the surface water environment. Despite the application of one dimensional flow transport, the study experience the impact of dispersion as decrease in concentration were observed in all the figures, the spread of the contaminant are based on the velocity of flow subjecting it to fast spread of campylobacter in surface water environment, particle density bacterial influence was also examined in its different dimensions, the particle densities of the bacterial was through transient frequencies, while another was through a microfluidic channel of flow in surface water, thus the distribution of a population and its heterogeneous size particle were based on difference carrier fluids, these also affected the concentration through heterogeneous velocities of surface water flows at different station point, the decrease in the transport system were monitored based on these two predominant parameters in the simulation, the generated parameters of concentrations at different stationed point of transport ranged from 24.38700365-3.422646182, 21.54119013- 3.170336995, 23.47218199-3.56121468, 19.59794838-2.705873785, 14.78899765-1.873477905, 12.58403842-1.536910683. the study has express the behaviour of the system in terms of its rapid decrease of campylobacter based on these factors, the concentration implies that the surface water Pollution should be subjected to clean up to reduce the rate of contamination to the minimum required standard, this will definitely make the surface water environmentally friendly. The study is imperative because it has expressed the rate of these two predominant parameters that can influenced the spread and the deposition of campylobacter in surface water environment.
Keywords: Mathematical Modeling, Dispersion Coefficient Density Bacterial and Campylobacter Transport
Introduction
Pathogens group of this type of species were Vibrio Cholera are from has such causes cholera, this has been observed to infect numerous human settlements, over millions of people each year Nelson et al., 2009 [1] Eluozo Afiibor 2018 [2]). For instance, records of the implementation of a suitable quantify to prevent the transmission of water borne pathogens (Colwell, 1996 [3]; Okun 1996 [4], Eluozo and Oba 2018 [5], Pandey 2012 [6]). Studies carried out in the Year past the application of geographic techniques has shown the spread and epicenter of cholera, this perception resulted to the locating of contaminated water body, because that it was observed to be responsible for spreading of the disease. Diseases such as Water borne (i.e., diarrhea, gastrointestinal illness) such rate are caused by various microbes such as bacteria, viruses, and protozoa, there are various reasons for numerous outbreaks as it stated by (Craun et al., 2006 [7] Eluozo and Ezeilo 2018 [8], Pandey 2012 [6]). Nigeria as a developing nation such as other Africa nations, waterborne diseases infect millions of people (Fenwick, 2006 [9]). Cryptosporadium, E. coli O157:H7, V. Cholera, and Salmonella was observed to be the fundamental outbreaks in this environment (Craun et al., 2006 [7], Eluozo and Ezeilo 2018a [10], Eluozo and Ezeilo 2018b [11], Eluozo and Ezeilo 2018c [12]). It was noted that in the mid late 18th century; cholera, diseases have infected high percentage millions of people around the globe (Colwell, 1996 [3]). More so , in relative conditions, there are current research studies carried out such as Diffey (1991) [13], Brookes et al. 2004 [14] Eluozo and Ezeilo 2018d [15], Jamieson et al.(2004) [16], Gerba and Smith (2005) [17], Gerba and McLeod (1976), John and Rose (2005) [18], Hipsey et al. 2008 [14] Eluozo and Afiibor 2018b [19], Eluozo and Afiibor 2018a [2]), and Pachepsky and Shelton (2011) [20] these there is a comprehensive research the has thoroughly reviewed the current advancement in this area, precisely, freshwater and estuarine sediments. However, these research studies have developed some other areas that has not been done to improve on the existing works, numerous research is on specific water bodies, examples of these are research studies carried out by, John and Rose (2005) [18] it focuses on ground water, Brookes (2004) [14], other works carried out focuses on reservoirs and lakes, and Jamieson et al. 2004 [16], Eluozo and Amadi 2019a [21], Amadi and Eluozo 2019b [22] while others focuses on agriculture watershed.
Theoretical Background
Governing equation

Nomenclatures
C = Concentration Campylobacter SPP
B = Particle density of bacterial
K = Dispersions. Velocity of flow
A = Fluid Density
X = Distance
Multiplying the equation through byC[x], we have:
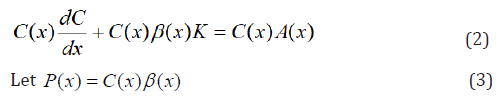
Then Equation (2), we have:
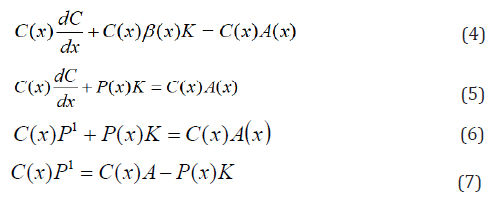
Differentiate 2nd term on the left hand side of (6) with respect to x, we have
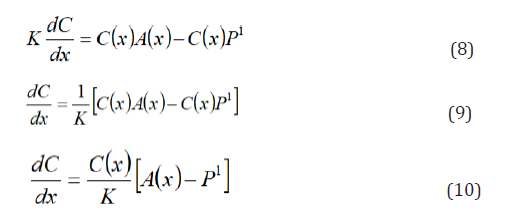
Applying separation of variables, by dividing through by C(x) and cross multiply by dx, gives:
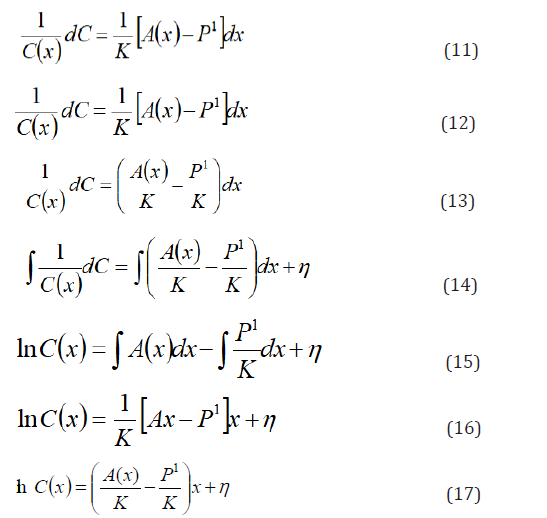
Taking exponent of the both side of the equation
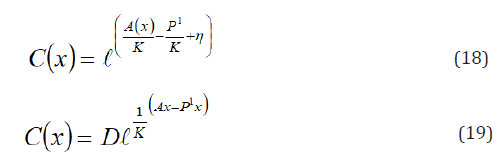
Materials and Method
Standard laboratory experiment where performed to monitor Campylobacter using the standard method for the experiment at different sample at different station, the water sample were collected in sequences base on specification stipulated at different locations, this samples collected at different location generated variations at different distance producing different Campylobacter concentration through physiochemical analysis, the experimental result were compared with the theoretical values for model validation [23].
Results and Discussion
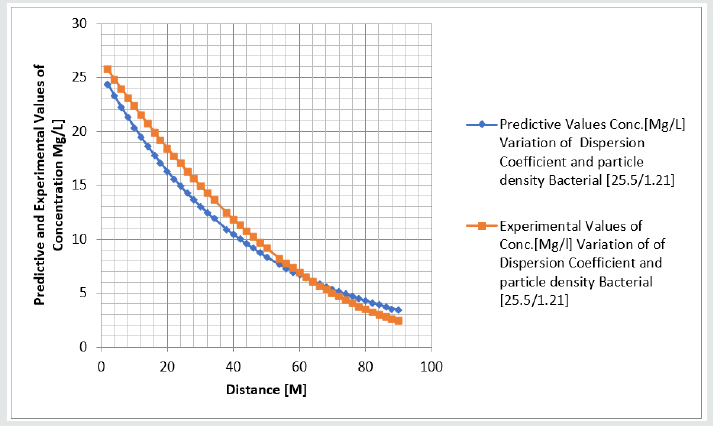
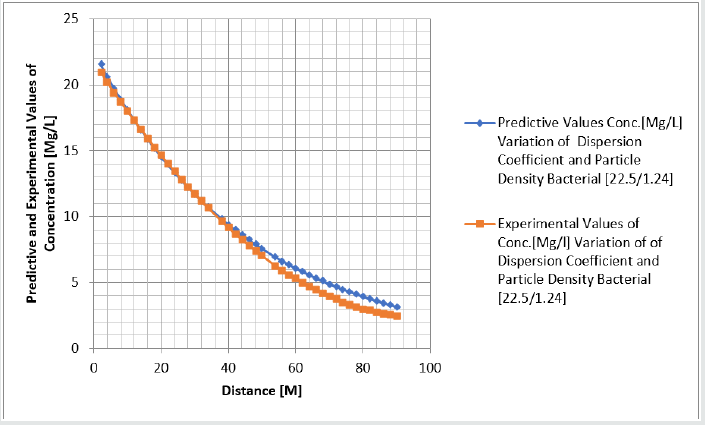
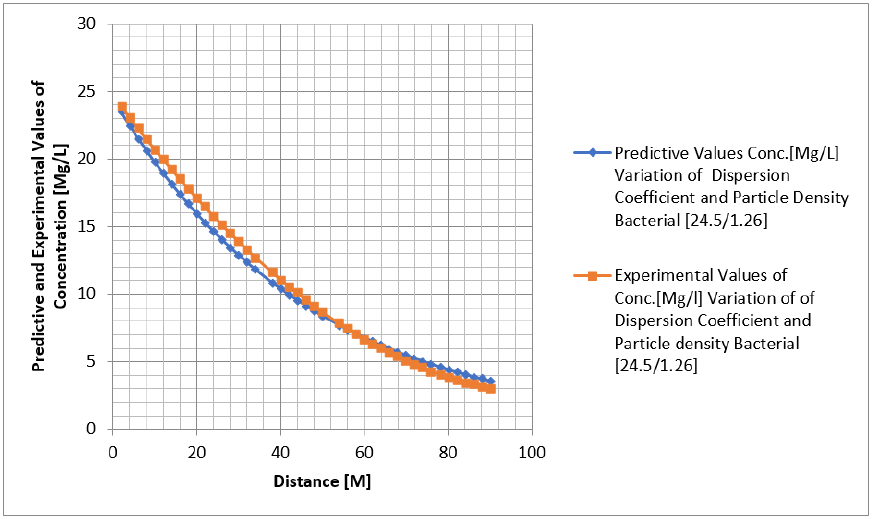
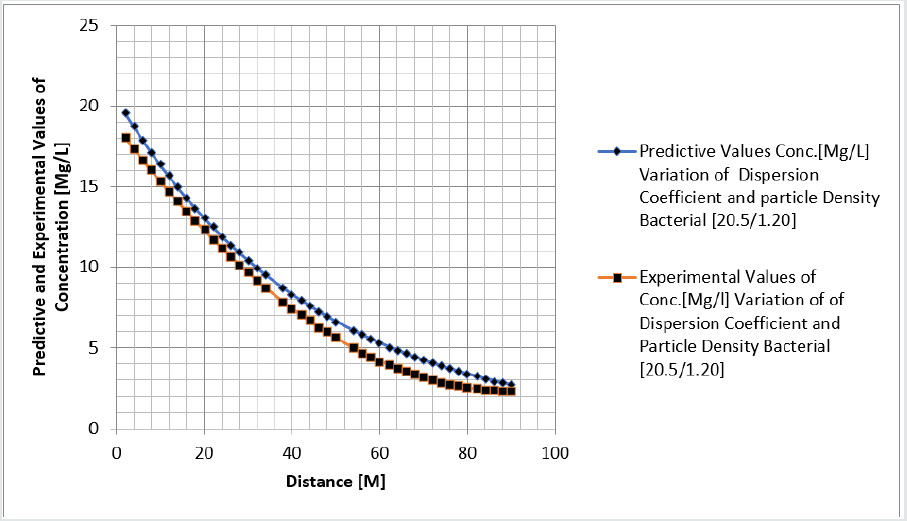
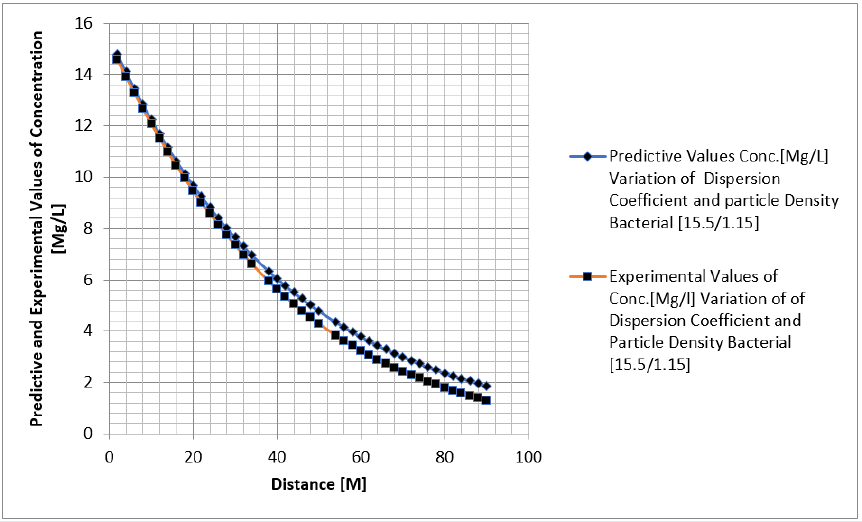
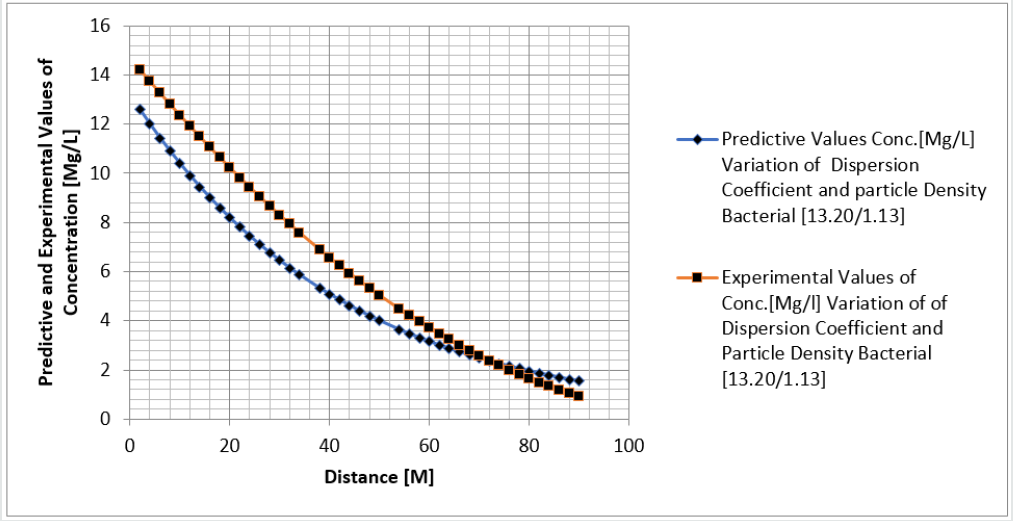
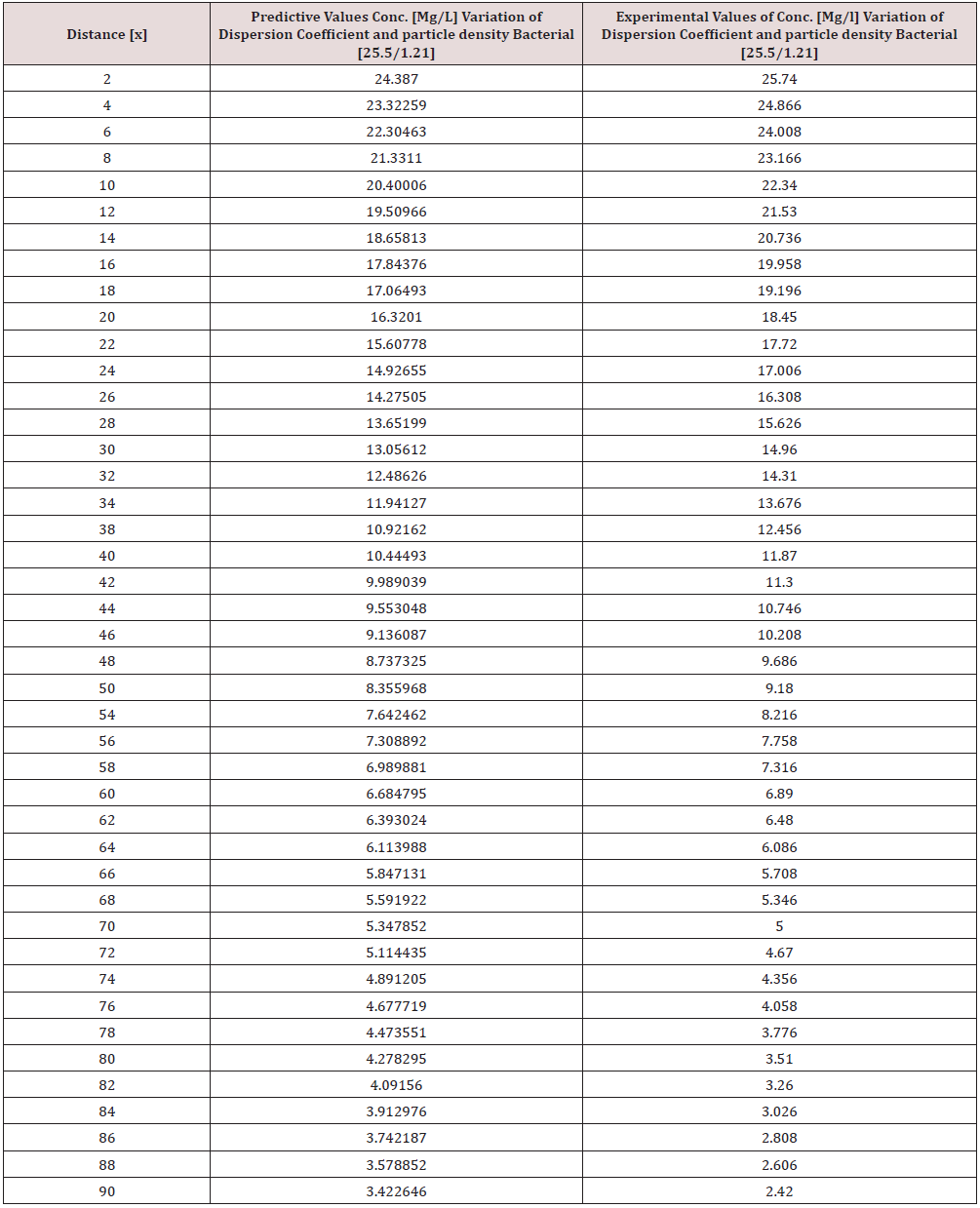
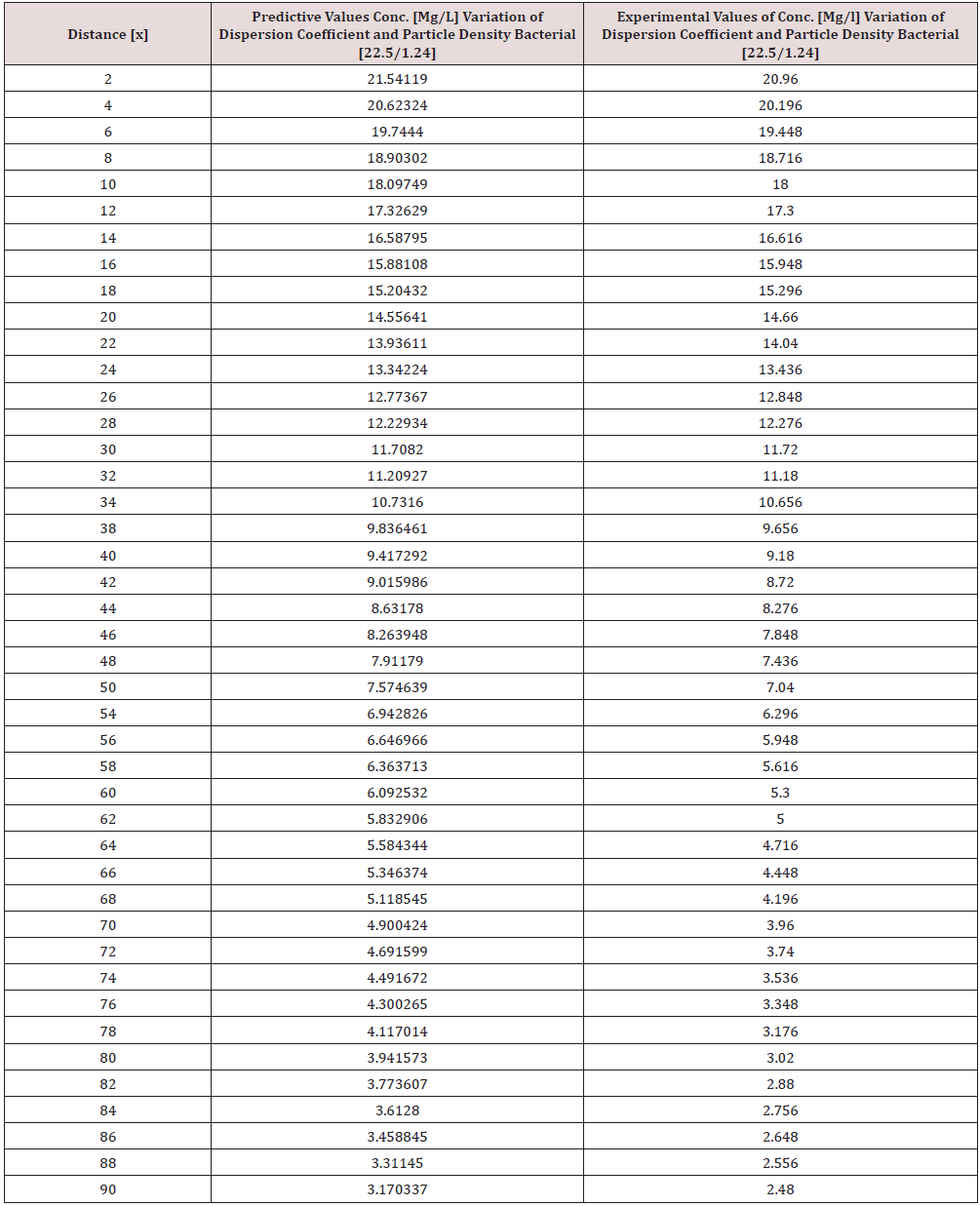
Tables 1-6 & Figure 1-6.
Figure 1-6 explained the behaviour of Campylobacter Concentration in surface water environment, the study through its expression on graphical representations, shows the rate of concentration from the initial point of discharge to the final monitored distance in the study environment, the figures from various location in studied environment experienced high to low concentration, but with different concentration between the initial point source of discharge to the final monitored distance in the study area, gradual decrease with respect to change in distanced was observed in all the studied locations, the rate of decrease in concentration was observed to be attributed to the dispersion coefficient and the particle densities of the bacterial, in surface water environment, the system developed monitor the influenced based on the imperative factors in surface water environment, the variation of velocity affected the dispersions of the microbes in terms of discharge in different point source, this implies that the dispersion influence on the transport of Campylobacter Concentration were based on the observed heterogeneous velocities in various point source of discharge in the study environment , while the particle density bacterial are observed through its mass transient frequency through the channel flow, it is monitored based on the discharge rate of population observed in its rate of heterogeneity particle size, while particle densities measured from carried fluids through its frequencies, this implies the shapes of the microbes that also determined the densities are affected by the microfluidic channel on the variation of heterogeneous fluid velocities, this system were influenced by these parameters as observed from the study carried out, the trend of the graph despite the variation of velocities in various station point source experience the effect from particle density of the bacterial, the predictive and the experimental values in all the figures developed best fits correlation.
Conclusion
The study of Campylobacter transport in surface water environment has been carried out applying modeling and simulation; the study expressed the behaviour of the Campylobacter transport in terms of influence from dispersion coefficient and particle densities of the bacterial in study area. The application of one dimensional flow system monitored the rate of migration at different point source of discharge, these are based on the predominant parameters that was monitored in the surface water environment, despite the application of one dimensional flow transport system, the dispersions in various location of discharge was examined to determine its rates of concentration at different station point of discharge, the dispersion on the contaminant are basically from the heterogeneity of the velocities that experience variations in various point sources, this condition examined affected the concentration of the contaminant in these stations point of discharge, the variation level of concentration were observed to experience some negative impact on it decrease with respect to change in distance, while that of the particle densities of the bacterial was through transient frequencies, while another was through a microfluidic channel of flow in surface water, thus the distribution of the population in heterogeneous size particles based on difference carrier fluids. These were also affected based on the heterogeneous velocities of surface water flows at different station point, these two predominant parameters examined has expressed in detail there impacts on the decrease of the contaminant with respect to change in distance, the study has definitely determined the impacts of these two parameters in Campylobacter transport in surface water environment.
References
- Nelson EJ, Harris JB, Glenn Morris J, Calderwood SB, Camilli A (2009) Cholera transmission: the host, pathogen and Bacteriophage dynamic. Nat Rev Microbiol 7(10): 693-702.
- Eluozo SN, Afiibor BB (2018) Dispersion and dynamics influences from phosphorus deposition on e-coli transport in coastal deltaic Lake. MOJ Applied Bionics and biomechanics 2(5).
- Colwell RR (1996) Global climate and infectious disease: The Cholera Paradigm. Science 274(5295): 2025-2031.
- Okun DA (1996) From cholera to cancer to cryptosporidiosis. Journal of Environmental Engineering 122(6): 453-458.
- Eluozo SN, Oba AL (2018) Modeling and simulation of cadmium transport influenced by high degree of saturation and porosity on homogeneous coarse depositions. MOJ Civil Engineering 4(4).
- Pandey PK (2012) Modeling In- Stream Escherichia coli Graduate Dissertation Iowa state university 62-75.
- Craun GF, Fraun MF, Calderon RL, Beach MJ (2006) Waterborne outbreaks reported in the United States. J Water Health 4(2): 19-30.
- Eluozo SN, Ezeilo FE (2018) Numerical Modeling of Nocardia Migration Influenced Transport Pressured by Dispersion and Velocity in Fine Sand Formation in Wetland Environment. Journal of Water Resources Engineering and Management 5(1): 25-32.
- Fenwick A (2006) Waterborne Infectious Diseases-Could they be consigned to History? Science 313: 1077-1081.
- Eluozo SN, Ezeilo FE (2018) Modeling Heterogeneous Porosity in Alluvia Plain Deposition in Deltaic Formation. Recent Trend in Civil Engineering & Technology 8(2): 1-10.
- Ezeilo FE, Eluozo SN (2018) Dispersion and Storage Coefficient Influences on Accumulation of Frankia Transport in Heterogeneous Silty and Fine Sand Formation. Warri Delta State of Nigeria. International Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering 4(4)4: 1-16.
- Eluozo SN, Ezeilo FE (2018) Predicting the Behaviour of Borrelia in Homogeneous Fine Sand in Coastal Area of Bakana. Recent Trend in Civil Engineering & Technology 8(2): 1-19.
- Diffey BL (1991) Solar Ultraviolet-Radiation Effects on Biological-Systems. Phys Med Biol 36(3): 299-328.
- Brookes JD, Antenucci J, Hipsey M, Burch MD, Ashbolt NJ, et al. (2004) Fate and transport of pathogens in lakes and reservoirs. Environment International 30(5): 741-759.
- Ezeilo FE, Eluozo SN (2018) Linear Phase Velocity Effect on Accumulation of Zinc in Homogeneous Fine Sand Applying Predictive Model. International Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering 4(4): 17-32.
- Jamieson R, Gordon R, Sharples K, Stratton G, Madani A (2002) Movement and persistence of fecal bacteria in agricultural soils and subsurface drainage water. Canadian Biosystems Engineering 44(6): 1.1-1.10.
- Gerba CP, Smith J (2005) Sources of pathogenic microorganisms and their fate during land application of wastes. Journal of Environmental Quality 34: 42-48.
- John DE, Rose JB (2005) Review of factors affecting microbial survival in groundwater. Environ Sci Technol 39(19): 7345-7356.
- Eluozo SN, Afiibor BB (2019) Mathematical Model to Monitor the Transport of Bordetella Influenced by Heterogeneous Porosity in Homogeneous Gravel Depositions. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 6(1).
- Pachepsky YA, Shelton DR (2011) Escherichia coli and fecal coliforms in fresh water and estuarine sediments. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science Technology 41(12): 1067-1110.
- Eluozo SN, Amadi CP (2019) Modeling and Simulation of Legionella Transport Influenced by Heterogeneous Velocity in Stream. Journal of Water Resource Engineering and Management 6(2): 25-31.
- Eluozo SN, Amadi CP (2019) Velocity and Oxygen Deficit Influence on the Transport of Francisela in Eleme Creek. Journal of Water Resource Engineering and Management 6(2): 43-48.
- Eluozo SN, Oba AL (2018) Predicting heterogeneous permeability coefficient pressured by heterogeneous seepage on coarse deposition. MOJ Civil Engineering 4(4).

Top Editors
-

Mark E Smith
Bio chemistry
University of Texas Medical Branch, USA -

Lawrence A Presley
Department of Criminal Justice
Liberty University, USA -

Thomas W Miller
Department of Psychiatry
University of Kentucky, USA -

Gjumrakch Aliev
Department of Medicine
Gally International Biomedical Research & Consulting LLC, USA -

Christopher Bryant
Department of Urbanisation and Agricultural
Montreal university, USA -

Robert William Frare
Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
New York University, USA -

Rudolph Modesto Navari
Gastroenterology and Hepatology
University of Alabama, UK -

Andrew Hague
Department of Medicine
Universities of Bradford, UK -

George Gregory Buttigieg
Maltese College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Europe -

Chen-Hsiung Yeh
Oncology
Circulogene Theranostics, England -
.png)
Emilio Bucio-Carrillo
Radiation Chemistry
National University of Mexico, USA -
.jpg)
Casey J Grenier
Analytical Chemistry
Wentworth Institute of Technology, USA -
Hany Atalah
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Mercer University school of Medicine, USA -

Abu-Hussein Muhamad
Pediatric Dentistry
University of Athens , Greece

The annual scholar awards from Lupine Publishers honor a selected number Read More...